Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Short-Term Fluctuations in Output, Employment, Financial Conditions, and Prices That We Call The Business Cycle
The Short-Term Fluctuations in Output, Employment, Financial Conditions, and Prices That We Call The Business Cycle
Uploaded by
Clevin CkOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Short-Term Fluctuations in Output, Employment, Financial Conditions, and Prices That We Call The Business Cycle
The Short-Term Fluctuations in Output, Employment, Financial Conditions, and Prices That We Call The Business Cycle
Uploaded by
Clevin CkCopyright:
Available Formats
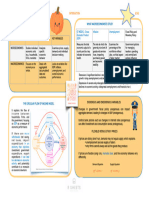
BUSINESS CYCLE
The short-term fluctuations in output, employment, financial conditions, and prices
that we call the business cycle.
Or all market economies show patterns of expansion and contraction known as
business cycles.
High prices, high unemployment (Nominal
GDP increases, real output falls)
INFLATION
(Expansion) (Contraction) Stable prices,
Stability Economic
growth ( Real
GDP grows)
RECESSION
Low prices, high unemployment (Real GDP
falls)
AS: total quantity of
ECONOMY ECONOMY
goods & services
nation’s businesses
willingly produce
and sell in a given
period
AD: Total
spending on
goods & services
by different
sectors of
economy (C+I+G+
INFLATION RECESSION
Xn)
Money Supply: Quantity of money in circulation in certain point of time. MS stable
Money (anything used as a commonly accepted medium of exchange) Prices Inflation/Recession
Export : receive (inflow
Gold+ gold n silver)
5000 Rs. Silver+
foreign Import: payment (
reserves ($) outflow gold n silver )
Paper currency, no intrinsic value
Business-cycle fluctuations in output, employment, and prices are often caused by
shifts in aggregate demand. These occur as consumers, businesses, or governments
change total spending relative to the economy’s productive capacity. When these
shifts in aggregate demand lead to sharp business downturns, the economy suffers
recessions or even depressions. A sharp upturn in economic activity can lead to
inflation.
Recession: Downturn of a business cycle is called a recession. A recession is a
recurring period of decline in total output, income, and employment, usually lasting
from 6 to 12 months and marked by contractions in many sectors of the economy. A
recession that is large in both scale and duration is called a depression. An alternative
definition sometimes used is that a recession occurs when real GDP has declined for
two consecutive calendar quarters.
Inflation:
The case of an economic expansion is just the opposite. Suppose that a war leads to a
sharp increase in government spending. As a result, the AD curve would shift to the
right, real output falls, unemployment, prices and inflation would rise.
You might also like
- CISSP October Slides - Learner Slides PDFDocument560 pagesCISSP October Slides - Learner Slides PDFVelicia Vera80% (5)
- MacroDocument6 pagesMacrocorvids75% (4)
- Case Study of The Change Management of British Airways After The Economic Crisis of 2008Document5 pagesCase Study of The Change Management of British Airways After The Economic Crisis of 2008Mirela-Elena Popa0% (1)
- AP.1901 Inventories.Document8 pagesAP.1901 Inventories.Erlinda Esguerra Guiang100% (9)
- 9th Annual Litigation Trends Survey Findings 2013 Fulbright ForumDocument60 pages9th Annual Litigation Trends Survey Findings 2013 Fulbright ForumchrispittmanNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Ganesh Kumar NDocument45 pagesMacroeconomics Ganesh Kumar NPanchami Padmasana Sarangi PGP 2022-24 BatchNo ratings yet
