Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine Gland Histology
Endocrine Gland Histology
Uploaded by
chloeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Guide To Complete Dentures VitaDocument150 pagesGuide To Complete Dentures VitaFrederico Diego Medeiros Lima67% (3)
- MTF, Sba-Gmt202: (Ne Osa)Document5 pagesMTF, Sba-Gmt202: (Ne Osa)Zahra HussainNo ratings yet
- Endo SystemDocument78 pagesEndo SystemTimmy OngNo ratings yet
- Moraj 3 ADocument12 pagesMoraj 3 AMohammed EljackNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry 2 Lec - W10 - Introduction To Endocrine GlandsDocument3 pagesClinical Chemistry 2 Lec - W10 - Introduction To Endocrine GlandsEmalchris AcadsNo ratings yet
- L8 & 9 Endocrine GlandsDocument39 pagesL8 & 9 Endocrine GlandsmachirajushandilyaNo ratings yet
- Histology and Microtechniques Biology 160 Prof. Maria Luisa J. Landingin Thyroid GlandDocument2 pagesHistology and Microtechniques Biology 160 Prof. Maria Luisa J. Landingin Thyroid GlandDavid YapNo ratings yet
- Omar THE ADRENAL GLANdDocument4 pagesOmar THE ADRENAL GLANdRenien Khim BahayaNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Glands Clinical Chemistry (Laboratory) : Lesson 7Document5 pagesAdrenal Glands Clinical Chemistry (Laboratory) : Lesson 7Cherry Ann ColechaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Lipid Metabolism Part 1Document6 pages2.1 Lipid Metabolism Part 1John LazaroNo ratings yet
- Lipida 1Document46 pagesLipida 1zikri manggala putraNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument7 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationAnonymous -No ratings yet
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument8 pagesChemistry ReviewerprnfbmsdqnNo ratings yet
- BMSN2202 Life Science II Year 2, 5 Year Curriculum Tutorial 3 PhysiologyDocument61 pagesBMSN2202 Life Science II Year 2, 5 Year Curriculum Tutorial 3 PhysiologyMiles HuiNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument13 pagesEndocrineElyka Alivan Valdez PolonioNo ratings yet
- Chemical Co - OrdinationDocument21 pagesChemical Co - OrdinationManinder KaurNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesEndocrine Systemwardahafif00No ratings yet
- Hormones DR KhawlaDocument14 pagesHormones DR Khawlaحسين علاوي طاميNo ratings yet
- 1 Adrenal CortexDocument15 pages1 Adrenal CortexMarion Lawrence LaraNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland Clinical Chemistry 2 (Laboratory) : LessonDocument4 pagesThyroid Gland Clinical Chemistry 2 (Laboratory) : LessonCherry Ann ColechaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System ReviewerDocument23 pagesEndocrine System ReviewerKimberly Joy GregorioNo ratings yet
- 337 Pdfsam NMS PhysiologyDocument166 pages337 Pdfsam NMS PhysiologydrpnnreddyNo ratings yet
- Histology of Endocrine GlandsDocument36 pagesHistology of Endocrine GlandsDaiva ŠiaulienėNo ratings yet
- ADIL BSN - 1C Manual Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesADIL BSN - 1C Manual Endocrine Systembernadil01No ratings yet
