Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 viewsTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words
Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words
Uploaded by
Diego GrañenaThe document provides a table summarizing English tenses. It lists the tense, affirmative/negative/question forms, use, and signal words for simple present, present progressive, simple past, past progressive, present perfect simple, present perfect progressive, past perfect simple, past perfect progressive, future I simple, future I progressive, future II simple, and future II progressive tenses. The table acts as a reference for determining which tense to use based on whether an action is habitual, ongoing, completed, or planned.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Reflective EssayDocument3 pagesReflective Essayapi-261601610No ratings yet
- My English Grammar Guide CompressDocument39 pagesMy English Grammar Guide CompressBenny LeeNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsGiannina Ailén MusacchioNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRanjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentMarinela AnghelNo ratings yet
- Tense TABLE DE PE NET - BUNDocument2 pagesTense TABLE DE PE NET - BUNMirela MarinNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument7 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAnonymous vqzyDYXkNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument3 pagesEnglish Tensescoquin8816No ratings yet
- Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesAffirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsKavitha RajendranNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: I Talked, )Document2 pagesSimple Present: I Talked, )Seminarski Radovi Iz IstorijeNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordslovely innocentNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument4 pagesTensesLiliia RakNo ratings yet
- Tenses Cuadro ResumenDocument4 pagesTenses Cuadro ResumenGuillermo NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsInga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument5 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAlfi Ramdhani PNo ratings yet
- Tenses - Ready Reckoner: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument7 pagesTenses - Ready Reckoner: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRajalakshmi Gajapathy100% (2)
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAngi BraileanuNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument4 pagesEnglish TensesLucaNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument2 pagesTable of English TensesOscar LunaNo ratings yet
- Times: I Talk, )Document11 pagesTimes: I Talk, )mugiNo ratings yet
- გრამატიკაDocument3 pagesგრამატიკაgio903371No ratings yet
- Guia de Ingles 11 de Informatica Semana 5 Ii PartialDocument5 pagesGuia de Ingles 11 de Informatica Semana 5 Ii PartialLizzy Yessenia Torres 11- 8 BCHNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDahliya DwitaNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRavi Teja AnneNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument2 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentClaudiaNo ratings yet
- Eng Grammar Parts of SpeechDocument3 pagesEng Grammar Parts of Speechsami karemNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument2 pagesTable of English TensesRasta FariNo ratings yet
- Cours 2bac L en 04Document2 pagesCours 2bac L en 04hkuuiNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument10 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsMina SamyNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jul 15, 2023Document2 pagesAdobe Scan Jul 15, 2023sumanta biswasNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Simple PresentNorvin TreminioNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument2 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentBogdan ChișcababiiNo ratings yet
- English Grammar OnlineDocument6 pagesEnglish Grammar OnlineNasir IqbalNo ratings yet
- 1.tense Table (At Start of Tenses)Document3 pages1.tense Table (At Start of Tenses)Adeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses by K.V.R.RaoDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses by K.V.R.RaoprasannabandiNo ratings yet
- Chart of English TensesDocument2 pagesChart of English TensesMaria ArtilesNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument2 pagesSimple Present: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsAdailton SamuelNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsMarko MillaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Quest Ion Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument5 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Quest Ion Use Signal Words: Simple Presentalokkumaroct1981No ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: GrammarDocument2 pagesTable of English Tenses: GrammarGenesis Belen0% (1)
