Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
175 viewsFinancial Information System
Financial Information System
Uploaded by
mobashreen m i sA financial information system (FIS) collects, stores, and analyzes financial data to support decision making. It tracks elements like accounting, budgets, payables, receivables, and generates reports. An FIS ensures financial obligations are met with minimal resources and provides accounting reports, budgets, forecasts, and "what-if" analyses. It must provide accurate, timely data and support auditing, reporting, budgeting, and financial statement preparation. An FIS has modules for accounting, budgets, payables, receivables, payroll, and other functions. It offers benefits like integrated information, expenditure control, and tighter budget oversight.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- SC01 Sophos Central Sales Overview v1.0.0Document51 pagesSC01 Sophos Central Sales Overview v1.0.0DaNi Velandia0% (1)
- DIGITAL MARKETING PLAN KFCDocument14 pagesDIGITAL MARKETING PLAN KFCmobashreen m i s100% (2)
- MIS PDF Notes Unit 4Document14 pagesMIS PDF Notes Unit 4Dr. MURALI KRISHNA VELAVETINo ratings yet
- Financial AccountingDocument19 pagesFinancial AccountingsaniaNo ratings yet
- F MisDocument2 pagesF MisyogeshvraoNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting G1Document9 pagesFinancial Accounting G1Precious Anne ValderramaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information System QuestionsDocument7 pagesAccounting Information System QuestionsMohsin ShaikhNo ratings yet
- What Are The Benefits of A Financial Management Information SystemDocument5 pagesWhat Are The Benefits of A Financial Management Information SystemSandra MagnoNo ratings yet
- 9511 1st AssignmentDocument7 pages9511 1st AssignmentUmair JavedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Accounting Information System: PeopleDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Accounting Information System: PeopleVIBHASH SHANKARNo ratings yet
- Financial Information System: Presented byDocument23 pagesFinancial Information System: Presented bySrimon DasNo ratings yet
- AFIS AssignmentDocument3 pagesAFIS Assignmentbsaf2147266No ratings yet
- Accounting Information SystemsDocument15 pagesAccounting Information SystemsPandu Rangarao100% (3)
- Accounting Information SystemDocument22 pagesAccounting Information SystemkvkumarnaveenNo ratings yet
- IM Unit 4Document28 pagesIM Unit 4Sara ZafarNo ratings yet
- AIS SummaryDocument5 pagesAIS SummaryKimboy Elizalde PanaguitonNo ratings yet
- FIST Lecture 1Document26 pagesFIST Lecture 1sforsanjida1No ratings yet
- Research ProjectDocument8 pagesResearch ProjectAriesNo ratings yet
- Finacial ISDocument6 pagesFinacial ISkaurbhatti78No ratings yet
- Accounting Information System-OverviewDocument15 pagesAccounting Information System-Overviewsema100% (1)
- Report For AIS 1Document5 pagesReport For AIS 1Samer IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Sistem Information AccountingDocument9 pagesSistem Information AccountingNicole Daniella JinggaNo ratings yet
- The Information System: An Accountant's PerspectiveDocument33 pagesThe Information System: An Accountant's PerspectiveLUIS ALFONSO DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Life and Works of Genoveva and NickDocument7 pagesLife and Works of Genoveva and Nickjoy sooyoungNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information SystemDocument5 pagesAccounting Information SystemAnnhtak PNo ratings yet
- Unit 9: Financial Information SystemDocument13 pagesUnit 9: Financial Information SystemSrishti VivekNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument2 pagesDefinitionKrisha TubogNo ratings yet
- AIS MidtermDocument13 pagesAIS MidtermJansen JacobNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information SystemDocument33 pagesAccounting Information SystemBir MallaNo ratings yet
- An Over View Regarding AISDocument15 pagesAn Over View Regarding AISDonia MohamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ReviewerDocument16 pagesChapter 1 Revieweranon_879788236No ratings yet
