Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PubMed Central, Table 1 - BMC Biol. 2017 15 - 53. Published Online 2017 Jun 29. Doi - 10.1186 - s12915-017-0392-4
PubMed Central, Table 1 - BMC Biol. 2017 15 - 53. Published Online 2017 Jun 29. Doi - 10.1186 - s12915-017-0392-4
Uploaded by
KarenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PubMed Central, Table 1 - BMC Biol. 2017 15 - 53. Published Online 2017 Jun 29. Doi - 10.1186 - s12915-017-0392-4
PubMed Central, Table 1 - BMC Biol. 2017 15 - 53. Published Online 2017 Jun 29. Doi - 10.1186 - s12915-017-0392-4
Uploaded by
KarenCopyright:
Available Formats
Source Macrophage subpopulation Functions Comments
Foetal Stromal mϕ Definitive erythropoiesis Adhesion receptor distinct from
liver Enucleation of erythrocytes phagocytosis
Foetal monocytes
Bone Monocytes Monocytosis Release controlled by CD169
marrow Stromal mϕ Haemopoietic islands, phagocytosis of erythroid nuclei Sialoadhesin (CD169) and integrin
mediate selective adhesion
Haemopoiesis: erythroid (Fe recycling), myeloid (PMN,
monocytes, eosinophils); plasma cells
Osteoclasts Bone remodelling Mutinucleated giant cells
CSF1, RANK ligand, vacuolar ATPase,
− +
polarised adhesion; F4/80 , CD68
Osteoblast interactions
+ +
Spleen Red pulp Clearance of senescent erythrocytes, PMN F4/80 , CD206
Haem catabolism, Fe recycling Induction Spi-C transcription factor
+,
Marginal zone, metallophils Sinusoidal—clearance of polysaccharides, antigens, CD169 CSF-1 dependent
microbes; stimulate migration
+ +
Outer marginal zone Phagocytic MARCO , SIGNR-1 , type I interferon
induction
++
White pulp Clearance of apoptotic T and B lymphocytes F4/80 negative, CD68
Migrating metallophils transfer antigen to DC, which migrate
to white pulp to activate T and B cells
Lymph Subcapsular macrophages Analogous to marginal zone
nodes Afferent lymph delivers DC and antigens and viruses to Subcapsular sinus macrophages capture
lymph node antigens for delivery to DC, for
activation of B and T lymphocytes
Medulla Activation of T and B cells Filter for mϕ which do not enter efferent
lymph
Gut Lamina propria mϕ Interaction microbiome, epithelium, innate (ILC2/3) and Active migration beneath epithelium of
acquired lymphocytes villi, sample the lumen
Modulation of inflammation and immune activation TGFbeta (F4/80, oral tolerance)
Submucosal mϕ Interactions with smooth muscle cells, myenteric and Peristalsis
autonomic nervous system
Peritoneal Large and small resident mϕ; elicited and Interactions B1 lymphocytes. Inflammation stimulates Prototypic in vivo inflammation model
+
cavity activated migration to draining lymph nodes and abdominal organs, Reservoir of mature GATA-6
such as liver, upon injury macrophages for repair
+
Liver Kupffer cells Sinusoidal, clearance, phagocytosis and receptor-mediated F4/80 , CR3 dim, Kupffer cell-specific
endocytosis, interactions with hepatocytes, acute phase CRIG and other lectins. Clearance
synthesis through contact and cytokines. Metabolism: iron, through CD206, SR-A, also by
See text for references
Given the complexity of tissue-resident populations and admixture of recruited monocytes in the steady state and stress, it is important to study properties in situ.