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument6 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentMarkoNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words Simple PresentDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words Simple Presentmanchiraju raj kumarNo ratings yet
- Tenses Chart Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument2 pagesTenses Chart Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsanamariaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument7 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAnonymous vqzyDYXkNo ratings yet
- The Fun Way To Learn EnglishDocument7 pagesThe Fun Way To Learn EnglishPatrascu CristiNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument4 pagesTensesalina.zorilaNo ratings yet
- Level 1Document1 pageLevel 1Melissa ReyesNo ratings yet
- InglesDocument3 pagesInglesazoljamiaidounNo ratings yet
- Grammar Reference. c1 UnedDocument38 pagesGrammar Reference. c1 UnedCristina Gonzalez GarridoNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument5 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsGopu PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Tense Positive/negative/question Usage Signal WordsDocument9 pagesSimple Present: Tense Positive/negative/question Usage Signal WordsSusila PonnusamyNo ratings yet
- Verbos, Adjetivos y Sustanfivos en InglésDocument242 pagesVerbos, Adjetivos y Sustanfivos en InglésVioleta Patricia Molet100% (1)
- TenseDocument2 pagesTenseKlaudia TerjékNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument3 pagesTable of English TensesMelinaNo ratings yet
- Tiempos Verbales Cuadro ColegioDocument2 pagesTiempos Verbales Cuadro ColegioelisaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questio N Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument4 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Questio N Use Signal Words: Simple PresentgissaNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Simple PresentSofiene GuedriNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses Chart: Tense Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesVerb Tenses Chart: Tense Use Signal WordsmllorenteNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument3 pagesEnglish Tensesimane0630852038No ratings yet
- Simple Tenses: The Present The Past The Future Simple Continuous PerfectDocument5 pagesSimple Tenses: The Present The Past The Future Simple Continuous PerfectGetu BogaleNo ratings yet
- MUZZY StoryBook (German)Document23 pagesMUZZY StoryBook (German)hikariyukai100% (1)
- Edpr 7521 Research ProposalDocument15 pagesEdpr 7521 Research Proposalapi-281750087No ratings yet
- Rubric For Manuscript SpeechDocument1 pageRubric For Manuscript SpeechYuri Anne Roleen MasangkayNo ratings yet
- 30 IELTS Writing Band 8.0Document31 pages30 IELTS Writing Band 8.0Elize WillyNo ratings yet
- Maths Unit PlanDocument26 pagesMaths Unit Planapi-465725385No ratings yet
- Test 1 ADocument12 pagesTest 1 AFernanda MagañaNo ratings yet
- Response To Request For Approval For Non Categorised ItemDocument3 pagesResponse To Request For Approval For Non Categorised ItemHery MukhlisNo ratings yet
- Social Media Marketing and Consumer Based BrandDocument2 pagesSocial Media Marketing and Consumer Based BrandJane DDNo ratings yet
- Universidad de La Guajira Centro de Lenguas-Sede MaicaoDocument13 pagesUniversidad de La Guajira Centro de Lenguas-Sede MaicaoGehiler C'otesNo ratings yet
- Prelim Exam - Facilitating LearningDocument4 pagesPrelim Exam - Facilitating LearningMarisa LangobanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 QuizDocument3 pagesChapter 3 Quizapi-234693246No ratings yet
- Week 12 DemandDocument45 pagesWeek 12 Demandasifa azeemNo ratings yet
- Kaplan Cirugia No Cardiaca PDFDocument584 pagesKaplan Cirugia No Cardiaca PDFNalemi JTNo ratings yet
- ISO TemplateDocument13 pagesISO TemplateGerard VillafloresNo ratings yet
- Stress Management-Subroto GhoshDocument43 pagesStress Management-Subroto GhoshSubroto Ghosh100% (2)
- 01 AI OverviewDocument85 pages01 AI OverviewPablo GleisnerNo ratings yet
- Concept of EthicsDocument1 pageConcept of EthicsUtkarsh Tripathi72No ratings yet
- Graduation SpeechDocument2 pagesGraduation SpeechToh Qin KaneNo ratings yet
- NICE Combined CalendarDocument1 pageNICE Combined CalendarMaknunNo ratings yet
