Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lipid Catabolism: Overview of Lipid Metabolism
Lipid Catabolism: Overview of Lipid Metabolism
Uploaded by
ninafatima allamCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Introduction BCHN 222 2022Document39 pagesIntroduction BCHN 222 2022Francisca ManyisaNo ratings yet
- LIPID METABOLISM Notes PDFDocument8 pagesLIPID METABOLISM Notes PDFToga BrandonNo ratings yet
- RX25 LipidmetDocument23 pagesRX25 LipidmetIlla AdengNo ratings yet
- Lipid Catabolism SummaryDocument9 pagesLipid Catabolism SummaryTaufiq HadiNo ratings yet
- ATP Production Through Lipid CatabolismDocument1 pageATP Production Through Lipid CatabolismZaivie VillanobosNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity#4Document4 pagesLearning Activity#4Angela ErandioNo ratings yet
- Cho L4 (Tca) 2020-2021Document23 pagesCho L4 (Tca) 2020-2021Sara AljadaniNo ratings yet
- Quiz: Calculate The Total ATP Produced From The Complete Metabolism of Stearic AcidDocument1 pageQuiz: Calculate The Total ATP Produced From The Complete Metabolism of Stearic Acidanita sukariniNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion Through Redox Reactions, A Cycle With Eight Renewable Reactants, and RegulationDocument29 pagesEnergy Conversion Through Redox Reactions, A Cycle With Eight Renewable Reactants, and RegulationJorge PalominoNo ratings yet
- Cho L4 (Tca) 2020-2021Document25 pagesCho L4 (Tca) 2020-2021RNo ratings yet
- Tca CycleDocument5 pagesTca CycleMituSamadderNo ratings yet
- Beta Oxidation of Fatty AcidsDocument4 pagesBeta Oxidation of Fatty AcidsAmisha ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- L4 FA OxidationDocument7 pagesL4 FA OxidationasakingofhNo ratings yet
- TCA CycleDocument47 pagesTCA CycleMita SeptianiNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid CycleDocument30 pagesCitric Acid CycleUsama AzizNo ratings yet
- The Citric AcidDocument14 pagesThe Citric AcidZina CabreraNo ratings yet
- HW8 - Metabolism 1Document2 pagesHW8 - Metabolism 1Christopher GalivoNo ratings yet
- PHYSIOLOGY - MetabolismDocument8 pagesPHYSIOLOGY - MetabolismsydneykatelynnNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid Cycle and Its RegulationDocument7 pagesCitric Acid Cycle and Its RegulationAVINASH PvkNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Synthesis 2019Document26 pagesFatty Acid Synthesis 2019Yousef KhallafNo ratings yet
- KrebcycleDocument5 pagesKrebcycleYana PajoNo ratings yet
- MODULE 7 Lesson1 - General Biology IDocument32 pagesMODULE 7 Lesson1 - General Biology IAlvin PaboresNo ratings yet
- 7-Catabolism of LipidsDocument38 pages7-Catabolism of Lipidsamel elabassNo ratings yet
- Beta OxidationDocument10 pagesBeta OxidationAiane Gramatica100% (1)
- Citric Acid Cycle PDFDocument26 pagesCitric Acid Cycle PDFjairajNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis SummaryDocument4 pagesGlycolysis SummaryApple Jane SenadosNo ratings yet
- The Ri Arboxylic Cid (TCA) Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle) (Krebs Cycle)Document22 pagesThe Ri Arboxylic Cid (TCA) Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle) (Krebs Cycle)Kiya AlemuNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid MetabolismDocument6 pagesFatty Acid MetabolismsagarNo ratings yet
- Abhishek Jha - TCA Cycle - Inhibition & RegulationDocument32 pagesAbhishek Jha - TCA Cycle - Inhibition & RegulationRavi RajNo ratings yet
- How Cells Release Energy Part 2Document13 pagesHow Cells Release Energy Part 2Jiro SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid Cycle (Tca)Document8 pagesCitric Acid Cycle (Tca)atifzeaNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid Cycle: Central Metabolic Cycle and Its SignificanceDocument4 pagesCitric Acid Cycle: Central Metabolic Cycle and Its SignificanceBiochemistry DenNo ratings yet