- Introduction - Accounting Information SystemsDocument6 pagesIntroduction - Accounting Information SystemsJuris AvilaNo ratings yet
- Mis in FinanceDocument19 pagesMis in FinanceDibyendu Paul0% (1)
- CAS AISdescriptionDocument5 pagesCAS AISdescriptionmika.tov1997No ratings yet
- Lecture-4: Course ID: BBA-305Document13 pagesLecture-4: Course ID: BBA-305Mansi VermaNo ratings yet
- Set Up and Operate A Computerized Accounting SystemDocument10 pagesSet Up and Operate A Computerized Accounting Systemabebe kumelaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information SystemDocument2 pagesAccounting Information SystemJansen Alonzo BordeyNo ratings yet
- Accounting Notes: Accounting Information: A Means To An EndDocument5 pagesAccounting Notes: Accounting Information: A Means To An EndNNo ratings yet
- Cost TyaDocument7 pagesCost TyaTya NwsNo ratings yet
- The Study of Accounting Information Systems:: Essential Concepts and ApplicationsDocument19 pagesThe Study of Accounting Information Systems:: Essential Concepts and ApplicationsNhoel RsNo ratings yet
- Importance of Information SystemsDocument148 pagesImportance of Information Systemsbauuaaa100% (1)
- Introduction To Accounting Information SystemsDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Accounting Information SystemsMARRIETTE JOY ABADNo ratings yet
- AIS Chapter 1 Questions AnswersDocument9 pagesAIS Chapter 1 Questions AnswersMR ANo ratings yet
- Usefulness of Accounting Information SystemsDocument5 pagesUsefulness of Accounting Information Systemsdiqyst33251No ratings yet
- Overview of AISDocument8 pagesOverview of AISBulelwa HarrisNo ratings yet
- Management Information System: Submitted by Presented byDocument18 pagesManagement Information System: Submitted by Presented byrani222No ratings yet
- CIS Accounting Information SystemDocument3 pagesCIS Accounting Information SystemJowielly JimenezNo ratings yet
- Financial Information SystemDocument1 pageFinancial Information SystemarshchandrakarNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information System (AIS) : PeopleDocument2 pagesAccounting Information System (AIS) : PeopleYuka Fujiwara100% (1)
- AIS Chapter 1Document31 pagesAIS Chapter 1Dr. Mohammad Noor AlamNo ratings yet
- 5 Dr. Abhay UpadhyayaDocument8 pages5 Dr. Abhay UpadhyayaRavi ModiNo ratings yet
- M01 - AIS (Introduction)Document6 pagesM01 - AIS (Introduction)wingsenigma 00No ratings yet
- Accounting Information SystemsDocument9 pagesAccounting Information SystemsSheila Mae AramanNo ratings yet
- Summary of Accounting Information SystemsDocument5 pagesSummary of Accounting Information SystemsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- MIS Unit - 2,3,4Document51 pagesMIS Unit - 2,3,4Chirag ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 1: Arrange-MentDocument7 pagesSheet - 1: Arrange-MentShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- Follow Who Know RoadDocument8 pagesFollow Who Know RoadIbrahimm Denis FofanahNo ratings yet
- MIS With Functional Areas of BusinessDocument33 pagesMIS With Functional Areas of BusinessShubham Agarwal100% (1)
- Accounting Information System ManuscriptDocument11 pagesAccounting Information System ManuscriptShivani GuptaNo ratings yet
- AKN4509 Accounting Information SystemsDocument57 pagesAKN4509 Accounting Information SystemsAgnes Teoh Sook SianNo ratings yet
- Start And Grow Your Own Consulting Business From Zero: Artificial Intelligence in Accounting Practical Applications Odoo 17: odoo consultations, #1.1From EverandStart And Grow Your Own Consulting Business From Zero: Artificial Intelligence in Accounting Practical Applications Odoo 17: odoo consultations, #1.1No ratings yet
- Mis in Manufacturing IndustryDocument34 pagesMis in Manufacturing Industrymobashreen m i sNo ratings yet
- Impact and Influence of Technology in Today's ContextDocument15 pagesImpact and Influence of Technology in Today's Contextmobashreen m i sNo ratings yet
- KANBAN JIT PPT FinalDocument56 pagesKANBAN JIT PPT Finalmobashreen m i sNo ratings yet