- BMS Fah EngineerDocument3 pagesBMS Fah EngineerZeeshan Jawed0% (1)
- 5.davy Crockett Saves The World - Lesson - BasalDocument10 pages5.davy Crockett Saves The World - Lesson - BasalSoe Soe MyatNo ratings yet
- Clinical NeurologyDocument745 pagesClinical NeurologyTabitha Muscas93% (14)
- Curriculum MapDocument1 pageCurriculum MapAnonymous xVTbc3T6No ratings yet
- Bais City National Science High SchoolDocument21 pagesBais City National Science High SchoolJai-JaiAdalidNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Personality and Work Outcome: Puan Siti Faizah Binti JamaluddinDocument3 pagesAssignment 1: Personality and Work Outcome: Puan Siti Faizah Binti Jamaluddinkhairul ikhwanNo ratings yet
- Group 5 - United KingdomDocument39 pagesGroup 5 - United KingdomAubrey PaborianNo ratings yet
- Professional Nursing OrganizationDocument4 pagesProfessional Nursing OrganizationCid Benedict PabalanNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document3 pagesModule 4luppy ccNo ratings yet
- Direct Gene Transfer Methods - Particle Bombardment & Electroporation Method.Document24 pagesDirect Gene Transfer Methods - Particle Bombardment & Electroporation Method.Prajwal BhanuNo ratings yet
Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words
Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words
Uploaded by
Diego Grañena0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views4 pagesThe document provides a table summarizing English tenses. It lists the tense, affirmative/negative/question forms, use, and signal words for simple present, present progressive, simple past, past progressive, present perfect simple, present perfect progressive, past perfect simple, past perfect progressive, future I simple, future I progressive, future II simple, and future II progressive tenses. The table acts as a reference for determining which tense to use based on whether an action is habitual, ongoing, completed, or planned.
Original Description:
Original Title
Table of English Tenses
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides a table summarizing English tenses. It lists the tense, affirmative/negative/question forms, use, and signal words for simple present, present progressive, simple past, past progressive, present perfect simple, present perfect progressive, past perfect simple, past perfect progressive, future I simple, future I progressive, future II simple, and future II progressive tenses. The table acts as a reference for determining which tense to use based on whether an action is habitual, ongoing, completed, or planned.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words
Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words
Uploaded by
Diego GrañenaThe document provides a table summarizing English tenses. It lists the tense, affirmative/negative/question forms, use, and signal words for simple present, present progressive, simple past, past progressive, present perfect simple, present perfect progressive, past perfect simple, past perfect progressive, future I simple, future I progressive, future II simple, and future II progressive tenses. The table acts as a reference for determining which tense to use based on whether an action is habitual, ongoing, completed, or planned.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
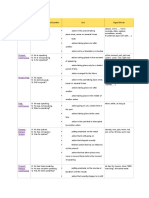
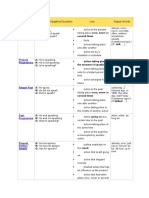
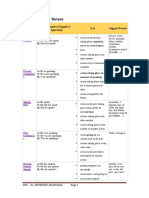
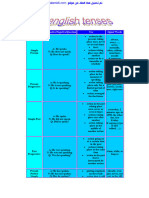
Table of English Tenses
Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words
always, every …, never,
action in the present taking place
Simple Present A: He speaks. normally, often, seldom,
N: He does not speak. once, never or several times sometimes, usually
Q: Does he speak? facts if sentences type I (If I talk,
…)
actions taking place one after
another
action set by a timetable or schedule
Present Progressive A: He is speaking. at the moment, just, just now,
action taking place in the moment
N: He is not speaking. Listen!, Look!, now, right
Q: Is he speaking? of speaking now
action taking place only for a
limited period of time
action arranged for the future
Simple Past A: He spoke. yesterday, 2 minutes ago, in
action in the past taking place once,
N: He did not speak. 1990, the other day, last
Q: Did he speak? never or several times Friday
actions taking place one after if sentence type II (If I
talked, …)
another
action taking place in the middle of
another action
Past Progressive A: He was speaking. when, while, as long as
action going on at a certain time in
N: He was not speaking.