- A. Simple Lipids: Examples of Compounds Belonging To The Steroid FamilyDocument5 pagesA. Simple Lipids: Examples of Compounds Belonging To The Steroid FamilyTRISHA MARIE CLEMENTENo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Endocrine Gland (Ductless Gland)Document50 pagesThe Endocrine System: Endocrine Gland (Ductless Gland)Mohammad AliNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument18 pagesEndocrine SystemdrynwhylNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument51 pagesThe Endocrine SystemQonitatul KhasanahNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System (2) 2Document20 pagesEndocrine System (2) 2negmm2226No ratings yet
- Biology Notes For Class 11 H ChapterDocument7 pagesBiology Notes For Class 11 H Chapterᴘᴀᴘɪᴛʜᴀ ᴋᴀɴɴᴀɴNo ratings yet
- DPP+L2 Endocrine SystemDocument59 pagesDPP+L2 Endocrine Systemjanhvisharma12006No ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument6 pagesEndocrine System NotesHannah Grace CorveraNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System XVDocument10 pagesEndocrine System XVaraineNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument40 pagesEndocrine SystemabdullahNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme LemakDocument53 pagesMetabolisme Lemakbuciin 29No ratings yet
- Endocrinology MergeDocument22 pagesEndocrinology MergeEricsson CarabbacanNo ratings yet
- 88 Endocrine LAB TRUE StudDocument49 pages88 Endocrine LAB TRUE Studbaylontishamae002No ratings yet
- Chemistry of Lipids. Digestion of Lipids. Lipid Oxidation: Biochemistry DepartmentDocument152 pagesChemistry of Lipids. Digestion of Lipids. Lipid Oxidation: Biochemistry DepartmentggfsedNo ratings yet
- Fluid-Mosaic Model of The Cell MembraneDocument1 pageFluid-Mosaic Model of The Cell Membranekoshinhk10No ratings yet
- Full Human Physiology Short NotesDocument11 pagesFull Human Physiology Short Notesseetharaman8341No ratings yet
- Endocrine and HormonesDocument26 pagesEndocrine and HormonesAntonette FrondozoNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument18 pagesThyroid GlandSaireen BalochNo ratings yet
- Anfis Endokrin Idk-1 ElsDocument60 pagesAnfis Endokrin Idk-1 ElsAuliya ArahmanNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland Cortisol AtfDocument4 pagesAdrenal Gland Cortisol Atf2ymyccmvfcNo ratings yet
- PlateletsDocument17 pagesPlateletsalinanaeem619No ratings yet
- Class 11 Bio Notes CH 3Document7 pagesClass 11 Bio Notes CH 3VinayNo ratings yet
- VND Ms-Powerpoint&rendition 1Document49 pagesVND Ms-Powerpoint&rendition 1Muhammad SamiNo ratings yet
- 047 Endocrinology Physiology Parathyroid Gland CalcitoninDocument4 pages047 Endocrinology Physiology Parathyroid Gland Calcitoninیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Hormones Note PDFDocument36 pagesBiochemistry of Hormones Note PDFNeyan100% (1)
- Lipid ChemDocument6 pagesLipid ChemKarla Faye UcangNo ratings yet
- Kris Finals Anaphy Lec NotesDocument16 pagesKris Finals Anaphy Lec NotespangilinankrisallenNo ratings yet
- Sex Hormones: Dr. Lotfi S. Bin Dahman MD, PHD Clinical Biochemistry HucomDocument22 pagesSex Hormones: Dr. Lotfi S. Bin Dahman MD, PHD Clinical Biochemistry Hucomعبدالحكيم النهديNo ratings yet
- Biochem Proteins ReviewerDocument4 pagesBiochem Proteins ReviewerStefany JoyNo ratings yet
- Phys 8Document39 pagesPhys 8sakwork30No ratings yet
- Kuliah Keempat (Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands)Document38 pagesKuliah Keempat (Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands)kiki rawitriNo ratings yet
- Met 8.2Document22 pagesMet 8.2LT DRAGONXNo ratings yet
- Endocrine OctoberDocument70 pagesEndocrine OctoberMohamed FarahatNo ratings yet
