Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Psych NCP
Psych NCP
Uploaded by
Jannen CasasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Psych NCP
Psych NCP
Uploaded by
Jannen CasasCopyright:
Available Formats
COLLEGE OF NURSING
Silliman University
Dumaguete City
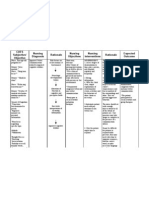
NURSING CARE PLAN
CUES/EVIDENCES NURSING DIAGNOSIS OBJECTIVES INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
INDEPENDENT:
SUBJECTIVE: Ineffective coping r/t After 2 weeks of our 1. Establish a trusting A trusting relationship
“Murag hapit nako mabuang situational crisis as care, the patient will be relationship with allows the client to
ani akong anxiety” evidenced by disturbed able to: the client. freely express his/her
“Sige rakog ka anxious most thought processes feelings and does not
of the time” 1. Demonstrate see the student nurse
“Nagsugod akong anxiety ways and ability as a threat.
mga 1 month pagsugod sa to cope
online class, feel nako di ko effectively. 2. Maintain the To enhance therapeutic
ka cope tungod pressured 2. Report a decrease trusting relationship and to
kayko sa acads ug sa family.” in restlessness. relationship with provide for meeting
“Feel nako gi control nakos 3. Verbalize a return the client by being psychological needs.
anxiety” to normal number available to her;
“Di kayko ka decide ug hours of sleep (6- answer her
tarong kay mabalaka ko if 8 hours) questions and
sakto ba or sayop akong 4. Verbalize signs queries, and
gihimo” and symptoms of respecting her
“Dili napod tarong akong pag increasing decisions/
tulog karon, mga 3-4 hours anxiety and 3. Discuss with the This is the first step in
nalang ako tulog kada gabii” intervene to client the teaching the client to
maintain anxiety situations that interrupt the escalation
OBJECTIVE: at manageable trigger anxiety. of anxiety.
- Shaky & sweaty level.
hands 5. Maintain eye 4. Provide a quiet Anxiety might be
- Feet constantly contact when environment as increased by noisy
tapping the floor talking to student much as possible. surroundings and
- Restless nurses and family cause panic to the
- Diaphoresis members. client.
- Dry skin, and patchy
lips 5. Teach relaxation Anxiety is minimized
- Unable to maintain exercises such as when the patient is
eye contact deep breathing relaxed and these are
- Easily distracted techniques, music effective non-
- therapy, or guided pharmacological ways
imagery. to decrease anxiety.
6. Encourage To assist client in
verbalization of dealing with anxiety.
fears and anxieties
and expression of
feelings of
depression and
anger. Let the
client know that
these are normal
reactions.
7. Remain with the Safety of the client is a
client when priority. A highly
anxiety attacks are anxious client should
severe. not be left alone.
DEPENDENT:
1. Administer Stimulate serotonin and
anxiolytics as dopamine receptors on
prescribed by the nerves, thereby altering
physician the chemical messages
that nerves receive.
2. Administer SSRIs Increases levels of
as prescribed by serotonin in the brain.
the physician SSRIs block the
reabsorption of
serotonin into neurons.
CUES/EVIDENCES NURSING DIAGNOSIS OBJECTIVES INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective data: Disturbed sleep pattern Independent:
At the end of the 2-
related to psychological week nursing care,
Awakens earlier than desired; stress 1. Determine type of Identification of
the client will be able
wakes up in the middle of the sleep pattern individual situation and
to:
night most of the time disturbance present, degree of interference
Verbalize including usual with functioning
Report of difficulty in falling understanding bedtime, determines need
asleep of relationship rituals/routines, for/appropriate
of anxiety and number of hours of interventions.
Her number of hours of sleep sleep sleep, time of
range from 3-4, which is lesser disturbance. arising,
than her usual (6-7 hrs) 7 months environmental
Identify
ago needs, and how
appropriate
much of a problem it
interventions
is to client.
to promote
sleep.