- S6 Product Market EqulibriumDocument40 pagesS6 Product Market EqulibriumShrija Majumder BJ22152No ratings yet
- FinalDocument27 pagesFinalmenonbindu80No ratings yet
- 4.6 Economic GrowthDocument13 pages4.6 Economic Growth294866No ratings yet
- Total (GDP, GNP, GNI) Number of Population: Measures of Economic ActivityDocument9 pagesTotal (GDP, GNP, GNI) Number of Population: Measures of Economic ActivityjjkjljNo ratings yet
- Econ 1BB3 - Notes 2Document3 pagesEcon 1BB3 - Notes 2seleneNo ratings yet
- Economic Assignment 2Document7 pagesEconomic Assignment 2Prateek_Ghai_303No ratings yet
- Chapter Six: National Income Accounting: Basic Concepts: GNP, GDP, Nominal and Real GNP/GDP, and GNP Per CapitaDocument16 pagesChapter Six: National Income Accounting: Basic Concepts: GNP, GDP, Nominal and Real GNP/GDP, and GNP Per CapitaYonas AddamNo ratings yet
- 6 - Aggregate Demand and SupplyDocument62 pages6 - Aggregate Demand and SupplyMạnh Nguyễn VănNo ratings yet
- Senior Question SolveDocument5 pagesSenior Question SolveMD Hafizul Islam HafizNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand: Session 16Document22 pagesAggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand: Session 16Raj PatelNo ratings yet
- Principles of Macro Economics PART 3Document4 pagesPrinciples of Macro Economics PART 3Duaa WajidNo ratings yet
- 2.2.1 The Characteristics of ADDocument25 pages2.2.1 The Characteristics of AD18kchohanNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics - Chapter 1Document19 pagesMacroeconomics - Chapter 1tomshave28No ratings yet
- Summaries MacroDocument12 pagesSummaries MacroRiccardo PicciulinNo ratings yet
- Macro NotesDocument28 pagesMacro NotesAlexis RheinNo ratings yet
- National Income Accounting PPT MBADocument58 pagesNational Income Accounting PPT MBARhea Mae Caramonte AmitNo ratings yet
- CFA Level 1 Eco - Aggregate Output, Prices, and Economic GrowthDocument22 pagesCFA Level 1 Eco - Aggregate Output, Prices, and Economic GrowthArun BabuNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Economics Chapter 6Document15 pagesFundamentals of Economics Chapter 6faraz aijazNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Demand PPTs-PART 1Document27 pagesAggregate Demand PPTs-PART 1Asim RiazNo ratings yet
- Notes in Video Activity 1Document7 pagesNotes in Video Activity 1Darra TanNo ratings yet
- Ma Econ Pol 2Document81 pagesMa Econ Pol 2Edimarf SatumboNo ratings yet
- (EN2020) Semana 13-14Document55 pages(EN2020) Semana 13-14david jimenezNo ratings yet
- 01 - NotesDocument6 pages01 - NotesChad FerninNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Notes PDFDocument23 pagesMacroeconomics Notes PDFJeon JeonNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - ECON 22358G - Chapter 10 - Part II - No AnswersDocument47 pagesLecture Notes - ECON 22358G - Chapter 10 - Part II - No AnswersnimugiritshaNo ratings yet
- EconDev IntroDocument22 pagesEconDev Introrolan.pana.shsNo ratings yet
- Important Basics of EconomyDocument4 pagesImportant Basics of EconomyRamana ReddyNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Intro. To Econ. II - 2023Document46 pagesLecture - Intro. To Econ. II - 2023AA1.2 Vilayvanh ChalernphonNo ratings yet
- Application of Macroeconomics Theory 6Document22 pagesApplication of Macroeconomics Theory 6RosarioEsperManisanNo ratings yet
- Short-Run Economic Fluctuations: Economic Activity Fluctuates From Year To YearDocument49 pagesShort-Run Economic Fluctuations: Economic Activity Fluctuates From Year To YearDinda Cici AuliaNo ratings yet