- Job Rotation, Gamification, Steps For EffectiveDocument24 pagesJob Rotation, Gamification, Steps For Effectivemobashreen m i sNo ratings yet
- Why Diversity Is Important in The OrganizationDocument45 pagesWhy Diversity Is Important in The Organizationmobashreen m i sNo ratings yet
- 4mat Model of Engagement and Training Pedagogy: Mobashreen M I S Mba Ii Year 1913323036024 DATE: 01/10/2020Document4 pages4mat Model of Engagement and Training Pedagogy: Mobashreen M I S Mba Ii Year 1913323036024 DATE: 01/10/2020mobashreen m i sNo ratings yet
- The Trainer The Provider The Consultant The Innovator The ManagerDocument12 pagesThe Trainer The Provider The Consultant The Innovator The Managermobashreen m i sNo ratings yet
- Digital Marketing PlanDocument15 pagesDigital Marketing Planmobashreen m i sNo ratings yet
- Reply SpeechDocument1 pageReply SpeechAleeya AliesyaNo ratings yet
- Grisna Sawining NPM. 18111007Document16 pagesGrisna Sawining NPM. 18111007Nurna Ningsih14No ratings yet
- What Exactly Is A GeodatabaseDocument13 pagesWhat Exactly Is A GeodatabasecosminmargineanNo ratings yet
- Konica Minolta Regius Model 110 Installation ManualDocument35 pagesKonica Minolta Regius Model 110 Installation ManualRodrigo Dos Santos SilvaNo ratings yet
- Multithreading in Java (Unit 4)Document19 pagesMultithreading in Java (Unit 4)SAV Sports100% (1)
- Virtual Storage Access Method (VSAM)Document49 pagesVirtual Storage Access Method (VSAM)Akash KumarNo ratings yet
- 3 SQLDocument62 pages3 SQLMai LinhNo ratings yet
- M27COM CW1 Group Report Coursework BriefDocument7 pagesM27COM CW1 Group Report Coursework Briefvalmont reedemNo ratings yet
- Contents:: Multiprocessors: Characteristics of Multiprocessor, Structure of MultiprocessorDocument52 pagesContents:: Multiprocessors: Characteristics of Multiprocessor, Structure of MultiprocessorMeenakshi PatelNo ratings yet
- H12 211 PDFDocument182 pagesH12 211 PDFtajindersinNo ratings yet
- SknewDocument4 pagesSknewAjay ChopraNo ratings yet
- Definition of UMA: Basis For Comparison UMA NumaDocument10 pagesDefinition of UMA: Basis For Comparison UMA NumaaagamNo ratings yet
- MigrationObjects OP enDocument1,122 pagesMigrationObjects OP enmitesh aher100% (2)
- Cybercrime Tactics and Techniques: Q3 2018: Provided byDocument27 pagesCybercrime Tactics and Techniques: Q3 2018: Provided byAndres Felipe CameroNo ratings yet
- Exam 70-662 Microsoft Exchange Server 2010, Configuring Install and Config Exchange ServersDocument6 pagesExam 70-662 Microsoft Exchange Server 2010, Configuring Install and Config Exchange Serversviti_93No ratings yet
- Enterprise Architecture PDFDocument175 pagesEnterprise Architecture PDFCarlos TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Backup and Restore Mysql DatabasesDocument5 pagesBackup and Restore Mysql DatabasesMatt HanNo ratings yet
- IFYP0023 Week 9 Lecture - Social Media & E-BusinessDocument52 pagesIFYP0023 Week 9 Lecture - Social Media & E-BusinessWenxin100% (1)
- Pc101 Document Exercise CertificateanddegreestableDocument1 pagePc101 Document Exercise CertificateanddegreestableCoco MariñoNo ratings yet
- ME2402-Computer Integrated ManufacturingDocument6 pagesME2402-Computer Integrated ManufacturingLarry SmithNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization Imp QuestionDocument2 pagesComputer Organization Imp QuestionHulk ManNo ratings yet
- Process Flow Diagram (For Subscribers Who Visits Merchant Business Premises)Document2 pagesProcess Flow Diagram (For Subscribers Who Visits Merchant Business Premises)Lovelyn ArokhamoniNo ratings yet
- UoN BIT Full-Time Pathway - 17 Aug 2010 - YSSDocument1 pageUoN BIT Full-Time Pathway - 17 Aug 2010 - YSSSusan VoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Customer Relationship ManagementDocument25 pagesChapter 16 Customer Relationship Managementsunchox123No ratings yet
- 09 Incorta AdministrationDocument59 pages09 Incorta AdministrationJaghanNo ratings yet
- Terraform Notes by Kishan-2Document30 pagesTerraform Notes by Kishan-2rahul100% (1)
- Contoh Studi Kasus ZachmanDocument15 pagesContoh Studi Kasus Zachmanindra sunardiNo ratings yet