Objective data: 2. Provide quiet Promotes relaxation and
Dark circles under eyes Report environment, cues for falling asleep.
improvement comfort measures Stimulating effects of
Frequent yawning in sleep (e.g., caffeine/alcohol
Restless pattern, back rub, wash interfere with ability to
increased hands/face, bath), fall asleep.
sense of well- and sleep aids, such
being, and as warm milk .
feeling well- Restrict use of
rested. caffeine and alcohol
before bedtime.
Promotes reduction of
3. Discuss use of
anxious feelings,
relaxation
resulting in improved
techniques/thoughts,
sleep/rest.
visualization.
Having a plan can
4. Suggest ways to
reduce anxiety about
handle waking/not
not sleeping.
sleeping (e.g.,do not
lie in bed and think,
but get up and
remain inactive, or
do something
boring).
Increases fatigue,
5. Involve client in
promotes sleep but
exercise program,
avoids excessive
avoiding exercise
stimulation from
within 2 hours of
activity before bedtime.
going to bed.
Sedative drugs interfere
with REM sleep and
6. Avoid use of
affect quality of rest. A
sedatives, when
rebound effect may lead
possible.
to intense dreaming,
nightmares, and more
disturbed sleep.
Collaborative Although drug is
recommended for short-
1. Administer term use only, it may
medications as be beneficial until other
indicated, e.g., therapeutic
zolpidem (Ambien) interventions are
successful.
You might also like
- ACT For Depression. A Clinician's Guide Using Acceptance & Commitment Therapy in Treating Depression - Zettle PDFDocument330 pagesACT For Depression. A Clinician's Guide Using Acceptance & Commitment Therapy in Treating Depression - Zettle PDFJosé Paz100% (13)
- Lived Experience of Working Student During PandemicDocument49 pagesLived Experience of Working Student During Pandemicjunalyn juson0% (1)
- NCP Disturbed Thought Process Related To SchizophreniaDocument6 pagesNCP Disturbed Thought Process Related To Schizophrenianaishel0% (1)
- Soapie Fdar Process RecordingDocument26 pagesSoapie Fdar Process Recordingjames100% (1)
- Jean Pearl R. Caoili Bsn3 NCB Diagnosis: Paranoid Schizophrenia Psychiatric Nursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals/ Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesJean Pearl R. Caoili Bsn3 NCB Diagnosis: Paranoid Schizophrenia Psychiatric Nursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals/ Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluationpj casteNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Charisa S. Simbajon BSN IvDocument8 pagesSubmitted By: Charisa S. Simbajon BSN IvCharisa Simbajon100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For DepressionDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan For DepressionCatherineNo ratings yet
- NCP PsychosisDocument3 pagesNCP PsychosisKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-is100% (1)
- Disturbed Thought Processes DescribeDocument2 pagesDisturbed Thought Processes DescribePRINCESS LARA CASILAONo ratings yet
- Hallucinations NCP PDFDocument3 pagesHallucinations NCP PDFANGELA ERES BALINGBING100% (2)
- NCP For SchizoDocument6 pagesNCP For SchizoGILIANNE MARIE JIMENEANo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveAngelaNo ratings yet
- Everyone Would Be Better Off Without Me" As Verbalized by The PatientDocument4 pagesEveryone Would Be Better Off Without Me" As Verbalized by The PatientDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Thought Process NCP Gallano May 22 2018Document3 pagesDisturbed Thought Process NCP Gallano May 22 2018Charles Mallari ValdezNo ratings yet
- Impaired Social InteractionDocument4 pagesImpaired Social InteractionAaron ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- NCP-Septic Shock (Acute Pain)Document3 pagesNCP-Septic Shock (Acute Pain)Ted anadiloNo ratings yet
- Cognitive TherapyDocument7 pagesCognitive Therapyshivani singhNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Nursing ManagementDocument56 pagesSchizophrenia Nursing ManagementHumphreyNo ratings yet
- Psych NCPDocument1 pagePsych NCPEliza Joy Franco RNNo ratings yet
