Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sense Organs Ppqs-Ms
Sense Organs Ppqs-Ms
Uploaded by
CHRISTOPHER SCALEOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sense Organs Ppqs-Ms
Sense Organs Ppqs-Ms
Uploaded by
CHRISTOPHER SCALECopyright:
Available Formats
Sense organs past paper question-Answers
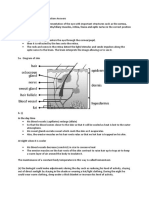
5 a. Produce an accurate representation of the eye with important structures such as the cornea,
iris, lens, suspensory ligaments/ciliary muscles, retina, fovea and optic nerve in the correct position
along with the correct labels.
How the eye works
• light from an object enters the eye through the cornea/pupil,
• then it is refracted by the lens onto the retina.
• The rods and cones in the retina detect the light/stimulus and sends impulses along the
optic nerve to the brain. The brain interprets the image allowing us to see it.
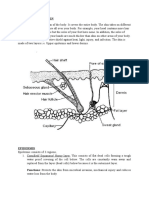
5a. Diagram of skin
b. (i)
In the day time
• His blood vessels (capillaries) enlarge (dilate)
• So that the blood comes closer to the skin so that it will be cooled as heat is lost to the outer
atmosphere.
• His sweat glands excrete sweat which cools the skin as it evaporates.
• Also, the erector muscles on his hair roots relax so that no hot hair is trapped on his skin.
At night when it is cooler
• His blood vessels decrease (constrict) in size to conserve heat
• The erector muscles on the hair roots of the skin contract to raise hair up to trap air to keep
a warm layer of air around the body to insulate it.
The maintenance of a constant body temperature in this way is called homeostasis
(ii) the biologist could make adjustments during the day such as reducing his level of activity, staying
out of direct sunlight by staying in the shade or wearing a hat/light clothing. During the night he
could wear warm clothing, sleep under a thick blanket or increase his level of activity.
You might also like
- Thermoregulation Worksheet AnswersDocument3 pagesThermoregulation Worksheet AnswersDrama MusicNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs Ppqs-MsDocument1 pageSense Organs Ppqs-MsToni-Krys HardyNo ratings yet
- The Eye and The SkinDocument19 pagesThe Eye and The SkinFezel HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Topic 14.4 Homeostasis Topic 14.5 Control of TemperatureDocument7 pagesTopic 14.4 Homeostasis Topic 14.5 Control of TemperaturenizaizzatiNo ratings yet
- F214Document16 pagesF214Rooqaya AhmedNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis: by Afshan HassanDocument19 pagesHomeostasis: by Afshan HassanZulnorain IrfanNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis 2024Document7 pagesHomeostasis 2024Natash MotheoNo ratings yet
- Human Senses: Monique MavronicolasDocument10 pagesHuman Senses: Monique MavronicolasMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
- 3-17 Nervous Handout p03-07Document5 pages3-17 Nervous Handout p03-07eddrobinson rumakiekNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs: Structure of Human EyeDocument8 pagesSense Organs: Structure of Human EyeRanveer SinghNo ratings yet
- 9 SkinDocument2 pages9 SkinDr.inerdevNo ratings yet
- Temperature and The Skin NotesDocument5 pagesTemperature and The Skin NotesBenjamin AttardNo ratings yet
- Forebrain: Prosencephalon : MusclesDocument4 pagesForebrain: Prosencephalon : MusclesZMCNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - HomeostasisDocument31 pagesChapter 14 - HomeostasisKareem DmourNo ratings yet
- ThermoregulationDocument32 pagesThermoregulationBoyan WeiNo ratings yet
- Sense OrgansDocument25 pagesSense OrgansSalma LabaranNo ratings yet
- An Organ That Receives and Relays Information About The Body's Senses To The BrainDocument59 pagesAn Organ That Receives and Relays Information About The Body's Senses To The BrainIsarra AmsaluNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument4 pagesBiologySha WnNo ratings yet