- Learn Python - For BeginnersDocument7 pagesLearn Python - For BeginnersremoondhakaNo ratings yet
- The Cloud Strategy Cookbook, 2019Document16 pagesThe Cloud Strategy Cookbook, 2019Jose SerranoNo ratings yet
Financial Information System
Financial Information System
Uploaded by
mobashreen m i s0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
175 views5 pagesA financial information system (FIS) collects, stores, and analyzes financial data to support decision making. It tracks elements like accounting, budgets, payables, receivables, and generates reports. An FIS ensures financial obligations are met with minimal resources and provides accounting reports, budgets, forecasts, and "what-if" analyses. It must provide accurate, timely data and support auditing, reporting, budgeting, and financial statement preparation. An FIS has modules for accounting, budgets, payables, receivables, payroll, and other functions. It offers benefits like integrated information, expenditure control, and tighter budget oversight.
Original Description:
FIS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA financial information system (FIS) collects, stores, and analyzes financial data to support decision making. It tracks elements like accounting, budgets, payables, receivables, and generates reports. An FIS ensures financial obligations are met with minimal resources and provides accounting reports, budgets, forecasts, and "what-if" analyses. It must provide accurate, timely data and support auditing, reporting, budgeting, and financial statement preparation. An FIS has modules for accounting, budgets, payables, receivables, payroll, and other functions. It offers benefits like integrated information, expenditure control, and tighter budget oversight.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
175 views5 pagesFinancial Information System
Financial Information System
Uploaded by
mobashreen m i sA financial information system (FIS) collects, stores, and analyzes financial data to support decision making. It tracks elements like accounting, budgets, payables, receivables, and generates reports. An FIS ensures financial obligations are met with minimal resources and provides accounting reports, budgets, forecasts, and "what-if" analyses. It must provide accurate, timely data and support auditing, reporting, budgeting, and financial statement preparation. An FIS has modules for accounting, budgets, payables, receivables, payroll, and other functions. It offers benefits like integrated information, expenditure control, and tighter budget oversight.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
FINANCIAL
INFORMATION
SYSTEM
ASSIGNMENT
MOBASHREEN M I S
MBA II YEAR
1913323036024
MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM
FINANCIAL INFORMATION SYSTEM
Financial Information System is a system that accumulates and analyses financial data in
order to make good financial management decisions in running the business.
Financial information systems are the software programs that can be set up to keep track of
banking, accounts payable and accounts receivable; to generate standard financial reports
such as a profit-and-loss statement; and to report the information in various formats.
The basic objective of the financial information system is to meet the firm's financial
obligations as they come due, using the minimal amount of financial resources consistent
with an established margin of safety. Outputs generated by the system include accounting
reports, operating and capital budgets, working capital reports, cash flow forecast, and
various what – if analysis reports. The evaluation of financial data may be performed
through ratio analysis, trend evaluation, and financial planning modeling
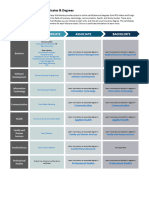
FIS must have the following capabilities:
Collect accurate, timely, complete, reliable information.
Provide adequate management reporting.
Support budget preparation and execution.
Facilitate financial statement preparation.
Support government-wide and agency policy decision.
Provide complete audit trail to facilitate audits.
