Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ns Plants
Ns Plants
Uploaded by
Mpho MathoboOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ns Plants
Ns Plants
Uploaded by
Mpho MathoboCopyright:
Available Formats
Learning Area : natural Sciences Grade : 5
Context : life and living Content : Plants
Time Frame : From 21 February To : 11 March
Learning Outcomes
Lo 1 : Scientific Investigations
The learner will be able to act confidently on curiosity about natural phenomena, &
to investigate relationships and solve problems in scientific; technological and
environmental contexts.
1.1 PLANS AN INVESTIGATION
Contributes ideas of familiar situations, needs or materials & identifies
interesting aspects, which could lead to investigations
1.2 CONDUCTS INVESTIGATION & COLLECTS DATA
Explores the possibilities in available materials, finding out how they can
be
1.3 EVALUATES DATA & COMMUNICATES FINDINGS
Talks about observations and suggests possible connections to other
situations
Lo 2 : constructing knowledge
The learner will know and be able to interpret and apply scientific; technological
and environmental knowledge.
2.1. RECALLS MEANINGFUL INFORMATION
At minimum, uses own most fluent language to name and describe
objects, material & organisms
2.2. CATEGORISES INFORMATION
Sorts objects & organisms by a visible property
Lo 3 : science, society and environment
The learner will be able to demonstrate an understanding of the interrelationships
between science and technology, society and environment.
3.1. UNDERSTANDS SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY IN THE CONTEXT OF HISTORY
AND INDIGENOUS KNOWLEDGE:
Describes how local indigenous culture have used scientific principles &
technological products for specific purposes
3.2. UNDERSTANDS THE IMPACT OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Identifies features of science and technological devices around him/her; &
tells about their purpose & usefulness
3.3. RECOGNIZES BIAS IN SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY:
Identifies difficulties some people may have in using technological devices.
LANGALIBALELE DUBE PRIMARY
Strands and Sub-strands
strands Planet Earth & Life &Living Energy & Change Matter &
Beyond Materials
Sub- Our place in Life process Energy Properties &
strands space transfer & uses of
systems materials
Atmosphere & Interaction Energy and Structures;
weather in development reactions &
environment in SA changes of
materials
The changing Biodiversity,
earth change &
continuity
Activity Day 1
1
Educator distributes prepared notes to learners. Learners cut
and paste the notes in their Natural Science books.
Day 2
The educator guides learners while reading the paragraphs about the background
information about plants under the following headings:
WHAT IS A PLANT?
Plants are one of the five main groups of living things. These groups are called
kingdoms. The plant kingdom includes such living things as grasses, trees, ferns,
bushes, and flowers. Botanists, the scientists who study plants,
WHAT ARE THE MAIN KINDS OF PLANTS?
Almost all the members of the plant kingdom are seed plants. They grow from
seeds. Most seed plants are flowering plants, or angiosperms.
WHAT ARE FLOWERING PLANTS?
People who plant flower gardens fill them with flowering plants. Almost
all the fruits and vegetables you eat come from flowering plants.
Flowering plants make seeds that are inside a covering. Angiosperm,
the name for flowering plants, means “enclosed seed.”
WHAT ARE OTHER SEED PLANTS?
Unlike flowering plants, some seed plants make seeds that are not inside a
covering. They are called gymnosperms, a word that means “naked seed.”
Day 3
Learners write about the following activity:
1. Write down five examples of plants kingdom
Learners’ books are marked. Learners write corrections.
Day 4
Learners define the following:
1. Botanist
2. Angiosperms
3. Gymnosperms
Educator marks learners’ books. Learners write corrections.
Day 5
Educator revises with learners the following terminology.
1. Botanist
2. Angiosperms
3. Gymnosperms
These terminologies are displayed on their classroom walls.
Day 6
Learners research about the different parts of plants as follows :
PARTS OF THE PLANT
Start>>All Programs>>Microsoft Encarta>>Encarta kids
2008>>science>>the environment>>plants>> parts of a plant.
Learners are then given the homework to write down the five
different parts of a plant
Day 7
Educator marks learners’ books. Learners write corrections.
Day 8
Learners research about the different parts of plants as follows :
PARTS OF THE LEAF
Start>>All Programs>>Microsoft Encarta>>Encarta kids
2008>>science>>the environment>>plants>> parts of a leaf
Learners are then given the homework to a labeled leaf of a plant
showing:
• petiole,
• blade,
• veins
Day 9
Educator marks learners books, learners write corrections
Day 10
PARTS OF THE FLOWER
Flowers help some plants reproduce, or make new plants.
Parts of a flower include petals, sepals, stamens, and the
pistil. Open the Microsoft Encarta program as follows:
Start>>All Programs>>Microsoft Encarta>>Encarta kids
2008>>science>>the environment>>plants>> parts of a flower.
