Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 6 Past N Prent Perfect
Chapter 6 Past N Prent Perfect
Uploaded by
Adeeb Hanif0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views8 pagesThe document summarizes the simple past and present perfect tenses in English. It provides examples of their positive, negative, and interrogative forms. It also notes some key points about each tense, such as how the simple past is used to refer to completed past events, while the present perfect can refer to events that started in the past but are still relevant to the present. It gives examples of time indicators that require the present perfect tense, such as prepositions of duration or adverbs denoting a timespan from the past to present.
Original Description:
PAST N PRESENT PERFECT
Original Title
Chapter 6 past n prent perfect
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the simple past and present perfect tenses in English. It provides examples of their positive, negative, and interrogative forms. It also notes some key points about each tense, such as how the simple past is used to refer to completed past events, while the present perfect can refer to events that started in the past but are still relevant to the present. It gives examples of time indicators that require the present perfect tense, such as prepositions of duration or adverbs denoting a timespan from the past to present.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views8 pagesChapter 6 Past N Prent Perfect
Chapter 6 Past N Prent Perfect
Uploaded by
Adeeb HanifThe document summarizes the simple past and present perfect tenses in English. It provides examples of their positive, negative, and interrogative forms. It also notes some key points about each tense, such as how the simple past is used to refer to completed past events, while the present perfect can refer to events that started in the past but are still relevant to the present. It gives examples of time indicators that require the present perfect tense, such as prepositions of duration or adverbs denoting a timespan from the past to present.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 8
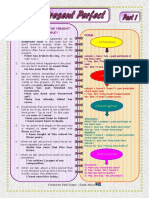
Chapter 6
I Have Been There
What’s on this chapter?
Information
Note for to share Positive
Present Form
Perfect Tense
Simple Past Tense
and
Present Perfect Tense
Note for Negative
Simple Past Form
Tense
Interrogative
Form
Information to share
• Simple past tense may refer to:
– one event complete in the past.
– repeated events completed in the past and no longer
happening.
– duration of an event completed in the past.
• Present perfect tense may refer to:
– events that started and finished in the past but bring
meaning to the present.
Positive Form
Subject Verb 2/to be Others
Past tense I bought the blue dress.
He was at the hall.
Subject Have verb 3/been Others
Present perfect Has verb 3/been
tense I have just finished.
He has been there.
Negative Form
Subject Didn’t verb 1 Others
Wasn’t/Weren’t
Past tense I didn’t go to the orchestra.
He wasn’t at the hall.
Subject Haven’t verb 3/been Others
Present perfect Hasn’t verb 3/been
tense I haven’t bought the blue dress.
He hasn’t been there.
Interrogative Form
Did Subject Verb 1 Others
Was/Were
Past tense Did you cook the food?
Was he at the hall?
Have Subject Verb 3 Others
Has
Present perfect Have you visited your friend?
tense
Has she been in Bali?
Note for Simple Past Tense
• Simple past tense
The regular ending for the past simple, for all
persons, is –ed.
Only the verb to be has two separate forms for the
past: was for the singular, were for the plural.
There are many verbs ending in –t such as learnt,
burnt, spilt, dwelt, etc.
The word ago requires the use of past tense, even if
the indicated time came almost up to the present,
e.g. They left one minute ago.
Note for Present Perfect Tense
• Present perfect tense
There are some indicators of time marking a past to
present event.