Q: Was he speaking? the past
actions taking place at the same
time
action in the past that is interrupted
by another action
Present Perfect Simple A: He has spoken. already, ever, just, never, not
putting emphasis on the result
N: He has not spoken. yet, so far, till now, up to
Q: Has he spoken? action that is still going on now
action that stopped recently
finished action that has an influence
on the present
action that has taken place once,
never or several times before the moment of
speaking
Present Perfect Progressive A: He has been speaking. all day, for 4 years, since
putting emphasis on the course or
N: He has not been speaking. 1993, how long?, the whole
Q: Has he been speaking? duration (not the result) week
action that recently stopped or is
still going on
finished action that influenced the
present
Past Perfect Simple A: He had spoken. already, just, never, not yet,
action taking place before a certain
N: He had not spoken. once, until that day
Q: Had he spoken? time in the past if sentence type III (If I had
sometimes interchangeable with talked, …)
past perfect progressive
putting emphasis only on the fact
(not the duration)
Past Perfect Progressive A: He had been speaking. for, since, the whole day, all
action taking place before a certain
N: He had not been speaking. day
Q: Had he been speaking?
time in the past
sometimes interchangeable with
past perfect simple
putting emphasis on the duration or
course of an action
Future I Simple A: He will speak. in a year, next …, tomorrow
action in the future that cannot be
N: He will not speak. If-Satz Typ I (If you ask her,
Q: Will he speak? influenced she will help you.)
spontaneous decision assumption: I think,
probably, perhaps
assumption with regard to the future
Future I Simple A: He is going to speak. in one year, next week,
decision made for the future
N: He is not going to speak. tomorrow
(going to) Q: Is he going to speak? conclusion with regard to the future
Future I Progressive A: He will be speaking. in one year, next week,
action that is going on at a certain
N: He will not be speaking. tomorrow
Q: Will he be speaking? time in the future
action that is sure to happen in the
near future
Future II Simple A: He will have spoken. by Monday, in a week
action that will be finished at a
N: He will not have spoken.
Q: Will he have spoken? certain time in the future
Future II Progressive A: He will have been speaking. for …, the last couple of
action taking place before a certain
N: He will not have been hours, all day long
speaking. time in the future
Q: Will he have been speaking? putting emphasis on the course of
an action
Conditional I Simple A: He would speak. if sentences type II
action that might take place
N: He would not speak. (If I were you, I would go
Q: Would he speak? home.)
Conditional I Progressive A: He would be speaking.
action that might take place
N: He would not be speaking.
Q: Would he be speaking? putting emphasis on the course /
duration of the action
Conditional II Simple A: He would have spoken. if sentences type III
action that might have taken place
N: He would not have spoken. (If I had seen that, I would
Q: Would he have spoken? in the past have helped.)
Conditional II Progressive A: He would have been speaking.