These and other organs, not included in this review, also contain interstitial macrophages (not included above)
You might also like
- Elite 100 NBME Concepts OutlineDocument158 pagesElite 100 NBME Concepts OutlineDeborah Peters100% (3)
- Immunology & Serology Review NotesDocument4 pagesImmunology & Serology Review Notesmaria email86% (7)
- Organic Chemistry Board Exam QuestionsDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry Board Exam QuestionsRiza Joie Versales100% (1)
- POTTs Disease PathoDocument3 pagesPOTTs Disease PathoEdgel QuidolesNo ratings yet
- Immunology & Serology Review Notes George Vincent Gellena, RMT, Mls (Ascpi)Document9 pagesImmunology & Serology Review Notes George Vincent Gellena, RMT, Mls (Ascpi)Angelo Jude CobachaNo ratings yet
- ISBB Aaaaa PDFDocument55 pagesISBB Aaaaa PDFSelena de LimaNo ratings yet
- LMC CursDocument31 pagesLMC CursEma ȚurcașNo ratings yet
- Immunology Chapter 2Document19 pagesImmunology Chapter 2Milad MovahediNo ratings yet
- Bolile Mieloproliferative CroniceDocument57 pagesBolile Mieloproliferative Cronicetrifex100% (2)
- ISBBhandoutDocument55 pagesISBBhandoutRed GillianNo ratings yet
- General Pathology EdgeDocument2 pagesGeneral Pathology EdgeskNo ratings yet
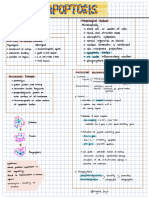
- ApoptosisDocument1 pageApoptosis121jcarunimaNo ratings yet
- JSD 1 15Document10 pagesJSD 1 15freeda.ampottiNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2211124720307117 MainDocument22 pages1 s2.0 S2211124720307117 Mainsri rezekiNo ratings yet
- Kuliah: Anatomi Fisiologi Sistem ImunDocument44 pagesKuliah: Anatomi Fisiologi Sistem ImunAminudin RomeoNo ratings yet
- IS Part 3Document10 pagesIS Part 3Xie OcquiolaNo ratings yet
- Hypersensitivity ImunobiologiDocument14 pagesHypersensitivity Imunobiologinisa humairoNo ratings yet
- MBS 600 2023Document289 pagesMBS 600 2023venture kulNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System HistologyDocument18 pagesCirculatory System HistologySilhouette SignNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulants and Arrhythmias 2020Document134 pagesAnticoagulants and Arrhythmias 2020Rex Yun WangNo ratings yet
- Bacterial MorphologyDocument2 pagesBacterial MorphologyJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Moh. Supriatna, Yusrina Istant Divisi PGD IKA RSDK/FK UNDIP SemarangDocument63 pagesMoh. Supriatna, Yusrina Istant Divisi PGD IKA RSDK/FK UNDIP SemarangimamNo ratings yet
- Cell Signalling Lodish CbibDocument3 pagesCell Signalling Lodish CbibShreyas DhuliyaNo ratings yet
- Clase 8 Alteraciones Plaquetas Lab Clin 2022Document31 pagesClase 8 Alteraciones Plaquetas Lab Clin 2022Abelardo MedianeroNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Immunity - 1Document15 pagesAdaptive Immunity - 1FN FajrinNo ratings yet
- Imun AwalDocument13 pagesImun AwalAdy RAstafaraNo ratings yet
- Pluripotent Stem Cell GuidebookDocument52 pagesPluripotent Stem Cell GuidebookJonathan Torralba TorrónNo ratings yet
- Hematology ReviewerDocument4 pagesHematology ReviewerAbigail Puno100% (1)
- Telomerase Regenerates Telomeres Using An RNA Template: LeadingDocument12 pagesTelomerase Regenerates Telomeres Using An RNA Template: Leadinganon_737973908No ratings yet
- Mouse (Mus Musculus)Document4 pagesMouse (Mus Musculus)Jhestine AbayanNo ratings yet
- Review Article Proteomic Technology "Lens" For Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Process Identification in OncologyDocument17 pagesReview Article Proteomic Technology "Lens" For Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Process Identification in OncologyAlexis PaivaNo ratings yet