- Ms20 - MacroeconomicsDocument2 pagesMs20 - MacroeconomicsSeokjin KimNo ratings yet
- F2F W10 - ReviewDocument9 pagesF2F W10 - Reviews3976142No ratings yet
- Circular Flow of IncomeDocument46 pagesCircular Flow of IncomeSumit PoojaraNo ratings yet
- Economics Duran and LachicaDocument1 pageEconomics Duran and LachicaAaron Daniel DuranNo ratings yet
- IG Business Chapter 24Document34 pagesIG Business Chapter 24JoyceeNo ratings yet
- Week 2 National Income-2Document41 pagesWeek 2 National Income-2elijah thonNo ratings yet
- Asistensi 2 After UTS: Chapter 33 & 34 By: Khaira Abdillah Source: Cengage LearningDocument111 pagesAsistensi 2 After UTS: Chapter 33 & 34 By: Khaira Abdillah Source: Cengage LearningReza FahleviNo ratings yet
- Ecodev Midterm Notes 1Document4 pagesEcodev Midterm Notes 1Nichole BombioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Applications of Macroeconomics Theory As A Basis For Understanding The Key Economic Variables Affecting The BusinessDocument52 pagesChapter 6 Applications of Macroeconomics Theory As A Basis For Understanding The Key Economic Variables Affecting The Businessaladdin oidacraNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Measurements Part 2Document16 pagesMacroeconomic Measurements Part 2Devillz AdvocateNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Demand: 1. Change in ConsumptionDocument10 pagesAggregate Demand: 1. Change in Consumptiondaehwi lolNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Macro EconomicsDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Macro EconomicsGaurav MeenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3: National Income: Where It Comes From and Where It GoesDocument30 pagesChapter-3: National Income: Where It Comes From and Where It GoesImtiaz ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- What Is Aggregate DemandqwertDocument8 pagesWhat Is Aggregate DemandqwertShahana KhanNo ratings yet
- l1 Ec Rsheets b2Document1 pagel1 Ec Rsheets b2eloise.vernierNo ratings yet
- 毛共筆Ch1 6Document44 pages毛共筆Ch1 6jocelyn.hy.chenNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument32 pagesNational IncomeShoaib MohammadNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow Diagram: Week 2 National Income Accounting (NIA)Document9 pagesCircular Flow Diagram: Week 2 National Income Accounting (NIA)MarisolNo ratings yet
- Assignm NT 2 EconDocument4 pagesAssignm NT 2 EconMeherun MehbuNo ratings yet
- Measuring A Nation's Income: AcroeconomicsDocument42 pagesMeasuring A Nation's Income: AcroeconomicsSyed ArslanNo ratings yet
- Sessions 6,7,8 - Demand Supply - Keynesian ModelDocument143 pagesSessions 6,7,8 - Demand Supply - Keynesian ModelAbhay SahuNo ratings yet
- 1 National IncomeDocument43 pages1 National IncomeARSLAN MEHMOODNo ratings yet
- Study Guide MacroeconomicsDocument32 pagesStudy Guide MacroeconomicsMaría Eduarda LaraNo ratings yet
- CB 2 - MacroDocument106 pagesCB 2 - MacroSurbi SabharwalNo ratings yet
- Economic Envt - National IncomeDocument30 pagesEconomic Envt - National IncomeRajat NigamNo ratings yet
- What Is Aggregate DemandqwertDocument9 pagesWhat Is Aggregate DemandqwertShahana KhanNo ratings yet
- 1st Session Economic FactorsDocument30 pages1st Session Economic FactorsazeyhyNo ratings yet
- CS Analytical Coding Interview QuestionsDocument1 pageCS Analytical Coding Interview QuestionsClevin CkNo ratings yet
- Sage HRMS and Sage Employee Self Service: Release NotesDocument15 pagesSage HRMS and Sage Employee Self Service: Release NotesClevin CkNo ratings yet
- Data Structures Concepts and Programming QuestionsDocument35 pagesData Structures Concepts and Programming QuestionsClevin CkNo ratings yet
