Professional Documents
Culture Documents
© 2006 Pearson Publishing Tel 01223 350555
© 2006 Pearson Publishing Tel 01223 350555
Uploaded by
Magd Osama0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views11 pagesThe document discusses the essential components of a healthy diet, including carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, fiber, and water. It explains that carbohydrates, fats, and proteins provide energy and building blocks for the body, while vitamins and minerals perform important regulatory functions and support growth, tissue repair, and physical activity. Fiber aids digestion and prevents constipation. Finally, water makes up the majority of the human body and must be regularly replenished.
Original Description:
Original Title
DDIIEETARY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the essential components of a healthy diet, including carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, fiber, and water. It explains that carbohydrates, fats, and proteins provide energy and building blocks for the body, while vitamins and minerals perform important regulatory functions and support growth, tissue repair, and physical activity. Fiber aids digestion and prevents constipation. Finally, water makes up the majority of the human body and must be regularly replenished.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views11 pages© 2006 Pearson Publishing Tel 01223 350555
© 2006 Pearson Publishing Tel 01223 350555
Uploaded by
Magd OsamaThe document discusses the essential components of a healthy diet, including carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, fiber, and water. It explains that carbohydrates, fats, and proteins provide energy and building blocks for the body, while vitamins and minerals perform important regulatory functions and support growth, tissue repair, and physical activity. Fiber aids digestion and prevents constipation. Finally, water makes up the majority of the human body and must be regularly replenished.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 11
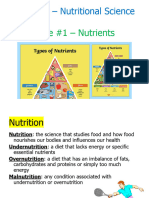
Diet
© 2006 Pearson Publishing Tel 01223 350555
Food
• Food is the body’s source of energy and basic
building blocks, enabling muscle movement,
growth and repair
• The food we eat should come from seven groups:
– Carbohydrates
– Fats
– Proteins
– Vitamins
– Minerals
– Fibre
– Water
• Each of these has a distinct job in fulfilling the
body’s dietary needs
Carbohydrates
• When broken down, carbohydrates provide the
body with glucose, the main source of energy
• Although energy can be gained from other
sources, carbohydrates can supply energy
quickly and efficiently
• Excess carbohydrate
in the body is directed
to the liver and converted
to glycogen, which is stored
in the liver or muscles
• Other excess carbohydrate
may be stored as fat
Fats
• Fats can release high levels of energy but
require a large amount of oxygen to do so
• They provide an energy source
when resting and sleeping
• Fat is stored in a layer
beneath the skin
• It keeps the body warm
and protects vital organs
Fats
• There are two types of fats:
– Saturated fats — found in
animal products such as
meat, cheese, milk and cream
– Unsaturated fats — found in
fish oils and products made
from vegetable seeds such
as sunflower and corn
• Saturated fats contain cholesterol,
which can clog arteries and lead
to high blood pressure and heart disease
• Fats are broken down into fatty acids
and glycerol during digestion
Proteins
• Proteins are the building
blocks of the body
• They repair and replace
damaged tissue and build
new tissue for growth
• During digestion, they are
broken down into their
constituent parts, amino acids
• 21 types of amino acids
are needed for our bodies
to work properly
Vitamins
• Vitamins have four main functions:
– They regulate chemical reactions in the body
– They help release energy from food
– They maintain resistance against disease
– They help with growth and