Preposition indicating duration, e.g. during, in,
over, since, for
Adverbials meaning past to present time, e.g. so
far, up to now, until now, up to the present
You might also like
- TOEIC Grammar Guide: 22 Grammar Rules You Must Know To Pass The TOEIC Exam!From EverandTOEIC Grammar Guide: 22 Grammar Rules You Must Know To Pass The TOEIC Exam!Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (15)
- The Combat Systema Guidebook by Kevin SecoursDocument141 pagesThe Combat Systema Guidebook by Kevin SecoursRussell Lawrence Benford91% (47)
- Wyrd Is Bond (Gang)Document100 pagesWyrd Is Bond (Gang)Gon_1313100% (3)
- Hi Teacher, Hello Guys, Good Evening Every Body. My Mane Is JPSR Welcome To The Class Today I Will Talk About Present Perfect Let's StartDocument2 pagesHi Teacher, Hello Guys, Good Evening Every Body. My Mane Is JPSR Welcome To The Class Today I Will Talk About Present Perfect Let's StartJP SALDAÑANo ratings yet
- Effective English For Teachers: 3 Simple Present and Present ContinuousDocument10 pagesEffective English For Teachers: 3 Simple Present and Present ContinuousRevana Difa FawzyNo ratings yet
- Effective English For Teachers: 3 Simple Present and Present ContinuousDocument10 pagesEffective English For Teachers: 3 Simple Present and Present ContinuousRevana Difa FawzyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Past Tense Dan Present PerfectDocument12 pagesChapter 7 Past Tense Dan Present PerfectDewi Miranda SaputriNo ratings yet
- Verbs, Tense, Aspect, and Mood: By: Acmad Yani, S.SDocument19 pagesVerbs, Tense, Aspect, and Mood: By: Acmad Yani, S.SametgembulNo ratings yet
- The Past Perfect Simple TenseDocument25 pagesThe Past Perfect Simple TensedragbliousNo ratings yet
- Reglas - Present PerfectDocument1 pageReglas - Present Perfectkeyko vera ruizNo ratings yet
- Actions That Occurred in The Past That Refer To The Time They Occurred and The Time They EndedDocument10 pagesActions That Occurred in The Past That Refer To The Time They Occurred and The Time They EndedBerwidita family'sNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple Grammar Guide Part 1 of 3 StudentsDocument4 pagesPresent Perfect Simple Grammar Guide Part 1 of 3 StudentsDIEGO ALEJANDRO HERNANDEZ LOPEZNo ratings yet
- Non-Finite Forms of The English VerbDocument33 pagesNon-Finite Forms of The English VerbfifiNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple - Grammar Guide Part 1 of 3Document5 pagesPresent Perfect Simple - Grammar Guide Part 1 of 3Igor NircaNo ratings yet
- When Do We Use The Present Perfect Simple? Form:: + AffirmativeDocument9 pagesWhen Do We Use The Present Perfect Simple? Form:: + AffirmativeJairo LuisNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple Grammar Guide Part 1 of 3 Grammar Guides - 1235Document5 pagesPresent Perfect Simple Grammar Guide Part 1 of 3 Grammar Guides - 1235tomaNo ratings yet
- 4TH MeetingDocument24 pages4TH MeetingIqbalsyahNo ratings yet
- Verbs Gerunds and Infinitive FinishDocument10 pagesVerbs Gerunds and Infinitive FinishYoga NurzamanNo ratings yet
- MEG 3 SummaryDocument13 pagesMEG 3 Summarytonettesmile2695No ratings yet
- FELn TenseDocument8 pagesFELn TenseMohammedselam MdNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document23 pagesPresentation 2Renaldy MamarasiNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Past Perfect and Past ParticipleDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Past Perfect and Past ParticipleVu VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Intermediate English Level: Julian Andres UniDocument9 pagesPre-Intermediate English Level: Julian Andres UniLUIS GERMAN GUARNIZO MEDINANo ratings yet
- Simple Past X Pres PerfectDocument28 pagesSimple Past X Pres PerfectAdriano Santos100% (1)
- Lectura Unidad 1Document15 pagesLectura Unidad 1brandon jonesNo ratings yet
