Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6.6 Reproductive Systems
6.6 Reproductive Systems
Uploaded by
janCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Viva in Medical Physiology 2nd (Kenneth) PDFDocument267 pagesViva in Medical Physiology 2nd (Kenneth) PDFThida100% (5)
- 4 Male and Female Reproductive Organs PPTDocument71 pages4 Male and Female Reproductive Organs PPTDanica Marie Sibay100% (2)
- Prenatal & Postnatal Growth of MandibleDocument44 pagesPrenatal & Postnatal Growth of MandibleAnkur SharmaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 3RD QuarterDocument13 pagesScience Reviewer 3RD QuarterKurt John DecenaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Review Year II 2019Document31 pagesMidterm Review Year II 2019nc23tengNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in HumansDocument14 pagesReproduction in HumansarnoldnsondojrNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Role of Hormones in The Female and Male Reproductive SystemDocument24 pagesLesson 3: Role of Hormones in The Female and Male Reproductive Systemnathanielstanaj.mNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument36 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemamyNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument69 pagesHuman Reproductionapi-202349222No ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument41 pagesHuman ReproductionMmabatho Vilakazi100% (1)
- Grade 10 Science Quarter 3Document23 pagesGrade 10 Science Quarter 3Mary Cuevas (Ari)No ratings yet
- 1 Reproductive Organs and Hormones 365Document37 pages1 Reproductive Organs and Hormones 365ErivieNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Organs and HormoneDocument37 pagesReproductive Organs and Hormoneishtiyakjafar jafarNo ratings yet
- Understanding Human Reproduction Education Presentation in Peach Violet Hand Drawn Lightly Textured StyleDocument19 pagesUnderstanding Human Reproduction Education Presentation in Peach Violet Hand Drawn Lightly Textured StylemarcosryanhmaranhaoNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument41 pagesHuman ReproductionsimphiwemakhonjwaNo ratings yet
- 1 Reproductive Organs and Hormones 365Document37 pages1 Reproductive Organs and Hormones 365Marvin ObraNo ratings yet
- MF009 6B Human Reproduction System James LDocument26 pagesMF009 6B Human Reproduction System James LPikuNo ratings yet
- Testis and Ovaries: Name - Nisha Rajali Class - 11-BDocument8 pagesTestis and Ovaries: Name - Nisha Rajali Class - 11-BSania BanoNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of The Male and Female Reproductive Systems Role of Hormones in Male and Female Reproductive SystemsDocument27 pagesParts and Functions of The Male and Female Reproductive Systems Role of Hormones in Male and Female Reproductive SystemsDivine GhagaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Human ReproductionDocument48 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Human ReproductionErmiasNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction: Male Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesHuman Reproduction: Male Reproductive SystemMd AmanNo ratings yet
- BiosiceDocument57 pagesBiosiceLJ. Lagaras vlogNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument20 pagesHormonesGabriel LanceNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System NotesDocument40 pagesReproductive System Notesakhtardilshad009No ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesMale Reproductive SystemRico CawasNo ratings yet
- U4 Lesson 4 Human ReproductionDocument27 pagesU4 Lesson 4 Human ReproductionShriNo ratings yet
- Presentation StudentDocument61 pagesPresentation Studentvsvm2009No ratings yet