- hypothal-hypof disorders part1 - копияDocument176 pageshypothal-hypof disorders part1 - копияElena Borş MorariNo ratings yet
- (Transes) Human Histology - 10 Endocrine GlandsDocument10 pages(Transes) Human Histology - 10 Endocrine GlandsReina CastronuevoNo ratings yet
- 9 - Cardio Vascular System - Part-1Document38 pages9 - Cardio Vascular System - Part-1janahamid889No ratings yet
- Acute AbdomenDocument7 pagesAcute AbdomenchloeNo ratings yet
- Acute AbdomenDocument7 pagesAcute AbdomenchloeNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain ICM 1 RHWDocument53 pagesLow Back Pain ICM 1 RHWchloeNo ratings yet
- Multiple TraumaDocument20 pagesMultiple TraumachloeNo ratings yet
- LO Kidney Week 5Document51 pagesLO Kidney Week 5chloeNo ratings yet
- International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) Symbols: ReviewersDocument2 pagesInternational Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) Symbols: ReviewersMauricio HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Dragon City Breeding TimesDocument17 pagesDragon City Breeding TimesAndRianEkaPuTra100% (1)
- Edgar Rice Burroughs - Tarzan 12 - Tarzan and The Lost EmpireDocument85 pagesEdgar Rice Burroughs - Tarzan 12 - Tarzan and The Lost EmpireNiloticNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For The Economics of Money Banking and Financial Markets 12th Edition MishkinDocument37 pagesSolution Manual For The Economics of Money Banking and Financial Markets 12th Edition Mishkinmaitlandmohammedfx100% (13)
- PHYLUM CNIDARIA-HandoutDocument2 pagesPHYLUM CNIDARIA-HandoutTeacher MarianoNo ratings yet
- Components of RPDDocument5 pagesComponents of RPDsareh_ghodsiNo ratings yet
- Comparative Zoology Lab ManualDocument51 pagesComparative Zoology Lab ManualMarjune DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Cip Validation Tool FinalDocument3 pagesCip Validation Tool Finalvincevillamora2k11No ratings yet
- Zarco Ordóñez KarlaDocument2 pagesZarco Ordóñez KarlaKarla ZarcoNo ratings yet
- Dr. Retno Pudji Rahayu, DRG, M.Kes Depart. Patologi Mulut Dan Maksilofasial FKG UnairDocument52 pagesDr. Retno Pudji Rahayu, DRG, M.Kes Depart. Patologi Mulut Dan Maksilofasial FKG UnairBima Ewando KabanNo ratings yet
- Induced Spawning in Fish CultureDocument8 pagesInduced Spawning in Fish CultureVijay KarotiaNo ratings yet
- 34 Veterinary Aip 2022 09 - 15 - 21Document23 pages34 Veterinary Aip 2022 09 - 15 - 21Budget OfficeNo ratings yet
- Capstone ProjectDocument26 pagesCapstone Projectapi-462238327No ratings yet
- Flora and Fauna of SikkimDocument8 pagesFlora and Fauna of Sikkimdavegi3069No ratings yet
- 588-Article Text (Word - Doc - Docx) - 2159-1-10-20211203Document7 pages588-Article Text (Word - Doc - Docx) - 2159-1-10-20211203Pak SulNo ratings yet
- Taboo Game For Teenagers and AdultsDocument10 pagesTaboo Game For Teenagers and AdultsEstherPoboSerradillaNo ratings yet
- Business ProposalDocument2 pagesBusiness ProposalNazifa100% (1)
- Examen de Corigenţă La Limba Engleza Clasa A VDocument22 pagesExamen de Corigenţă La Limba Engleza Clasa A VAvram Paula-roxanaNo ratings yet
- Results Anatomy Shellfish LabDocument17 pagesResults Anatomy Shellfish LabSyafiqa UmairahNo ratings yet
- Wildlife Vaasa Festival - Book of Entries 2006Document164 pagesWildlife Vaasa Festival - Book of Entries 2006Wildlife Vaasa Festival / Ilias MissyrisNo ratings yet
