Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings (States of Matter) - Notes2
Chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings (States of Matter) - Notes2
Uploaded by
charan213Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings (States of Matter) - Notes2
Chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings (States of Matter) - Notes2
Uploaded by
charan213Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter-1
MATTER IN OUR SURROUNDINGS
II. States of Matter
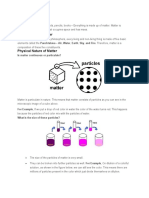
Matter around us exists in three different states which are solid, liquid and gas.
These states of matter arise due to the variation in the characteristics of the
particles of matter.
Solid State: Solid is defined as that form of matter which possesses rigidity,
incompressible and hence has a definite shape and volume.
Liquid State: Liquid is defined as that form of water which possesses fixed
volume, but has no fixed shape.
Gaseous State: Gases can be defined as that form of water which possesses high
compressibility and hence has neither definite shape nor definite volume.
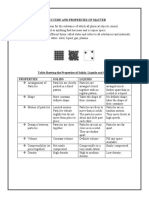
Comparison of some important properties (characteristics) of solids liquids
and gases:
Property Solids Liquids Gases
Shape Have fixed Do not have fixed Do not have fixed
shape shape but take shape shape
of the container
Volume Fixed volume Fixed volume Do not have fixed
volume but take
volume container
Arrangement of Closely packed Loosely packed Very loosely packed
particles
Inter-particle Less inter- More than solids but Most inter-particle
space particle space less than gases space
Force of Maximum Less than solids but Least force of
attraction force of more than gases attraction
attraction
Density Most dense Less than solids but Least dense
more than gases
*Rigidity Solids are rigid Liquids are not rigid Gases are not rigid
*Fluidity Cannot flow Can flow Can flow
*Compressibilit Cannot Can compress(more Most compressible
y compress than solids but less
(least) than gases)
Kinetic energy Least in solids More than solids but Highest in gases
less than gases
Diffusion Least rate of Higher than solids but Highest rate of
diffusion less than gases diffusion
*Rigidity: The property by which a substance (solid) retain its shape when an
external force is applied.
Fluidity: The property by which a substance (liquids &gases) flow from one place
to another thereby changing its shape when an external force is applied.
Compressibility: The property by which a substance (gas) occupies less volume
when an external force is applied.
Q. Explain: (i) Sponge though compressible is a solid.
(ii) Rubber band though stretchable is a solid.
(iii) When sugar and common salt are kept in different jars, they take the
shape of the jars. Are they solids?
Q.Draw the schematic pictures of the three states of matter that shows the motion
of particles. (Reader pg no.5, fig-1.5)
You might also like
- Trace SCDocument184 pagesTrace SCcharan213100% (1)
- Quiz 1-1Document2 pagesQuiz 1-1Leslie S. AndresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings (States of Matter) - Notes2Document2 pagesChapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings (States of Matter) - Notes2Perajothi PalanirajaNo ratings yet
- NOTES, Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument2 pagesNOTES, Matter in Our Surroundingslogabi3459No ratings yet
- 9 Chemistry Chapter 1 Part B Notes 1624285704Document8 pages9 Chemistry Chapter 1 Part B Notes 1624285704RajiNo ratings yet
- Properties of Matter: Chemistry (Form 1)Document36 pagesProperties of Matter: Chemistry (Form 1)MiniMonster 123No ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument13 pagesKinetic Molecular TheoryJaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- P.E.N.School Class: Vi, Vii VisakhapatnamDocument2 pagesP.E.N.School Class: Vi, Vii VisakhapatnamAnonymous IqtpuNEF0No ratings yet
- MATTER-All The Thing Which Occupies Space That Is Has Volume and Mass IsDocument8 pagesMATTER-All The Thing Which Occupies Space That Is Has Volume and Mass Istara tuitionNo ratings yet
- Particles in Solids, Liquids, and GasesDocument6 pagesParticles in Solids, Liquids, and Gasesjhunior carlos eduardo gamboa herreraNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument5 pagesMatter in Our Surroundingslogabi3459No ratings yet
- LN1 Chem NotesDocument4 pagesLN1 Chem Notesridhimarani16207No ratings yet