An FIS will consist of several elements with different functions. The core of an FIS could be
expected to include the following modules and systems:
General ledger
Budgetary accounting
Accounts payable
Accounts receivable
The noncore or other modules
Payroll system
Budget development
Procurement
Project ledger
Asset module.
Advantages of FIS
There are many advantages of implementing an FIS. A few of them are listed below:
Integrated financial information
Flexibility of reporting and additional control over expenditure
Tighter views of budgets versus actual
Less administration required within the business
Features of Financial Information System
a) Clarity/Understandability
b) Reliability
c) Relevance
d) Presentation
e) Security
f) Cost Effective
g) Comparability
h) Availability
i) Robust in terms of producing information
j) Verifiability
The applications of FIS in financial analysis are:
a) Cash flow analysis
b) Budget analysis
c) Ratio analysis and management norms
d) Sources and uses of funds
e) Maintenance cost analysis
Components of Financial Information System
Financial Information System generally consists of six main components: people,
procedures, data, software, information technology infrastructure and internal control.
People: These are the users of the FIS. Internal users include accountants and other financial
officers of the company. Then there are also users outside the organization that can be
given access to the AIS. Some such external users are auditors, consultants, tax authorities
etc.
Procedures: These are the procedures the system follows to collect and process data. The
database for such a process can be internal (like employee names, sales figures) or external
databases (like customer orders, tax slabs etc). The feeding of the data can be both manual
as well as automated.
Data: FIS mainly deals with all kinds of financial and commercial data. Any data that is
pertinent to the financial of the firm will be input data for an FIS. Care must be taken that
the data entered is accurate and complete. Examples of such data include general ledger,
invoices, orders, payroll, bills etc.
Software: FIS software performs all the functions of storing, processing, analysing, retrieving
financial data of a company. The software can be generalized software that is available in
the market or can be specialized software created specifically for a particular company and
its accounting needs. Some of this software has an inbuilt internal control and audit options.
They even help in tax management.
Information Technology Infrastructure: Information technology infrastructure is just a fancy
name for the hardware used to operate the financial information system. These can include
computers, laptops, servers, printers, scanners, secondary storage hardware etc. Perhaps
most importantly, the hardware selected for an FIS must be compatible with the intended
software.
Internal Controls: Internal controls of a FIS are the security measures it contains to protect
sensitive data. These can be as simple as passwords or as complex as biometric
identification. FIS must have internal controls to protect against unauthorized computer
access and to limit access to authorized users which includes some users inside the
company.
Examples
1.If a business has:
Cash = $15 million
Marketable securities = $20 million
Inventory = $25 million
Short-term Debt = $15 million
Accounts Payables = $15 million
Current assets = 15 + 20 + 25 = 60 million
Current liabilities = 15 + 15 = 30 million
Current ratio = 60 million / 30 million = 2.0
2. Alpha Inc. has the following information
Cost of Goods Sold – $600,000
Beginning inventory – $110,000
Ending inventory – $130,000
Find out the inventory turnover ratios
Average inventory of Alpha Inc. would be = (The beginning inventory + the ending
inventory)/2
= ($110,000 + $130,000)/2 = $240,000/2 = $120,000.
Using the inventory ratio, we get:
Inventory Turnover ratio = Cost of Goods Sold / Average Inventories
OR
Inventory Turnover ratio= $600,000 / $120,000 = 5
3. IF a company has an average accounts receivable balance of $200,000 and annual sales of
$1,200,000 then its DSO figure is:
Days Sales Outstanding=
$ 200,000
$ 1,200,000
X 365
= 60.8 days
The company requires 60.8 days to collect a typical invoice.