- TCA Cycle and ETC 2015 E.C.Document47 pagesTCA Cycle and ETC 2015 E.C.Abdurehman KasimNo ratings yet
- BCH 2602 Ass2Document13 pagesBCH 2602 Ass2grimsdellaNo ratings yet
- TCA CycleDocument31 pagesTCA CycleTafzeela VengusNo ratings yet
- TCA III Summary - PPSXDocument7 pagesTCA III Summary - PPSXBio SciencesNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid Cycle or Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle or Krebs CycleDocument16 pagesCitric Acid Cycle or Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle or Krebs CycleMuhammad AmjadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Fatty Acid Catabolism: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesChapter 17 Fatty Acid Catabolism: Multiple Choice QuestionsSheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- TCA AssignmentDocument7 pagesTCA Assignmentradhika19053No ratings yet
- Biochemistry 20 Class Notes Saakaar 20 Batch For IIT JAM 2Document46 pagesBiochemistry 20 Class Notes Saakaar 20 Batch For IIT JAM 2Adeeti RaiNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration STUDY GUIDEDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration STUDY GUIDEJee MascardoNo ratings yet
- Ho10 Tca & EtsDocument26 pagesHo10 Tca & EtstresnowahyudienNo ratings yet
- Lec Notes Carbohydrate Metabolism Glycolysis Kreb Cycle ETCDocument12 pagesLec Notes Carbohydrate Metabolism Glycolysis Kreb Cycle ETCJonah Micah MangacoNo ratings yet
- Kreb CycleDocument6 pagesKreb Cycle211BT014 Jeev Sheen JosephNo ratings yet
- Kreb Cycle-2Document14 pagesKreb Cycle-2ayeshayaseen908No ratings yet
- Adenosine TriphosphateDocument3 pagesAdenosine TriphosphateEvan Charl MoraledaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 Fatty Acid MetabolismDocument65 pagesLecture 11 Fatty Acid MetabolismBiology BảoNo ratings yet
- Pyruvate, Krebs, ElectransDocument7 pagesPyruvate, Krebs, Electransfionadaguman2002No ratings yet
- Activation of Fatty Acids: Beta Oxidation Is The Process by WhichDocument5 pagesActivation of Fatty Acids: Beta Oxidation Is The Process by WhichAriel RezaNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantDocument32 pagesRespiration in Plantx2h9ptt6mrNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid CycleDocument33 pagesCitric Acid CycleMimi AlyssaNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid CycleDocument17 pagesCitric Acid CycleattyNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Synthesis 11.12.19Document18 pagesFatty Acid Synthesis 11.12.19Sanreet Randhawa100% (1)
- Lipid Metabolism 2023Document36 pagesLipid Metabolism 2023Moses MutsikwiNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid CycleDocument20 pagesCitric Acid CycleAastha SinhaNo ratings yet
- The Citric Acid CycleDocument5 pagesThe Citric Acid CycleCarlton GrantNo ratings yet
- 10 CacDocument26 pages10 Cacazyhuang77No ratings yet
- Citric Acid Cycle 1: C483 Spring 2013Document18 pagesCitric Acid Cycle 1: C483 Spring 2013Tazyinul Qoriah AlfauziahNo ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism PDFDocument6 pagesLipid Metabolism PDFCharmaine ShiellerNo ratings yet
- BIODocument3 pagesBIOJoycey TNo ratings yet
- What Makes Your Family Different and Similar To OtDocument1 pageWhat Makes Your Family Different and Similar To Otninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- Endurance It Includes Cardiovascular and Muscular or Stamina. This Component IsDocument3 pagesEndurance It Includes Cardiovascular and Muscular or Stamina. This Component Isninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- Reflection in Holy RosaryDocument1 pageReflection in Holy Rosaryninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- Global Health Initiative - 1Document14 pagesGlobal Health Initiative - 1ninafatima allam0% (1)