- Design Patterns: What and HowDocument8 pagesDesign Patterns: What and HowClevin CkNo ratings yet
- Real Time Face Detection and Tracking Using Opencv: Mamata S.KalasDocument4 pagesReal Time Face Detection and Tracking Using Opencv: Mamata S.KalasClevin CkNo ratings yet
- Library - Management SystemDocument68 pagesLibrary - Management SystemClevin CkNo ratings yet
- Federal BudgetDocument4 pagesFederal BudgetClevin CkNo ratings yet
- Rumi HostlesDocument92 pagesRumi HostlesClevin CkNo ratings yet
- Tugas AK Hal 337Document45 pagesTugas AK Hal 337Selvy ApriliantyNo ratings yet
- Topic: Student Politics in PakistanDocument7 pagesTopic: Student Politics in PakistanIrfan FarooqNo ratings yet
- Sp-Ishares-Nasdaq-Biotechnology-Etf-3-31 02-13-2023Document20 pagesSp-Ishares-Nasdaq-Biotechnology-Etf-3-31 02-13-2023jorge huerta durazoNo ratings yet
- The Danube 3D: Europeity and EuropeismDocument14 pagesThe Danube 3D: Europeity and EuropeismcursantcataNo ratings yet
- Traffic Monitoring GuideDocument18 pagesTraffic Monitoring GuideaskarahNo ratings yet
- Tata Aig Mediprime Insurance BrochureDocument2 pagesTata Aig Mediprime Insurance Brochurerehmy082No ratings yet
- PP 18 The Missa LectaDocument13 pagesPP 18 The Missa LectaRicardo TerrabuzziNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument50 pagesGlobal WarmingLeah Oljol RualesNo ratings yet
- Copia de The Green Banana Lecturas I 2020Document4 pagesCopia de The Green Banana Lecturas I 2020Finn SolórzanoNo ratings yet
- Bancassurance PDFDocument251 pagesBancassurance PDFdivyansh singh33% (3)
- Brigham Exploration (BEXP)Document2 pagesBrigham Exploration (BEXP)andrewbloggerNo ratings yet
- CP T Chotpradit 12723584Document287 pagesCP T Chotpradit 12723584Maxim ZagorskyNo ratings yet
- The Insiders Game How Elites Make War and Peace Elizabeth N Saunders Full ChapterDocument67 pagesThe Insiders Game How Elites Make War and Peace Elizabeth N Saunders Full Chapterjoann.lamb584100% (16)
- Korean Made Easy For Beginners 2nd Edition by Seu 22Document36 pagesKorean Made Easy For Beginners 2nd Edition by Seu 22takoshaloshviliNo ratings yet
- Mushoku Tensei - Volume 02 - Juvenile Period - Home Teacher Chapter (Baka-Tsuki) (Autogenerated)Document257 pagesMushoku Tensei - Volume 02 - Juvenile Period - Home Teacher Chapter (Baka-Tsuki) (Autogenerated)anibeastNo ratings yet
- Swot PanasonicDocument2 pagesSwot PanasonicXingMei StarszsisNo ratings yet
- Tenses For Talking About The NewsDocument5 pagesTenses For Talking About The NewsThunder BurgerNo ratings yet
- VERNACULAR ARCHITECTURE (Mud)Document26 pagesVERNACULAR ARCHITECTURE (Mud)Ashina Gupta100% (1)
- Unit 7 Exercises To StsDocument7 pagesUnit 7 Exercises To StsHưng TrầnNo ratings yet
- Fouts Def 2nd Production of DocumentsDocument88 pagesFouts Def 2nd Production of Documentswolf woodNo ratings yet
- Criminalogy and Penology Aditya KumarDocument9 pagesCriminalogy and Penology Aditya KumarTejaswi BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Introduction - Online Car Booking Management SystemDocument5 pagesIntroduction - Online Car Booking Management SystemTadese JegoNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Assignment For MISDocument11 pagesE-Commerce Assignment For MISIrfan Amin100% (1)
- Module MAPEH 8 4thDocument21 pagesModule MAPEH 8 4thEdnell VelascoNo ratings yet
- Mobilia Products, Inc. v. Umezawa, 452 SCRA 736Document15 pagesMobilia Products, Inc. v. Umezawa, 452 SCRA 736JNo ratings yet
- Afisco Insurance Corp v. CADocument3 pagesAfisco Insurance Corp v. CAJulianNo ratings yet