You might also like
- SC01 Sophos Central Sales Overview v1.0.0Document51 pagesSC01 Sophos Central Sales Overview v1.0.0DaNi Velandia0% (1)
- DIGITAL MARKETING PLAN KFCDocument14 pagesDIGITAL MARKETING PLAN KFCmobashreen m i s100% (2)
- MIS PDF Notes Unit 4Document14 pagesMIS PDF Notes Unit 4Dr. MURALI KRISHNA VELAVETINo ratings yet
- Financial AccountingDocument19 pagesFinancial AccountingsaniaNo ratings yet
- F MisDocument2 pagesF MisyogeshvraoNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting G1Document9 pagesFinancial Accounting G1Precious Anne ValderramaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information System QuestionsDocument7 pagesAccounting Information System QuestionsMohsin ShaikhNo ratings yet
- What Are The Benefits of A Financial Management Information SystemDocument5 pagesWhat Are The Benefits of A Financial Management Information SystemSandra MagnoNo ratings yet
- 9511 1st AssignmentDocument7 pages9511 1st AssignmentUmair JavedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Accounting Information System: PeopleDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Accounting Information System: PeopleVIBHASH SHANKARNo ratings yet
- Financial Information System: Presented byDocument23 pagesFinancial Information System: Presented bySrimon DasNo ratings yet
- AFIS AssignmentDocument3 pagesAFIS Assignmentbsaf2147266No ratings yet
- Accounting Information SystemsDocument15 pagesAccounting Information SystemsPandu Rangarao100% (3)
- Accounting Information SystemDocument22 pagesAccounting Information SystemkvkumarnaveenNo ratings yet
- IM Unit 4Document28 pagesIM Unit 4Sara ZafarNo ratings yet
- AIS SummaryDocument5 pagesAIS SummaryKimboy Elizalde PanaguitonNo ratings yet
- FIST Lecture 1Document26 pagesFIST Lecture 1sforsanjida1No ratings yet
- Research ProjectDocument8 pagesResearch ProjectAriesNo ratings yet
- Finacial ISDocument6 pagesFinacial ISkaurbhatti78No ratings yet
- Accounting Information System-OverviewDocument15 pagesAccounting Information System-Overviewsema100% (1)
- Report For AIS 1Document5 pagesReport For AIS 1Samer IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Sistem Information AccountingDocument9 pagesSistem Information AccountingNicole Daniella JinggaNo ratings yet
- The Information System: An Accountant's PerspectiveDocument33 pagesThe Information System: An Accountant's PerspectiveLUIS ALFONSO DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Life and Works of Genoveva and NickDocument7 pagesLife and Works of Genoveva and Nickjoy sooyoungNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information SystemDocument5 pagesAccounting Information SystemAnnhtak PNo ratings yet
- Unit 9: Financial Information SystemDocument13 pagesUnit 9: Financial Information SystemSrishti VivekNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument2 pagesDefinitionKrisha TubogNo ratings yet
- AIS MidtermDocument13 pagesAIS MidtermJansen JacobNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information SystemDocument33 pagesAccounting Information SystemBir MallaNo ratings yet
- An Over View Regarding AISDocument15 pagesAn Over View Regarding AISDonia MohamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ReviewerDocument16 pagesChapter 1 Revieweranon_879788236No ratings yet
- Introduction - Accounting Information SystemsDocument6 pagesIntroduction - Accounting Information SystemsJuris AvilaNo ratings yet
- Mis in FinanceDocument19 pagesMis in FinanceDibyendu Paul0% (1)
- CAS AISdescriptionDocument5 pagesCAS AISdescriptionmika.tov1997No ratings yet
- Lecture-4: Course ID: BBA-305Document13 pagesLecture-4: Course ID: BBA-305Mansi VermaNo ratings yet
- Set Up and Operate A Computerized Accounting SystemDocument10 pagesSet Up and Operate A Computerized Accounting Systemabebe kumelaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information SystemDocument2 pagesAccounting Information SystemJansen Alonzo BordeyNo ratings yet