- N C PDocument3 pagesN C PTrixia Diaz100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Objective: Admission DiagnosisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Objective: Admission DiagnosisJe ZalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Analysis Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluat IONDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Analysis Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluat IONAlex SilvanoNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Nursingintervention Rationale Evaluation Discharge PlanningDocument5 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Nursingintervention Rationale Evaluation Discharge PlanningBSN 3B-Bulatao,Goergie Ann L. CPUSNNo ratings yet
- NCP SchizDocument12 pagesNCP SchizKristine Reyes - MerleNo ratings yet
- Psych NCPDocument4 pagesPsych NCPnoman-053No ratings yet
- NCP 2Document2 pagesNCP 2ampalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On Anxiety: Assessment Nursing Diagnose Planning Intervention Rational EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan On Anxiety: Assessment Nursing Diagnose Planning Intervention Rational Evaluationtariq nNo ratings yet
- Social IsolationDocument2 pagesSocial IsolationFlos Carmeli MontanaNo ratings yet
- 5 NCPDocument3 pages5 NCPAllord Lacanilao Bungay0% (1)
- Schizphrenia Nursing Car PlanDocument2 pagesSchizphrenia Nursing Car PlanAmjad AliNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Nikolai P. Funcion, FSUU-SNDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Nikolai P. Funcion, FSUU-SNNikolai FuncionNo ratings yet
- NCP Depression1Document1 pageNCP Depression1kyreNo ratings yet
- Self Cre DeficitDocument3 pagesSelf Cre DeficitSteph_Toinkz_240No ratings yet
- NCP Close Complete Fracture Knowledge DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP Close Complete Fracture Knowledge DeficitArt Christian Ramos0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With SchizophreniaDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Patient With SchizophreniaMary Luz De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- High Percentage of Sleep Disturbances Can Affect The Recovery of The PatientDocument1 pageHigh Percentage of Sleep Disturbances Can Affect The Recovery of The PatientMatt SinnungNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Sensory PerceptionDocument3 pagesDisturbed Sensory PerceptionJoenna GaloloNo ratings yet
- NCP - Major Depressive DisorderDocument7 pagesNCP - Major Depressive DisorderJaylord Verazon100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Low SelfDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Low SelfMarissa AsimNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia NCPDocument4 pagesSchizophrenia NCPDen-rashier M. Jamsuri100% (1)
- Nurse Patient Interaction: I. Background InformationDocument6 pagesNurse Patient Interaction: I. Background InformationLizli LoredoNo ratings yet
- Focus-Nursing Care Plan For Sleep DisordersDocument9 pagesFocus-Nursing Care Plan For Sleep DisordersMae AzoresNo ratings yet
- Process Recording Dra JoseDocument9 pagesProcess Recording Dra JoseBest of pinoyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Hopelessness NCPDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Hopelessness NCPRammiel Saylo CarlosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For CamoxDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For CamoxRolena Johnette B. PiñeroNo ratings yet
- Process RecordingDocument12 pagesProcess Recordingchristian_cayle100% (1)
- HoplessnessDocument16 pagesHoplessnessHamza IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Com/4-Cholecystitis - Cholelithiasis - Nursing-Care - Plans/2/ 6-OverviewDocument2 pagesCom/4-Cholecystitis - Cholelithiasis - Nursing-Care - Plans/2/ 6-OverviewCharles Belonio Dorado100% (1)
- Alzheimer S Disease Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesAlzheimer S Disease Nursing Care Planmp1757No ratings yet
- Tonsilitis NCPDocument2 pagesTonsilitis NCPFATIMA MARYAMA USMANNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Acute Pain Related To Inflammatory Response Secondary To InfectionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Acute Pain Related To Inflammatory Response Secondary To InfectionTammy De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- NCP Violence - OtherDocument2 pagesNCP Violence - OtherRosean Venus SilangNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPShubhangi SarwanNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia Gravis NCPDocument1 pageMyasthenia Gravis NCPCzarina0% (1)
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPNik Rose ElNo ratings yet
