Professional Documents
Culture Documents
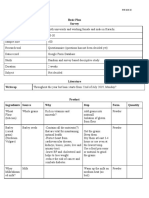
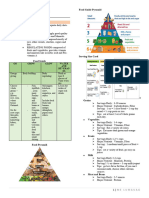
Increase Absorption:: Nutrient RDI Increase/decrease Absorption Sources Comments To Meet RDI
Increase Absorption:: Nutrient RDI Increase/decrease Absorption Sources Comments To Meet RDI
Uploaded by
StephanieOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Increase Absorption:: Nutrient RDI Increase/decrease Absorption Sources Comments To Meet RDI
Increase Absorption:: Nutrient RDI Increase/decrease Absorption Sources Comments To Meet RDI
Uploaded by
StephanieCopyright:
Available Formats
Nutrient RDI Increase/decrease absorption Sources Comments To meet RDI
Complete proteins containing significant amounts of
all 9 essential amino acids include soy (edamame,
tofu), hemp seeds, quinoa, buckwheat, freekeh
Increase absorption:
Vitamin B6 (which is found in Complete protein sources can be created by eating
protein sources anyway) ~ helps beans/legumes with whole grains, or beans/legumes
enzymes bread down protein and with seeds/nuts.
Protein 48 g carry amino acids to the Legumes, soy, nuts, seeds, For example, beans/legumes are high in lysine but
bloodstream wholegrains low in tryptophan, methionine, and cystine, whilst
whole grains/nuts & seeds are low in lysine but high
Complex carbohydrates ~ in tryptophan, methionine, and cystine.
releases insulin in body which
helps muscles absorb amino acids
However all plant-based sources of protein contain all
9 essential amino acids, and if you consume enough
calories it is difficult to be deficient.
Vegetables, legumes, fruits,
Fibre 25 g wholegrains, nuts, seeds
Increase absorption: To get 3g ALA a day:
Vitamins - B6, B12, biotin (B7), Conversion rates in healthy young women of ALA to - 15g chia seeds
Omega 3 250 mg (EPA, DHA) niacin (B3), folic acid (B9) ALAs: flaxseeds, chia seeds, hemp EPA is approx. 21%, whilst conversion of ALA to DHA - 15g ground flaxseed
3g (ALA) seeds, walnuts - 32g hemp seeds
Minerals - zinc, magnesium, is approx. 9%. - 50g walnuts
selenium - 1/2 tbsp of flaxseed oil
Vegetables (especially sweet Good for eyes, immune system, skin
Vitamin A 700 μg potatoes & pumpkins), fruits
Fat-soluble
Good for cell growth, development, & function
Decrease absorption: Legumes, nuts, seeds (especially
Thiamin (Vit B1) 1.1 mg Too much coffee or tea pepitas) Water-soluble, therefore twice as much is lost when
foods are boiled as opposed to frying or microwaving
Vegetables, nuts (especially Good for cell growth, development, & function
Riboflavin (Vit B2) 1.1 mg almonds), soy
Water-soluble
Good for digestive system, skin, nervous system, liver
Niacin (Vit B3) 14 mg Vegetables, nuts, legumes
Water-soluble
Necessary for making blood cells and for converting
food into energy. Promotes healthy skin, hair, eyes, &
Pantothenic Acid (Vit B5) 5 mg Vegetables, legumes, nuts liver.
Found in most vegetables and foods. It's very rare to
be deficient unless malnourished.
Involved in protein metabolism, cognitive
development, immune function, hemoglobin
Pyridoxine (Vit B6) 1.3 mg Legumes, vegetables formation
Water-soluble
Good for hair, skin, nails, liver
Biotin (Vit B7) 300 μg Nuts, legumes, soy, vegetables
Water-soluble
Good for brain health, memory, red blood cell
Vegetables, legumes, nuts & seeds generation & maintainance
Folate (Vit B9) 400 μg (especially pepitas & peanuts), fruit
Water-soluble
Nervous system, red blood cell production, digestion
Fortified plant milks/foods, & brain function
Cobalamin (Vit B12) 2.4 μg nutritional yeast
Water-soluble
Good for skin, bones, & tissue, and helps prevent
infections & heal wounds, antioxidant
Water-soluble
Vitamin C 45 mg Fruits (especially citrus), vegetables Vitamin C is required for the biosynthesis of collagen
which plays a role in wound healing as it is an
essential component of connective tissue
Vitamin C has been shown to regenerate other
antioxidants in the body including Vitamin E
Hormone that controls calcium levels in the blood.
Needed for strong bones, muscles, and overall health. 10-30 minutes in the sun 3 times a week
Vitamin D 20 μg The Sun! is sufficient
Fat-soluble
Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, aids immune function
Vitamin E 15 mg Nuts, seeds, vegetables
Fat-soluble
Important for bone health
Vitamin K 90 μg Vegetables (especially kale &
spinach), legumes Fat-soluble
1 cup protein-plus milk = 300mg
Increase absorption: 1 cup calci-plus milk = 400mg
Vitamin D 1/4 pack tofu = 81mg
Fortified plant-milks & foods, nuts, Good for teeth, bones, blood clotting, nerves & 25g chia seeds = 158mg
Calcium 1,000 mg Decrease absorption: seeds, soy muscle tissue. 25g hemp seeds = 17mg
Fibre 25g ground flaxseeds = 62mg
Too much sodium & caffeine 25g walnuts = 25mg
Needed for development of essential thyroid
Sea vegetables (e.g. seaweed, nori hormones that regulate the body's metabolic rate
Iodine 150 μg sheets etc.), fortified breads (with and promote growth & development throughout the
iodised salt) body including the brain.
Increase absorption:
Vitamin C Helps to transport oxygen around the body,
important for producing energy, optimal immune
Iron 18 mg Decrease absorption: Legumes, soy, nuts, pepitas, oats, function, and storing oxygen in our muscles. 1/2 cup oats = 3 mg
wholegrains, fortified foods 1/4 pack of tofu (90g) = 4mg
Fibre Vitamin C increases absorption of non-heme iron
Calcium (plant-based iron) up to 3x
Tannins in tea and coffee
Copper 1.2 mg Seeds, nuts, soybeans, legumes, Needed to build strong tissue, maintain blood
vegetables volume, and producing energy.
Helps regulate protein synthesis, muscle & nerve
Vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds, function, blood glucose control, blood pressure
Magnesium 310 mg wholegrains regulation, transports calcium and potassium ions
across cell membranes.
Vegetables, tree fruits (e.g. Helps nerves & muscle function, moves nutrients and
Potassium 2,800 mg avocados, apples, oranges, waste around cells, offsets the effect of sodium in
bananas), legumes raising blood pressure.
Oats, brown rice, vegetables, fruit, Bone health, skin health (helps to form collagen),
Manganese 5 mg black pepper, chickpeas, pepitas, blood sugar control.
soy, grains
Most people consume more than
enough sodium through added salt Helps maintain the correct volume of circulating
Sodium 690 mg in their diet. We should aim to blood and tissue fluids in the body.
keep our sodium content as low as
possible.
1/2 cup oats = 3 mg
Essential for immune system function, wound 1/2 cup of cooked chickpeas = 1.3 mg
healing, blood clotting, thyroid function 2 tbsp tahini = 1.4 mg
28g chia seeds = 1 mg
8 mg Decrease absorption: Legumes, nuts, seeds, wholegrains May require up to 50% more than the recommended 10g hemp seeds = 1 mg
Zinc 12 mg (plant-based) Fibre (oats especially), fortified foods intake as the bioavailability of zinc from plant-based 1/4 cup sunflower seeds = 4 mg
sources is much lower. This is due to phytic acid in 1/4 cup pumpkin seeds = 4 mg
sources like pulses which can hinder zinc absorption, 1/4 cup cashews = 4 mg
but soaking decreases those inhibitors. 1/4 cup almonds = 2 mg
1/4 cup pine nuts = 4 mg
Selenium 55 μg Brazil nuts, pepitas, chia seeds, Antioxidant, boosts immunity, heart health, improves 1 brazil nut a day is sufficient
mushrooms blood flow, regulates thyoid function
Muscle, nerve, & kidney function, repairs tissue and
Phosphorus 700 mg Nuts, seeds, legumes cells, helps build bones
When it comes to sugar, you should limit intake to 10% of daily calories
e.g. On a 1500 calorie diet, maximum sugar intake is 150 calories which equals 9-10 tsp of sugar (37-42g)
You might also like
- Fod1060 Canadian Heritage Foods LabsDocument6 pagesFod1060 Canadian Heritage Foods Labsapi-131290142No ratings yet
- Metabolic Balance Diet: General GuidelinesDocument5 pagesMetabolic Balance Diet: General GuidelinesAlinaelena Hatneanu100% (1)
- Vitamin/Mineral Chart Health Psychology: Vitamins Minerals Health Benefits Vitamin Source Recommended Daily IntakeDocument3 pagesVitamin/Mineral Chart Health Psychology: Vitamins Minerals Health Benefits Vitamin Source Recommended Daily IntakeQuarmina HesseNo ratings yet
- Food Supply Chain and Logistics - Midterm ExamDocument7 pagesFood Supply Chain and Logistics - Midterm ExamthemylaporeladNo ratings yet
- Nutrilite RefChartDocument4 pagesNutrilite RefChartgirishkumarhm50% (4)
- Xs Webhealth Vitamin and Mineral Reference Chart: Fat Soluble VitaminsDocument5 pagesXs Webhealth Vitamin and Mineral Reference Chart: Fat Soluble VitaminsmadhanavNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Minerals in Our Food PDFDocument5 pagesVitamins and Minerals in Our Food PDFRaman KatariaNo ratings yet
- Types of Nutrients CONSUMER CHEMISTRYDocument9 pagesTypes of Nutrients CONSUMER CHEMISTRYkeijeiNo ratings yet
- Quick Start Guide: The Body EcologyDocument15 pagesQuick Start Guide: The Body EcologymNo ratings yet
- B VitaminsDocument1 pageB VitaminsAmaterasuNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument7 pagesVitaminsMuhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- FYP Basic Plan 1Document5 pagesFYP Basic Plan 1RBS Associates Pvt Ltd. KhiNo ratings yet
- Food Groups and BeveragesDocument5 pagesFood Groups and BeveragesJoseph Louis BautistaNo ratings yet
- (Mr. Ghani Kunto) APAC Plant-Based Protein Trends and ImplicationsDocument18 pages(Mr. Ghani Kunto) APAC Plant-Based Protein Trends and ImplicationssharanNo ratings yet
- List of VitaminDocument12 pagesList of VitaminMariem Liouéne KarouiNo ratings yet
- Herbal Hills: Wheat-O-PowerDocument47 pagesHerbal Hills: Wheat-O-PowerKamran AlamNo ratings yet
- Food Groups ChartDocument2 pagesFood Groups ChartGisselNo ratings yet
- Diabet CopmpleteDocument65 pagesDiabet CopmpleteBebe StefanescuNo ratings yet
- Niacin: Water-Soluble VitaminsDocument3 pagesNiacin: Water-Soluble VitaminsMinette EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Ingles 1.1Document1 pageIngles 1.1Valentina Perez RiañoNo ratings yet
- Read The Article. Than Complete The Chart. Food Groups Intake VegetablesDocument2 pagesRead The Article. Than Complete The Chart. Food Groups Intake VegetablesCarolin MercedesNo ratings yet
- Vitamins & MineralsDocument8 pagesVitamins & Mineralswardahmohammad2022No ratings yet
- NSG 104.1-Torralba-Diet Plan ExamDocument3 pagesNSG 104.1-Torralba-Diet Plan ExamAubrey Dynise C. TorralbaNo ratings yet
- Daily Menu PlanDocument30 pagesDaily Menu PlanRyan YewNo ratings yet
- Vitamins in Human BodyDocument3 pagesVitamins in Human BodyJawad AnsariNo ratings yet
- SHSS Joint SX Education Booklet CH 3 - Nutrition For Energy and Optimal HealingDocument7 pagesSHSS Joint SX Education Booklet CH 3 - Nutrition For Energy and Optimal HealingGregg ArmisteadNo ratings yet
- T TP 1678804691 Vegan Eatwell Guide Display Poster - Ver - 2Document1 pageT TP 1678804691 Vegan Eatwell Guide Display Poster - Ver - 2PegNo ratings yet
- RishtaDocument4 pagesRishtazehra rizviNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument52 pagesScienceAppu MansaNo ratings yet
- 6-10 NCERT - BABA Science-Compilaton - CompressedDocument22 pages6-10 NCERT - BABA Science-Compilaton - Compressedsagartheshine666No ratings yet
- Well 2 Pager - Basic Product TrainingDocument87 pagesWell 2 Pager - Basic Product TrainingAnik EtNo ratings yet
- What To Eat During Pregnancy Infographic TabletDocument1 pageWhat To Eat During Pregnancy Infographic TabletDarren MooreNo ratings yet
- Print + Mcqs 03 FirstDocument14 pagesPrint + Mcqs 03 FirstAamir ShabbirNo ratings yet
- 1 - PL - LAB - NCM105NDT - Basic Tools in NutritionDocument4 pages1 - PL - LAB - NCM105NDT - Basic Tools in NutritionMa Ellen LumauagNo ratings yet
- GCSE FPN Nutrition Revision BookletDocument50 pagesGCSE FPN Nutrition Revision BookletTaufik RahmadiNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Diets: A. Normal Diet B. Modified DietDocument7 pagesTherapeutic Diets: A. Normal Diet B. Modified Dietbrian samNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 GSA NOA AcademyDocument24 pagesLecture 5 GSA NOA AcademyFazila umNo ratings yet
- Nutrient Function Sources: Water-Soluble VitaminsDocument3 pagesNutrient Function Sources: Water-Soluble VitaminsTaylor Swift's GatekeeperNo ratings yet
- Q4 Las 1 P.EDocument6 pagesQ4 Las 1 P.EZiarineNo ratings yet
- SHK IngredientsBenefits ChartDocument1 pageSHK IngredientsBenefits ChartSonia GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Dr. Rob Top 10 Brain Rewiring FoodsDocument6 pagesDr. Rob Top 10 Brain Rewiring FoodsDušan PaničNo ratings yet
- Nutri PeDocument4 pagesNutri PeDaniel ArshNo ratings yet
- Nutrients Why - Benefits, Risk & Side Effects Side Effects (Overdose) How-Natural Source/ Supplements DosesDocument7 pagesNutrients Why - Benefits, Risk & Side Effects Side Effects (Overdose) How-Natural Source/ Supplements Dosesjohnsonkk125No ratings yet
- Vitamins - Their Functions and Sources - HealthLink BCDocument2 pagesVitamins - Their Functions and Sources - HealthLink BCasadzamanchathaNo ratings yet
- Best Bet DietDocument5 pagesBest Bet DietSayra AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Detox Food PlanDocument2 pagesDetox Food PlanEllice O. MonizNo ratings yet
- Low Fiber Diet Academy of Nutrition and DieteticsDocument3 pagesLow Fiber Diet Academy of Nutrition and DieteticsTipografie TipografieNo ratings yet
- Nutrient Role in Nutrition and Health Common Food SourcesDocument2 pagesNutrient Role in Nutrition and Health Common Food SourcesronaldoNo ratings yet
- FOOD AND HEALTH Unit IV and VDocument24 pagesFOOD AND HEALTH Unit IV and VPackianathan SarathNo ratings yet
- Zinc Vegetarian Nutrition 2014 PDFDocument2 pagesZinc Vegetarian Nutrition 2014 PDFNikita ZhukNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument3 pagesVitaminsJamil Samira E. BuizonNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument3 pagesVitaminsJamil Samira E. BuizonNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument3 pagesVitaminsJamil Samira E. BuizonNo ratings yet
- Protein Vegetarian Nutrition PDFDocument2 pagesProtein Vegetarian Nutrition PDFLuna AzulNo ratings yet
- Vitamins HidrDocument96 pagesVitamins HidrDeea LobonțiuNo ratings yet
- Attachment 4Document30 pagesAttachment 4Barak KilimoNo ratings yet
- Essential Vitamin Guide: Find It inDocument4 pagesEssential Vitamin Guide: Find It inbasuthker raviNo ratings yet
- Exam Meal PlanDocument4 pagesExam Meal PlanVishal DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition During Cancer Treatment: Food Group Nutrients Provided Serving Sizes / ExamplesDocument2 pagesNutrition During Cancer Treatment: Food Group Nutrients Provided Serving Sizes / ExamplesHansley Templeton CookNo ratings yet
- Fighting Diabetes-Ole of Furits and VegetablesDocument12 pagesFighting Diabetes-Ole of Furits and VegetablesJune DumdumayaNo ratings yet
- Listening U1A3. Gian Marco OrdoñezDocument2 pagesListening U1A3. Gian Marco OrdoñezGian Marco Ordoñez ChuquimiaNo ratings yet
- Mahsa BallroomDocument8 pagesMahsa BallroomNovalishaNo ratings yet
- The History of CoffeeDocument3 pagesThe History of Coffeereyes princessNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Final InglesDocument3 pagesTrabajo Final InglesLeidy CacñahuarayNo ratings yet
- Sithccc - Prepare Food To Meet Special Dietary RequirementssaeDocument18 pagesSithccc - Prepare Food To Meet Special Dietary RequirementssaeChemistry SoniaNo ratings yet
- Safety Hygiene in Side The Galley Onboard The ShipDocument2 pagesSafety Hygiene in Side The Galley Onboard The ShipAna Marie ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- AvacardoDocument12 pagesAvacardokshah29No ratings yet
- WFDocument9 pagesWFVarun Sharma100% (1)
- Limites UEDocument16 pagesLimites UEernesto arriazaNo ratings yet
- 1-Products and ByproductsDocument5 pages1-Products and Byproductsabdulrahman saadNo ratings yet
- Grade 2.liquids Good For YouDocument1 pageGrade 2.liquids Good For YouLucy CataquisNo ratings yet
- 2023 Nutrion Month Narrative ReportDocument10 pages2023 Nutrion Month Narrative ReportLorelynSonioMoseNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Factors Affecting Carcass YieldDocument7 pagesModule 4 - Factors Affecting Carcass Yieldarln mndzNo ratings yet
- Wine Woods ApoDocument3 pagesWine Woods Apomlbsept22No ratings yet
- Dessert Semi Detailed Lesson Plan inDocument2 pagesDessert Semi Detailed Lesson Plan inArjhona Bacay-LucasNo ratings yet
- Price ListDocument3 pagesPrice ListAvishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Abbyland Foods Abbotsford WI Inhumane Animal Handling USDA FSIS PDFDocument3 pagesAbbyland Foods Abbotsford WI Inhumane Animal Handling USDA FSIS PDFghostgripNo ratings yet
- Dietary Managment in Kidney Disease - Mrs. Mariam Allaik KamareddineDocument68 pagesDietary Managment in Kidney Disease - Mrs. Mariam Allaik KamareddineGabrielle SandovalNo ratings yet
- .Diabetic Recipes With MR Bee - 1660298973000Document5 pages.Diabetic Recipes With MR Bee - 1660298973000Nelliate Chakauya MakuvireNo ratings yet
- Ingredients: Bulalo RecipeDocument3 pagesIngredients: Bulalo RecipesakuraNo ratings yet
- Soil Fertilty Senior EssayDocument12 pagesSoil Fertilty Senior EssayTilahun MikiasNo ratings yet
- Haru ProgrammeDocument2 pagesHaru ProgrammeSophia Insyirah OsmanNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Pemberian Pakan Sapi Bali: Ervina Wahyuni Dan Muh. AminDocument7 pagesManajemen Pemberian Pakan Sapi Bali: Ervina Wahyuni Dan Muh. AminWindi Ayutia PutriNo ratings yet
- SNT Research EssayDocument6 pagesSNT Research Essayapi-640140770No ratings yet
- FMCG Monitor / Insight For 2021 Q2Document14 pagesFMCG Monitor / Insight For 2021 Q2DikaAnindyajatiNo ratings yet
- Prasna BHDocument4 pagesPrasna BHmksingh_22No ratings yet
- How Much or How Many Esl Grammar Exercises WorksheetDocument2 pagesHow Much or How Many Esl Grammar Exercises WorksheetMihaiNo ratings yet