Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quiz #2 - CH 4 & 5: Question 1 (48 Marks)
Quiz #2 - CH 4 & 5: Question 1 (48 Marks)
Uploaded by
JamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quiz #2 - CH 4 & 5: Question 1 (48 Marks)
Quiz #2 - CH 4 & 5: Question 1 (48 Marks)
Uploaded by
JamCopyright:
Available Formats
Quiz #2 - Ch 4 & 5
Question 1 (48 marks)
Enterprise Ltd has forecast its sales revenues and inventory purchases for the last five
Sales Purchases
August $ 27,000 $ 20,000
September $ 16,000 $ 17,000
October $ 28,000 $ 29,000
November $ 39,000 $ 28,000
December $ 30,000 $ 28,000
More information is below. In addition, its minimum required cash balance is $5,000. If
there is a cash balance in excess of $5,000, Enterprise Ltd will pay down any outstanding debt (if applicable).
Proportion of sales on credit 80%
Accounts receivable collected month after sale 75%
Accounts receivable collected two months after sale 15%
Accounts receivable nerer collected (bad debts) 10%
Purchases are paid for 1 month after they occur
Cash on hand at September 30 $ 6,000
Outstanding debt at September 30 $ 2,000
a) Prepare a schedule of cash receipts for October, November, and December.
b) Prepare a cash budget for the same period.
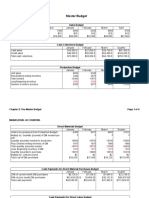
August September October November December
Sale $ 27,000 $ 16,000 $ 28,000 $ 39,000 $ 30,000
Credit 80 % 21600 12800 22400 31200 24000
Collection Cash Sale 5600 7800 6000
75% In Following Month 9600 16800 23400
15% In Second Month 3240 1920 3360
Total Collection 18440 26520 32760
Cash Budget
Cash receipts 18440 26520 32760
Cash payments 17000 29000 28000
Net cash flow $ 1,440.00 $ (2,480.00) $ 4,760.00
Beginning cash balance 6000 5440 2960
Cumulative cash balance $ 7,440.00 $ 2,960.00 $ 7,720.00
Monthly loan or (repayment) (2000) 0 0
Cumulative loan balance 0 0 0
Ending cash balance $ 5,440.00 $ 2,960.00 $ 7,720.00
Still due Bad debt not collected : Bad Debts :
To be collected from August Sale = (21,600 ) 10 % = $ 2,160.00
To be collected from September Sale = (12,800 ) 10 % = 1280.00
Total Bad Debts = $ 3,440.00
The Sterling Tire Company’s income statement for 2018 is below:
STERLING TIRE COMPANY
Income Statement
Year ended December 31, 2018
Sales 36,000 tires @ $ 54 each 1,944,000
Less: Variable costs 36,000 tires @ $ 36 each 1,296,000
Contribution Margin 648,000
Less: Fixed cost 250,000
Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) 398,000
Interest 80,000
Earnings 318,000
Income tax 95,400
Earnings $222,600
Given this income statement, compute the following to two decimal places.
a) Degree of operating leverage.
b) Degree of financial leverage.
c) Degree of combined leverage.
d) Does financial or operating leverage have the greater impact?
Solution :
Q= $ 36000 P = $ 54 VC = $ 36 FC = $ 250,000 I = $ 80,000
a) Degree of operating leverage.
Q (P- VC) $ 36000 ( 54 - 36 )
DOL ͇ ͇
Q (P- VC) - FC $ 36000 ( 54 - 36 ) - $ 250,000
$ 36,000 ( 18 ) $648,000.00
͇
$ 36,000 (18) - $ 250,000 $ 648,000.00 - $ 250,000.00
$648,000.00
1.63x
$398,000.00
b) Degree of financial leverage.
EBIT $398,000.00
DFL ͇ ͇
EBIT - I $ 398,000.00 - 80,000.00
$398,000.00
͇ 1.3x
$318,000.00
c) Degree of combined leverage.
Q ( P- VC ) $ 36,000.00 (54-36)
DCL ͇ ͇
Q ( P- VC) - FC - I $36000.00 (54-36) -250,000.00 - 80,000.00
$648,000 $648,000.00
=
$ 648,000.00 - $ 250,000.00 - $ 80,000.00 $318,000.00
2.04
d) Does financial or operating leverage have the greater impact?