- NCP & Discharge PlanningDocument12 pagesNCP & Discharge PlanningStephanie Mae Amoylen OdchigueNo ratings yet
- CASE PRESENTATION PP - Anxiety. Tiffany GordonDocument6 pagesCASE PRESENTATION PP - Anxiety. Tiffany GordonTiffany GordonNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Thought ProcessDocument4 pagesDisturbed Thought ProcessJessieRamosAnicetoNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Psych NCPDocument3 pagesPsych NCPJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: "Nabalaka Ko Kay First Time Nako Ma-Operahan, Basin Pud Maunsa Si Baby," AsDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: "Nabalaka Ko Kay First Time Nako Ma-Operahan, Basin Pud Maunsa Si Baby," Asunnamed personNo ratings yet
- NCM117 NCPDocument2 pagesNCM117 NCPHANNAH MICOLE GAERLANNo ratings yet
- Ncm112a Allncpforcancers BalangueDocument11 pagesNcm112a Allncpforcancers BalangueNurse NotesNo ratings yet
- BLS ACLS ComplilationDocument218 pagesBLS ACLS ComplilationJannen Casas100% (1)
- Pulmonary Insufficiency:: Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument72 pagesPulmonary Insufficiency:: Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- HANDOUT Family Planning ProgramDocument3 pagesHANDOUT Family Planning ProgramJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- El Filibusterismo Characters and SummaryDocument4 pagesEl Filibusterismo Characters and SummaryJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Combine Bladder Irrigation Post Mortem Special MouthDocument88 pagesCombine Bladder Irrigation Post Mortem Special MouthJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Assessment Clients With Life Threatening Conditions / Medical EmergenciesDocument23 pagesAssessment Clients With Life Threatening Conditions / Medical EmergenciesJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Ward Week 1Document65 pagesWard Week 1Jannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Assisting in Gastric LavageDocument5 pagesAssisting in Gastric LavageJannen Casas100% (1)
- Closed Bladder Irrigation - Prodecure ManualDocument12 pagesClosed Bladder Irrigation - Prodecure ManualJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- AGRAVANTE BROMO CASAS GAD Case StudyDocument14 pagesAGRAVANTE BROMO CASAS GAD Case StudyJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Phases of Chronic IllnessDocument21 pagesPhases of Chronic IllnessJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Psych NCPDocument3 pagesPsych NCPJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Post-Operative Nutrition: Things You Need To Know AboutDocument2 pagesPost-Operative Nutrition: Things You Need To Know AboutJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Care of Patients With Manipulative Behavior: Anja Shanelle Fontelo & Shekinah BromoDocument5 pagesCare of Patients With Manipulative Behavior: Anja Shanelle Fontelo & Shekinah BromoJannen Casas100% (1)
- Jannen ADocument1 pageJannen AJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Resource Unit On NephrectomyDocument14 pagesCollege of Nursing: Resource Unit On NephrectomyJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Case Pres-Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument167 pagesCase Pres-Pulmonary TuberculosisJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Provides Baseline Information For Monitoring Changes and Evaluating The Effectiveness of TherapyDocument8 pagesProvides Baseline Information For Monitoring Changes and Evaluating The Effectiveness of TherapyJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Casas - Annotated Reading CHNDocument2 pagesCasas - Annotated Reading CHNJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Community Organizing & Participatory Action Research (Copar)Document5 pagesCommunity Organizing & Participatory Action Research (Copar)Jannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Economic of Mass MediaDocument4 pagesEconomic of Mass MediaJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Elementary School Middle School High School: Emotional Red FlagsDocument1 pageElementary School Middle School High School: Emotional Red FlagsJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Edited COVID19 HANDOUT Requina SindiongDocument5 pagesEdited COVID19 HANDOUT Requina SindiongJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange RebusquilloDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange RebusquilloJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Ward Class On Cystic FibrosisDocument58 pagesWard Class On Cystic FibrosisJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Social Work in Psychiatric SettingsDocument40 pagesSocial Work in Psychiatric SettingsAnnPSWNo ratings yet