- Reproductive Tract Cancers: Prevention, Early Diagnosis & Treatment Modalities For Knowledge & AwarenessDocument96 pagesReproductive Tract Cancers: Prevention, Early Diagnosis & Treatment Modalities For Knowledge & AwarenessMOHIT MAROONo ratings yet
- Wa0020Document52 pagesWa0020michaelNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Part3 HumanReproductionDocument27 pagesReproduction Part3 HumanReproductionbiology.alfonsinaNo ratings yet
- BIO NotesDocument7 pagesBIO Notesjohnbenedictsaavedra3No ratings yet
- LESSON 3 - Animal-ReproductionDocument88 pagesLESSON 3 - Animal-ReproductionMary Emmanuelle MañusNo ratings yet
- LFSC REVISION BRIEF NOTES BOOKLET P1 LAST PUSH CAPRICORN SOUTHDocument29 pagesLFSC REVISION BRIEF NOTES BOOKLET P1 LAST PUSH CAPRICORN SOUTHqueenrorisang95No ratings yet
- N-315: Family Health Nursing: Course Coordinator & Instructor: Mrs. Deepa ThomasDocument41 pagesN-315: Family Health Nursing: Course Coordinator & Instructor: Mrs. Deepa ThomasDeepa ThomasNo ratings yet
- Jabba JabbaDocument49 pagesJabba JabbaCombustible DragonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 36-1 Reproductive SystemsDocument25 pagesChapter 36-1 Reproductive Systemsnancie8No ratings yet
- All MCN MidtermDocument207 pagesAll MCN MidtermInah SaritaNo ratings yet
- File 0441Document149 pagesFile 0441Kellie ManganNo ratings yet
- Biology of Human Reproductive SystemDocument51 pagesBiology of Human Reproductive Systemlen lehangNo ratings yet
- Topic 17: ReproductionDocument29 pagesTopic 17: ReproductionEva SidhaniNo ratings yet
- CR 010232Document20 pagesCR 010232kgothatso maleteNo ratings yet
- FEMALE and MALE REPRUDUCTION SYSTEMDocument23 pagesFEMALE and MALE REPRUDUCTION SYSTEMHalseyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document84 pagesChapter 1ismailmohamad373No ratings yet
- Science 10 - Reproductive Health SystemDocument43 pagesScience 10 - Reproductive Health SystemGian Xyrelance IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Reviewer (HumanRep) : PRELIMDocument10 pagesReviewer (HumanRep) : PRELIMHazel GeronimoNo ratings yet
- B11.5 Hormones in Human Reproduction EdDocument16 pagesB11.5 Hormones in Human Reproduction EdBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- CH 46 - Reproductive SystemDocument70 pagesCH 46 - Reproductive SystemSofiaNo ratings yet
- HANDOUTS Finals CH 19Document26 pagesHANDOUTS Finals CH 19hii385156No ratings yet
- Menstrual CycleDocument32 pagesMenstrual CycleJowelyn MaderalNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument43 pagesHuman Reproductive Systembabaaijaz01No ratings yet
- Female ReprodDocument42 pagesFemale Reprodhailu tasheNo ratings yet
- Reproduction SystemDocument81 pagesReproduction SystemGabrielle GreyNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Module 1.3 Reproductive SystemDocument113 pagesQuarter 3 Module 1.3 Reproductive Systemsano.kthNo ratings yet
- PP5.Human Reproduction (Updated)Document65 pagesPP5.Human Reproduction (Updated)hellohlayisoNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction MindmapDocument10 pagesHuman Reproduction MindmapSuyagya PundirNo ratings yet
- Biology 2 Lecture 10 - Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesBiology 2 Lecture 10 - Reproductive SystemRYLE IBANEZNo ratings yet
- Physiology MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 2022Document69 pagesPhysiology MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 2022kalalijoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Endocrine IntegumentaryDocument94 pagesReproductive Endocrine IntegumentaryMilyn Mae PalganNo ratings yet
- Animal Form and Function 2: School of Biotechnology, International UniversityDocument79 pagesAnimal Form and Function 2: School of Biotechnology, International UniversityThu AnhNo ratings yet
