Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Digestive System: Faculty of Math and Science, Makassar State University Email
Digestive System: Faculty of Math and Science, Makassar State University Email
Uploaded by
Nur RahmahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Digestive System: Faculty of Math and Science, Makassar State University Email
Digestive System: Faculty of Math and Science, Makassar State University Email
Uploaded by
Nur RahmahCopyright:
Available Formats
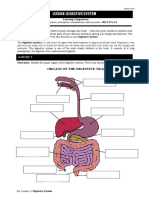
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
Nur Rahmah1), 2021
Faculty of Math and Science, Makassar State University
Email: nurrahmah5501@gmail.com
Abstract
The digestive system breaks down dietary food into small nutrient molecules that can be absorbed
into the plasma for distribution to the body cells. Digestive enzymes are produced primarily by the
pancreas and enterocytes. The production of enzymes by the pancreas, such as amylases and lipases,
is under nervous and hormonal control and increases substantially. Amylase is an enzyme that
catalyses the breakdown of starch into sugars. Amylase is present in human saliva, where it begins
the chemical process of digestion. This practicum aims to determine the working processes of the
amylase enzyme and to determine the digestion process of fat. This practicum will be held on
Saturday, April 24th 2021, from 11.00 AM to 15.00 PM, at the 3rd Floor Zoology Laboratory,
Department of Biology, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Makassar State University.
The results obtained are that the test for the effect of temperature on the work of amylase is blue so
that there is positive starch in the salivary amylase solution, the test for the effect of pH on the work
of amylase turns clear, and on homogeneous bile with fat which proves bile acids can break down fat
in the body.
Keywords: Amilylases, Bile, Digestive, Starch
1. INTRODUCTION Enzymes are one or more polypeptide
Humans eat for many different reasons: groups (protein) which functions as a catalyst
because they are hungry, because they are (compound that is speed up the reaction process
bored, because they are stressed, or simply without reacting) in a chemical reaction.
because the food smells and tastes good. The Enzymes work by attaching themselves to the
biological reason for eating, however, is to molecular surface of the substances it reacts
replenish nutrients and to provide energy to and with thereby speeding up the reaction
support the body's functions. The task of the process. Acceleration happened because the
digestive system is to break down food into the enzyme decreases the activation energy with in
elements that the body can use and to eliminate itself will make the reaction easier. Partly large
as waste whatever is left over. enzymes work typically, meaning each type
Digestion is a process of breakdown enzymes can only work on one kind of
complex compounds into smaller compounds. compound or chemical reaction. This is due to
Digestion is a process of breakdown complex differences in chemical structure each enzyme
compounds into smaller compounds. Process that is fixed. For example, the α- enzyme
the breakdown of these compounds yields that amylase can only be used in the process of
energy essential for the needs of cells, tissues, breaking down starch into glucose.
organs and creatures life. Digestion is a In the digestive system there is also bile
chemical process. Chemical process requires which functions to help break down fat and
the presence of enzymes for chemical changes help digestive enzymes work. Bile build-up
in materials basically. Enzymes play a role in occurs in the liver cells (liver). Liver cells first
increasing speed reaction without affecting the form bile salts from cholesterol. The reaction
reaction product and not participating react. In between cholesterol and various substances in
the process of digestion, enzymes are produced liver cells produces water and a neutral pH
by various organs, such as the small intestine, compound called bile salts. The bile salts then
salivary glands and stomach. Enzymes are mix with water, cholesterol, copper minerals,
specific in the breakdown process complex and bilirubin to form bile. This practicum aims
ingredients (carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins to determine the working processes of the
and minerals). amylase enzyme and to determine the digestion
process of fat.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW AND
HYPOTHESIS DEVELOPMENT
The digestive system breaks down dietary Enzymes are proteins that function as
food into small nutrient molecules that can be biocatalysts in cells life. The advantages of
absorbed into the plasma for distribution to the enzymes over ordinary catalysts are (1) it can
body cells. It also transfers water and increase higher product; (2) works at a
electrolytes from the external environment into relatively neutral pH and a relative temperature
the internal environment. It eliminates low; and (3) specific and selective to certain
undigested food residues to the external substrates. According to Reed (1991), the
environment in the feces (Sherwood, 2010). optimum temperature for α-amylase enzymes
Digestion is regulated by a number of range from 70ºC - 90ºC. In addition, amylase
important hormones, which are secreted from enzymes are active in the pH range 5.2 –5.6
the liver, the pancreas, and the gastrointestinal (Novozyme, 2010). This is supported by
tract, as well as from fat cells. These hormones Fogarty (1983), α-amylase enzymes are
include leptin, which controls hunger generally stable in the pH range 5-8 (Jayanti,
sensations by acting on cells in the 2011).