- YALE BROWN-TOC en Niños - Confiabilidad y ValidezDocument7 pagesYALE BROWN-TOC en Niños - Confiabilidad y ValidezLaura Brondo100% (1)
- MSCCFT 1st Year Assignments 2018-19Document14 pagesMSCCFT 1st Year Assignments 2018-19V. J. Thomas0% (1)
- Anxiety: Psychiatric DisordersDocument21 pagesAnxiety: Psychiatric DisordersNdoo NdooNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper - Behavioral Problems and TypesDocument2 pagesReflection Paper - Behavioral Problems and TypesFirdaus AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Autism Europe, PERSONS WITH AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDERS Identification, Understanding, InterventionDocument28 pagesAutism Europe, PERSONS WITH AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDERS Identification, Understanding, Interventioninfo-TEANo ratings yet
- Position Paper-Pascua, PinedaDocument2 pagesPosition Paper-Pascua, PinedaAlexander NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Personal Development: Quarter 1 - Module 4: Mental HealthDocument32 pagesPersonal Development: Quarter 1 - Module 4: Mental HealthSherry-Ann TulauanNo ratings yet
- Stages of Change ModelDocument4 pagesStages of Change Modelcarmen_georgescu1968No ratings yet
- Motivation Chapter 12 Lesson 1Document5 pagesMotivation Chapter 12 Lesson 1api-245168163No ratings yet
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy For Women Diagnosed With Binge EatingDocument12 pagesAcceptance and Commitment Therapy For Women Diagnosed With Binge EatingPamela MaercovichNo ratings yet
- The Attuned TherapistDocument19 pagesThe Attuned Therapistnihilius790% (1)
- Shyness & Anxiety: A Review of LiteratureDocument8 pagesShyness & Anxiety: A Review of Literatureapi-285426523No ratings yet
- PowerPoint Cognitive DisordersDocument22 pagesPowerPoint Cognitive Disordersiqra-j100% (2)
- Using The CARE-IndexDocument10 pagesUsing The CARE-IndexDesi PhykiNo ratings yet
- Five Ps - Clinical Case Formulation-1 PDFDocument3 pagesFive Ps - Clinical Case Formulation-1 PDFSolainy Torres DuarteNo ratings yet
- Islam Today Magazine March - AprilDocument48 pagesIslam Today Magazine March - AprilamirdemNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Factors Responsible For Relapses in Schizophrenic Patients at Kampala International University Teaching Hospital, Uganda.Document14 pagesAssessment of Factors Responsible For Relapses in Schizophrenic Patients at Kampala International University Teaching Hospital, Uganda.KIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- Kansas State Drug Mortality Statistics by CountyDocument7 pagesKansas State Drug Mortality Statistics by CountyGet TreatmentNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument12 pagesCase Studyapi-662404021No ratings yet
- Kendler, Kenneth S. - Parnas, Josef - Philosophical Issues in Psychiatry - Explanation, Phenomenology, and Nosology-The Johns Hopkins University Press (2015)Document422 pagesKendler, Kenneth S. - Parnas, Josef - Philosophical Issues in Psychiatry - Explanation, Phenomenology, and Nosology-The Johns Hopkins University Press (2015)Ziggy GonNo ratings yet
- Examples of Confrontive Coping Strategies Include Trying To Figure Out Different Ways To Handle The SituationDocument2 pagesExamples of Confrontive Coping Strategies Include Trying To Figure Out Different Ways To Handle The SituationsundarirakhmanNo ratings yet
- Gamification in Healthcare: Perspectives of Mental Health Service Users and Health ProfessionalsDocument10 pagesGamification in Healthcare: Perspectives of Mental Health Service Users and Health ProfessionalsMaria HassanNo ratings yet
- Whole Person Dementia Assessment (Mast Excerpt)Document12 pagesWhole Person Dementia Assessment (Mast Excerpt)Health Professions Press, an imprint of Paul H. Brookes Publishing Co., Inc.No ratings yet
- ManosamvadDocument4 pagesManosamvadShreya BajajNo ratings yet
- Community Health NursingDocument4 pagesCommunity Health NursingMusa NyamwandaNo ratings yet
- Chazz StatementsDocument10 pagesChazz Statementsthe fifth estateNo ratings yet