- Sperm, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSperm, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Understanding Diabetes: Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Diabetes: Anatomy and PhysiologyJas Castro JoveroNo ratings yet
- Glomerulonephritis Medical Student Lecture 2Document67 pagesGlomerulonephritis Medical Student Lecture 2ibnbasheer100% (12)
- Infertility: Kindu Y, LecturerDocument77 pagesInfertility: Kindu Y, LecturerCHALIE MEQUNo ratings yet
- Executive FunctionsDocument9 pagesExecutive FunctionsnieotyagiNo ratings yet
- A Standardized Classification of Hypospadias: Marek OrkiszewskiDocument5 pagesA Standardized Classification of Hypospadias: Marek OrkiszewskibenimhepfiNo ratings yet
- Zoo JR Vii M02 Mouth PartsDocument23 pagesZoo JR Vii M02 Mouth PartsmysixthidisNo ratings yet
- Cherry LoopDocument6 pagesCherry Loopchirag sahgalNo ratings yet
- 10 MODULE VI (Part 1,2,3) Minor Blood Group SystemsDocument56 pages10 MODULE VI (Part 1,2,3) Minor Blood Group SystemsKarl GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Alzimer DiseaseDocument58 pagesAlzimer DiseaseIndra Dhoot100% (1)
- Cytokines and Interferons Types and FunctionsDocument25 pagesCytokines and Interferons Types and FunctionsSereen Abd El-rahmanNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in ScienceMaricel MacabangunNo ratings yet
- The Human Excretory System Functions To Remove Waste From The Human BodyDocument2 pagesThe Human Excretory System Functions To Remove Waste From The Human BodyrawatanandNo ratings yet
- EASA Human Performance PDFDocument15 pagesEASA Human Performance PDFMoslem GrimaldiNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System TerminologiesDocument4 pagesCirculatory System TerminologiesavduqueNo ratings yet
- Dopamine Is An: StructureDocument16 pagesDopamine Is An: StructureYue BiohazardNo ratings yet
- Tooth Structure AnomaliesDocument12 pagesTooth Structure AnomaliesDrSajal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Histology of Large IntestineDocument38 pagesHistology of Large IntestinedoyoumatterindeedNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry HormonesDocument13 pagesBiochemistry HormonesKeziah GillNo ratings yet
- Haemorrhage & ShockDocument22 pagesHaemorrhage & ShockAmiNo ratings yet
- Intrapapillary Injection Technique For ChildrenDocument2 pagesIntrapapillary Injection Technique For ChildrenTyara MekarinaNo ratings yet
- Pain Mechanism: Walton and Torabinejad. Principles and Practice of Endodontics 3Document6 pagesPain Mechanism: Walton and Torabinejad. Principles and Practice of Endodontics 3nilafebryNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Clinical Medicine and Dentistry Kampala International University Western Campus UgandaDocument11 pagesFaculty of Clinical Medicine and Dentistry Kampala International University Western Campus UgandaKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- Broadie 2Document12 pagesBroadie 2Stefana NanuNo ratings yet
- November 2017Document1 pageNovember 2017api-234695862No ratings yet
- Histology of The EarDocument3 pagesHistology of The EarSyahrain SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Test Study GuideDocument26 pagesCardiovascular System Test Study GuideEstherThompsonNo ratings yet
- Cells Tissues and Organs of The Immune System ClassDocument57 pagesCells Tissues and Organs of The Immune System ClassKoushali Banerjee100% (2)
- The Rood Approach TheraExDocument8 pagesThe Rood Approach TheraExLall Jingerppang100% (1)
6.6 Reproductive Systems
6.6 Reproductive Systems
Uploaded by
janCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
6.6 Reproductive Systems
6.6 Reproductive Systems
Uploaded by
janCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 6.