Ans : operating leverage have the greater impact
You might also like
- Problem SolvingDocument10 pagesProblem SolvingRegina De LunaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Advanced Financial Accounting 10th Edition by Christensen PDFDocument71 pagesTest Bank For Advanced Financial Accounting 10th Edition by Christensen PDFa1086940450% (2)
- Revision Questions - CH 17 - QuestionsDocument3 pagesRevision Questions - CH 17 - QuestionsMinh ThưNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document2 pagesAssignment 5NABILAH KHANSA 1911000089No ratings yet
- Warner Company Statement of Cash FlowsDocument2 pagesWarner Company Statement of Cash FlowsKailash KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 MankiwDocument9 pagesChapter 13 Mankiwcik sitiNo ratings yet
- Problem 8.17: Cash Budget For The Month of December 1. Ashton CompanyDocument3 pagesProblem 8.17: Cash Budget For The Month of December 1. Ashton CompanyAbdul MoeezNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1Document3 pagesExercise 1ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- 20 - Assignment 4 CTRDocument2 pages20 - Assignment 4 CTRCamilo ToroNo ratings yet
- Cash Receipts March April May June JulyDocument1 pageCash Receipts March April May June JulyJPNo ratings yet
- 20 - Assignment 4 CTRDocument2 pages20 - Assignment 4 CTRCamilo ToroNo ratings yet
- BUSN AssigmentDocument4 pagesBUSN AssigmentMalik Khurram AwanNo ratings yet
- ABC Company Is Preparing A Cash Budget For The Months of OctoberDocument8 pagesABC Company Is Preparing A Cash Budget For The Months of OctoberScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- FALL Class 7 - Cash Budgeting - Ch9 - GDBA - Note # 7 - TEACHERDocument7 pagesFALL Class 7 - Cash Budgeting - Ch9 - GDBA - Note # 7 - TEACHERAkankshaNo ratings yet
- Collections:: Less: DisbursementDocument5 pagesCollections:: Less: DisbursementMukul KadyanNo ratings yet
- In Class Excel - 825 - WorkingDocument98 pagesIn Class Excel - 825 - WorkingIanNo ratings yet
- PA Biweekly5 G1Document3 pagesPA Biweekly5 G1Quang NguyenNo ratings yet
- 2 Tutorial Question and Answer On Cash BudgetDocument4 pages2 Tutorial Question and Answer On Cash BudgetHasnita Hasan BudinNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Financial Management: Spreadsheet TemplatesDocument9 pagesFoundations of Financial Management: Spreadsheet Templatesalaa_h1100% (1)
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2Joe MajchrzakNo ratings yet
- Revision Questions - CH 17 - SolutionsDocument4 pagesRevision Questions - CH 17 - SolutionsMinh ThưNo ratings yet
- Requirement 1: Shazam Cash BudgetDocument4 pagesRequirement 1: Shazam Cash BudgetVixen Aaron EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Acct 2020 Excel Budget ProblemDocument6 pagesAcct 2020 Excel Budget Problemapi-307661249No ratings yet
- TK4 AkuntasniDocument7 pagesTK4 AkuntasniSarah NurfadilahNo ratings yet
- Tugas Kelompok Akuntansi Ke 4Document10 pagesTugas Kelompok Akuntansi Ke 4grup apa iniNo ratings yet
- Startup Balance Sheet TemplateDocument4 pagesStartup Balance Sheet TemplateDishari DuttaNo ratings yet
- Bi-Weekly 4-Group 6-PA3Document5 pagesBi-Weekly 4-Group 6-PA3Bích Vy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Partnership Worksheet 7Document4 pagesPartnership Worksheet 7Timo wernereNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Statement of Financial Position XYZ CompanyDocument5 pagesAsynchronous Statement of Financial Position XYZ CompanyDiana Fernandez MagnoNo ratings yet
- Isfi Nuraida - Anggaran KasDocument86 pagesIsfi Nuraida - Anggaran KasGhinaNo ratings yet
- Mayes 8e CH04 SolutionsDocument48 pagesMayes 8e CH04 SolutionsRamez Ahmed0% (1)