the repair of tissues
• For example, vitamin C is
needed to form collagen,
a key component
of all connective tissues
• Vitamins are found as traces
in food substances, including
fresh fruit and vegetables
Minerals
• Minerals are inorganic chemicals found in most
fresh food
• The more a person exercises,
the greater the mineral
intake needed
• Excessive mineral salt can
contribute to high blood pressure
Minerals
Minerals include:
• Iron — helps produce red blood
cells which carry more oxygen
around the body preventing
fatigue — found in red meat
and green vegetables
• Calcium — helps blood to clot, aiding recovery
from injury, and strengthens bones and muscles —
found in milk, cheese and cereals
• Iodine — aids normal growth,
essential for athletes as it
helps energy production —
found in milk and saltwater fish
Fibre
• Fibre plays an important part in the process of
digestion and is the non-digestible part of fruit,
vegetables and cereals
• The main functions of fibre are to provide
the bulk for food, encourage slow, even
release of sugars and prevent constipation
Water
• Water makes up two-thirds
of our body contents
• There is a constant loss of
water throughout the day —
this must be replaced to
prevent dehydration
You might also like
- General Curse Breaking PrayersDocument12 pagesGeneral Curse Breaking Prayersmotmagic100% (2)
- Nutrition 101: Brought To You by The University of HoustonDocument20 pagesNutrition 101: Brought To You by The University of Houstonriki187No ratings yet
- MZA Userguide PDFDocument8 pagesMZA Userguide PDFmark canolaNo ratings yet
- AutomationDocument36 pagesAutomationParvez AlamNo ratings yet
- Concrete WorkDocument1 pageConcrete WorkChandru100% (1)
- The Generation of Postmemory: Writing and Visual Culture After The HolocaustDocument13 pagesThe Generation of Postmemory: Writing and Visual Culture After The HolocaustColumbia University Press100% (2)
- Balanced DietDocument30 pagesBalanced DietDaniel AmonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Section 1 (Nutrients)Document26 pagesChapter 7 Section 1 (Nutrients)lolyvwuNo ratings yet
- Nutrition 101 Presentation PDFDocument20 pagesNutrition 101 Presentation PDFViktória MolnárNo ratings yet
- Food and Nutrition PPT TANMAYDocument12 pagesFood and Nutrition PPT TANMAYTanmay SinghalNo ratings yet
- Nutrition PPT PresentationDocument33 pagesNutrition PPT PresentationSrinivasan Ravi100% (1)
- Nutrition IntroductionDocument25 pagesNutrition IntroductionRoda dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: © 2005 Jupiterimages CorporationDocument12 pagesNutrition: © 2005 Jupiterimages CorporationJanfreid BaniquedNo ratings yet
- NUTRITION - Macronutrients OfficialDocument45 pagesNUTRITION - Macronutrients OfficialAsawni McDowellNo ratings yet
- Stage I. Health ProblemsDocument24 pagesStage I. Health ProblemsBalajinagarajan AlagappanNo ratings yet
- Stage I. Health ProblemsDocument24 pagesStage I. Health ProblemsBalajinagarajan AlagappanNo ratings yet
- Nutrition 101: Brought To You by The University of HoustonDocument20 pagesNutrition 101: Brought To You by The University of HoustonRaquel AgasaNo ratings yet
- Balanced DietDocument20 pagesBalanced DietUnza WaqarNo ratings yet
- U6 L1 Nutrition CHS-1Document34 pagesU6 L1 Nutrition CHS-1Joshua FloresNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Report in NutritionDocument30 pagesGroup 1 Report in Nutritionfe espinosaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Protein FatsDocument18 pagesCarbohydrates Protein Fatskristinealborte123No ratings yet
- Six Essential NutrientsDocument11 pagesSix Essential NutrientsChristine Ma-eh MarquezNo ratings yet
- Nutrition ReportingDocument28 pagesNutrition ReportingMa.Kristelle Anne L. PachecoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition BasicsDocument49 pagesNutrition Basicstoty-berryNo ratings yet
- Nutrition For HealthDocument10 pagesNutrition For HealthSherwin G. Iliw-iliwNo ratings yet
- Digestion Part 1Document28 pagesDigestion Part 1JakeNo ratings yet