6: ReProduCTIve SySTEmS
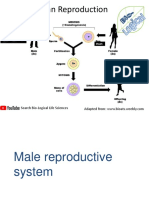
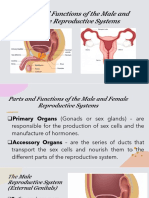
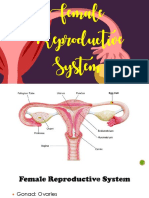
Human Reproductive Systems
Male System: Female System:
Ureter Uterus
Vas
Deferens Bladder
Seminal
Prostate Vesicle
Gland
Urethra Erectile Endometrium Ovary
Tissue
Epididymis Fimbria
Fallopian Tube
Penis Testis (Oviduct) Vagina
Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle involves four key hormones and describes Follicular Phase Luteal Phase
the recurring changes that occur to enable pregnancy
Pituitary
LH
FSH
Pituitary Hormones (FSH and LH):
• Stimulate follicular growth within the ovaries
Follicle
• Stimulate estrogen secretion (from the ovarian follicles)
• Stimulate progesterone secretion (from corpus luteum) Maturing Follicle Corpus Luteum
• A mid-cycle surge in LH triggers ovulation (egg release)
Ovarian
Estrogen
Ovarian Hormones (estrogen and progesterone): Progesterone
• Promote development / thickening of the endometrium
Uterus
• Promote FSH / LH secretion during the follicular phase
• Inhibit FSH / LH secretion during the luteal phase
Day 1 5 10 15 20 25 28
Reproductive Theories
One of the earliest theories involving how human reproduction occurs was the ‘soil and seed’ theory proposed by Aristotle
• Males provide all the information for life in a ‘seed’, which forms an egg when mixed with menstrual blood (the ‘soil’)
William Harvey dissected deer after the mating season and was unable to identify embryos until several months after mating
• He concluded that the ‘soil and seed’ theory was incorrect and that menstrual blood did not contribute to fetal growth
Sex Development In Vitro Fertilisation
Fertilisation requires a combination of male and female ‘seeds’ • Stop normal menstrual cycle with drugs
• Hormone treatments to induce ovulation
Male sex is determined by a gene on the Y chromosome which
• Extract multiple eggs from female
causes gonads to develop as testes and secrete testosterone
• Sperm sample is collected from male
• Testosterone produces sperm and male sex characteristics
• Fertilisation occurs externally (in vitro)
Female reproductive organs develop in the absence of this gene • Implantation of embryos into surrogate
• Estrogen and progesterone develop female sex characteristics • Test for pregnancy to determine success
You might also like
- Viva in Medical Physiology 2nd (Kenneth) PDFDocument267 pagesViva in Medical Physiology 2nd (Kenneth) PDFThida100% (5)
- 4 Male and Female Reproductive Organs PPTDocument71 pages4 Male and Female Reproductive Organs PPTDanica Marie Sibay100% (2)
- Prenatal & Postnatal Growth of MandibleDocument44 pagesPrenatal & Postnatal Growth of MandibleAnkur SharmaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 3RD QuarterDocument13 pagesScience Reviewer 3RD QuarterKurt John DecenaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Review Year II 2019Document31 pagesMidterm Review Year II 2019nc23tengNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in HumansDocument14 pagesReproduction in HumansarnoldnsondojrNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Role of Hormones in The Female and Male Reproductive SystemDocument24 pagesLesson 3: Role of Hormones in The Female and Male Reproductive Systemnathanielstanaj.mNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument36 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemamyNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument69 pagesHuman Reproductionapi-202349222No ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument41 pagesHuman ReproductionMmabatho Vilakazi100% (1)
- Grade 10 Science Quarter 3Document23 pagesGrade 10 Science Quarter 3Mary Cuevas (Ari)No ratings yet
- 1 Reproductive Organs and Hormones 365Document37 pages1 Reproductive Organs and Hormones 365ErivieNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Organs and HormoneDocument37 pagesReproductive Organs and Hormoneishtiyakjafar jafarNo ratings yet
- Understanding Human Reproduction Education Presentation in Peach Violet Hand Drawn Lightly Textured StyleDocument19 pagesUnderstanding Human Reproduction Education Presentation in Peach Violet Hand Drawn Lightly Textured StylemarcosryanhmaranhaoNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument41 pagesHuman ReproductionsimphiwemakhonjwaNo ratings yet
- 1 Reproductive Organs and Hormones 365Document37 pages1 Reproductive Organs and Hormones 365Marvin ObraNo ratings yet
- MF009 6B Human Reproduction System James LDocument26 pagesMF009 6B Human Reproduction System James LPikuNo ratings yet
- Testis and Ovaries: Name - Nisha Rajali Class - 11-BDocument8 pagesTestis and Ovaries: Name - Nisha Rajali Class - 11-BSania BanoNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of The Male and Female Reproductive Systems Role of Hormones in Male and Female Reproductive SystemsDocument27 pagesParts and Functions of The Male and Female Reproductive Systems Role of Hormones in Male and Female Reproductive SystemsDivine GhagaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Human ReproductionDocument48 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Human ReproductionErmiasNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction: Male Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesHuman Reproduction: Male Reproductive SystemMd AmanNo ratings yet
- BiosiceDocument57 pagesBiosiceLJ. Lagaras vlogNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument20 pagesHormonesGabriel LanceNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System NotesDocument40 pagesReproductive System Notesakhtardilshad009No ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesMale Reproductive SystemRico CawasNo ratings yet
- U4 Lesson 4 Human ReproductionDocument27 pagesU4 Lesson 4 Human ReproductionShriNo ratings yet
- Presentation StudentDocument61 pagesPresentation Studentvsvm2009No ratings yet
- Reproductive Tract Cancers: Prevention, Early Diagnosis & Treatment Modalities For Knowledge & AwarenessDocument96 pagesReproductive Tract Cancers: Prevention, Early Diagnosis & Treatment Modalities For Knowledge & AwarenessMOHIT MAROONo ratings yet
- Wa0020Document52 pagesWa0020michaelNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Part3 HumanReproductionDocument27 pagesReproduction Part3 HumanReproductionbiology.alfonsinaNo ratings yet
- BIO NotesDocument7 pagesBIO Notesjohnbenedictsaavedra3No ratings yet
- LESSON 3 - Animal-ReproductionDocument88 pagesLESSON 3 - Animal-ReproductionMary Emmanuelle MañusNo ratings yet
- LFSC REVISION BRIEF NOTES BOOKLET P1 LAST PUSH CAPRICORN SOUTHDocument29 pagesLFSC REVISION BRIEF NOTES BOOKLET P1 LAST PUSH CAPRICORN SOUTHqueenrorisang95No ratings yet
- N-315: Family Health Nursing: Course Coordinator & Instructor: Mrs. Deepa ThomasDocument41 pagesN-315: Family Health Nursing: Course Coordinator & Instructor: Mrs. Deepa ThomasDeepa ThomasNo ratings yet
- Jabba JabbaDocument49 pagesJabba JabbaCombustible DragonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 36-1 Reproductive SystemsDocument25 pagesChapter 36-1 Reproductive Systemsnancie8No ratings yet
- All MCN MidtermDocument207 pagesAll MCN MidtermInah SaritaNo ratings yet
- File 0441Document149 pagesFile 0441Kellie ManganNo ratings yet
- Biology of Human Reproductive SystemDocument51 pagesBiology of Human Reproductive Systemlen lehangNo ratings yet
- Topic 17: ReproductionDocument29 pagesTopic 17: ReproductionEva SidhaniNo ratings yet
- CR 010232Document20 pagesCR 010232kgothatso maleteNo ratings yet
- FEMALE and MALE REPRUDUCTION SYSTEMDocument23 pagesFEMALE and MALE REPRUDUCTION SYSTEMHalseyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document84 pagesChapter 1ismailmohamad373No ratings yet
- Science 10 - Reproductive Health SystemDocument43 pagesScience 10 - Reproductive Health SystemGian Xyrelance IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Reviewer (HumanRep) : PRELIMDocument10 pagesReviewer (HumanRep) : PRELIMHazel GeronimoNo ratings yet
- B11.5 Hormones in Human Reproduction EdDocument16 pagesB11.5 Hormones in Human Reproduction EdBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- CH 46 - Reproductive SystemDocument70 pagesCH 46 - Reproductive SystemSofiaNo ratings yet
- HANDOUTS Finals CH 19Document26 pagesHANDOUTS Finals CH 19hii385156No ratings yet
- Menstrual CycleDocument32 pagesMenstrual CycleJowelyn MaderalNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument43 pagesHuman Reproductive Systembabaaijaz01No ratings yet
- Female ReprodDocument42 pagesFemale Reprodhailu tasheNo ratings yet
- Reproduction SystemDocument81 pagesReproduction SystemGabrielle GreyNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Module 1.3 Reproductive SystemDocument113 pagesQuarter 3 Module 1.3 Reproductive Systemsano.kthNo ratings yet
- PP5.Human Reproduction (Updated)Document65 pagesPP5.Human Reproduction (Updated)hellohlayisoNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction MindmapDocument10 pagesHuman Reproduction MindmapSuyagya PundirNo ratings yet
- Biology 2 Lecture 10 - Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesBiology 2 Lecture 10 - Reproductive SystemRYLE IBANEZNo ratings yet
- Physiology MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 2022Document69 pagesPhysiology MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 2022kalalijoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Endocrine IntegumentaryDocument94 pagesReproductive Endocrine IntegumentaryMilyn Mae PalganNo ratings yet
- Animal Form and Function 2: School of Biotechnology, International UniversityDocument79 pagesAnimal Form and Function 2: School of Biotechnology, International UniversityThu AnhNo ratings yet
- Sperm, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSperm, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Understanding Diabetes: Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Diabetes: Anatomy and PhysiologyJas Castro JoveroNo ratings yet
- Glomerulonephritis Medical Student Lecture 2Document67 pagesGlomerulonephritis Medical Student Lecture 2ibnbasheer100% (12)
- Infertility: Kindu Y, LecturerDocument77 pagesInfertility: Kindu Y, LecturerCHALIE MEQUNo ratings yet
- Executive FunctionsDocument9 pagesExecutive FunctionsnieotyagiNo ratings yet
- A Standardized Classification of Hypospadias: Marek OrkiszewskiDocument5 pagesA Standardized Classification of Hypospadias: Marek OrkiszewskibenimhepfiNo ratings yet
- Zoo JR Vii M02 Mouth PartsDocument23 pagesZoo JR Vii M02 Mouth PartsmysixthidisNo ratings yet
- Cherry LoopDocument6 pagesCherry Loopchirag sahgalNo ratings yet
- 10 MODULE VI (Part 1,2,3) Minor Blood Group SystemsDocument56 pages10 MODULE VI (Part 1,2,3) Minor Blood Group SystemsKarl GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Alzimer DiseaseDocument58 pagesAlzimer DiseaseIndra Dhoot100% (1)
- Cytokines and Interferons Types and FunctionsDocument25 pagesCytokines and Interferons Types and FunctionsSereen Abd El-rahmanNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in ScienceMaricel MacabangunNo ratings yet
- The Human Excretory System Functions To Remove Waste From The Human BodyDocument2 pagesThe Human Excretory System Functions To Remove Waste From The Human BodyrawatanandNo ratings yet
- EASA Human Performance PDFDocument15 pagesEASA Human Performance PDFMoslem GrimaldiNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System TerminologiesDocument4 pagesCirculatory System TerminologiesavduqueNo ratings yet
- Dopamine Is An: StructureDocument16 pagesDopamine Is An: StructureYue BiohazardNo ratings yet
- Tooth Structure AnomaliesDocument12 pagesTooth Structure AnomaliesDrSajal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Histology of Large IntestineDocument38 pagesHistology of Large IntestinedoyoumatterindeedNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry HormonesDocument13 pagesBiochemistry HormonesKeziah GillNo ratings yet
- Haemorrhage & ShockDocument22 pagesHaemorrhage & ShockAmiNo ratings yet
- Intrapapillary Injection Technique For ChildrenDocument2 pagesIntrapapillary Injection Technique For ChildrenTyara MekarinaNo ratings yet
- Pain Mechanism: Walton and Torabinejad. Principles and Practice of Endodontics 3Document6 pagesPain Mechanism: Walton and Torabinejad. Principles and Practice of Endodontics 3nilafebryNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Clinical Medicine and Dentistry Kampala International University Western Campus UgandaDocument11 pagesFaculty of Clinical Medicine and Dentistry Kampala International University Western Campus UgandaKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- Broadie 2Document12 pagesBroadie 2Stefana NanuNo ratings yet
- November 2017Document1 pageNovember 2017api-234695862No ratings yet
- Histology of The EarDocument3 pagesHistology of The EarSyahrain SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Test Study GuideDocument26 pagesCardiovascular System Test Study GuideEstherThompsonNo ratings yet
- Cells Tissues and Organs of The Immune System ClassDocument57 pagesCells Tissues and Organs of The Immune System ClassKoushali Banerjee100% (2)
- The Rood Approach TheraExDocument8 pagesThe Rood Approach TheraExLall Jingerppang100% (1)