Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2018 Work Plan Year 9 Ext Sem 1
2018 Work Plan Year 9 Ext Sem 1
Uploaded by
Maan Patel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views3 pagesThis mathematics work plan outlines the curriculum for a Year 9 extended mathematics class over semester 1 of 2018. It includes 8 topics to be covered from weeks 1 to 12, with 2-3 lessons devoted to each chapter. Key learning activities are listed for each topic. Formative and summative assessments include opening and skills assessment tasks, investigations, and a common test at the end of semester 1 to evaluate students' understanding of algebraic expansions and simplifications, linear equations, sets, radicals, coordinate geometry, measurement, and other concepts.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis mathematics work plan outlines the curriculum for a Year 9 extended mathematics class over semester 1 of 2018. It includes 8 topics to be covered from weeks 1 to 12, with 2-3 lessons devoted to each chapter. Key learning activities are listed for each topic. Formative and summative assessments include opening and skills assessment tasks, investigations, and a common test at the end of semester 1 to evaluate students' understanding of algebraic expansions and simplifications, linear equations, sets, radicals, coordinate geometry, measurement, and other concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views3 pages2018 Work Plan Year 9 Ext Sem 1
2018 Work Plan Year 9 Ext Sem 1
Uploaded by
Maan PatelThis mathematics work plan outlines the curriculum for a Year 9 extended mathematics class over semester 1 of 2018. It includes 8 topics to be covered from weeks 1 to 12, with 2-3 lessons devoted to each chapter. Key learning activities are listed for each topic. Formative and summative assessments include opening and skills assessment tasks, investigations, and a common test at the end of semester 1 to evaluate students' understanding of algebraic expansions and simplifications, linear equations, sets, radicals, coordinate geometry, measurement, and other concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
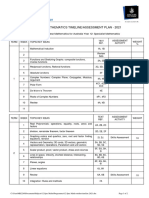
MATHEMATICS WORK PLAN - SEMESTER 1 2018
YEAR 9 EXTENDED MATHEMATICS
Week Chapter Learning Activities HOTS CCP HISTORY Assessment Activities
Review Chapter 1 – Algebra (2 lessons)
T1 Opening Problem Pg 88
Review Chapter 2 – Indices (2 lessons)
Wk 1
Ex 5A – The Distributive Law
5 – Algebraic Ex 5B – The Product (a+ b)(c +d )
2 Expansions and
Ex 5C – Difference of Two Squares
Simplification
Ex 5D – Perfect Squares
Skills Assessment Task –
3 Ex 5E – Further Expansion
Chapter 5
Ex 7A – Linear Equations Opening Problem Pg 126
4
7 – Linear Ex 7B – Rational Equations Discussion Pg 134
Equations Ex 7C – Problem Solving Activity Linear Equations Skills Assessment Task –
5
Ex 7D – Mixture Problems Pg 129 and Pg 132 Chapter 7
Ex 4A – Sets Opening Problem Pg66
6 Ex 4B – Special Number Sets Activity Pg 75 , 76
4 – Sets and Venn Ex 4C – Set Builder Notation
Diagrams Ex 4D – Complement of a Set
Skills Assessment Task –
7 Ex 4E – Venn Diagrams Puzzle Pg 77
Chapters 4
Ex 4F – Problem Solving with Venn Diagrams
Ex 8A – Square Roots OP Pg 142
8 Ex 8B – Rules for Square Roots Historical note
Ex 8C – Solving x 2=k Pythagoras Pg 142
8 – Radicals and
Pythagoras Ex 8D – Pythagoras’ Theorem Investigation – Surf
9 Discussion Pg 150
Ex 8E – The Converse of Pythagoras’ Theorem Rescue
Ex 8F – Pythagorean Triples Skills Assessment Task –
10 Activity Pg 154
Ex 8G – Problem Solving using Pythagoras Chapter 8
Ex 10A – The Distance Between Two Points
OP Pg 194
11 Ex 10B – Midpoints
Ex 10C – Gradient
10 – Coordinate Ex 10D – Axes Intercepts Use GC to draw graphs
T2 Wk 1 Geometry Ex 10E – The Equation of a Line Activity Pg 215 Moving
Ex 10F – Graphing Lines from Equations staircases
Ex 10G – Vertical and Horizontal Lines Skills Assessment Task –
2
Ex 10H – Finding the Equation of a Line Chapter 10
3 NAPLAN PRACTICE – Calculator and Non Calculator
Ex 9A – Length
Ex 9B – Perimeter OP pg 168
4
Ex 9C – Area
9 – Length and Ex 9D – Area Formulae
Area Ex 9E – Areas of Composite Figures
Investigation – The
5 Ex 11A – Solids Activity Pg 186
Shadehouse Pg 182
11 – Further Ex 11B – Surface Area