- Innate Immunity Acquired Immunity HLA System Mechanisms of Tissue Damage Autoimmune Disease Immunity & InfectionDocument238 pagesInnate Immunity Acquired Immunity HLA System Mechanisms of Tissue Damage Autoimmune Disease Immunity & InfectionAnonymous wVgEAr6No ratings yet
- Note 26-Sep-2020Document18 pagesNote 26-Sep-2020VickyNo ratings yet
- ACAIDDocument3 pagesACAIDSnehaNo ratings yet
- Exd 1194 f1-3Document3 pagesExd 1194 f1-3Svatsan SriNo ratings yet
- Immunology Usmle Hsu Notes PDFDocument64 pagesImmunology Usmle Hsu Notes PDFAyeshaArifNo ratings yet
- Presentation: Neuroendocrine Control of ImmunodulationDocument17 pagesPresentation: Neuroendocrine Control of Immunodulationdrchetan20078839No ratings yet
- Elearning Lymphatic Organs 2 2023newDocument28 pagesElearning Lymphatic Organs 2 2023newpiano357sidNo ratings yet
- GegwegwDocument27 pagesGegwegwSaverioFortunatoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Mono - EBVDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Mono - EBVSharon EspinaNo ratings yet
- BOOK TRANS MegakaryopoiesisDocument3 pagesBOOK TRANS MegakaryopoiesisPaul LesterNo ratings yet
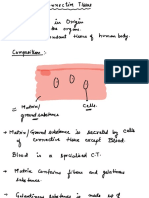
- Lecture 3connective TissueDocument20 pagesLecture 3connective TissueMohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Platelet Production, Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesChapter 13 - Platelet Production, Structure and FunctionAira UsiNo ratings yet
- Innate & Adaptive Immunity (DR - Soraya Rezeki, MKT)Document30 pagesInnate & Adaptive Immunity (DR - Soraya Rezeki, MKT)Dyah Wahlia100% (1)
- Lesson 6-PLATELETS - HEMA - REVIEWERDocument2 pagesLesson 6-PLATELETS - HEMA - REVIEWER2B VILORIA, Kristine Joyce D.No ratings yet
- L6B7 ImmunologyDocument4 pagesL6B7 ImmunologyMichael WongNo ratings yet
- 07 WitkoDocument32 pages07 WitkoErwanNo ratings yet
- Micro F2.Chapter 7 - 2022Document4 pagesMicro F2.Chapter 7 - 2022عبدالرحمن عابدNo ratings yet
- Table of HML Infections - Numbers-Feuil1Document3 pagesTable of HML Infections - Numbers-Feuil1naazaninrahat76No ratings yet
- Pathology TablesDocument3 pagesPathology TablesSamNo ratings yet
- Organsof ImmunityDocument38 pagesOrgansof ImmunitysaimNo ratings yet
- ANPS 020 Cornbrooks 02-07-14Document23 pagesANPS 020 Cornbrooks 02-07-14vyilmazNo ratings yet
- B. Respiratory System - V11 Completed - 1605Document50 pagesB. Respiratory System - V11 Completed - 1605Abiraamii ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Termofisher Guide Stem CellDocument60 pagesTermofisher Guide Stem Cellnadhifa akNo ratings yet
- HematopoiesisDocument35 pagesHematopoiesistika Purnama SariNo ratings yet
- Cells of Immune SystemDocument35 pagesCells of Immune Systemdurga.mv1804No ratings yet
- INNATE IMMUNITY InflammationDocument3 pagesINNATE IMMUNITY InflammationMichelle San Miguel FeguroNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0735109704921043 MainDocument1 page1 s2.0 S0735109704921043 MainLutfia HilmaNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Protein LocalizationDocument54 pagesPowerpoint Protein LocalizationJoseph BenaiahNo ratings yet
- Cell Motility: From Molecules to OrganismsFrom EverandCell Motility: From Molecules to OrganismsAnne RidleyNo ratings yet
- The Epigenetics of Autoimmune DiseasesFrom EverandThe Epigenetics of Autoimmune DiseasesMoncef ZoualiNo ratings yet
- The "Write" Way: A Judicial Clerk's Guide To Writing For The CourtDocument92 pagesThe "Write" Way: A Judicial Clerk's Guide To Writing For The Courtunknown07blackstarNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument1 pageReadmedan maliwatNo ratings yet