- Cerebrovasculara Ccident: Holy Angel University Angeles City College of NursingDocument124 pagesCerebrovasculara Ccident: Holy Angel University Angeles City College of Nursingninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- Rih - Acute Stroke Brain Ge Lightspeed VCT ProtocolDocument1 pageRih - Acute Stroke Brain Ge Lightspeed VCT Protocolninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- Proposal Covid 19Document3 pagesProposal Covid 19ninafatima allam0% (1)
- Bar TerminologiesDocument207 pagesBar Terminologiesninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 ReflectionDocument2 pagesCOVID 19 Reflectionninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- History of PiatDocument5 pagesHistory of Piatninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- Covid 19Document3 pagesCovid 19ninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY SYSTEMchartDocument1 pageRESPIRATORY SYSTEMchartninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- Formulating A Nursing Care Plan: S++aint Paul University PhilippinesDocument7 pagesFormulating A Nursing Care Plan: S++aint Paul University Philippinesninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- Lipid MetabolismDocument134 pagesLipid MetabolismEmmaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For The Dental Hygienists Guide To Nutritional Care 5th Edition by Stegeman DownloadDocument14 pagesTest Bank For The Dental Hygienists Guide To Nutritional Care 5th Edition by Stegeman Downloadwhitneycoxmrtsgiwdkx100% (24)
- CHAPTER I BASIC CONCEPT NUTRITION AND DIET THERAPY Questions01Document30 pagesCHAPTER I BASIC CONCEPT NUTRITION AND DIET THERAPY Questions01Jeeyan DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Steatorrhea: Section A2/ Group IvDocument43 pagesSteatorrhea: Section A2/ Group IvKristian Cada100% (4)
- Relationship Between Butyrylcholinesterase Activity and LipidDocument10 pagesRelationship Between Butyrylcholinesterase Activity and LipidIris Betzaida Molina PintorNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lecture ScheduleDocument1 pageBiochemistry Lecture ScheduleTheBoss 20No ratings yet
- Lipids Metabolism ReviewerDocument2 pagesLipids Metabolism RevieweroperanacireNo ratings yet
- LG - Lipid MetabolismDocument116 pagesLG - Lipid MetabolismRawa AyubNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption of Lipid 12Document36 pagesDigestion and Absorption of Lipid 12Pranjul MishraNo ratings yet
- Biologic Actions of Thyroid Hormones: Presented By:Yesha Ahmed Virk M-21011 Roll # (M-21011Tom-21015)Document15 pagesBiologic Actions of Thyroid Hormones: Presented By:Yesha Ahmed Virk M-21011 Roll # (M-21011Tom-21015)demonleolucifer3467No ratings yet
- LipidsDocument31 pagesLipidsJosephine AcioNo ratings yet
- ABX Pentra Triglycerides CPDocument4 pagesABX Pentra Triglycerides CPAstri AmaliaNo ratings yet
- BCM 202 Quality AssuranceDocument18 pagesBCM 202 Quality AssuranceTeeNo ratings yet
- Lipidss (Autosaved)Document21 pagesLipidss (Autosaved)ANo ratings yet
- Biological Chemistry (Medicine, 2 Course)Document7 pagesBiological Chemistry (Medicine, 2 Course)Joy JoyNo ratings yet
- 6.digetion of LipidsDocument23 pages6.digetion of LipidsMilkoo sabaNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Effects of 3,5-Diiodo-L-Thyronine Giammanco M Et AlDocument11 pagesMetabolic Effects of 3,5-Diiodo-L-Thyronine Giammanco M Et AlMarco GiammancoNo ratings yet
- Ch15 Metabolism of Dietary LipidsDocument37 pagesCh15 Metabolism of Dietary LipidsWahab KhaniNo ratings yet
- 1 Vstup Do Patologii DystrofiiDocument18 pages1 Vstup Do Patologii DystrofiiPraveen NayakNo ratings yet