Measurement OP Pg 220
Ex 11C – Volume
Time in Aboriginal Skills Assessment Task –
6 Ex 11D – Capacity
Culture Pg 239 Chapters 9 and 11
Ex 11E – Time
Asian Calendars Pg 240
COMMON TEST – Algebraic Expansions and Simplification, Linear Equations, Sets and Venn Diagrams,
7
Radicals and Pythagoras, Coordinate Geometry, Length and Area, Further Measurement
ASSESSMENT RUBRIC Name: __________________________ Grade:
Criteria 0 1 2 3 4 5
Understanding of concepts and
None Limited Basic Generally competent Some depth Comprehensive
relationships
Mostly effective selection Highly effective selection
Some selection and Generally effective selection
and application to find and application to find
Selection and application of Limited attempt with limited application to find some and application to find
mostly accurate solutions to efficient and accurate
Mathematical techniques and No attempt accuracy in solving routine accurate solutions to mostly accurate solutions to
routine and some complex solutions to routine and
algorithms problems routine problems in some routine problems in a
problems in a variety of complex problems in a
contexts. variety of contexts.
contexts. variety of contexts.
Successful application and Successful application and
Attempt with limited Some application to find Successful application to
Application of Mathematical models No attempt some development to find development to find concise
accuracy partially accurate results find most accurate results
most accurate results and accurate solutions
Mostly appropriate and
Generally appropriate and Appropriate and effective
Attempted with limited Some appropriate use to effective use to find mostly
effective use to find mostly use to find accurate
Use of electronic technology No attempt accuracy in solving routine find some accurate solutions accurate solutions to
accurate solutions to solutions to routine and
problems. to routine problems. routine and some complex
routine problems. complex problems
problems.
Interpretation of mathematical results
None Limited Some Generally appropriate Most appropriate Comprehensive
in the context of the problem
Understanding of reasonableness and
None Limited Some awareness Some understanding Some depth Comprehensive
limitations of mathematical results
Use of appropriate mathematical
notation, representation and None Limited Some appropriate Generally appropriate Most accurate Proficient and accurate
terminology
Generally effective Mostly effective Highly effective
Some communication with
communication and communication and communication and
Communication of mathematical ideas No attempt Limited attempt attempted reasoning and/or
reasoning to develop some reasoning to develop mostly reasoning to develop logical
argument
logical arguments logical arguments. and concise arguments
Most effective development
Development and testing of Limited attempt of a Attempt of a reasonable Development and testing of Effective development and
No attempt and testing of valid
conjectures conjecture conjecture a greatly valid conjecture testing of valid conjectures
conjectures
Year 9 Achievement Standard
By the end of Year 9, students solve problems involving simple interest. They interpret ratio and scale factors in similar figures. Students explain similarity of triangles. They recognise the
connections between similarity and the trigonometric ratios. Students compare techniques for collecting data from primary and secondary sources. They make sense of the position of the mean
and median in skewed, symmetric and bi-modal displays to describe and interpret data.
Students apply the index laws to numbers and express numbers in scientific notation. They expand binomial expressions. They find the distance between two points on the Cartesian plane and
the gradient and midpoint of a line segment. They sketch linear and non-linear relations. Students calculate areas of shapes and the volume and surface area of right prisms and cylinders.
They use Pythagoras’ Theorem and trigonometry to find unknown sides of right-angled triangles. Students calculate relative frequencies to estimate probabilities, list outcomes for two-step
experiments and assign probabilities for those outcomes. They construct histograms and back-to-back stem-and-leaf plots.