- Tell Nader & Tell Baqrta 2012-2-1Document47 pagesTell Nader & Tell Baqrta 2012-2-1Shadi GarmaNo ratings yet
- 10 Effective Ayurvedic Treatment For Hair LossDocument9 pages10 Effective Ayurvedic Treatment For Hair Lossrpav77No ratings yet
- Equine BehaviorDocument366 pagesEquine BehaviorTheresaGraziano100% (4)
- 264 2002 Article 312Document4 pages264 2002 Article 312Anonymous ygv5h1MRNo ratings yet
- Chicken Embryo As A Diabetic Animal ModelDocument107 pagesChicken Embryo As A Diabetic Animal ModelSrinivasan KrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Legal Med. Report-QueenDocument61 pagesLegal Med. Report-QueenQuinnee VallejosNo ratings yet
- Daftar Harga Sumber Ps Ciracas Per Februari 2021: Harga Dapat Berubah Sewaktu-Waktu Tanpa Pemberitahuan SebelumnyaDocument3 pagesDaftar Harga Sumber Ps Ciracas Per Februari 2021: Harga Dapat Berubah Sewaktu-Waktu Tanpa Pemberitahuan SebelumnyaJ Timboel SitohangNo ratings yet
- Tabla 28 HomologadaDocument272 pagesTabla 28 HomologadaVeronica AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Hippo RevisedDocument13 pagesHippo RevisedflyingpieceofmeatNo ratings yet
Endocrine Gland Histology
Endocrine Gland Histology
Uploaded by
chloeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endocrine Gland Histology
Endocrine Gland Histology
Uploaded by
chloeCopyright:
Available Formats
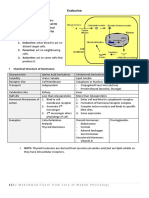
Nama : Ervinna Tantri (Angkatan 2019)
NIM : 01071190034
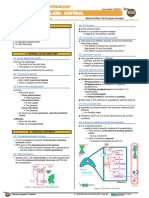
Types of Glands Image Explanation
Composed of :
• Chromophils stained
- Basophils [B]:
corticotrophs (ACTH,
A LPH), gonadotrophs
(FSH, LH, ICSH) and
Anterior Pituitary thyrotrophs (TSH)
B - Acidophils [A]:
C somatotrophs (GH)
and lactotrophs (PRL)
• Chromophrobes [C] stain
Thyroid Follicles:
• Follicular Cells [F] =
produce thyroid hormones
and TSH receptors
F C • Colloid/Thyroglobulins [T]
Thyroid
T = inactive storage for T4
and T3 hormones
Parafollicular Cells / C Cells [C] =
Secrete calcitonin
Composed of:
• Principal/Chief cells [P]
mainly densely packed.
Parathyroid O P • Clumping of acidophilic
degenerated derivatives of
principal cells called
oxyphil cells [O].
Islets of Langerhans composed of:
• α cell produces glucagon
• β cell produces insulin
Pancreas • δ or D cell produces
somatostatin
• PP cell produces
pancreatic polypeptide
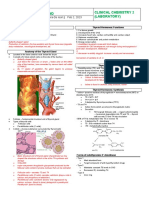
Nama : Ervinna Tantri (Angkatan 2019)
NIM : 01071190034
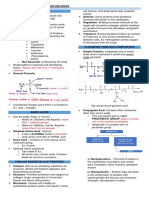
Inside the capsule [C] of adrenal
gland is an adrenal cortex, which
has 3 concentric zones:
• Zona glomerulosa [G], 15%
of cortex, produced
mineralocorticoids, its
principal product is
aldosterone, the major
regulator of salt balance.
G • Zona Fasciculata [F], 65-
80% of cortex, filled with
lipid droplets and appear
vacuolated, produced
glucocorticoid, especially
Adrenal
F cortisol, which stimulates
gluconeogenesis in many
cells and glycogen
synthesis in the liver.
R
• Zona Reticularis [R], 10%
of cortex, contains fewer
M lipid droplets and more
lipofuscin ligament,
produced cortisol and
primarily weak androgens,
including
dehydroepiandrosterone
(DHEA).
Last inner part is the adrenal
medulla [M]/chromaffin cells, that
is functioned for storage and
secretion of catecholamines, such
as epinephrine or norepinephrine.