action that might have taken place
N: He would not have been
speaking. in the past
Q: Would he have been speaking? puts emphasis on the course /
duration of the action
You might also like
- Reflective EssayDocument3 pagesReflective Essayapi-261601610No ratings yet
- My English Grammar Guide CompressDocument39 pagesMy English Grammar Guide CompressBenny LeeNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsGiannina Ailén MusacchioNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRanjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentMarinela AnghelNo ratings yet
- Tense TABLE DE PE NET - BUNDocument2 pagesTense TABLE DE PE NET - BUNMirela MarinNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument7 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAnonymous vqzyDYXkNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument3 pagesEnglish Tensescoquin8816No ratings yet
- Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesAffirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsKavitha RajendranNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: I Talked, )Document2 pagesSimple Present: I Talked, )Seminarski Radovi Iz IstorijeNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordslovely innocentNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument4 pagesTensesLiliia RakNo ratings yet
- Tenses Cuadro ResumenDocument4 pagesTenses Cuadro ResumenGuillermo NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsInga ElenaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument5 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAlfi Ramdhani PNo ratings yet
- Tenses - Ready Reckoner: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument7 pagesTenses - Ready Reckoner: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRajalakshmi Gajapathy100% (2)
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAngi BraileanuNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument4 pagesEnglish TensesLucaNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument2 pagesTable of English TensesOscar LunaNo ratings yet
- Times: I Talk, )Document11 pagesTimes: I Talk, )mugiNo ratings yet
- გრამატიკაDocument3 pagesგრამატიკაgio903371No ratings yet
- Guia de Ingles 11 de Informatica Semana 5 Ii PartialDocument5 pagesGuia de Ingles 11 de Informatica Semana 5 Ii PartialLizzy Yessenia Torres 11- 8 BCHNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDahliya DwitaNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRavi Teja AnneNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument2 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentClaudiaNo ratings yet
- Eng Grammar Parts of SpeechDocument3 pagesEng Grammar Parts of Speechsami karemNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument2 pagesTable of English TensesRasta FariNo ratings yet
- Cours 2bac L en 04Document2 pagesCours 2bac L en 04hkuuiNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument10 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsMina SamyNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jul 15, 2023Document2 pagesAdobe Scan Jul 15, 2023sumanta biswasNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Simple PresentNorvin TreminioNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument2 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentBogdan ChișcababiiNo ratings yet
- English Grammar OnlineDocument6 pagesEnglish Grammar OnlineNasir IqbalNo ratings yet
- 1.tense Table (At Start of Tenses)Document3 pages1.tense Table (At Start of Tenses)Adeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses by K.V.R.RaoDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses by K.V.R.RaoprasannabandiNo ratings yet
- Chart of English TensesDocument2 pagesChart of English TensesMaria ArtilesNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument2 pagesSimple Present: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsAdailton SamuelNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsMarko MillaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Quest Ion Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument5 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Quest Ion Use Signal Words: Simple Presentalokkumaroct1981No ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: GrammarDocument2 pagesTable of English Tenses: GrammarGenesis Belen0% (1)
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument6 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentMarkoNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words Simple PresentDocument4 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words Simple Presentmanchiraju raj kumarNo ratings yet
- Tenses Chart Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument2 pagesTenses Chart Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsanamariaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument7 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAnonymous vqzyDYXkNo ratings yet