hypothalamus in the brain; gastrin, which Bile acids are made in the liver by the
prompts the release of acid and increases cytochrome P450-mediated oxidation of
muscle activity in the stomach; glucagon, cholesterol. They are conjugated with taurine or
which stimulates the release of glucose from the amino acid glycine, or with a sulfate or a
the liver into the blood; and insulin, which glucuronide, and are then stored in the
stimulates the absorption of glucose from the gallbladder, which concentrates the salts by
blood into muscles and other tissues (Rogers, removing the water. Bile acids serve other
2011). functions, including eliminating cholesterol
Digestive enzymes are produced primarily from the body, driving the flow of bile to
by the pancreas and enterocytes. The eliminate catabolites from the liver,
production of enzymes by the pancreas, such as emulsifying lipids and fat-soluble vitamins in
amylases and lipases, is under nervous and the intestine to form micelles that can be
hormonal control and increases substantially transported via the lacteal system, and aiding in
during the first 6 weeks after birth (Pluske the reduction of the bacteria flora found in the
2001). During the first 3–4 weeks of life, fetal small intestine and biliary tract. Conjugated
enterocytes that have high endocytotic activity bile acids are more efficient at emulsifying fats
are gradually replaced by adult-type because, at intestinal pH, they are more ionized
enterocytes devoid of such activity. The than unconjugated bile acids (Sharma, 12).
process occurs in a proximal-to-distal direction Bile acids are synthesized by the liver and
in the intestine and is an important part of secreted through the gallbladder into intestinal
intestinal maturation. Changes in enterocyte lumen, then produces compounds emphipatik
generation influence the expression of brush or often called bile salts. The bile salt serves as
border enzymes (Zimmerman, 2012). a detergent, that is breaks down fat into smaller
Amylase is an enzyme that catalyses the formsand absorb fat. Bile acid synthesis that
breakdown of starch into sugars. Amylase is happens in the liver to become its bile salts then
present in human saliva, where it begins the secrete into the intestine and excreted from the
chemical process of digestion. Among other body through feces (Harjana, 2016).
proteins, alpha-amylase is synthesized and
secreted by acinar cells, which make up more 3. PRACTICUM METHODS
than eighty percent of The cells in the major a. Time and Place
salivary gland. The α-amylases are calcium This practicum will be held on Saturday,
metalloenzymes, completely unable to function April 24th 2021, from 11.00 AM to 15.00
in the absence of calcium. By acting at random PM, at the 3rd Floor Zoology Laboratory,
locations along the starch chain, α-amylase Department of Biology, Faculty of
breaks down long-chain carbohydrates, Mathematics and Natural Sciences,
ultimately yielding maltotriose and maltose Makassar State University.
from amylose, or maltose, glucose and limit b. Tools and Materials
dextrin from amylopectin (Abed, 2012). I. Tools
a) Activity 1 h) Record the result by putting a
1) Syringe positive sign (+) for positive
2) 4 Test tube reactions for blue and a
3) Tube rack negative sign (-) for negative
4) Drop pipette reactions in red.
5) Petri dishes for carbohydrate 2) Experiments on the effect of pH on
hydrolysis test amylase action
6) Water baths filled with water a) Give the serial number of the
4°C, 25°C, 37°C, and 70°C. four test tubes and place them
7) Stopwatch on the tube rack
b) Activity 2 b) Add 3 ml of amylase
1) Surgical tools preparation in each tube
2) Straight pin c) Add 3 ml of pH 4 buffer
3) 5 test tubes solution into 1 tube, 3 ml of pH
4) Tube rack 7 buffer solution into a tube of
5) Syringe 2, 3 ml of buffer solution pH 9
6) Stopwatch into tube 3, and 3 ml of
II. Materials aquades into tube 4.
a) Activity 1 d) Put in a water bath at 37 ° C for
1) Starch solution 5 minutes. shake for 5
2) Buffer solution pH 4, pH 7, pH minutes, 15 minutes, and 30
9 minutes. Collect samples at
3) Iodine solution times of 5 minutes, 15 minutes,
4) Water and 30 minutes.
5) Salivary glands e) Perform a flour hydrolysis test
b) Activity 2 by adding iodine solution.
1) coconut oil II. Activity 2
2) Aquades a) Take the gallbladder (fasical fallea)
3) Alcohol 70% from the frog that has been killed.