- TM - S Q Bank 2nd Edition BiochemistryDocument29 pagesTM - S Q Bank 2nd Edition BiochemistryArthi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Understanding Normal and Clinical Nutrition PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Understanding Normal and Clinical Nutrition PDFjackie.holmes595100% (26)
- Advanced Nutrition PosterDocument2 pagesAdvanced Nutrition Posterapi-345265343No ratings yet
- Biochem 2Document5 pagesBiochem 2D MacNo ratings yet
- Nutrition 400: Introduction To Nutritional Biochemistry: Styblo@med - Unc.eduDocument5 pagesNutrition 400: Introduction To Nutritional Biochemistry: Styblo@med - Unc.edurennyabhaskaran_4560No ratings yet
- Abu Bakar Hashaam (3153) LipidsDocument5 pagesAbu Bakar Hashaam (3153) LipidsAsad RazaNo ratings yet
- Course Title:: Mrs A. Na'AllahDocument3 pagesCourse Title:: Mrs A. Na'AllahFajinmi IsraelNo ratings yet
- 7-Catabolism of LipidsDocument38 pages7-Catabolism of Lipidsamel elabassNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Physiology: Department of Physiology CHS, UniosunDocument59 pagesGastrointestinal Physiology: Department of Physiology CHS, UniosunTeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24)Document10 pagesChapter 24)Hazel LopezNo ratings yet
Lipid Catabolism: Overview of Lipid Metabolism
Lipid Catabolism: Overview of Lipid Metabolism
Uploaded by
ninafatima allamOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lipid Catabolism: Overview of Lipid Metabolism
Lipid Catabolism: Overview of Lipid Metabolism
Uploaded by
ninafatima allamCopyright:
Available Formats
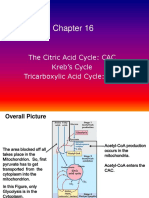
Lipid Catabolism
Overview of Lipid Metabolism:
The major aspects of lipid metabolism are involved with Fatty Acid Oxidation to
produce energy or the synthesis of lipids which is called Lipogenesis. Lipid
metabolism is closely connected to the metabolism of carbohydrates which may be
converted to fats. This can be seen in the diagram on the left. The metabolism of both
is upset by diabetes mellitus.
The first step in lipid metabolism is the hydrolysis of the lipid in the cytoplasm to
produce glycerol and fatty acids.
Since glycerol is a three carbon alcohol, it is metabolized quite readily into an
intermediate in glycolysis, dihydroxyacetone phosphate. The last reaction is readily
reversible if glycerol is needed for the synthesis of a lipid.
The hydroxyacetone, obtained from glycerol is metabolized into one of two possible
compounds. Dihydroxyacetone may be converted into pyruvic acid through
the glycolysis pathway to make energy.
In addition, the dihydroxyacetone may also be used in gluconeogenesis to make
glucose-6-phosphate for glucose to the blood or glycogen depending upon what is
required at that time.
Fatty acids are oxidized to acetyl CoA in the mitochondria using the fatty acid spiral.
The acetyl CoA is then ultimately converted into ATP, CO2, and H2O using the citric
acid cycle and the electron transport chain.
Fatty acids are synthesized from carbohydrates and occasionally from proteins.
Actually, the carbohydrates and proteins have first been catabolized into acetyl CoA.
Depending upon the energy requirements, the acetyl CoA enters the citric acid cycle
or is used to synthesize fatty acids in a process known as LIPOGENESIS.
Energy Production Fatty Acid Oxidation:
"Visible" ATP:
In the fatty acid spiral, there is only one reaction which directly uses ATP
and that is in the initiating step. So this is a loss of ATP and must be
subtracted later.
A large amount of energy is released and restored as ATP during the
oxidation of fatty acids. The ATP is formed from both the fatty acid spiral
and the citric acid cycle.
Connections to Electron Transport and ATP:
One turn of the fatty acid spiral produces ATP from the interaction of the
coenzymes FAD (step 1) and NAD+ (step 3) with the electron transport
chain. Total ATP per turn of the fatty acid spiral is:
Electron Transport Diagram - (e.t.c.)