- Pres Perf Simple Vs Past SimpleDocument1 pagePres Perf Simple Vs Past SimpleDANIELA CHIRITANo ratings yet
- Sub-Categorization of Verbs: Grammar ReviewDocument25 pagesSub-Categorization of Verbs: Grammar ReviewdecvikooNo ratings yet
- Review of Grammar RulesDocument9 pagesReview of Grammar RulesBethNo ratings yet
- 23 Toefl Grammar RulesDocument45 pages23 Toefl Grammar Rulessakurakinomoto744544No ratings yet
- Present Perfect Progressive TenseDocument15 pagesPresent Perfect Progressive TenseJustine Jhon AdolfoNo ratings yet
- Booklet B2Document8 pagesBooklet B2ninacalle0782No ratings yet
- Week 1 English Iii Session 2 Unit 2: Express YourselfDocument48 pagesWeek 1 English Iii Session 2 Unit 2: Express YourselfCarlosCristobalNo ratings yet
- CET Reviewer B5Document12 pagesCET Reviewer B5Morielle UrsulumNo ratings yet
- MODULE For Grammar and VocabularyDocument36 pagesMODULE For Grammar and Vocabularycharizetante219No ratings yet
- Book 2 Grammar Unit 10 Present PerfectDocument18 pagesBook 2 Grammar Unit 10 Present PerfectLamis KhalidNo ratings yet
- Functional Grammar: Patterns and Usage: VoicesDocument29 pagesFunctional Grammar: Patterns and Usage: VoicesAarishti SinghNo ratings yet
- Black and White Pastel Scrapbook Company Profile PresentationDocument7 pagesBlack and White Pastel Scrapbook Company Profile PresentationPika CaniaNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Vs Present Perfect Worksheet Soriano Delgado AdrianDocument6 pagesSimple Past Vs Present Perfect Worksheet Soriano Delgado AdrianAdrian Soriano DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 2 Verbs PDFDocument8 pagesPertemuan 2 Verbs PDFriko cmenoxNo ratings yet
- English ReportDocument96 pagesEnglish Reportluvofcherri02No ratings yet
- VerbDocument20 pagesVerbJelena MitrovicNo ratings yet
- Basic Grammar 3Document12 pagesBasic Grammar 3Jeliza EscalañaNo ratings yet
- Simple Past vs. Present PerfectDocument16 pagesSimple Past vs. Present PerfectAnnisa Nurul HanifahNo ratings yet
- ENGL111: ExamplesDocument6 pagesENGL111: ExamplesMarian TorresNo ratings yet
- Clase 9 - English 2Document15 pagesClase 9 - English 2casuda1818No ratings yet
- How Do We Use This TenseDocument8 pagesHow Do We Use This TenseFlorentina DespoiuNo ratings yet
- Present ContinuousDocument7 pagesPresent ContinuousGuadalupe AcostaNo ratings yet
- Module - 2 - Past Progressive-Simple Past ModificadoDocument8 pagesModule - 2 - Past Progressive-Simple Past ModificadoJohana LaraNo ratings yet
- Review of English Tenses PDF - VCDocument30 pagesReview of English Tenses PDF - VCHamzaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 - Simple Past and Present PerfectDocument19 pagesUNIT 2 - Simple Past and Present PerfectOliver TorresNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan Grade 7Document5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan Grade 7unpopularbut happyNo ratings yet
- DLI Grammer PamDocument27 pagesDLI Grammer PamMohammed Abdulkareem JwabrehNo ratings yet
- Grammar Reference: El Past Simple: Afirmativa, Negativa I InterrogativaDocument1 pageGrammar Reference: El Past Simple: Afirmativa, Negativa I InterrogativaMontseNo ratings yet
- We Use of Verbs To Refer To, Actions or Situations in The Present in The Past and in The FutureDocument78 pagesWe Use of Verbs To Refer To, Actions or Situations in The Present in The Past and in The FutureHaryatmo TriNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument5 pagesEnglishapi-354037574No ratings yet
- 9 Present Perfect TenseDocument6 pages9 Present Perfect Tensekha irunNo ratings yet
- Q2 Week 3 Perfect TensesDocument43 pagesQ2 Week 3 Perfect TensesCathy Mae Castillo RiveraNo ratings yet
- Tenses of The VerbDocument22 pagesTenses of The VerbLouiseNo ratings yet