4) Xylene b) Pour the contents into a clean test
5) Frog bile tube by cutting off the surface of
6) Ether the gallbladder a little.
c. Work Procedure c) Dilute with distilled water until the
I. Activity 1 volume becomes 2 ml.
1) Experiments effect of temperature d) Put a mark on the test tube and
on amylase action place it on the tube rack
a) Drink water then rinse your e) Fill each tube with 2 ml of turmeric
mouth to produce salivary oil.
amylase. f) Add to tube 1 with 5 ml of distilled
b) Place serial number 4 test tubes water. In tube 2 with 5 ml of 70%
and host 3 ml of tube amylase alcohol, tube 3 with 3 ml of xylene.
preparations 1,2,3, and 4. In tube 4 with 3 ml of bile salt
c) Put tube 1 into a 4°C water solution and in tube 5 there is
bath tube 2 into a 37°C water nothing extra.
bath, and tube 3 in a 70°C g) Shake the tubes and observe what
water bath and tube 4 in a happens to the homogeneous
25°C water bath as control. mixing.
d) Add 5 ml of starch solution to h) Repeat the examination 15 minutes
each tube. and 30 minutes later.
e) Shake for 5 minutes and place
back on each tube.
4. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
f) Take a small sample of each
I. Activity 1
mixture and place it in a petri
1) Experiments effect of temperature
dish.
on amylase action
g) Add iodine solution.
Tubes Temperature Reaction Notes the action of amylase, tubes 1,2,3, and 4
1 4ºC + Blue containing salivary glands and added starch
2 37ºC + Blue with each having a temperature of 4ºC, 37 ºC,
3 70ºC + Blue 70 ºC, and 25 ºC, then the sample is taken a
4 25ºC + Blue little and added iodine solution turns blue, this
indicates that starch is present in the amylase
2) Experiments on the effect of pH saliva. If there is starch amylose inside sample
on amylase action solution, it will have an effect in dark blue
formation, this thin caused by the presence of
Tubes Buffer 5 15 30 iodine molecules which is bound in the
Solutio minut minut minut amylose helix coil starch. Iodine is not very
n es es es dissolves in water, making it an iodine reagent
1 Ph 4 White White White made by dissolving iodine inside potassium
(clear) (clear) (clear) iodide solution. This makes up linear triiodide
2 pH 7 White White White complex ion solution. Ion the triiodide ion is
(clear) (clear) (clear) bonded into the coil helix of starch causes
3 pH 9 White White White intensity blue-black color (Zhizhuanget.al,
(clear) (clear) (clear) 2006).