- Cash Inflows: Cash Surplus/loan RequirementDocument7 pagesCash Inflows: Cash Surplus/loan RequirementMIRZA WAQAR BAIGNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Fiancial StatementsDocument15 pagesConsolidated Fiancial StatementsChristie SabidorNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1 - Assignment 1Document5 pagesAssessment 1 - Assignment 1Ten NineNo ratings yet
- Problem 18.5: Statement of Cash Flows, Direct and Indirect MethodsDocument1 pageProblem 18.5: Statement of Cash Flows, Direct and Indirect MethodsAnh BùiNo ratings yet
- Prooblem 4-5 No. 2 Journal EntriesDocument12 pagesProoblem 4-5 No. 2 Journal EntriesJoseph LimbongNo ratings yet
- Practice CF Scooter KeyDocument4 pagesPractice CF Scooter KeyAllie LinNo ratings yet
- Problem 2Document9 pagesProblem 2Caila Nicole ReyesNo ratings yet
- Financial PlanningDocument6 pagesFinancial Planningakimasa raizeNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Preparation April 4Document3 pagesFinancial Statement Preparation April 4Sher Adeeb Bin Faisal 2115167690No ratings yet
- ActivityDocument49 pagesActivityAshanti ashley gueseNo ratings yet
- Tugas Latihan Chapter 10 Dan 11Document2 pagesTugas Latihan Chapter 10 Dan 11Arnalistan EkaNo ratings yet
- Statement AnalysisDocument4 pagesStatement AnalysisrameelNo ratings yet
- 02 Edu91 FM Practice Sheets QuestionsDocument77 pages02 Edu91 FM Practice Sheets Questionsprince soniNo ratings yet
- Computation For Exercise 1Document10 pagesComputation For Exercise 1Xyzra AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Budget TemplateDocument21 pagesBudget TemplateUmar SulemanNo ratings yet
- Solution: P7-3 (L03) Bad-Debt Reporting-Aging: InstructionsDocument8 pagesSolution: P7-3 (L03) Bad-Debt Reporting-Aging: InstructionsHerry SugiantoNo ratings yet
- Abraar Dairy and Farming Financial Template-1Document13 pagesAbraar Dairy and Farming Financial Template-1Ganacsi KaabNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Ex - 230721 - 002228Document7 pagesCash Flow Ex - 230721 - 002228Mohamed TahaNo ratings yet
- ACCT 315 AssignmentDocument11 pagesACCT 315 AssignmenthumaNo ratings yet
- AE 112 Midterm QUIZ 2 - SolutionsDocument10 pagesAE 112 Midterm QUIZ 2 - SolutionsAllondra DapengNo ratings yet
- Hampton Freeze, Inc. Balance Sheet 31-Dec-16 AssetsDocument23 pagesHampton Freeze, Inc. Balance Sheet 31-Dec-16 AssetsAman ShahNo ratings yet
- 21 (6) - 4A 12e SDocument5 pages21 (6) - 4A 12e SashibhallauNo ratings yet
- Non-Current Asset: Balance Sheet 31-Dec-20Document4 pagesNon-Current Asset: Balance Sheet 31-Dec-20Shehzadi Mahum (F-Name :Sohail Ahmed)No ratings yet
- ACCT1115 - Group Case Section A17 Part 2 Group 1Document7 pagesACCT1115 - Group Case Section A17 Part 2 Group 1Maria Jana Minela IlustreNo ratings yet
- The Sharpe Corporation's ProjectedDocument3 pagesThe Sharpe Corporation's Projectedmadnansajid8765No ratings yet
- Mini Exercise Answer KeyDocument3 pagesMini Exercise Answer KeyKaren TumabiniNo ratings yet
- Financial Plan:: The Following Sections Will Outline Important Financial InformationDocument17 pagesFinancial Plan:: The Following Sections Will Outline Important Financial InformationpalwashaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Accounting Information Systems Problems With SolutionsDocument22 pages1 - Accounting Information Systems Problems With Solutionsbusiness docNo ratings yet
- 1822 F0242 Ljfa TK1-W2-R4 Team3Document10 pages1822 F0242 Ljfa TK1-W2-R4 Team3Wenni MarineNo ratings yet
- Visual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsFrom EverandVisual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Analysis of Tax Administration in Asia and the Pacific—Sixth EditionFrom EverandA Comparative Analysis of Tax Administration in Asia and the Pacific—Sixth EditionNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: Review of AccountingDocument58 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Review of AccountingJamNo ratings yet