Step 1 - FAD into e.t.c. = 2 ATP
Step 3 - NAD+ into e.t.c. = 3 ATP
Total ATP per turn of spiral = 5 ATP
In order to calculate total ATP from the fatty acid spiral, you must calculate
the number of turns that the spiral makes. Remember that the number of
turns is found by subtracting one from the number of acetyl CoA produced.
See the graphic on the left bottom.
Example with Palmitic Acid = 16 carbons = 8 acetyl groups
Number of turns of fatty acid spiral = 8-1 = 7 turns
ATP from fatty acid spiral = 7 turns and 5 per turn = 35 ATP.
This would be a good time to remember that single ATP that was needed to
get the fatty acid spiral started. Therefore subtract it now.
NET ATP from Fatty Acid Spiral = 35 - 1 = 34 ATP
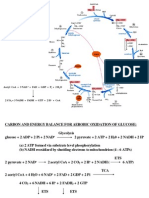
Review ATP Summary for Citric Acid Cycle:
The acetyl CoA produced from the fatty acid spiral enters the citric acid
cycle. When calculating ATP production, you have to show how many
acetyl CoA are produced from a given fatty acid as this controls how many
"turns" the citric acid cycle makes.
Starting with acetyl CoA, how many ATP are made using the citric acid
cycle? E.T.C = electron transport chain
Step ATP produced
7 1
+
Step 4 (NAD to E.T.C.) 3
+
Step 6 (NAD to E.T.C.) 3
+
Step10 (NAD to E.T.C.) 3
Step 8 (FAD to E.T.C.) 2
NET 12 ATP
ATP Summary for Palmitic Acid - Complete Metabolism:
The phrase "complete metabolism" means do reactions until you
end up with carbon dioxide and water. This also means to use
fatty acid spiral, citric acid cycle, and electron transport as
needed.
Starting with palmitic acid (16 carbons) how many ATP are
made using fatty acid spiral? This is a review of the above
panel E.T.C = electron transport chain
ATP (used -) (produced
Step
+)
Step 1 (FAD to E.T.C.) +2
+
Step 4 (NAD to E.T.C.) +3
Total ATP +5
7 turns 7 x 5 = 35
initial step -1
NET 34 ATP
The fatty acid spiral ends with the production of 8 acetyl CoA
from the 16 carbon palmitic acid.
Starting with one acetyl CoA, how many ATP are made
using the citric acid cycle? Above panel gave the answer of 12
ATP per acetyl CoA.
E.T.C = electron transport chain
Step ATP produced
One acetyl CoA per turn
+12 ATP
C.A.C.
8 Acetyl CoA = 8 turns
8 x 12 = 96 ATP
C.A.C.
Fatty Acid Spiral 34 ATP
GRAND TOTAL 130 ATP
You might also like
- Introduction BCHN 222 2022Document39 pagesIntroduction BCHN 222 2022Francisca ManyisaNo ratings yet
- LIPID METABOLISM Notes PDFDocument8 pagesLIPID METABOLISM Notes PDFToga BrandonNo ratings yet
- RX25 LipidmetDocument23 pagesRX25 LipidmetIlla AdengNo ratings yet
- Lipid Catabolism SummaryDocument9 pagesLipid Catabolism SummaryTaufiq HadiNo ratings yet
- ATP Production Through Lipid CatabolismDocument1 pageATP Production Through Lipid CatabolismZaivie VillanobosNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity#4Document4 pagesLearning Activity#4Angela ErandioNo ratings yet
- Cho L4 (Tca) 2020-2021Document23 pagesCho L4 (Tca) 2020-2021Sara AljadaniNo ratings yet
- Quiz: Calculate The Total ATP Produced From The Complete Metabolism of Stearic AcidDocument1 pageQuiz: Calculate The Total ATP Produced From The Complete Metabolism of Stearic Acidanita sukariniNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion Through Redox Reactions, A Cycle With Eight Renewable Reactants, and RegulationDocument29 pagesEnergy Conversion Through Redox Reactions, A Cycle With Eight Renewable Reactants, and RegulationJorge PalominoNo ratings yet
- Cho L4 (Tca) 2020-2021Document25 pagesCho L4 (Tca) 2020-2021RNo ratings yet
- Tca CycleDocument5 pagesTca CycleMituSamadderNo ratings yet