You might also like
- Guide To Complete Dentures VitaDocument150 pagesGuide To Complete Dentures VitaFrederico Diego Medeiros Lima67% (3)
- MTF, Sba-Gmt202: (Ne Osa)Document5 pagesMTF, Sba-Gmt202: (Ne Osa)Zahra HussainNo ratings yet
- Endo SystemDocument78 pagesEndo SystemTimmy OngNo ratings yet
- Moraj 3 ADocument12 pagesMoraj 3 AMohammed EljackNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry 2 Lec - W10 - Introduction To Endocrine GlandsDocument3 pagesClinical Chemistry 2 Lec - W10 - Introduction To Endocrine GlandsEmalchris AcadsNo ratings yet
- L8 & 9 Endocrine GlandsDocument39 pagesL8 & 9 Endocrine GlandsmachirajushandilyaNo ratings yet
- Histology and Microtechniques Biology 160 Prof. Maria Luisa J. Landingin Thyroid GlandDocument2 pagesHistology and Microtechniques Biology 160 Prof. Maria Luisa J. Landingin Thyroid GlandDavid YapNo ratings yet
- Omar THE ADRENAL GLANdDocument4 pagesOmar THE ADRENAL GLANdRenien Khim BahayaNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Glands Clinical Chemistry (Laboratory) : Lesson 7Document5 pagesAdrenal Glands Clinical Chemistry (Laboratory) : Lesson 7Cherry Ann ColechaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Lipid Metabolism Part 1Document6 pages2.1 Lipid Metabolism Part 1John LazaroNo ratings yet
- Lipida 1Document46 pagesLipida 1zikri manggala putraNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument7 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationAnonymous -No ratings yet
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument8 pagesChemistry ReviewerprnfbmsdqnNo ratings yet
- BMSN2202 Life Science II Year 2, 5 Year Curriculum Tutorial 3 PhysiologyDocument61 pagesBMSN2202 Life Science II Year 2, 5 Year Curriculum Tutorial 3 PhysiologyMiles HuiNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument13 pagesEndocrineElyka Alivan Valdez PolonioNo ratings yet
- Chemical Co - OrdinationDocument21 pagesChemical Co - OrdinationManinder KaurNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesEndocrine Systemwardahafif00No ratings yet
- Hormones DR KhawlaDocument14 pagesHormones DR Khawlaحسين علاوي طاميNo ratings yet
- 1 Adrenal CortexDocument15 pages1 Adrenal CortexMarion Lawrence LaraNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland Clinical Chemistry 2 (Laboratory) : LessonDocument4 pagesThyroid Gland Clinical Chemistry 2 (Laboratory) : LessonCherry Ann ColechaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System ReviewerDocument23 pagesEndocrine System ReviewerKimberly Joy GregorioNo ratings yet
- 337 Pdfsam NMS PhysiologyDocument166 pages337 Pdfsam NMS PhysiologydrpnnreddyNo ratings yet
- Histology of Endocrine GlandsDocument36 pagesHistology of Endocrine GlandsDaiva ŠiaulienėNo ratings yet
- ADIL BSN - 1C Manual Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesADIL BSN - 1C Manual Endocrine Systembernadil01No ratings yet
- A. Simple Lipids: Examples of Compounds Belonging To The Steroid FamilyDocument5 pagesA. Simple Lipids: Examples of Compounds Belonging To The Steroid FamilyTRISHA MARIE CLEMENTENo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Endocrine Gland (Ductless Gland)Document50 pagesThe Endocrine System: Endocrine Gland (Ductless Gland)Mohammad AliNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument18 pagesEndocrine SystemdrynwhylNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument51 pagesThe Endocrine SystemQonitatul KhasanahNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System (2) 2Document20 pagesEndocrine System (2) 2negmm2226No ratings yet
- Biology Notes For Class 11 H ChapterDocument7 pagesBiology Notes For Class 11 H Chapterᴘᴀᴘɪᴛʜᴀ ᴋᴀɴɴᴀɴNo ratings yet