4 Aquade White White White In the experiment of the effect of ph on the
s (clear) (clear) (clear) work of the enzyme, each test tube was filled
with a phosphate buffer solution at different
pHs, namely tube 1 pH 4, tube 2 pH 7, tube 3
II. Activity 2 pH 9, and tube 4 filled with aquades. Then
Tu Solution 5 15 30 shaken for 5 minutes, 15 minutes, and 30
bes minutes minutes minutes minutes. After that, a small sample of salivary
1 Aquadest Hetero- Hetero- Hetero- amylase was taken and added with iodine
geneous geneous geneous solution, then shaken. It was observed that the
2 Alkohol Hetero- Hetero- Hetero- salivary lamilase turned clear at 5, 15, and 30
geneous geneous geneous minutes. Effect of pH on amylase enzyme
3 Xylene Homo- Homo- Homo- activity determining the activity of the amylase
genous genous genous enzyme based on the time of breakdown of
4 Coconut Homo- Homo- Homo- starch into glucose at various pH with the
oil genous genous genous addition of iodine as an indicator which gives a
5 Bile Turbid Turbid Turbid blue color and will turn clear.
In the second activity experiment, the tubes
Amylase enzyme is adigestive enzymes, containing distilled water, 70% alcohol, xylene,
mainly carried out by the pancreas and salivary frog bile, and no additional were each added
glands. The main function of the enzyme with 2 ml of coconut oil, then shaken for 5
amylase is to break down starches in food so minutes, 15 minutes, and 30 minutes. In this
they can be used by body. The amylase enzyme experiment, data obtained from heterogeneous
is classified as a hydrolase enzyme, which is a aquades tubes, heterogeneous alcohol,
catalyst for the bond breaking reaction. homogeneous xylene, homogeneous bile, and
Enzyme activity is influenced by several no additional cloudiness. Xylene and bile show
factors, including pH and temperature. that coconut oil is soluble in this solution. Bile
Enzymes can work at optimum pH and and coconut oil form a homogeneous solution
temperature. The optimum temperature of the and no separation is formed - a separation of
amylase enzyme is 70ºC - 90ºC and the substances is formed. Therefore, it can be
optimum pH is 5-8. proven that bile can dissolve fat or break down
In this practicum, 2 activities were carried fat so that it does not separate from other
out, namely an experiment to determine the solutions. The human body is made up of 70%
working processes of the amylase enzyme (the water. Water in the digestive system functions
effect of temperature and pH on the work of as a solvent for nutrients in food so that it is
amylase), and an experiment to determine the easily absorbed by the body. However, there is
process of digestion of fat. based on the results one nutrient that cannot be dissolved by water,
of observations on the effect of temperature on namely fat. The new fat and water can be
mixed with the help of an emulsifier or Sharma Kirti Rani. 2012. Review on Bile Acid
coagulating agent. This kind of emulsifying Analysis. Int J Pharm Biomed Sci. ISSN:
property is owned by bile acids. Bile acids 0976-5263. 3(2)
have a surface in a way that allows them to
hold fat and water together. Sherwood Lauralee. 2010. Human Physiology:
From Cells to Systems Seventh Edition.
USA: Yolanda Cossio
5. CONCLUSION
The digestive system is a process of Zimmerman Jeffrey J., et al. 2012. Diseases of
breakdown complex compounds into smaller Swine 10th Edition. USA: Wiley-Blackwell
compounds. Amylase is one digestive enzymes
which are mainly produced by salivary glands.
The main function of the enzyme amylase is to
break down starches in food so they can be
used by body. Amylase enzyme Enzymes can
work at optimum pH and temperature. The
optimum temperature of the amylase enzyme is
70ºC - 90ºC and the optimum pH is 5-8. In the
test for the effect of temperature on the work of
amylase, the salivary amylase mixed with
iodine changes color to blue which proves that
there is starch in the solution. On the effect of
pH on the activity of the enzyme amylase,
salivary amylase with the addition of iodine as
an indicator that gives a blue color and will turn
clear. In the digestive system water cannot
dissolve fat. New fats can be broken down in
the body with the help of bile acids. This has
been proven in experiments with frog bile
mixed with coconut oil to produce a
homogeneous solution.
6. REFERENCES
Abed Hayder Hamed. 2012. Alpha – amylase
enzyme evaluation In Saliva of acutely
stressed student. MDJ. 9(1)
Harjana Tri, Kartika R. P., and Tutik Rahayu.
2016. Potensi Buah Salak (Salacca Edulis,
R.) sebagai Suplemen Hipolipidemik
Ditinjau dari Gambaran Histopatologi
Jantung dan Hepar Mencit Yang Diberi
Diet Rendah Lemak. Jurnal Sains Dasar.
5(2)
Jayanti Risha Tiara. 2011. Pengaruh pH, Suhu
Hidrolisis Enzim Α-Amilase Dan Ragi
Roti Untuk Produksi Etanol Menggunakan
Pati Bekatul. Skripsi. Surakarta: Jurusan
Biologi FMIPA UNS
Rogers Kara, Senior Editor, Biomedical
Science. 2011. The Human Body The
Digestive System. New York: Britannica
Educational Publishing
You might also like
- CASE STUDY Intestinal ObstructionDocument68 pagesCASE STUDY Intestinal ObstructionMaria Paula Bungay91% (23)
- KS3 Science Revision WorksheetsDocument104 pagesKS3 Science Revision WorksheetsSofia M Vigo Aguiar100% (6)
- Enzyme PacketDocument3 pagesEnzyme PacketBelinda RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Updated Presentation Note - 082207Document3 pagesUpdated Presentation Note - 082207Joshua AladenikaNo ratings yet