You might also like
- A-Level Maths Videos (Owen PPTs Etc)Document3 pagesA-Level Maths Videos (Owen PPTs Etc)Ghalia DoshanNo ratings yet
- Commanding The Laws of Wealth by Bob ProctorDocument20 pagesCommanding The Laws of Wealth by Bob ProctorKyle Hartman Music67% (3)
- 2018 Work Plan Year 9 Ext Sem 2Document3 pages2018 Work Plan Year 9 Ext Sem 2Maan PatelNo ratings yet
- 2023 Y8 DV AT2 NotificationDocument2 pages2023 Y8 DV AT2 NotificationCamloc LuNo ratings yet
- Subject: ةداملا: Mathematics class: فصلا: ةيونسلا ةطخلا 2013 Yearly Plan 2012-2013Document9 pagesSubject: ةداملا: Mathematics class: فصلا: ةيونسلا ةطخلا 2013 Yearly Plan 2012-2013Aisha QasimNo ratings yet
- Anastasia Kelly Unit 4 - Exponentials 2020-21Document2 pagesAnastasia Kelly Unit 4 - Exponentials 2020-21rudywahudiNo ratings yet
- Methods Revision GuideDocument2 pagesMethods Revision Guideapi-737716525No ratings yet
- Math Textbook Anwers Chapter 7Document44 pagesMath Textbook Anwers Chapter 7Coen WalterNo ratings yet
- A2 FM Tutorials and Revision PageDocument2 pagesA2 FM Tutorials and Revision PagelakhtariyavedNo ratings yet
- 2016-2017 Big Ideas Algebra IIDocument3 pages2016-2017 Big Ideas Algebra IIDavid WalkeNo ratings yet
- 2023 Y8 Core AT2 NotificationDocument2 pages2023 Y8 Core AT2 NotificationCamloc LuNo ratings yet
- AS Maths Tutorials - Pure: Worksheet With Video SolutionsDocument3 pagesAS Maths Tutorials - Pure: Worksheet With Video SolutionsAbdi WhamheadNo ratings yet
- 11 University Physics Outline 2020Document8 pages11 University Physics Outline 2020wefasdfNo ratings yet
- Ogspot: Sixth Semester B.Sc. Degree Examination, March (Cucbcss-Ug) P Phy 6B (El) - Computational PhysicsDocument3 pagesOgspot: Sixth Semester B.Sc. Degree Examination, March (Cucbcss-Ug) P Phy 6B (El) - Computational PhysicsPhysicsQuestionNo ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematics Curriculum - OverviewDocument15 pagesDiscrete Mathematics Curriculum - OverviewSayed AliNo ratings yet
- Prepared by Ladybird: Topics Year (No. of Question in Exam) 2007 2008 2009 Form 4Document2 pagesPrepared by Ladybird: Topics Year (No. of Question in Exam) 2007 2008 2009 Form 4sewcinNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Further Maths 2019: Matrices ChecklistDocument1 pageUnit 4 Further Maths 2019: Matrices ChecklistAngus DelaneyNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Further Maths 2019: Matrices ChecklistDocument1 pageUnit 4 Further Maths 2019: Matrices ChecklistAngus DelaneyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet (Engineering Maths-Hnd1: SECTION A (Sequences)Document6 pagesTutorial Sheet (Engineering Maths-Hnd1: SECTION A (Sequences)enow reneNo ratings yet
- Geometry Outline 2009Document5 pagesGeometry Outline 2009SimonBorgert100% (2)
- FEA&CM Lecture-16Document44 pagesFEA&CM Lecture-16shivaNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument8 pagesExamray salmonNo ratings yet
- 2017 Precalch Chapter 1 NotesDocument30 pages2017 Precalch Chapter 1 NotesVino DhNo ratings yet
- Math F4Document12 pagesMath F4Kennedy Otieno OnyangoNo ratings yet
- Jacobian Elliptic Functions and Theta FunctionsDocument15 pagesJacobian Elliptic Functions and Theta FunctionsAlexandra Nicoleta Teisi100% (1)
- Test PrepDocument5 pagesTest Prepkrishna sahuNo ratings yet
- Math Scheme Form 4Document16 pagesMath Scheme Form 4griggztNo ratings yet
- 16 - Jacobian Elliptic Functions and Theta FunctionsDocument15 pages16 - Jacobian Elliptic Functions and Theta FunctionsJohnNo ratings yet
- AS Maths Tutorial - Pure (Linked To Textbook)Document1 pageAS Maths Tutorial - Pure (Linked To Textbook)Arathy VaseeharanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Traffic Lights - Mathematics Methods 2024 V2-2Document8 pagesUnit 1 - Traffic Lights - Mathematics Methods 2024 V2-2shanwa.brileeNo ratings yet
- 07 QuicksortDocument9 pages07 Quicksortislamemad079No ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-04-28 at 16.50.59Document16 pagesScreenshot 2024-04-28 at 16.50.59stuti.mehta005No ratings yet