- Dav International School, Ahmedabad Science Standard in Text and Back Exercise QuestionsDocument11 pagesDav International School, Ahmedabad Science Standard in Text and Back Exercise QuestionsVedantNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Solid, Liquid, Gas ? Asked by (Student), On 18/10/10 AnswersDocument7 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Solid, Liquid, Gas ? Asked by (Student), On 18/10/10 AnswersRahul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Matters in Our SurroundingDocument48 pagesMatters in Our SurroundingXm PiratesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surrounding NotesDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Matter in Our Surrounding NotesAanvi TripathiNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument3 pagesStates of Mattermohammed mahdyNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument12 pagesRevision Notes On Matter in Our SurroundingsRudra aminNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument26 pagesMatter in Our SurroundingsULTRA BOSSNo ratings yet
- FORM 1: Chaper 3: The States of MatterDocument1 pageFORM 1: Chaper 3: The States of MatterBin HadithonNo ratings yet
- Fluids Unit Review - AnswersDocument4 pagesFluids Unit Review - Answersisele1977No ratings yet
- States of Matter 1Document7 pagesStates of Matter 1Science 039 XIIA Shreshthata PujariNo ratings yet
- The Particle Nature of MatterDocument25 pagesThe Particle Nature of MatterMaria bonny aquinoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Matter and Its Properties Page 1Document15 pagesUnit 1 Matter and Its Properties Page 1merci. MariaNo ratings yet
- 1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Solid and Liquids AutosavedDocument16 pages1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Solid and Liquids Autosavedhinacay.jonNo ratings yet
- States of MattesDocument3 pagesStates of Mattesyashmiganegoda13No ratings yet
- "Molecular Behavior": Properties of Matter Solid Liquid GAS 1Document3 pages"Molecular Behavior": Properties of Matter Solid Liquid GAS 1Rej GarbosaNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument13 pagesStates of MatterkianpenamanteNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings ( Prashant Kirad ) (1)Document41 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings ( Prashant Kirad ) (1)nidhimathapati123No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument3 pagesChapter 2 - The Particulate Nature of MatterMahad AsimNo ratings yet
- Booklet 2 Particles LWi ANSWERSDocument45 pagesBooklet 2 Particles LWi ANSWERS18811301255No ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document5 pagesAssignment 5Ramim KhanNo ratings yet
- PDF Document-1Document3 pagesPDF Document-1vijay kumarNo ratings yet
- SelfStudys DocumentDocument3 pagesSelfStudys DocumentManjot SinghNo ratings yet
- Intervention LAS (Matter and Its Properties)Document4 pagesIntervention LAS (Matter and Its Properties)Doll MartinezNo ratings yet
- NeverthelessDocument12 pagesNeverthelessravi chandranNo ratings yet
- 6.1 States of Matter Summary WorksheetDocument2 pages6.1 States of Matter Summary WorksheetCarterNo ratings yet
- Properties of MatterDocument25 pagesProperties of MatterShiera MontillaNo ratings yet
- 3 States of MatterDocument19 pages3 States of Matterwahyuno100% (1)
- Properties of Gas (Solid, Liquid) - Project YakapDocument16 pagesProperties of Gas (Solid, Liquid) - Project YakapGeraldine Angel MirandaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Theory Sept.17Document1 pageKinetic Molecular Theory Sept.17Clint ArranchadoNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings (N)Document5 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings (N)MGMT1 armNo ratings yet
- 9 PPT Matter in Our Surroundings LatestDocument53 pages9 PPT Matter in Our Surroundings Latestvbxjbp8hd5No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Particulate Nature of Matter: SolidsDocument5 pagesChapter 1: The Particulate Nature of Matter: SolidsAshrafNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Solid, Liquid, and Gaseous StatesDocument9 pagesThe Difference Between Solid, Liquid, and Gaseous StatesFikriZalsyaNo ratings yet
- Matter (Science Form 1 - Short Notes)Document1 pageMatter (Science Form 1 - Short Notes)jrpyroNo ratings yet
- MATTERDocument1 pageMATTERL NarineNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Solids Liquids and GasesDocument3 pagesStates of Matter Solids Liquids and GasesMatipa DembureNo ratings yet
- Revision On Particles TheoryDocument35 pagesRevision On Particles TheoryHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Matter: Natural ScienceDocument10 pagesUnit 7 Matter: Natural ScienceClase Tercero ANo ratings yet
- MatterDocument7 pagesMatterEmylie Alvarez LantoriaNo ratings yet
- Solid Liquid GasDocument1 pageSolid Liquid GasUser UnidentifiedNo ratings yet
- Booklet 2 ParticlesDocument43 pagesBooklet 2 Particles18811301255No ratings yet