- Nutrition-: Science or Study of Food and The Ways in Which The Body Uses FoodDocument14 pagesNutrition-: Science or Study of Food and The Ways in Which The Body Uses FoodOsiris HernandezNo ratings yet
- The Body's Need For Food (Autosaved)Document33 pagesThe Body's Need For Food (Autosaved)nina lykka calaraNo ratings yet
- NUTRITION Power PointDocument18 pagesNUTRITION Power Pointdnorton5437No ratings yet
- Bic 341 Lecture Note by DR OnyekweluDocument62 pagesBic 341 Lecture Note by DR OnyekweluNmesomaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition PowerpointDocument28 pagesNutrition PowerpointJocelyn TablateNo ratings yet
- 1 ClassificationDocument50 pages1 ClassificationNiña MarieNo ratings yet
- Nutri PrelimsDocument15 pagesNutri PrelimsGabNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument74 pagesUntitledMELENIE JOY MAMAWANNo ratings yet
- Diet & Nutrition Advanced Ver 1Document52 pagesDiet & Nutrition Advanced Ver 1Ina100% (1)
- Public Health Nutrition: Its Importance For Health Promotion & Health PreservationDocument36 pagesPublic Health Nutrition: Its Importance For Health Promotion & Health PreservationSumaia Rahman100% (1)
- Manage Nutritional ProblemDocument37 pagesManage Nutritional ProblemBat ManNo ratings yet
- Manage Nutritional ProblemDocument53 pagesManage Nutritional ProblemBat ManNo ratings yet
- The Need For FOODDocument17 pagesThe Need For FOODZoodle JNo ratings yet
- Unit 7-HUMAN NUTRITIONDocument31 pagesUnit 7-HUMAN NUTRITIONfreefortnie75No ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Note #1 - NutritionDocument19 pagesUnit 1 - Note #1 - NutritioncasbutchNo ratings yet
- The Different Sources and Function of Nutrients: Protein, Vitamins, Minerals, Carbohydrates, Fats, WaterDocument21 pagesThe Different Sources and Function of Nutrients: Protein, Vitamins, Minerals, Carbohydrates, Fats, WaterCharity Faith EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Chaitanya Deemed University: Food and NutritionDocument14 pagesChaitanya Deemed University: Food and NutritionVenkatasairamreddy KandulaNo ratings yet
- Principal of NutritionDocument77 pagesPrincipal of NutritionIfeoma JulietNo ratings yet
- 6 Essential Nutrients PDFDocument15 pages6 Essential Nutrients PDFJuan Rodriguez Jr100% (1)
- 1 Food and Nutrition BasicsDocument36 pages1 Food and Nutrition BasicsANGEL GRACE LLAUDERESNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Human NutritionDocument45 pagesChapter 7 Human Nutritionjzdf2d9nnvNo ratings yet
- Itsmejarong PE 01 NutritionDocument21 pagesItsmejarong PE 01 Nutritiondave lucasNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 Prelims NotesDocument24 pagesNCM 105 Prelims NotesJustine FloresNo ratings yet
- XII P.E.Unit-VDocument5 pagesXII P.E.Unit-VRiddhi LokhandeNo ratings yet
- G9 Lesson 2-TleDocument43 pagesG9 Lesson 2-TleIma blinkNo ratings yet
- 26 July 2018: Geology 101 Report Page ! of ! 1 2Document6 pages26 July 2018: Geology 101 Report Page ! of ! 1 2Anshu MovvaNo ratings yet
- Cypt Yat Healthy Eating To Fuel ActivityDocument21 pagesCypt Yat Healthy Eating To Fuel ActivityAsok MarioNo ratings yet
- Composition of FoodsDocument18 pagesComposition of FoodsGrace BarbozaNo ratings yet
- The Basic Body Nutrients RequirementsDocument23 pagesThe Basic Body Nutrients RequirementsCharity Faith EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Staying HealthyDocument9 pagesStaying HealthyAbel BatistaNo ratings yet
- Balance Diet 321Document5 pagesBalance Diet 321Aroob YaseenNo ratings yet
- 3RD GR Science - Dec 15THDocument14 pages3RD GR Science - Dec 15THROSMERI LUISA MERCADO VALERIANONo ratings yet
- Food & Nutrition: Indian Hills Middle SchoolDocument15 pagesFood & Nutrition: Indian Hills Middle SchoolAlfie DilagNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 NutrientsDocument28 pagesLecture 9 NutrientsNemia PaclibarNo ratings yet
- Askep Nutrisi d3 Kep-DikonversiDocument71 pagesAskep Nutrisi d3 Kep-DikonversiRihhadatul RifdahNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument37 pagesNutritioncervanamonica13No ratings yet
- CH 5 Lesson 2 and 3 NotesDocument3 pagesCH 5 Lesson 2 and 3 NotesAkariyah AndersonNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate and Protien DigestionDocument57 pagesCarbohydrate and Protien DigestionpvzvsrqzcdNo ratings yet
- ICT G8 Worksheet 7Document7 pagesICT G8 Worksheet 7Magd OsamaNo ratings yet
- ICT G8 Worksheet 6Document5 pagesICT G8 Worksheet 6Magd OsamaNo ratings yet
- G1 Extra Revision 4 BlocksDocument13 pagesG1 Extra Revision 4 BlocksMagd OsamaNo ratings yet
- ICT G8 Worksheet 5 (Revised)Document6 pagesICT G8 Worksheet 5 (Revised)Magd OsamaNo ratings yet
- G1 Plants Work BookDocument13 pagesG1 Plants Work BookMagd OsamaNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficiency Food Chains: Organism How It Gets Its EnergyDocument6 pagesEnergy Efficiency Food Chains: Organism How It Gets Its EnergyMagd OsamaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Study SheetDocument6 pagesDigestive System Study SheetMagd OsamaNo ratings yet
- HOPE 12 Budget of WorkDocument2 pagesHOPE 12 Budget of WorkRonald Francis Sanchez VirayNo ratings yet
- Integrated Budget & Accounting System (iBAS++)Document46 pagesIntegrated Budget & Accounting System (iBAS++)Hamanta RoyNo ratings yet
- Ga8238 PDFDocument3 pagesGa8238 PDFAstri Indra MustikaNo ratings yet
- 6 MD 85Document1,256 pages6 MD 85Yahya DarNo ratings yet
- 93admit Card Semester-V 011 12-01-2022 16-51-1Document37 pages93admit Card Semester-V 011 12-01-2022 16-51-1Spotify premiumNo ratings yet
- Set 6: Knowledge Representation: The Propositional Calculus: Chapter 7 R&NDocument85 pagesSet 6: Knowledge Representation: The Propositional Calculus: Chapter 7 R&NQaisar HussainNo ratings yet
- Griffin 1Document4 pagesGriffin 1Janine NogueraNo ratings yet
- Master Degree InformationDocument3 pagesMaster Degree InformationBivash NiroulaNo ratings yet
- Exoglove Research PaperDocument8 pagesExoglove Research Papersanket jainNo ratings yet
- Sensor Fusion For Automotive ApplicationsDocument113 pagesSensor Fusion For Automotive ApplicationsadarshsasidharanNo ratings yet
- Zapanta Vs PeopleDocument7 pagesZapanta Vs PeopleEricson Sarmiento Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Mechanism On Scissor Lift Operation Report PDFDocument4 pagesMechanism On Scissor Lift Operation Report PDFAMY SHAKYLLA BINTI ADEHAM / UPMNo ratings yet
- Invariants and Monovariants: Adithya Bhaskar January 24, 2016Document5 pagesInvariants and Monovariants: Adithya Bhaskar January 24, 2016zarif hossainNo ratings yet
- BC23000122Document1 pageBC23000122azharNo ratings yet
- Phu Kien Khuon Song Ngu - 20190921Document3 pagesPhu Kien Khuon Song Ngu - 20190921Loc NguyenNo ratings yet
- Calculating The Temperature RiseDocument8 pagesCalculating The Temperature Risesiva anandNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Control Using Genetic Fuzzy-PI ControllerDocument7 pagesDiabetic Control Using Genetic Fuzzy-PI ControllerIndana Firdausi NuzulaNo ratings yet
- Routing Security - MUM - MikroTik PDFDocument120 pagesRouting Security - MUM - MikroTik PDFAlex EnriquezNo ratings yet
- The Leads Science Academy: Write Short Answers of The Following QuestionsDocument2 pagesThe Leads Science Academy: Write Short Answers of The Following Questionssir zahidNo ratings yet
- Naiad GettingstartedDocument37 pagesNaiad GettingstartedYurivanovNo ratings yet
- Module 4 ResearchDocument9 pagesModule 4 ResearchJegg AsisNo ratings yet
- Flexible Assessment Activities and Flexible Learning StrategiesDocument5 pagesFlexible Assessment Activities and Flexible Learning StrategiesAisa EdzaNo ratings yet
- Narrative Research: July 2020Document14 pagesNarrative Research: July 2020musawar420No ratings yet
- Overview of Extended RealityDocument7 pagesOverview of Extended RealityAkul DevtaNo ratings yet
- Amol Sanap Teacher ResumeDocument3 pagesAmol Sanap Teacher ResumeAmol SanapNo ratings yet