- Program Ma Yang Dal Ton 2009Document13 pagesProgram Ma Yang Dal Ton 2009khai_83No ratings yet
- 2019 Year 10 Mathematics (Extended) Student Workplan Semester 2Document3 pages2019 Year 10 Mathematics (Extended) Student Workplan Semester 2Maan PatelNo ratings yet
- Break Down O1Document6 pagesBreak Down O1Saad GulfamNo ratings yet
- Parametric Functions Ext1 (3U) HSCDocument7 pagesParametric Functions Ext1 (3U) HSCJoseph GameilNo ratings yet
- Gr11PreCal PDFDocument234 pagesGr11PreCal PDFpransguNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Plan Year 13 PureDocument3 pagesCurriculum Plan Year 13 PureShalini JainNo ratings yet
- Apio 2008Document9 pagesApio 2008Adam Muhammad SyachNo ratings yet
- UACE Mathematics 2015 Paper 1Document4 pagesUACE Mathematics 2015 Paper 1amone patrickNo ratings yet
- CE1008 Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesCE1008 Lesson PlanRaja RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Combine Add-Math Book 2Document190 pagesCombine Add-Math Book 2Diana GautamNo ratings yet
- Higher Exam Study Guide 2023Document3 pagesHigher Exam Study Guide 2023Euan McConnachieNo ratings yet
- Class RevisionDocument26 pagesClass RevisionSuvir GajadhurNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 OutlineDocument2 pagesUnit 2 OutlineshanechidzikweNo ratings yet
- Solid Area Scan Conversion or Visible Surface DetectionDocument67 pagesSolid Area Scan Conversion or Visible Surface Detectionshivam kumarNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5 ADocument4 pagesExercise 5 AStanleyNo ratings yet
- IE-411 Assignment No.1 Team No.1Document18 pagesIE-411 Assignment No.1 Team No.1Mohammad KashifNo ratings yet
- Ajms 498 23Document11 pagesAjms 498 23BRNSS Publication Hub InfoNo ratings yet
- GCSE Higher Year 1Document27 pagesGCSE Higher Year 1Nayem Hossain HemuNo ratings yet
- II Ass Mn5201 Finite Element Applications in ManufacturingDocument2 pagesII Ass Mn5201 Finite Element Applications in ManufacturinggfdczxNo ratings yet
- Enrichment Enhanced Math 10Document2 pagesEnrichment Enhanced Math 10Ralph NilloNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Control System PDFDocument12 pagesPneumatic Control System PDFANANT KULKARNINo ratings yet
- 11 Maths Syllabus 21-22Document1 page11 Maths Syllabus 21-22Sanjeet YadavNo ratings yet
- MCR3U Unit 1 Notes - Rational ExpressionsDocument21 pagesMCR3U Unit 1 Notes - Rational ExpressionsHassan SubhieNo ratings yet
- 12 Maths Syllabus 21-22Document1 page12 Maths Syllabus 21-22Ashish TiwariNo ratings yet
- Intermediate 2 - Prelim ChecklistDocument3 pagesIntermediate 2 - Prelim ChecklistknoxmathsNo ratings yet
- 11 Maths Studies Term 1 OverviewDocument2 pages11 Maths Studies Term 1 OverviewLaurencia Merry ChrismayantiNo ratings yet
- Modular Forms and Special Cycles on Shimura Curves. (AM-161)From EverandModular Forms and Special Cycles on Shimura Curves. (AM-161)No ratings yet
- Integration of One-forms on P-adic Analytic Spaces. (AM-162)From EverandIntegration of One-forms on P-adic Analytic Spaces. (AM-162)No ratings yet
- Biology Practical Easwar AlladaDocument6 pagesBiology Practical Easwar AlladaMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- 12 Spec Maths Student Timeline 2021Document2 pages12 Spec Maths Student Timeline 2021Maan PatelNo ratings yet
- Actively Fit: SmokingDocument4 pagesActively Fit: SmokingMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- Scienceworld: Stannard WilliamsonDocument53 pagesScienceworld: Stannard WilliamsonMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- How To Write A SynopsisDocument1 pageHow To Write A SynopsisMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- Year 9 English Drama Text Response Text: Play Script Adaptation of Bram Stoker's Dracula Genre: Gothic/HorrorDocument5 pagesYear 9 English Drama Text Response Text: Play Script Adaptation of Bram Stoker's Dracula Genre: Gothic/HorrorMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- 2017 Independent Reading Student Task PlannerDocument2 pages2017 Independent Reading Student Task PlannerMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- Speediest Car: Year 10 Physical SciencesDocument6 pagesSpeediest Car: Year 10 Physical SciencesMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- CM-PR-DSG-01 Rev.02 Design ProcedureDocument10 pagesCM-PR-DSG-01 Rev.02 Design ProcedurePeter Sare WolloNo ratings yet