- Sense Organ: in Latin Sensus-To Feel, To PerceiveDocument17 pagesSense Organ: in Latin Sensus-To Feel, To PerceiveselesmabNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Ch. 9 The Senses NotesDocument7 pagesAnatomy Ch. 9 The Senses Notesprincepalestine100% (1)
- Somatic and Special SensesDocument20 pagesSomatic and Special SensesKASIMU MAHMUD HAMZANo ratings yet
- Sense Organs NotesDocument13 pagesSense Organs NotesVijay Laxmi MundhraNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm - Divides The Thoracic From TheDocument7 pagesDiaphragm - Divides The Thoracic From TheRizzalyn OrtizNo ratings yet
- Medsurg Neuro Sense OrgansDocument25 pagesMedsurg Neuro Sense Organsj UNo ratings yet
- The Mammalian Skin and LiverDocument7 pagesThe Mammalian Skin and LiverHarun IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Human Sense Organs PrelimDocument50 pagesHuman Sense Organs PrelimJersen Mae MaglabeNo ratings yet
- Concept 2 Notes - Senses For StudentsDocument21 pagesConcept 2 Notes - Senses For StudentsKaranNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs YaminiDocument27 pagesSense Organs Yaminichamanchula hemanthkumarNo ratings yet
- Sensory System: By: Sugiono, PHDDocument33 pagesSensory System: By: Sugiono, PHDRay SragaNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Response NotesDocument5 pagesCoordination and Response Noteskavya.gulatiNo ratings yet
- 645e3d4fe4b003b879fda56a OriginalDocument9 pages645e3d4fe4b003b879fda56a OriginalSuprit JainNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Nervous SystemDocument26 pagesDisorders of The Nervous Systemshishiminaj100% (1)
- Faal PenglihatanDocument87 pagesFaal PenglihatanObet Agung 天No ratings yet
- Integumentary System: The Body'S External ProtectionDocument38 pagesIntegumentary System: The Body'S External ProtectionRai BalisacanNo ratings yet
- Biology SS3 Summer School E-NotesDocument27 pagesBiology SS3 Summer School E-Notespraiseforever90No ratings yet
- D) COORDINATIONDocument10 pagesD) COORDINATIONamarashah182No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentSamuel ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Responding To The Environment CH 25.2 7thDocument19 pagesResponding To The Environment CH 25.2 7ththegedusNo ratings yet
- Y3 Bio Notes Unit 2Document38 pagesY3 Bio Notes Unit 2SANJAY SHIVANINo ratings yet
- 07c Investigating The SkinDocument8 pages07c Investigating The Skinapi-275510930No ratings yet
- Organs Systems of The BodyDocument12 pagesOrgans Systems of The BodyJan Michael SalomonNo ratings yet
- Tissues Animal 2Document40 pagesTissues Animal 2trisha quitanNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument69 pagesAnatomynawinnawmu1026No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument296 pagesNervous SystemDr. Serin KuriakoseNo ratings yet
- Anatomic Structures: St. Paul University PhilippinesDocument6 pagesAnatomic Structures: St. Paul University PhilippinesRobin TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Special Senses Unit IV For StdsDocument52 pagesSpecial Senses Unit IV For StdsanwarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Eye: Dr. Y. Lokesh KumarDocument37 pagesAnatomy of Eye: Dr. Y. Lokesh KumarLokesh KumarNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary SystemDocument19 pagesThe Integumentary SystemInigo Galima SusanNo ratings yet
- Ln.11 Skin-The Jack of All Trades - NotesDocument3 pagesLn.11 Skin-The Jack of All Trades - Noteshiteshseema2008No ratings yet
- Sense Organ: Diyah Candra AnitaDocument35 pagesSense Organ: Diyah Candra AnitaNamulondo Mwajib Bogere100% (1)
- General Biology 2Document5 pagesGeneral Biology 2Kim Ashley Padernal MandronNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - SenseDocument8 pagesChapter 10 - Sensebussniesm05No ratings yet