Educators asks learners to label the flower pasted
in their books.
Day 11
Educator marks learners books, learners write corrections
DAY 12
LEARNERS RESEARCH HOW PLANTS MAKE FOOD
Start>>All Programs>>Microsoft Encarta>>Encarta kids
2008>>science>>the environment>>plants>> how plants
make food
CLASSWORK: WHAT IS PHOTOSYNTHESIS?
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5825)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- My Children!my Africa!Document30 pagesMy Children!my Africa!lindokuhleadmire88No ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Undercover by John Bevere TagalogDocument5 pagesUndercover by John Bevere TagalogAngela Bainca Amper86% (21)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Chap 24Document16 pagesChap 24Phú NguyễnNo ratings yet
- The Count of Monte CristoDocument12 pagesThe Count of Monte CristoElla AustriaNo ratings yet
- A Is For Allah J Is For JihadDocument6 pagesA Is For Allah J Is For JihadJobhiyar7123No ratings yet
- Marketing Practices and Its Effect To The Income of Agricultural Supply StoresDocument55 pagesMarketing Practices and Its Effect To The Income of Agricultural Supply StoresZipporah de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Intro To Genetic EngineeringDocument84 pagesIntro To Genetic EngineeringMhimi ViduyaNo ratings yet
- 2007 Justicia, Rebeca ECUADOR'S CHOCO ANDEAN CORRIDOR: A LANDSCAPE APPROACH FOR CONSERVATION AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENTDocument248 pages2007 Justicia, Rebeca ECUADOR'S CHOCO ANDEAN CORRIDOR: A LANDSCAPE APPROACH FOR CONSERVATION AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENTRebeca JusticiaNo ratings yet
- 101 Facts About VikingsDocument6 pages101 Facts About VikingsJulio Cesar RamosNo ratings yet
- Statutory Interpretation: Katharine MathesonDocument28 pagesStatutory Interpretation: Katharine MathesonKofi Mc SharpNo ratings yet
- 9702 m19 Ms 12Document3 pages9702 m19 Ms 12And rewNo ratings yet
- NFC Technology Using RfidDocument7 pagesNFC Technology Using Rfidtrance 2k17No ratings yet
- Private Files Module 3 Practical Research 2 Conceptual Framework and Hypothesis PDFDocument20 pagesPrivate Files Module 3 Practical Research 2 Conceptual Framework and Hypothesis PDFLovely IñigoNo ratings yet
- Socio Unit3Document12 pagesSocio Unit3priya sharmaNo ratings yet
- Hassett Et Al. (Monkey Toy Preferences) NotesDocument33 pagesHassett Et Al. (Monkey Toy Preferences) NotesKarthiNo ratings yet
- 計概OCW筆記Document21 pages計概OCW筆記陳宥汝No ratings yet
- SAP Integration ManagerDocument7 pagesSAP Integration Managerapi-78387994No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in English Grade 7Document6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in English Grade 7Marijoe CayangaNo ratings yet
- QIDS SR16 DepressionDocument3 pagesQIDS SR16 DepressionSergioMSaraivaNo ratings yet
- Integration Broker BasicsDocument6 pagesIntegration Broker Basicsharikishore14No ratings yet
- Materi 3 Materi 3 Rerangka Konseptual IASBDocument20 pagesMateri 3 Materi 3 Rerangka Konseptual IASBgadi3szzNo ratings yet
- NMTC Test Papers Prelims All Levels 2016Document15 pagesNMTC Test Papers Prelims All Levels 2016tannyNo ratings yet
- Tanuj Bohra - HRM - Individual Assignment PDFDocument6 pagesTanuj Bohra - HRM - Individual Assignment PDFTanuj BohraNo ratings yet
- Educ - MidtermDocument8 pagesEduc - MidtermAn Jannette AlmodielNo ratings yet
- MHRM 2016 PDFDocument16 pagesMHRM 2016 PDFבעילום שם משתמשNo ratings yet
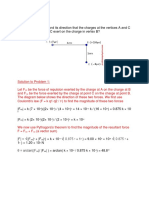
- Problem and Solution Electric FieldDocument10 pagesProblem and Solution Electric FieldSansen Diamante Colipano Jr.No ratings yet
- Gallantry AwardsDocument10 pagesGallantry AwardsSmita BachhavNo ratings yet
- Preposition, Conjunction and ParticiplesDocument22 pagesPreposition, Conjunction and ParticiplesAudrey MonicaNo ratings yet
- Metropolitan Bank V CablizoDocument10 pagesMetropolitan Bank V CablizoLe Obm SizzlingNo ratings yet
- 3-Medical Gases Systems. The Third Lecture.Document17 pages3-Medical Gases Systems. The Third Lecture.Fireproof Sistemas ElectromecánicosNo ratings yet