- Short Questions For Ayub Khan DownfallDocument9 pagesShort Questions For Ayub Khan Downfallabdullah sheikhNo ratings yet
- PVC Foam Furniture Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesPVC Foam Furniture Sheet PDFAbdul Majid100% (1)
- Vigil Incidents HistoryDocument42 pagesVigil Incidents HistoryJohn Petrovich WayneNo ratings yet
- Customers Satisfaction On ATMDocument33 pagesCustomers Satisfaction On ATMabdullahi shafiuNo ratings yet
- YOGESH PROJECT (1) - Converted (1) (1) 23Document71 pagesYOGESH PROJECT (1) - Converted (1) (1) 23Satyam BobadeNo ratings yet
- Immuno DiffusionDocument3 pagesImmuno DiffusionSai SridharNo ratings yet
- जनावरहरूमा फेनबेन्डाजोलको प्रयोग (Use of Fenbendazole in animals)Document17 pagesजनावरहरूमा फेनबेन्डाजोलको प्रयोग (Use of Fenbendazole in animals)Jibachha SahNo ratings yet
- 2016 CV - Curriculum Vitae Duy Anh 1Document11 pages2016 CV - Curriculum Vitae Duy Anh 1Cao Quang HưngNo ratings yet
- Technical InstructionsDocument6 pagesTechnical InstructionsSadinjana LakshanNo ratings yet
- Economics For Business and ManagementDocument56 pagesEconomics For Business and ManagementABDALLAHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Non Verbal CommunicationDocument7 pagesChapter 7 - Non Verbal CommunicationCarolyn NacesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-Managing Quality: 07/20/2022 1 Arsi University Om Mba-2020Document33 pagesChapter 7-Managing Quality: 07/20/2022 1 Arsi University Om Mba-2020temesgen yohannesNo ratings yet
- A Meta-Analysis of Motivational Interviewing Twenty-Five Years of Empirical StudiesDocument24 pagesA Meta-Analysis of Motivational Interviewing Twenty-Five Years of Empirical StudiesJavieraRamírezSánchezNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan Quarter 3 Week 1 Tle Agri-6 MARCH 1-5, 2021Document1 pageWeekly Home Learning Plan Quarter 3 Week 1 Tle Agri-6 MARCH 1-5, 2021Mariano CañadaNo ratings yet
- 420 Economic Survey Chapter 11 Thalinomics IndiashastraDocument1 page420 Economic Survey Chapter 11 Thalinomics IndiashastraKarambir Singh DhayalNo ratings yet
- Health Talk ExcerciseDocument5 pagesHealth Talk ExcerciseNyalen Hakom100% (1)
- Module 2 Year 4Document16 pagesModule 2 Year 4mioraffandyNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics 1Document64 pagesAnalog Electronics 1AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Principle of ManagementDocument6 pagesPrinciple of ManagementArthiNo ratings yet
- CCPM TaiwanDocument241 pagesCCPM TaiwanIsmael SandovalNo ratings yet
- CDP+ Version 10 (Guide)Document124 pagesCDP+ Version 10 (Guide)Pew IcamenNo ratings yet
- PFI ES-5-1993 Cleaning of Fabricated PipingDocument4 pagesPFI ES-5-1993 Cleaning of Fabricated PipingRodrigo Chambilla VernazaNo ratings yet
- Measuring Strain in RocksDocument2 pagesMeasuring Strain in Rocksdarebusi1No ratings yet
- Managed Pressure Drilling Modeling & Simulation (A Case Study)Document8 pagesManaged Pressure Drilling Modeling & Simulation (A Case Study)Mejbahul SarkerNo ratings yet
- A Bad Workman Always Blames His ToolsDocument6 pagesA Bad Workman Always Blames His ToolsTimothy BrownNo ratings yet
- Analysis of New Topology For 7 - Level Asymmetrical Multilevel Inverter and Its Extension To 19 LevelsDocument19 pagesAnalysis of New Topology For 7 - Level Asymmetrical Multilevel Inverter and Its Extension To 19 LevelsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Terror of Pediatric Medicine DR SircusDocument258 pagesThe Terror of Pediatric Medicine DR SircusAngel Francisco100% (1)