- Beta Oxidation of Fatty AcidsDocument4 pagesBeta Oxidation of Fatty AcidsAmisha ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- L4 FA OxidationDocument7 pagesL4 FA OxidationasakingofhNo ratings yet
- TCA CycleDocument47 pagesTCA CycleMita SeptianiNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid CycleDocument30 pagesCitric Acid CycleUsama AzizNo ratings yet
- The Citric AcidDocument14 pagesThe Citric AcidZina CabreraNo ratings yet
- HW8 - Metabolism 1Document2 pagesHW8 - Metabolism 1Christopher GalivoNo ratings yet
- PHYSIOLOGY - MetabolismDocument8 pagesPHYSIOLOGY - MetabolismsydneykatelynnNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid Cycle and Its RegulationDocument7 pagesCitric Acid Cycle and Its RegulationAVINASH PvkNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Synthesis 2019Document26 pagesFatty Acid Synthesis 2019Yousef KhallafNo ratings yet
- KrebcycleDocument5 pagesKrebcycleYana PajoNo ratings yet
- MODULE 7 Lesson1 - General Biology IDocument32 pagesMODULE 7 Lesson1 - General Biology IAlvin PaboresNo ratings yet
- 7-Catabolism of LipidsDocument38 pages7-Catabolism of Lipidsamel elabassNo ratings yet
- Beta OxidationDocument10 pagesBeta OxidationAiane Gramatica100% (1)
- Citric Acid Cycle PDFDocument26 pagesCitric Acid Cycle PDFjairajNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis SummaryDocument4 pagesGlycolysis SummaryApple Jane SenadosNo ratings yet
- The Ri Arboxylic Cid (TCA) Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle) (Krebs Cycle)Document22 pagesThe Ri Arboxylic Cid (TCA) Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle) (Krebs Cycle)Kiya AlemuNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid MetabolismDocument6 pagesFatty Acid MetabolismsagarNo ratings yet
- Abhishek Jha - TCA Cycle - Inhibition & RegulationDocument32 pagesAbhishek Jha - TCA Cycle - Inhibition & RegulationRavi RajNo ratings yet
- How Cells Release Energy Part 2Document13 pagesHow Cells Release Energy Part 2Jiro SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid Cycle (Tca)Document8 pagesCitric Acid Cycle (Tca)atifzeaNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid Cycle: Central Metabolic Cycle and Its SignificanceDocument4 pagesCitric Acid Cycle: Central Metabolic Cycle and Its SignificanceBiochemistry DenNo ratings yet
- TCA Cycle and ETC 2015 E.C.Document47 pagesTCA Cycle and ETC 2015 E.C.Abdurehman KasimNo ratings yet
- BCH 2602 Ass2Document13 pagesBCH 2602 Ass2grimsdellaNo ratings yet
- TCA CycleDocument31 pagesTCA CycleTafzeela VengusNo ratings yet
- TCA III Summary - PPSXDocument7 pagesTCA III Summary - PPSXBio SciencesNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid Cycle or Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle or Krebs CycleDocument16 pagesCitric Acid Cycle or Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle or Krebs CycleMuhammad AmjadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Fatty Acid Catabolism: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesChapter 17 Fatty Acid Catabolism: Multiple Choice QuestionsSheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- TCA AssignmentDocument7 pagesTCA Assignmentradhika19053No ratings yet
- Biochemistry 20 Class Notes Saakaar 20 Batch For IIT JAM 2Document46 pagesBiochemistry 20 Class Notes Saakaar 20 Batch For IIT JAM 2Adeeti RaiNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration STUDY GUIDEDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration STUDY GUIDEJee MascardoNo ratings yet
- Ho10 Tca & EtsDocument26 pagesHo10 Tca & EtstresnowahyudienNo ratings yet
- Lec Notes Carbohydrate Metabolism Glycolysis Kreb Cycle ETCDocument12 pagesLec Notes Carbohydrate Metabolism Glycolysis Kreb Cycle ETCJonah Micah MangacoNo ratings yet