- Tenses of The VerbDocument22 pagesTenses of The VerbLouiseNo ratings yet
- Present Simple 4iv11Document5 pagesPresent Simple 4iv11García Peña SebastianNo ratings yet
- InglesDocument13 pagesInglesTramites Transito YopalNo ratings yet
- The Passive - Present PassiveDocument6 pagesThe Passive - Present PassiveAnduel SelamajNo ratings yet
- Learn Sanskrit The Natural WayDocument144 pagesLearn Sanskrit The Natural WayLinga Reddy C100% (1)
- Mangala Eng BiodataDocument14 pagesMangala Eng BiodataS. Mangala Satyan100% (1)
- 1era Practica de Inglès 2Document5 pages1era Practica de Inglès 2Yeison SosaNo ratings yet
- Rekod Bacaan Bahasa Tamil 2023Document36 pagesRekod Bacaan Bahasa Tamil 2023g-54321079No ratings yet
- Adrados-Graeca in H.Document8 pagesAdrados-Graeca in H.luciano cordoNo ratings yet
- Indias Gift To The WorldDocument62 pagesIndias Gift To The Worldsantoshpinge3417No ratings yet
- Critique No.3 Language Use in The UniversityDocument1 pageCritique No.3 Language Use in The UniversityElia Kim FababeirNo ratings yet
- Theories of Language and GenderDocument3 pagesTheories of Language and GenderRisma Dwi AryantiNo ratings yet
- Simple Past TenseDocument26 pagesSimple Past TenseNadhira SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Varna and Jati Andre Beteille: Varna by Jati Indicates Much More Than A Simple Linguistic Shift. ItDocument13 pagesVarna and Jati Andre Beteille: Varna by Jati Indicates Much More Than A Simple Linguistic Shift. ItDEEPAK VIRMANINo ratings yet
- Name: Claivan Jade Rejuso Jabajab Year/Section/Course: 2 - A BEEDDocument2 pagesName: Claivan Jade Rejuso Jabajab Year/Section/Course: 2 - A BEEDJabajab Klayban jaydNo ratings yet
- Laos and Ethnic Minority CulturesDocument263 pagesLaos and Ethnic Minority CulturesBenjamin MeltzerNo ratings yet
- Speaking Cefr EVALUATION FORMSDocument8 pagesSpeaking Cefr EVALUATION FORMSAzeif FiezaNo ratings yet
- Björnskallar Och Magiska Bilder: - Skogsfinsk Religion Och Folktro I Materiella KällorDocument35 pagesBjörnskallar Och Magiska Bilder: - Skogsfinsk Religion Och Folktro I Materiella KällorJannes EngqvistNo ratings yet
- Manobo and MāoriDocument17 pagesManobo and Māorikervin jayloNo ratings yet
- Rio Azul An Ancient Maya City by Richard E. W. AdamsDocument72 pagesRio Azul An Ancient Maya City by Richard E. W. AdamsLuceroNo ratings yet
- The Disease Terminology in The Medical Codex of Hilandar N: Facta UniversitatisDocument12 pagesThe Disease Terminology in The Medical Codex of Hilandar N: Facta UniversitatisMarinazdrNo ratings yet
- The History of Serbia (PDFDrive)Document439 pagesThe History of Serbia (PDFDrive)marijana993No ratings yet
- 314477-FLW Vaesen Draug v1Document5 pages314477-FLW Vaesen Draug v1bilou hertNo ratings yet
- Ernst Steinkellner Agents and Actions in Classical Tibetan ArbeitskreisDocument128 pagesErnst Steinkellner Agents and Actions in Classical Tibetan ArbeitskreisTsz Shan HuiNo ratings yet
- KoszaryczDocument301 pagesKoszaryczПавлюкБогданNo ratings yet
- Básico2-Unit3 (Solo para Malena)Document116 pagesBásico2-Unit3 (Solo para Malena)Jamilet DianaNo ratings yet
- Is Maglera Sotho - Google SearchDocument1 pageIs Maglera Sotho - Google Searchmaqalikathabiso5No ratings yet
- Cced 2000Document183 pagesCced 2000Nazrul OzellNo ratings yet
- School Form 1 (SF 1) School RegisterDocument3 pagesSchool Form 1 (SF 1) School RegisterDonavie Gamora QuinonesNo ratings yet
- Hand Out No. 6 (23 of January, 2019) : Future Indicative Active-ContinuedDocument2 pagesHand Out No. 6 (23 of January, 2019) : Future Indicative Active-ContinuedZechariah QamarNo ratings yet
- The Last Leaf Reading Comprehension: Who Said It ?Document3 pagesThe Last Leaf Reading Comprehension: Who Said It ?Yusmely OllarvesNo ratings yet
- Kalilang ProgramDocument1 pageKalilang ProgramAisah SultanNo ratings yet