- Sensory Systems Kd12Document32 pagesSensory Systems Kd12Diana Quimpan CilloNo ratings yet
- Gs Grade 4Document119 pagesGs Grade 4Mekonnen AssefaNo ratings yet
- 3-17 Nervous Handout p08-12Document5 pages3-17 Nervous Handout p08-12eddrobinson rumakiekNo ratings yet
- Eyes Health AssessmenttDocument34 pagesEyes Health AssessmenttMhiaBuenafeNo ratings yet
- Sensory OrgansDocument11 pagesSensory OrgansCurex QANo ratings yet
- Better Sleep: How to Fall Asleep Faster, Overcome Insomnia, and Feel EnergizedFrom EverandBetter Sleep: How to Fall Asleep Faster, Overcome Insomnia, and Feel EnergizedNo ratings yet
- Form 4 EndoftermintegratedsciencedecemberDocument14 pagesForm 4 EndoftermintegratedsciencedecemberCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Types of Asexual ReproductionDocument3 pagesTypes of Asexual ReproductionCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Form 5 EndoftermintegratedsciencedecemberDocument16 pagesForm 5 EndoftermintegratedsciencedecemberCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Form 1 Integrated Science MidtermDocument9 pagesForm 1 Integrated Science MidtermCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Unit 1 MarkschemeudatedDocument21 pagesUnit 1 MarkschemeudatedCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Form 5 EndoftermbiologyexamdecemberDocument16 pagesForm 5 EndoftermbiologyexamdecemberCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Employment Questionnaire CompletedDocument2 pagesEmployment Questionnaire CompletedCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- End of Term Exam: Integrated Science Form 1: Name: - TeacherDocument7 pagesEnd of Term Exam: Integrated Science Form 1: Name: - TeacherCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Test: Sawaiwittayakarn School Grade 7: M 1/1, 1/2, 1/3 and 1/4 ClassDocument6 pagesTest: Sawaiwittayakarn School Grade 7: M 1/1, 1/2, 1/3 and 1/4 ClassCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Form 5 EndoftermhumanandsocialbiodecemberDocument13 pagesForm 5 EndoftermhumanandsocialbiodecemberCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam For Form 3 CompleteDocument8 pagesMidterm Exam For Form 3 CompleteCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- May Pen High School End of Term Exam: Name: - TeacherDocument11 pagesMay Pen High School End of Term Exam: Name: - TeacherCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Test: Sawaiwittayakarn School Grade 8: 2/1, 2/2, 2/3 and 2/4 Class: - Name: - Total - /38Document8 pagesTest: Sawaiwittayakarn School Grade 8: 2/1, 2/2, 2/3 and 2/4 Class: - Name: - Total - /38CHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- 0a Final Exam Timetable Summer Session 1 2021Document9 pages0a Final Exam Timetable Summer Session 1 2021CHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Form 5 INTESCIENCE COMPLETEDocument9 pagesMidterm Exam Form 5 INTESCIENCE COMPLETECHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- 0 FINAL Assessment EXAMTIMETABLE MODULE 5, 2021.2Document1 page0 FINAL Assessment EXAMTIMETABLE MODULE 5, 2021.2CHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Join NCU Church in Building A Temple For God: June 17, 2021Document2 pagesJoin NCU Church in Building A Temple For God: June 17, 2021CHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Biology Markscheme2021updatedDocument18 pagesBiology Markscheme2021updatedCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Form 4 INTESCI COMPLETEDocument10 pagesMidterm Exam Form 4 INTESCI COMPLETECHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Form 5 HSB COMPLETEDocument11 pagesMidterm Exam Form 5 HSB COMPLETECHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- CXC Biology TopicsDocument1 pageCXC Biology TopicsCHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet