Professional Documents
Culture Documents
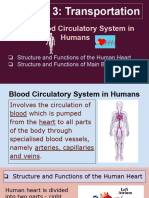
6.2 The Blood System
6.2 The Blood System
Uploaded by
janOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
6.2 The Blood System
6.2 The Blood System
Uploaded by
janCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 6.
2: THE BLOOD SySTEm
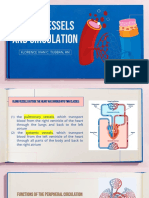
Circulation
William Harvey proposed the modern understanding of the circulatory system
Vena Cava Pulmonary
According to Harvey: Vein
• The major blood vessels (arteries & veins) are connected by a single network
ORGAN LUNG
• Blood flow is unidirectional (due to the presence of one-way valves)
• The heart is a central pump (arteries = from heart ; veins = to heart) Pulmonary
Aorta Artery
• Blood flows continuously and is not consumed by the body
It has further been dicovered that: RIGHT SIDE LEFT SIDE
• Arteries and veins are connected by capillaries (via arterioles & venules) Body → Lungs Lungs → Body
• There is a separate circulation for the lungs (pulmonary versus systemic) (Deoxygenated) (Oxygenated)
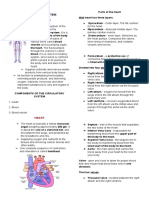
Blood Vessels
Arteries Veins Capillaries
• Transport blood from the heart • Transport blood to the heart • Facilitate material exchange
• Blood at high pressure (80-120 mmHg) • Blood at low pressure (<15 mmHg) • Blood at low pressure (~10 mmHg)
• Walls are thick (muscle and elastin) • Walls are thin (with wider lumen) • Walls made of single layer of cells
• Walls stretch or contract with pulse • Have valves to prevent pooling • Extremely narrow lumen (~10 µm)
Capillaries may be categorised as:
• Continuous (intact basement membrane)
• Fenestrated (have endothelial pores)
• Sinusoidal (discontinuous membrane)
endothelium basement
collagen muscle/elastic fibres collagen muscle/elastic fibres (single layer) membrane
Blood Blood Flow
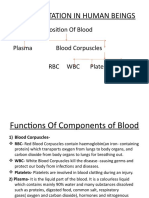
Blood contains three main elements: A heart pumps blood around the body via two distinct circulatory pathways
• Red blood cells (transport oxygen)
Right Side (of heart):
• White blood cells (fight infections)
• Deoxygenated blood (from tissues) enters right atrium via the vena cava
• Platelets (responsible for clotting)
• Blood in the right ventricle is pumped to lungs via the pulmonary artery
The blood fluid (plasma) transports: • Gas exchange at the lungs (capillaries ⟷ alveoli) oxygenates the blood
• Nutrients (e.g. glucose)
Left Side (of heart):
• Antibodies
• Oxygenated blood (from lungs) enters left atrium via the pulmonary vein
• Carbon dioxide • Blood in the left ventricle is pumped to the body tissues via the aorta
• Hormones
• Material exchange occurs at the respiring tissue (deoxygenates the blood)
• Oxygen
• Urea Valves in veins ensure proper circulation by preventing backflow of blood
• Heat NACHO-UH! • Contraction of skeletal muscles may compress veins to aid blood flow
You might also like
- UK Foundation Programme SJT Questions PDFDocument382 pagesUK Foundation Programme SJT Questions PDFstanley100% (4)
- Basic Surgical InstrumentsDocument37 pagesBasic Surgical Instrumentsapi-2658787991% (33)
- Circulatory SystemDocument31 pagesCirculatory SystemGeonardo100% (3)
- Practical English Book 1 Answer KeyDocument29 pagesPractical English Book 1 Answer Keyanna39100% (4)
- SETDocument40 pagesSETIkre1967% (3)
- If Clause On ConversationDocument7 pagesIf Clause On ConversationIis Indria DamayantiNo ratings yet
- 6.2 The Blood SystemDocument43 pages6.2 The Blood SystemPhilip ForintonNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System 1Document4 pagesCirculatory System 1Jhes D.No ratings yet
- Chap +5+Cardiovascular+SyDocument39 pagesChap +5+Cardiovascular+SySalman MasriNo ratings yet
- C10 Transport in Human and Animal (Ans)Document4 pagesC10 Transport in Human and Animal (Ans)CHUA PHEI THNG MoeNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument84 pagesCirculatory SystemAprille CastroNo ratings yet
- Human Cardiovascular System: Introduction ToDocument76 pagesHuman Cardiovascular System: Introduction ToJunje SemeonNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System PDFDocument5 pagesCirculatory System PDFNibshian Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory / Transport System: For 1O Grade Igcse Semesta Bilingual Boarding SchoolDocument52 pagesCirculatory / Transport System: For 1O Grade Igcse Semesta Bilingual Boarding SchoolThe Deep Sea IdNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Vessels PDFDocument10 pagesCH 11 Vessels PDFIbra TutorNo ratings yet