- Quiz 10 - CH 16Document4 pagesQuiz 10 - CH 16JamNo ratings yet
- Quiz # 1Document1 pageQuiz # 1JamNo ratings yet
- Answer Assignment 1 - V1-2 - Fall 2020Document14 pagesAnswer Assignment 1 - V1-2 - Fall 2020JamNo ratings yet
- Sales: P1-,27A, OAO - 1LZB, O00 - )Document1 pageSales: P1-,27A, OAO - 1LZB, O00 - )Lovely Mae LariosaNo ratings yet
- Ashkenazi CompaniesDocument1 pageAshkenazi CompaniesAbd AL Rahman Shah Bin Azlan ShahNo ratings yet
- Financial Modeling Chapter 2 Calculating Cost of Capital 2015Document64 pagesFinancial Modeling Chapter 2 Calculating Cost of Capital 2015NEERAJ N RCBSNo ratings yet
- Business Mathematics: Quarter 1, Week 6 - Module 8 Differentiating Mark-Up From Margins-ABM - BM11BS-Ih-3Document11 pagesBusiness Mathematics: Quarter 1, Week 6 - Module 8 Differentiating Mark-Up From Margins-ABM - BM11BS-Ih-3Dave Sulam100% (2)
- ch01 ProblemsDocument7 pagesch01 Problemsapi-274120622No ratings yet
- Cost INGDocument49 pagesCost INGvyavahareanant145No ratings yet
- ACCA F9 Financial Management Class NotesDocument185 pagesACCA F9 Financial Management Class NotesIt'z Pragmatic IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Inclass ActivitiesDocument4 pagesTopic 1 - Inclass Activitiescat chiNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow StatementDocument12 pagesCash Flow StatementChikwason Sarcozy MwanzaNo ratings yet
- 200 500 Imo Board Meeting 20230215Document19 pages200 500 Imo Board Meeting 20230215Contra Value BetsNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-11-24 at 12.39.51 PMDocument5 pagesScreenshot 2022-11-24 at 12.39.51 PMAliyuddin NadzirNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - Emily CruzDocument7 pagesAnswer Key - Emily Cruzelriatagat850% (1)
- Depreciation Accounts 1. Answer The Following. (4 Marks Each)Document2 pagesDepreciation Accounts 1. Answer The Following. (4 Marks Each)Yashvi FulwalaNo ratings yet
- The Following Are Selected Transactions That May Affect Shareholders Equity PDFDocument1 pageThe Following Are Selected Transactions That May Affect Shareholders Equity PDFFreelance WorkerNo ratings yet
- Construction Contracts-IAS 11 & Rev Rec & Journals-EY-PG22Document22 pagesConstruction Contracts-IAS 11 & Rev Rec & Journals-EY-PG22varadu1963No ratings yet
- Case Study On Equity ValuationDocument3 pagesCase Study On Equity ValuationUbaid DarNo ratings yet
- BBA 1st Financial AccountingDocument3 pagesBBA 1st Financial AccountingAbbas Sky50% (4)
- 15 - 16 Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesDocument39 pages15 - 16 Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesKyeien100% (1)
- IAS 32, IFRS7,9 Financial InstrumentsDocument6 pagesIAS 32, IFRS7,9 Financial InstrumentsMazni Hanisah100% (2)
- BBA-VI 562 Subjective Dec 2016Document2 pagesBBA-VI 562 Subjective Dec 2016Saif ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Cpa Review School of The Philippines ManilaDocument7 pagesCpa Review School of The Philippines Manilaxara mizpahNo ratings yet
- A Quiz 6: CH 7 (15 Minutes) : No. MahasiswaDocument1 pageA Quiz 6: CH 7 (15 Minutes) : No. MahasiswaaurenisaNo ratings yet
- Duration 2 Hours Max Marks 70Document25 pagesDuration 2 Hours Max Marks 70AgANo ratings yet
- Problems Cash Flow AnalysisDocument18 pagesProblems Cash Flow Analysisleilo4kaNo ratings yet
- SAP Transaction ListDocument34 pagesSAP Transaction ListBatheiah BolisettiNo ratings yet
- FAR 4309 Investment in Debt Securities 2Document6 pagesFAR 4309 Investment in Debt Securities 2ATHALIAH LUNA MERCADEJASNo ratings yet
- True or FalseDocument7 pagesTrue or FalseColline ZoletaNo ratings yet
- Profit and Loss and Balance Sheet From Trial Balalace With Charts of AccountDocument8 pagesProfit and Loss and Balance Sheet From Trial Balalace With Charts of AccountAndaleeb AmeeriNo ratings yet