- Accounting Notes: Accounting Information: A Means To An EndDocument5 pagesAccounting Notes: Accounting Information: A Means To An EndNNo ratings yet
- Cost TyaDocument7 pagesCost TyaTya NwsNo ratings yet
- The Study of Accounting Information Systems:: Essential Concepts and ApplicationsDocument19 pagesThe Study of Accounting Information Systems:: Essential Concepts and ApplicationsNhoel RsNo ratings yet
- Importance of Information SystemsDocument148 pagesImportance of Information Systemsbauuaaa100% (1)
- Introduction To Accounting Information SystemsDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Accounting Information SystemsMARRIETTE JOY ABADNo ratings yet
- AIS Chapter 1 Questions AnswersDocument9 pagesAIS Chapter 1 Questions AnswersMR ANo ratings yet
- Usefulness of Accounting Information SystemsDocument5 pagesUsefulness of Accounting Information Systemsdiqyst33251No ratings yet
- Overview of AISDocument8 pagesOverview of AISBulelwa HarrisNo ratings yet
- Management Information System: Submitted by Presented byDocument18 pagesManagement Information System: Submitted by Presented byrani222No ratings yet
- CIS Accounting Information SystemDocument3 pagesCIS Accounting Information SystemJowielly JimenezNo ratings yet
- Financial Information SystemDocument1 pageFinancial Information SystemarshchandrakarNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information System (AIS) : PeopleDocument2 pagesAccounting Information System (AIS) : PeopleYuka Fujiwara100% (1)
- AIS Chapter 1Document31 pagesAIS Chapter 1Dr. Mohammad Noor AlamNo ratings yet
- 5 Dr. Abhay UpadhyayaDocument8 pages5 Dr. Abhay UpadhyayaRavi ModiNo ratings yet
- M01 - AIS (Introduction)Document6 pagesM01 - AIS (Introduction)wingsenigma 00No ratings yet
- Accounting Information SystemsDocument9 pagesAccounting Information SystemsSheila Mae AramanNo ratings yet
- Summary of Accounting Information SystemsDocument5 pagesSummary of Accounting Information SystemsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- MIS Unit - 2,3,4Document51 pagesMIS Unit - 2,3,4Chirag ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 1: Arrange-MentDocument7 pagesSheet - 1: Arrange-MentShaheen MahmudNo ratings yet
- Follow Who Know RoadDocument8 pagesFollow Who Know RoadIbrahimm Denis FofanahNo ratings yet
- MIS With Functional Areas of BusinessDocument33 pagesMIS With Functional Areas of BusinessShubham Agarwal100% (1)
- Accounting Information System ManuscriptDocument11 pagesAccounting Information System ManuscriptShivani GuptaNo ratings yet
- AKN4509 Accounting Information SystemsDocument57 pagesAKN4509 Accounting Information SystemsAgnes Teoh Sook SianNo ratings yet
- Start And Grow Your Own Consulting Business From Zero: Artificial Intelligence in Accounting Practical Applications Odoo 17: odoo consultations, #1.1From EverandStart And Grow Your Own Consulting Business From Zero: Artificial Intelligence in Accounting Practical Applications Odoo 17: odoo consultations, #1.1No ratings yet
- Mis in Manufacturing IndustryDocument34 pagesMis in Manufacturing Industrymobashreen m i sNo ratings yet
- Impact and Influence of Technology in Today's ContextDocument15 pagesImpact and Influence of Technology in Today's Contextmobashreen m i sNo ratings yet
- KANBAN JIT PPT FinalDocument56 pagesKANBAN JIT PPT Finalmobashreen m i sNo ratings yet
- Job Rotation, Gamification, Steps For EffectiveDocument24 pagesJob Rotation, Gamification, Steps For Effectivemobashreen m i sNo ratings yet
- Why Diversity Is Important in The OrganizationDocument45 pagesWhy Diversity Is Important in The Organizationmobashreen m i sNo ratings yet
- 4mat Model of Engagement and Training Pedagogy: Mobashreen M I S Mba Ii Year 1913323036024 DATE: 01/10/2020Document4 pages4mat Model of Engagement and Training Pedagogy: Mobashreen M I S Mba Ii Year 1913323036024 DATE: 01/10/2020mobashreen m i sNo ratings yet