- Tissues and Intro To Circulation 2014 2Document51 pagesTissues and Intro To Circulation 2014 2Chantae JulienNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Circulatory SystemDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Circulatory SystemPrisha ChhedaNo ratings yet
- The Cardio Vascular SystemDocument36 pagesThe Cardio Vascular SystemKrizza Kyle Sarmon MancaoNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Digestion: FunctionsDocument2 pagesMechanical Digestion: FunctionsAna MárquezNo ratings yet
- XI-1 Adinda Caesaria Bunga Astiti Hanin Rialsa Meitha Anindya Raisa CeciliaDocument20 pagesXI-1 Adinda Caesaria Bunga Astiti Hanin Rialsa Meitha Anindya Raisa CeciliaadiriadheeNo ratings yet
- Intro On Circulatory System-UoC - 191123Document29 pagesIntro On Circulatory System-UoC - 191123Hidayah Mohamad raniNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Blood Vessels Lab - HandoutDocument7 pagesAnaphy Blood Vessels Lab - HandoutAEGEL DARO TORRALBANo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Sbi3u The Circulatory System Introduction and Human Circulatory SystemDocument39 pagesDokumen - Tips - Sbi3u The Circulatory System Introduction and Human Circulatory Systempacheco TimeNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 Cardiovascular SystemDocument36 pagesTopic 9 Cardiovascular SystemAlejandra CastilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9. Transport in AnimalDocument46 pagesChapter 9. Transport in AnimalCharxd zzNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument15 pagesThe Cardiovascular SystemRyan Kim FabrosNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System (Blood Vessels and Circulation) : Roger Joseph II R. Jecino, R.N., M.DDocument53 pagesCardiovascular System (Blood Vessels and Circulation) : Roger Joseph II R. Jecino, R.N., M.DIan MendezNo ratings yet
- 024-Premedical Circulatory SystemDocument31 pages024-Premedical Circulatory Systemchealzea asuncsionNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System What Is A Circulatory System?: HeartDocument4 pagesCirculatory System What Is A Circulatory System?: HeartVianney LaplanaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Vascular SystemDocument51 pagesCardiac Vascular SystemYasir Altaf WaniNo ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument32 pagesBlood Vesselsabdullahwajd530No ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY MIDTERMSDocument19 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY MIDTERMSteressaubungenNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Dr. Ridwan Rahman SalehDocument45 pagesCardiovascular System: Dr. Ridwan Rahman Salehnurhidayati harunNo ratings yet
- 9.3 Blood VesselsDocument14 pages9.3 Blood VesselsNathan TeferaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument24 pagesCardiovascular Systemjimjose antonyNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic and Blood Vessel NotesDocument5 pagesLymphatic and Blood Vessel NotesPrat BhatNo ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument10 pagesBlood Vesselsmixiaoquan98No ratings yet
- Circulatory System NotesDocument10 pagesCirculatory System Notesdanlayton75% (4)
- 3.2.2 Blood Circulatory System in HumansDocument19 pages3.2.2 Blood Circulatory System in HumanslovenialawNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: MVZ Carinthia ZapataDocument50 pagesCirculatory System: MVZ Carinthia ZapataFernando ZendejasNo ratings yet
- محاضرة فسلجة 6 رقم 638097619114528622Document26 pagesمحاضرة فسلجة 6 رقم 638097619114528622محمد عليNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument30 pagesCirculatory SystemFiraol DiribaNo ratings yet
- 4mgdskmlswg6dvazveij Signature Poli 150701080131 Lva1 App6892 PDFDocument42 pages4mgdskmlswg6dvazveij Signature Poli 150701080131 Lva1 App6892 PDFsaurabh chaturvediNo ratings yet
- Cardio SystemDocument3 pagesCardio SystemAlowee AbelloNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Blood VesselsDocument8 pagesAnaphy Blood Vesselsvtangarocan33932No ratings yet
- 4 - Blood Vessel AnatomyDocument23 pages4 - Blood Vessel AnatomyRashpal SidhuNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument22 pagesCirculatory Systemparitosh7_886026No ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument43 pagesBlood VesselsJessica AcostaNo ratings yet
- This Powerpoint Is Hosted On Please Visit For 100's More Free PowerpointsDocument21 pagesThis Powerpoint Is Hosted On Please Visit For 100's More Free PowerpointsMisbakhul MunirNo ratings yet
- Blood CirculationDocument58 pagesBlood CirculationSabashnee GovenderNo ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument48 pagesBlood VesselsGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems - Circulatory System-3Document11 pagesHuman Body Systems - Circulatory System-3benjaminblakkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Animal TransportDocument6 pagesChapter 9 - Animal TransportHashtag []No ratings yet
- VisibleBody Blood VesselsDocument20 pagesVisibleBody Blood VesselscascaveletteNo ratings yet
- Blood Vessels: Blood Vessels Are How Blood Travels Through The BodyDocument20 pagesBlood Vessels: Blood Vessels Are How Blood Travels Through The BodyRoger RonconiNo ratings yet
- Ana CardioDocument3 pagesAna CardioFIONA DANE MAURERANo ratings yet
- CVS I IntroDocument80 pagesCVS I IntroMunewer AbdellaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument15 pagesCirculatory Systemsafiealrahman.2009No ratings yet
- Life Processes, Class XDocument31 pagesLife Processes, Class XPiyushNo ratings yet
- PMLS 2 LEC Module 3Document8 pagesPMLS 2 LEC Module 3Peach DaquiriNo ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument46 pagesBlood Vesselsapi-3740505No ratings yet
- CN111 CardioVascular SystemDocument43 pagesCN111 CardioVascular SystemSydney AchaiNo ratings yet
- Unit 06 Blood VesselsDocument101 pagesUnit 06 Blood VesselsJohnykutty JosephNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Anti TBDocument7 pagesAnti TBAudrey Austria IINo ratings yet
- Case MorbiliDocument49 pagesCase MorbiliSiLpi HamidiyahNo ratings yet
- Kjod 44 177 PDFDocument7 pagesKjod 44 177 PDFRebin AliNo ratings yet
- Treatment Considerations, and Nursing Implications: Cardiovascular Disease and HIV: PathophysiologyDocument12 pagesTreatment Considerations, and Nursing Implications: Cardiovascular Disease and HIV: PathophysiologyRicardo Costa da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Types and Collection of Urine SpecimenDocument12 pagesTypes and Collection of Urine SpecimengireeshsachinNo ratings yet
- DeuteromycotaDocument10 pagesDeuteromycotaReeza MegavitryNo ratings yet
- Transits of MarsDocument20 pagesTransits of MarsReiki MasterNo ratings yet
- Cross Contamination Control Facility DesignDocument22 pagesCross Contamination Control Facility DesignAlok Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Amoxillin Glimepirid Amoxillin Metronidazol Metformin: Ambroxol Tablet Ambroxol TabletDocument10 pagesAmoxillin Glimepirid Amoxillin Metronidazol Metformin: Ambroxol Tablet Ambroxol TabletSeptia MonalisaNo ratings yet
- SaftyDocument3 pagesSaftyAnonymous ABLtDDvKuiNo ratings yet
- Carestation 620 Spec Sheet Rev5Document8 pagesCarestation 620 Spec Sheet Rev5Kittiwat WongsuwanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Experience With Vaginal Gestrinone in Pentravan in The Treatment of Endometriosis PainDocument5 pagesClinical Experience With Vaginal Gestrinone in Pentravan in The Treatment of Endometriosis PainRamona RusuNo ratings yet
- Stok Opname Apotek Fidela FarmaDocument13 pagesStok Opname Apotek Fidela FarmaFidelafarmaNo ratings yet
- Jaypees Triple A Pediatric PDFDocument121 pagesJaypees Triple A Pediatric PDFAshraf AboNo ratings yet
- Dr. AnjumAP PDFDocument10 pagesDr. AnjumAP PDFخانقاہ نورانیہNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Drug Therapy in GeriatricsDocument4 pagesChapter 11 - Drug Therapy in Geriatricsdlneisha61100% (1)
- Preventive Medicine 4.7 - Case-Control StudyDocument5 pagesPreventive Medicine 4.7 - Case-Control StudyLiza Elaine Ulep CawasNo ratings yet
- Susunan Acara Seminar PIT XII - Rev 6 FullDocument6 pagesSusunan Acara Seminar PIT XII - Rev 6 FullSindy Amalia FNo ratings yet
- A Pictorial Guide For The Second Trimester Ultrasound: EducationDocument16 pagesA Pictorial Guide For The Second Trimester Ultrasound: EducationSultan AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Sample Size For An Unmatched Case-Control Study: Kevin M. Sullivan, PHD, MPH, Mha: Minn M. Soe, MD, MPH, MCTMDocument3 pagesSample Size For An Unmatched Case-Control Study: Kevin M. Sullivan, PHD, MPH, Mha: Minn M. Soe, MD, MPH, MCTMPande Doddy HaryadiNo ratings yet
- CCES PUB SubstanceClassification EDocument55 pagesCCES PUB SubstanceClassification Efree121No ratings yet
- 8021 MSDSDocument4 pages8021 MSDSAhmed Emad AhmedNo ratings yet
- FC 01Document591 pagesFC 01generationfm.power7989No ratings yet
- Hip Fractures in Elderly - Shanojan ThiyagalingamDocument26 pagesHip Fractures in Elderly - Shanojan ThiyagalingamDr. Shanojan Thiyagalingam, FRCPC FACPNo ratings yet
- (123doc) Opthalmic Microsurgical Suturing Techniques Part 9Document15 pages(123doc) Opthalmic Microsurgical Suturing Techniques Part 9TEODORA MIHAELA PELEASANo ratings yet