- Three States of MatterDocument36 pagesThree States of MatterFozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- F1 Chapter 5 MatterDocument13 pagesF1 Chapter 5 Matteralya sophiaNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings: Subhashree NayakDocument3 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings: Subhashree NayakSatya NayakNo ratings yet
- 5 States of MatterDocument21 pages5 States of MatterUnknown ScoutNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Particle Theory PDFDocument38 pagesKinetic Particle Theory PDFMuhammad Darrel Keefa100% (1)
- Characteristics of MatterDocument15 pagesCharacteristics of MatterTen ESONo ratings yet
- PhyDocument33 pagesPhysnkjdvhiheihNo ratings yet
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Koc Standard FOR Process Flow Measurement: Standards PublicationDocument75 pagesKoc Standard FOR Process Flow Measurement: Standards Publicationcharan213No ratings yet
- To Computer Vision: Ahmed Eslam Mohammed Solyman (M.D.)Document29 pagesTo Computer Vision: Ahmed Eslam Mohammed Solyman (M.D.)charan213No ratings yet
- #03 Maa Shutdown Free Issue MaterialDocument32 pages#03 Maa Shutdown Free Issue Materialcharan213No ratings yet
- AttendanceDocument159 pagesAttendancecharan213No ratings yet
- Project EstimationDocument112 pagesProject EstimationJanine Leah Candelaria Biendima100% (1)
- Painting On Stones Purs 2020Document27 pagesPainting On Stones Purs 2020Ivo PursNo ratings yet
- Planning A Research Project and Formulating Research QuestionsDocument15 pagesPlanning A Research Project and Formulating Research QuestionsaspiredNo ratings yet
- H2 - MYE - Revision Package - Binomial Distribution - SolutionsDocument3 pagesH2 - MYE - Revision Package - Binomial Distribution - SolutionsTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- A Mystery We Have Yet To UnfoldDocument1 pageA Mystery We Have Yet To UnfoldNina LimNo ratings yet
- Historical Research: Unit IIIDocument18 pagesHistorical Research: Unit IIIDr. Nisanth.P.MNo ratings yet
- Comparison of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar - Strengths and WeaknessesDocument5 pagesComparison of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar - Strengths and WeaknessesMostafa AbdelrahmanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 PhiloPsychoDocument32 pagesLesson 2 PhiloPsychoKisha Trixie FernandoNo ratings yet
- Principles of MedtechDocument93 pagesPrinciples of MedtechAngel Cascayan Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Scientific Method of Solving ProblemDocument3 pagesScientific Method of Solving ProblemUmar SulemanNo ratings yet
- Academic Performance and HOTSDocument5 pagesAcademic Performance and HOTSBaby Jane Millo100% (1)
- Life Science Thesis TitleDocument7 pagesLife Science Thesis Titlegjbyse71100% (2)
- PreviewpdfDocument52 pagesPreviewpdfEliezer Alves MartinsNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of MusicDocument57 pagesPhilosophy of MusicSilvestreBoulez100% (2)
- Research I Q2M4 - Data Log Book & ISEF FormsDocument3 pagesResearch I Q2M4 - Data Log Book & ISEF FormsAlmie PabiaNo ratings yet
- Activity SheetsDocument9 pagesActivity SheetsRhian RiaNo ratings yet
- CladogramDocument25 pagesCladogramDianne SagunNo ratings yet
- Week 12 MYP 3 PHY HWDocument4 pagesWeek 12 MYP 3 PHY HWAnchal ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Descriptive CorrelationalDocument23 pagesDescriptive CorrelationalHareth DanNo ratings yet
- Metacognitive Analogy IntructionDocument21 pagesMetacognitive Analogy IntructionPat BitaraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document32 pagesLecture 1Shruti DhariyaNo ratings yet
- Fields of Physical GeographyDocument5 pagesFields of Physical GeographyTrisha Ace Betita ElisesNo ratings yet
- ACTAPaperDocument6 pagesACTAPaperSetiyo PrajokoNo ratings yet
- WK 3B-4A Historical AntecedentsDocument48 pagesWK 3B-4A Historical AntecedentsMark GabonNo ratings yet
- 10.understanding Management Accounting Practices A Personal JourneyDocument7 pages10.understanding Management Accounting Practices A Personal JourneyBhupendra RaiNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument5 pagesBiologypennypen190No ratings yet
- Exam 1 Ziya YusifovDocument13 pagesExam 1 Ziya Yusifovziyayusifov28No ratings yet
- For Print Chapter 1Document29 pagesFor Print Chapter 1Nm TurjaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Electric FieldsDocument3 pagesChapter 22 Electric FieldsShaker Ullah Chowdhury100% (1)
- Definition:: Dba 102: Principles of Management Session 1: Intoroduction To ManagementDocument4 pagesDefinition:: Dba 102: Principles of Management Session 1: Intoroduction To ManagementNilufar RustamNo ratings yet