- The Trainer The Provider The Consultant The Innovator The ManagerDocument12 pagesThe Trainer The Provider The Consultant The Innovator The Managermobashreen m i sNo ratings yet
- Digital Marketing PlanDocument15 pagesDigital Marketing Planmobashreen m i sNo ratings yet
- Reply SpeechDocument1 pageReply SpeechAleeya AliesyaNo ratings yet
- Grisna Sawining NPM. 18111007Document16 pagesGrisna Sawining NPM. 18111007Nurna Ningsih14No ratings yet
- What Exactly Is A GeodatabaseDocument13 pagesWhat Exactly Is A GeodatabasecosminmargineanNo ratings yet
- Konica Minolta Regius Model 110 Installation ManualDocument35 pagesKonica Minolta Regius Model 110 Installation ManualRodrigo Dos Santos SilvaNo ratings yet
- Multithreading in Java (Unit 4)Document19 pagesMultithreading in Java (Unit 4)SAV Sports100% (1)
- Virtual Storage Access Method (VSAM)Document49 pagesVirtual Storage Access Method (VSAM)Akash KumarNo ratings yet
- 3 SQLDocument62 pages3 SQLMai LinhNo ratings yet
- M27COM CW1 Group Report Coursework BriefDocument7 pagesM27COM CW1 Group Report Coursework Briefvalmont reedemNo ratings yet
- Contents:: Multiprocessors: Characteristics of Multiprocessor, Structure of MultiprocessorDocument52 pagesContents:: Multiprocessors: Characteristics of Multiprocessor, Structure of MultiprocessorMeenakshi PatelNo ratings yet
- H12 211 PDFDocument182 pagesH12 211 PDFtajindersinNo ratings yet
- SknewDocument4 pagesSknewAjay ChopraNo ratings yet
- Definition of UMA: Basis For Comparison UMA NumaDocument10 pagesDefinition of UMA: Basis For Comparison UMA NumaaagamNo ratings yet
- MigrationObjects OP enDocument1,122 pagesMigrationObjects OP enmitesh aher100% (2)
- Cybercrime Tactics and Techniques: Q3 2018: Provided byDocument27 pagesCybercrime Tactics and Techniques: Q3 2018: Provided byAndres Felipe CameroNo ratings yet
- Exam 70-662 Microsoft Exchange Server 2010, Configuring Install and Config Exchange ServersDocument6 pagesExam 70-662 Microsoft Exchange Server 2010, Configuring Install and Config Exchange Serversviti_93No ratings yet
- Enterprise Architecture PDFDocument175 pagesEnterprise Architecture PDFCarlos TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Backup and Restore Mysql DatabasesDocument5 pagesBackup and Restore Mysql DatabasesMatt HanNo ratings yet
- IFYP0023 Week 9 Lecture - Social Media & E-BusinessDocument52 pagesIFYP0023 Week 9 Lecture - Social Media & E-BusinessWenxin100% (1)
- Pc101 Document Exercise CertificateanddegreestableDocument1 pagePc101 Document Exercise CertificateanddegreestableCoco MariñoNo ratings yet
- ME2402-Computer Integrated ManufacturingDocument6 pagesME2402-Computer Integrated ManufacturingLarry SmithNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization Imp QuestionDocument2 pagesComputer Organization Imp QuestionHulk ManNo ratings yet
- Process Flow Diagram (For Subscribers Who Visits Merchant Business Premises)Document2 pagesProcess Flow Diagram (For Subscribers Who Visits Merchant Business Premises)Lovelyn ArokhamoniNo ratings yet
- UoN BIT Full-Time Pathway - 17 Aug 2010 - YSSDocument1 pageUoN BIT Full-Time Pathway - 17 Aug 2010 - YSSSusan VoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Customer Relationship ManagementDocument25 pagesChapter 16 Customer Relationship Managementsunchox123No ratings yet
- 09 Incorta AdministrationDocument59 pages09 Incorta AdministrationJaghanNo ratings yet
- Terraform Notes by Kishan-2Document30 pagesTerraform Notes by Kishan-2rahul100% (1)
- Contoh Studi Kasus ZachmanDocument15 pagesContoh Studi Kasus Zachmanindra sunardiNo ratings yet
- Learn Python - For BeginnersDocument7 pagesLearn Python - For BeginnersremoondhakaNo ratings yet
- The Cloud Strategy Cookbook, 2019Document16 pagesThe Cloud Strategy Cookbook, 2019Jose SerranoNo ratings yet