- Kreb CycleDocument6 pagesKreb Cycle211BT014 Jeev Sheen JosephNo ratings yet
- Kreb Cycle-2Document14 pagesKreb Cycle-2ayeshayaseen908No ratings yet
- Adenosine TriphosphateDocument3 pagesAdenosine TriphosphateEvan Charl MoraledaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 Fatty Acid MetabolismDocument65 pagesLecture 11 Fatty Acid MetabolismBiology BảoNo ratings yet
- Pyruvate, Krebs, ElectransDocument7 pagesPyruvate, Krebs, Electransfionadaguman2002No ratings yet
- Activation of Fatty Acids: Beta Oxidation Is The Process by WhichDocument5 pagesActivation of Fatty Acids: Beta Oxidation Is The Process by WhichAriel RezaNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantDocument32 pagesRespiration in Plantx2h9ptt6mrNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid CycleDocument33 pagesCitric Acid CycleMimi AlyssaNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid CycleDocument17 pagesCitric Acid CycleattyNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Synthesis 11.12.19Document18 pagesFatty Acid Synthesis 11.12.19Sanreet Randhawa100% (1)
- Lipid Metabolism 2023Document36 pagesLipid Metabolism 2023Moses MutsikwiNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid CycleDocument20 pagesCitric Acid CycleAastha SinhaNo ratings yet
- The Citric Acid CycleDocument5 pagesThe Citric Acid CycleCarlton GrantNo ratings yet
- 10 CacDocument26 pages10 Cacazyhuang77No ratings yet
- Citric Acid Cycle 1: C483 Spring 2013Document18 pagesCitric Acid Cycle 1: C483 Spring 2013Tazyinul Qoriah AlfauziahNo ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism PDFDocument6 pagesLipid Metabolism PDFCharmaine ShiellerNo ratings yet
- BIODocument3 pagesBIOJoycey TNo ratings yet
- What Makes Your Family Different and Similar To OtDocument1 pageWhat Makes Your Family Different and Similar To Otninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- Endurance It Includes Cardiovascular and Muscular or Stamina. This Component IsDocument3 pagesEndurance It Includes Cardiovascular and Muscular or Stamina. This Component Isninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- Reflection in Holy RosaryDocument1 pageReflection in Holy Rosaryninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- Global Health Initiative - 1Document14 pagesGlobal Health Initiative - 1ninafatima allam0% (1)
- Cerebrovasculara Ccident: Holy Angel University Angeles City College of NursingDocument124 pagesCerebrovasculara Ccident: Holy Angel University Angeles City College of Nursingninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- Rih - Acute Stroke Brain Ge Lightspeed VCT ProtocolDocument1 pageRih - Acute Stroke Brain Ge Lightspeed VCT Protocolninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- Proposal Covid 19Document3 pagesProposal Covid 19ninafatima allam0% (1)
- Bar TerminologiesDocument207 pagesBar Terminologiesninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 ReflectionDocument2 pagesCOVID 19 Reflectionninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- History of PiatDocument5 pagesHistory of Piatninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- Covid 19Document3 pagesCovid 19ninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY SYSTEMchartDocument1 pageRESPIRATORY SYSTEMchartninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- Formulating A Nursing Care Plan: S++aint Paul University PhilippinesDocument7 pagesFormulating A Nursing Care Plan: S++aint Paul University Philippinesninafatima allamNo ratings yet