- Autonomous DronesDocument1 pageAutonomous Dronesisrael samuelNo ratings yet
- Lab Spot SpeedDocument11 pagesLab Spot SpeedshazwanNo ratings yet
- English Quiz Personal Letter and Invitation Card - Print - QuizizzDocument5 pagesEnglish Quiz Personal Letter and Invitation Card - Print - Quizizzriyanti putriNo ratings yet
- SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/ UndertakingDocument12 pagesSECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/ UndertakingWellington Ricardo Conceição da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science: 2 Grading Grade 8 "Remediation"Document11 pagesEarth Science: 2 Grading Grade 8 "Remediation"Shane Catherine BesaresNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Lesson 5.1 - Nano-WorldDocument1 pageThis Study Resource Was: Lesson 5.1 - Nano-WorldLee SuarezNo ratings yet
- MTH 234 Exam Review 3 SolutionsDocument11 pagesMTH 234 Exam Review 3 SolutionsDonald ChurchNo ratings yet
- Nano AllDocument183 pagesNano AllvenuNo ratings yet
- Simulation Modelling For Automated Guided Vehicle Introduction To The Loading Process of Ro-Ro ShipsDocument12 pagesSimulation Modelling For Automated Guided Vehicle Introduction To The Loading Process of Ro-Ro ShipsHo Van RoiNo ratings yet
- Roles of Statistics in ResearchDocument18 pagesRoles of Statistics in ResearchJevan A. Calaque100% (2)
- USP 1228 DepyrogenationDocument5 pagesUSP 1228 Depyrogenationmustafa huseiny100% (1)
- Weber - Profile & Guide EN 2020Document48 pagesWeber - Profile & Guide EN 2020sandipbharNo ratings yet
- ARC1043 2023 Assignment 9 BriefDocument2 pagesARC1043 2023 Assignment 9 BriefRocky ShiNo ratings yet
- Zlib - Pub - Swarm Intelligence Methods For Statistical RegressionDocument137 pagesZlib - Pub - Swarm Intelligence Methods For Statistical RegressionASDSADNo ratings yet
- MMF60R580Q Datasheet v1.2 20210610Document10 pagesMMF60R580Q Datasheet v1.2 20210610Ferney Martinez Romero Martinez RomeroNo ratings yet
- 2021 Winter FinalDocument3 pages2021 Winter FinalHAITOF BADR-EDDINENo ratings yet
- 2 Work Effectively With OthersDocument36 pages2 Work Effectively With OthersBelay KassahunNo ratings yet
- Traditional Land ManagementDocument9 pagesTraditional Land ManagementNicola DunneNo ratings yet
- HAP1 Review: Dr. Garry NiedermayerDocument37 pagesHAP1 Review: Dr. Garry Niedermayersweta paudelNo ratings yet
- Social Worker CV by SlidesgoDocument45 pagesSocial Worker CV by SlidesgoHadiNo ratings yet
- An Improved Savings Method For Vehicle Routing ProblemDocument6 pagesAn Improved Savings Method For Vehicle Routing ProblemMy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Pioneer English Delhi 11 Sep 2023Document12 pagesPioneer English Delhi 11 Sep 2023Vishal DhimanNo ratings yet
- Extender D252 PDFDocument10 pagesExtender D252 PDFhammyNo ratings yet
- Paul Marik Vitamin C CHESTDocument10 pagesPaul Marik Vitamin C CHESTIrwan YongnardiNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Feb 2021 Class 10 English Supplementary Footprints Without Feet Chapter 6Document3 pagesNcert Solutions Feb 2021 Class 10 English Supplementary Footprints Without Feet Chapter 6NAWIN AMIRTHARAJNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Intellectual RevolutionDocument129 pagesLesson 1 Intellectual RevolutionMuttia SelgasNo ratings yet
- CODEV Ch1Document10 pagesCODEV Ch1Sadegh SobhiNo ratings yet
- Voronoi PatranDocument11 pagesVoronoi PatranKaran DuttNo ratings yet