- The Fun Way To Learn EnglishDocument7 pagesThe Fun Way To Learn EnglishPatrascu CristiNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument4 pagesTensesalina.zorilaNo ratings yet
- Level 1Document1 pageLevel 1Melissa ReyesNo ratings yet
- InglesDocument3 pagesInglesazoljamiaidounNo ratings yet
- Grammar Reference. c1 UnedDocument38 pagesGrammar Reference. c1 UnedCristina Gonzalez GarridoNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDocument5 pagesTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsGopu PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: Tense Positive/negative/question Usage Signal WordsDocument9 pagesSimple Present: Tense Positive/negative/question Usage Signal WordsSusila PonnusamyNo ratings yet
- Verbos, Adjetivos y Sustanfivos en InglésDocument242 pagesVerbos, Adjetivos y Sustanfivos en InglésVioleta Patricia Molet100% (1)
- TenseDocument2 pagesTenseKlaudia TerjékNo ratings yet
- Table of English TensesDocument3 pagesTable of English TensesMelinaNo ratings yet
- Tiempos Verbales Cuadro ColegioDocument2 pagesTiempos Verbales Cuadro ColegioelisaNo ratings yet
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questio N Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDocument4 pagesTense Affirmative/Negative/Questio N Use Signal Words: Simple PresentgissaNo ratings yet
- Table of English Tenses: Simple PresentDocument3 pagesTable of English Tenses: Simple PresentSofiene GuedriNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses Chart: Tense Use Signal WordsDocument3 pagesVerb Tenses Chart: Tense Use Signal WordsmllorenteNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument3 pagesEnglish Tensesimane0630852038No ratings yet
- Simple Tenses: The Present The Past The Future Simple Continuous PerfectDocument5 pagesSimple Tenses: The Present The Past The Future Simple Continuous PerfectGetu BogaleNo ratings yet
- MUZZY StoryBook (German)Document23 pagesMUZZY StoryBook (German)hikariyukai100% (1)
- Edpr 7521 Research ProposalDocument15 pagesEdpr 7521 Research Proposalapi-281750087No ratings yet
- Rubric For Manuscript SpeechDocument1 pageRubric For Manuscript SpeechYuri Anne Roleen MasangkayNo ratings yet
- 30 IELTS Writing Band 8.0Document31 pages30 IELTS Writing Band 8.0Elize WillyNo ratings yet
- Maths Unit PlanDocument26 pagesMaths Unit Planapi-465725385No ratings yet
- Test 1 ADocument12 pagesTest 1 AFernanda MagañaNo ratings yet
- Response To Request For Approval For Non Categorised ItemDocument3 pagesResponse To Request For Approval For Non Categorised ItemHery MukhlisNo ratings yet
- Social Media Marketing and Consumer Based BrandDocument2 pagesSocial Media Marketing and Consumer Based BrandJane DDNo ratings yet
- Universidad de La Guajira Centro de Lenguas-Sede MaicaoDocument13 pagesUniversidad de La Guajira Centro de Lenguas-Sede MaicaoGehiler C'otesNo ratings yet
- Prelim Exam - Facilitating LearningDocument4 pagesPrelim Exam - Facilitating LearningMarisa LangobanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 QuizDocument3 pagesChapter 3 Quizapi-234693246No ratings yet
- Week 12 DemandDocument45 pagesWeek 12 Demandasifa azeemNo ratings yet
- Kaplan Cirugia No Cardiaca PDFDocument584 pagesKaplan Cirugia No Cardiaca PDFNalemi JTNo ratings yet
- ISO TemplateDocument13 pagesISO TemplateGerard VillafloresNo ratings yet
- Stress Management-Subroto GhoshDocument43 pagesStress Management-Subroto GhoshSubroto Ghosh100% (2)
- 01 AI OverviewDocument85 pages01 AI OverviewPablo GleisnerNo ratings yet
- Concept of EthicsDocument1 pageConcept of EthicsUtkarsh Tripathi72No ratings yet
- Graduation SpeechDocument2 pagesGraduation SpeechToh Qin KaneNo ratings yet
- NICE Combined CalendarDocument1 pageNICE Combined CalendarMaknunNo ratings yet
- BMS Fah EngineerDocument3 pagesBMS Fah EngineerZeeshan Jawed0% (1)
- 5.davy Crockett Saves The World - Lesson - BasalDocument10 pages5.davy Crockett Saves The World - Lesson - BasalSoe Soe MyatNo ratings yet
- Clinical NeurologyDocument745 pagesClinical NeurologyTabitha Muscas93% (14)
- Curriculum MapDocument1 pageCurriculum MapAnonymous xVTbc3T6No ratings yet
- Bais City National Science High SchoolDocument21 pagesBais City National Science High SchoolJai-JaiAdalidNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Personality and Work Outcome: Puan Siti Faizah Binti JamaluddinDocument3 pagesAssignment 1: Personality and Work Outcome: Puan Siti Faizah Binti Jamaluddinkhairul ikhwanNo ratings yet
- Group 5 - United KingdomDocument39 pagesGroup 5 - United KingdomAubrey PaborianNo ratings yet
- Professional Nursing OrganizationDocument4 pagesProfessional Nursing OrganizationCid Benedict PabalanNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document3 pagesModule 4luppy ccNo ratings yet
- Direct Gene Transfer Methods - Particle Bombardment & Electroporation Method.Document24 pagesDirect Gene Transfer Methods - Particle Bombardment & Electroporation Method.Prajwal BhanuNo ratings yet