- DPP+L2 Endocrine SystemDocument59 pagesDPP+L2 Endocrine Systemjanhvisharma12006No ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument6 pagesEndocrine System NotesHannah Grace CorveraNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System XVDocument10 pagesEndocrine System XVaraineNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument40 pagesEndocrine SystemabdullahNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme LemakDocument53 pagesMetabolisme Lemakbuciin 29No ratings yet
- Endocrinology MergeDocument22 pagesEndocrinology MergeEricsson CarabbacanNo ratings yet
- 88 Endocrine LAB TRUE StudDocument49 pages88 Endocrine LAB TRUE Studbaylontishamae002No ratings yet
- Chemistry of Lipids. Digestion of Lipids. Lipid Oxidation: Biochemistry DepartmentDocument152 pagesChemistry of Lipids. Digestion of Lipids. Lipid Oxidation: Biochemistry DepartmentggfsedNo ratings yet
- Fluid-Mosaic Model of The Cell MembraneDocument1 pageFluid-Mosaic Model of The Cell Membranekoshinhk10No ratings yet
- Full Human Physiology Short NotesDocument11 pagesFull Human Physiology Short Notesseetharaman8341No ratings yet
- Endocrine and HormonesDocument26 pagesEndocrine and HormonesAntonette FrondozoNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument18 pagesThyroid GlandSaireen BalochNo ratings yet
- Anfis Endokrin Idk-1 ElsDocument60 pagesAnfis Endokrin Idk-1 ElsAuliya ArahmanNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland Cortisol AtfDocument4 pagesAdrenal Gland Cortisol Atf2ymyccmvfcNo ratings yet
- PlateletsDocument17 pagesPlateletsalinanaeem619No ratings yet
- Class 11 Bio Notes CH 3Document7 pagesClass 11 Bio Notes CH 3VinayNo ratings yet
- VND Ms-Powerpoint&rendition 1Document49 pagesVND Ms-Powerpoint&rendition 1Muhammad SamiNo ratings yet
- 047 Endocrinology Physiology Parathyroid Gland CalcitoninDocument4 pages047 Endocrinology Physiology Parathyroid Gland Calcitoninیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Hormones Note PDFDocument36 pagesBiochemistry of Hormones Note PDFNeyan100% (1)
- Lipid ChemDocument6 pagesLipid ChemKarla Faye UcangNo ratings yet
- Kris Finals Anaphy Lec NotesDocument16 pagesKris Finals Anaphy Lec NotespangilinankrisallenNo ratings yet
- Sex Hormones: Dr. Lotfi S. Bin Dahman MD, PHD Clinical Biochemistry HucomDocument22 pagesSex Hormones: Dr. Lotfi S. Bin Dahman MD, PHD Clinical Biochemistry Hucomعبدالحكيم النهديNo ratings yet
- Biochem Proteins ReviewerDocument4 pagesBiochem Proteins ReviewerStefany JoyNo ratings yet
- Phys 8Document39 pagesPhys 8sakwork30No ratings yet
- Kuliah Keempat (Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands)Document38 pagesKuliah Keempat (Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands)kiki rawitriNo ratings yet
- Met 8.2Document22 pagesMet 8.2LT DRAGONXNo ratings yet
- Endocrine OctoberDocument70 pagesEndocrine OctoberMohamed FarahatNo ratings yet
- hypothal-hypof disorders part1 - копияDocument176 pageshypothal-hypof disorders part1 - копияElena Borş MorariNo ratings yet
- (Transes) Human Histology - 10 Endocrine GlandsDocument10 pages(Transes) Human Histology - 10 Endocrine GlandsReina CastronuevoNo ratings yet
- 9 - Cardio Vascular System - Part-1Document38 pages9 - Cardio Vascular System - Part-1janahamid889No ratings yet
- Acute AbdomenDocument7 pagesAcute AbdomenchloeNo ratings yet
- Acute AbdomenDocument7 pagesAcute AbdomenchloeNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain ICM 1 RHWDocument53 pagesLow Back Pain ICM 1 RHWchloeNo ratings yet
- Multiple TraumaDocument20 pagesMultiple TraumachloeNo ratings yet
- LO Kidney Week 5Document51 pagesLO Kidney Week 5chloeNo ratings yet