- Lipid MetabolismDocument134 pagesLipid MetabolismEmmaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For The Dental Hygienists Guide To Nutritional Care 5th Edition by Stegeman DownloadDocument14 pagesTest Bank For The Dental Hygienists Guide To Nutritional Care 5th Edition by Stegeman Downloadwhitneycoxmrtsgiwdkx100% (24)
- CHAPTER I BASIC CONCEPT NUTRITION AND DIET THERAPY Questions01Document30 pagesCHAPTER I BASIC CONCEPT NUTRITION AND DIET THERAPY Questions01Jeeyan DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Steatorrhea: Section A2/ Group IvDocument43 pagesSteatorrhea: Section A2/ Group IvKristian Cada100% (4)
- Relationship Between Butyrylcholinesterase Activity and LipidDocument10 pagesRelationship Between Butyrylcholinesterase Activity and LipidIris Betzaida Molina PintorNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lecture ScheduleDocument1 pageBiochemistry Lecture ScheduleTheBoss 20No ratings yet
- Lipids Metabolism ReviewerDocument2 pagesLipids Metabolism RevieweroperanacireNo ratings yet
- LG - Lipid MetabolismDocument116 pagesLG - Lipid MetabolismRawa AyubNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption of Lipid 12Document36 pagesDigestion and Absorption of Lipid 12Pranjul MishraNo ratings yet
- Biologic Actions of Thyroid Hormones: Presented By:Yesha Ahmed Virk M-21011 Roll # (M-21011Tom-21015)Document15 pagesBiologic Actions of Thyroid Hormones: Presented By:Yesha Ahmed Virk M-21011 Roll # (M-21011Tom-21015)demonleolucifer3467No ratings yet
- LipidsDocument31 pagesLipidsJosephine AcioNo ratings yet
- ABX Pentra Triglycerides CPDocument4 pagesABX Pentra Triglycerides CPAstri AmaliaNo ratings yet
- BCM 202 Quality AssuranceDocument18 pagesBCM 202 Quality AssuranceTeeNo ratings yet
- Lipidss (Autosaved)Document21 pagesLipidss (Autosaved)ANo ratings yet
- Biological Chemistry (Medicine, 2 Course)Document7 pagesBiological Chemistry (Medicine, 2 Course)Joy JoyNo ratings yet
- 6.digetion of LipidsDocument23 pages6.digetion of LipidsMilkoo sabaNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Effects of 3,5-Diiodo-L-Thyronine Giammanco M Et AlDocument11 pagesMetabolic Effects of 3,5-Diiodo-L-Thyronine Giammanco M Et AlMarco GiammancoNo ratings yet
- Ch15 Metabolism of Dietary LipidsDocument37 pagesCh15 Metabolism of Dietary LipidsWahab KhaniNo ratings yet
- 1 Vstup Do Patologii DystrofiiDocument18 pages1 Vstup Do Patologii DystrofiiPraveen NayakNo ratings yet
- TM - S Q Bank 2nd Edition BiochemistryDocument29 pagesTM - S Q Bank 2nd Edition BiochemistryArthi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Understanding Normal and Clinical Nutrition PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Understanding Normal and Clinical Nutrition PDFjackie.holmes595100% (26)
- Advanced Nutrition PosterDocument2 pagesAdvanced Nutrition Posterapi-345265343No ratings yet
- Biochem 2Document5 pagesBiochem 2D MacNo ratings yet
- Nutrition 400: Introduction To Nutritional Biochemistry: Styblo@med - Unc.eduDocument5 pagesNutrition 400: Introduction To Nutritional Biochemistry: Styblo@med - Unc.edurennyabhaskaran_4560No ratings yet
- Abu Bakar Hashaam (3153) LipidsDocument5 pagesAbu Bakar Hashaam (3153) LipidsAsad RazaNo ratings yet
- Course Title:: Mrs A. Na'AllahDocument3 pagesCourse Title:: Mrs A. Na'AllahFajinmi IsraelNo ratings yet
- 7-Catabolism of LipidsDocument38 pages7-Catabolism of Lipidsamel elabassNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Physiology: Department of Physiology CHS, UniosunDocument59 pagesGastrointestinal Physiology: Department of Physiology CHS, UniosunTeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24)Document10 pagesChapter 24)Hazel LopezNo ratings yet