- International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) Symbols: ReviewersDocument2 pagesInternational Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) Symbols: ReviewersMauricio HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Dragon City Breeding TimesDocument17 pagesDragon City Breeding TimesAndRianEkaPuTra100% (1)
- Edgar Rice Burroughs - Tarzan 12 - Tarzan and The Lost EmpireDocument85 pagesEdgar Rice Burroughs - Tarzan 12 - Tarzan and The Lost EmpireNiloticNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For The Economics of Money Banking and Financial Markets 12th Edition MishkinDocument37 pagesSolution Manual For The Economics of Money Banking and Financial Markets 12th Edition Mishkinmaitlandmohammedfx100% (13)
- PHYLUM CNIDARIA-HandoutDocument2 pagesPHYLUM CNIDARIA-HandoutTeacher MarianoNo ratings yet
- Components of RPDDocument5 pagesComponents of RPDsareh_ghodsiNo ratings yet
- Comparative Zoology Lab ManualDocument51 pagesComparative Zoology Lab ManualMarjune DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Cip Validation Tool FinalDocument3 pagesCip Validation Tool Finalvincevillamora2k11No ratings yet
- Zarco Ordóñez KarlaDocument2 pagesZarco Ordóñez KarlaKarla ZarcoNo ratings yet
- Dr. Retno Pudji Rahayu, DRG, M.Kes Depart. Patologi Mulut Dan Maksilofasial FKG UnairDocument52 pagesDr. Retno Pudji Rahayu, DRG, M.Kes Depart. Patologi Mulut Dan Maksilofasial FKG UnairBima Ewando KabanNo ratings yet
- Induced Spawning in Fish CultureDocument8 pagesInduced Spawning in Fish CultureVijay KarotiaNo ratings yet
- 34 Veterinary Aip 2022 09 - 15 - 21Document23 pages34 Veterinary Aip 2022 09 - 15 - 21Budget OfficeNo ratings yet
- Capstone ProjectDocument26 pagesCapstone Projectapi-462238327No ratings yet
- Flora and Fauna of SikkimDocument8 pagesFlora and Fauna of Sikkimdavegi3069No ratings yet
- 588-Article Text (Word - Doc - Docx) - 2159-1-10-20211203Document7 pages588-Article Text (Word - Doc - Docx) - 2159-1-10-20211203Pak SulNo ratings yet
- Taboo Game For Teenagers and AdultsDocument10 pagesTaboo Game For Teenagers and AdultsEstherPoboSerradillaNo ratings yet
- Business ProposalDocument2 pagesBusiness ProposalNazifa100% (1)
- Examen de Corigenţă La Limba Engleza Clasa A VDocument22 pagesExamen de Corigenţă La Limba Engleza Clasa A VAvram Paula-roxanaNo ratings yet
- Results Anatomy Shellfish LabDocument17 pagesResults Anatomy Shellfish LabSyafiqa UmairahNo ratings yet
- Wildlife Vaasa Festival - Book of Entries 2006Document164 pagesWildlife Vaasa Festival - Book of Entries 2006Wildlife Vaasa Festival / Ilias MissyrisNo ratings yet
- Tell Nader & Tell Baqrta 2012-2-1Document47 pagesTell Nader & Tell Baqrta 2012-2-1Shadi GarmaNo ratings yet
- 10 Effective Ayurvedic Treatment For Hair LossDocument9 pages10 Effective Ayurvedic Treatment For Hair Lossrpav77No ratings yet
- Equine BehaviorDocument366 pagesEquine BehaviorTheresaGraziano100% (4)
- 264 2002 Article 312Document4 pages264 2002 Article 312Anonymous ygv5h1MRNo ratings yet
- Chicken Embryo As A Diabetic Animal ModelDocument107 pagesChicken Embryo As A Diabetic Animal ModelSrinivasan KrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Legal Med. Report-QueenDocument61 pagesLegal Med. Report-QueenQuinnee VallejosNo ratings yet
- Daftar Harga Sumber Ps Ciracas Per Februari 2021: Harga Dapat Berubah Sewaktu-Waktu Tanpa Pemberitahuan SebelumnyaDocument3 pagesDaftar Harga Sumber Ps Ciracas Per Februari 2021: Harga Dapat Berubah Sewaktu-Waktu Tanpa Pemberitahuan SebelumnyaJ Timboel SitohangNo ratings yet
- Tabla 28 HomologadaDocument272 pagesTabla 28 HomologadaVeronica AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Hippo RevisedDocument13 pagesHippo RevisedflyingpieceofmeatNo ratings yet