- 39 AnswerDocument9 pages39 AnswerJasmine Nicole EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Experiment 11 - Digestion of FoodstuffsDocument7 pagesExperiment 11 - Digestion of FoodstuffsMark Ryan Tripole100% (1)
- Chapter 03 DigestionDocument11 pagesChapter 03 DigestionaibutyNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Food Digestion Lumiguid 1Document7 pagesLaboratory Food Digestion Lumiguid 1Carea CruzNo ratings yet
- ReadingDocument2 pagesReadingGuritnaNugrahaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes and Digestion Group 2Document111 pagesEnzymes and Digestion Group 2Cassey Hilario100% (4)
- The Biochemistry of Digestion, Absorption and Detoxification by Prof. Dr. Hedef D. El-YassinDocument64 pagesThe Biochemistry of Digestion, Absorption and Detoxification by Prof. Dr. Hedef D. El-YassinSayhidoen CepexNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument8 pagesDigestive SystemAnggi WangriadiNo ratings yet
- Digestion: By: Roselita O. Natividad and Teresita G Montaño, PHD Nat. Science - Ateneo de Zamboanga UniversityDocument5 pagesDigestion: By: Roselita O. Natividad and Teresita G Montaño, PHD Nat. Science - Ateneo de Zamboanga UniversityMini BossNo ratings yet
- Digestion Review SheetDocument7 pagesDigestion Review SheetPaola MontenegroNo ratings yet
- PHYSIOLOGY OF DIGESTION Lec 7Document22 pagesPHYSIOLOGY OF DIGESTION Lec 7Laiba NaeemNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Overview of The Digestive System Physiology of Digestion and AbsorptionDocument26 pagesDigestive System: Overview of The Digestive System Physiology of Digestion and AbsorptionTemz HlubyNo ratings yet
- Analisis de Heces CompletoDocument10 pagesAnalisis de Heces CompletoIvonne SVNo ratings yet
- Reviewer ElsDocument8 pagesReviewer ElsAnsel Francis RapsingNo ratings yet
- Digestion SlideDocument18 pagesDigestion SlideezebelluciNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Parts and FunctionDocument15 pagesDigestive System: Parts and FunctionMica BernardoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition-GSCI1045 Lecture - Week 4Document12 pagesNutrition-GSCI1045 Lecture - Week 4Nicholas ObasiNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and DigestionDocument8 pagesNutrition and DigestionjeffchegzodNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Week 7-Module 7Document9 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Week 7-Module 7Carl Gabriel GravilezNo ratings yet
- 6 Human PhysiologyDocument29 pages6 Human PhysiologyRaynaahNo ratings yet
- Digestive System #3Document10 pagesDigestive System #3Roosebel De Tauro SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Digestive SystemDocument17 pagesBiochemistry of Digestive SystemnishibuchiNo ratings yet
- Updated Presentation Note - 091343Document3 pagesUpdated Presentation Note - 091343Joshua AladenikaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System 2022-23Document28 pagesDigestive System 2022-23Fady Fady100% (1)
- Lab 10 DigestiveDocument9 pagesLab 10 DigestiveBechris BambiNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Digestion and Absorption: Digestion of Food MoleculesDocument24 pages6.1 Digestion and Absorption: Digestion of Food MoleculesWILSON KosheyNo ratings yet
- Calamba Doctors' College: Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Lesson 5Document13 pagesCalamba Doctors' College: Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Lesson 5Melody DoriaNo ratings yet
- Bsczo 301Document386 pagesBsczo 301JjelNo ratings yet
- git pqDocument18 pagesgit pqtaiwodamola789No ratings yet
- DigestionDocument22 pagesDigestionapi-200177496No ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Enzymes PPT 1Document39 pagesGastrointestinal Enzymes PPT 1Ayesha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Human & Social Biology 4th FormDocument23 pagesHuman & Social Biology 4th Formhedasdudh100% (1)
- Transcript The Digestive System - A Journey Through Your Body (Week 5)Document3 pagesTranscript The Digestive System - A Journey Through Your Body (Week 5)siphadube365No ratings yet
- BiochemDocument10 pagesBiochemWaseem Abbas ShaikhNo ratings yet
- The Role of Enzymes in The Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesThe Role of Enzymes in The Digestive SystemJeanAnzurezNo ratings yet
- C ScienceDocument12 pagesC Scienceshaunmakonese9No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Answer KeyDocument2 pagesChapter 8 Answer KeyzakiyaNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Human Digestive System For SSC Exam PDFDocument2 pagesBiology Notes Human Digestive System For SSC Exam PDFनितीन लाठकरNo ratings yet
- Lesson: Digestive System: Activity 1Document5 pagesLesson: Digestive System: Activity 1Akane ForestNo ratings yet
- 09 DigestionDocument85 pages09 DigestionSumihar PasaribuNo ratings yet
- The Digestion ProcessDocument7 pagesThe Digestion ProcessKim Szydney RachoNo ratings yet
- Biopharmaceutics-01 AssignmentDocument14 pagesBiopharmaceutics-01 AssignmentRA TanvirNo ratings yet
- Sains Revision Chapter 3.3 Human Digestive SystemDocument13 pagesSains Revision Chapter 3.3 Human Digestive SystemKELVIN WONG HUNG LIANG MoeNo ratings yet
- How Is Food DigestedDocument12 pagesHow Is Food DigestedNationalKidNo ratings yet
- Basic Nutrition Chapt 1 2022Document59 pagesBasic Nutrition Chapt 1 2022a.joshuaNo ratings yet
- Physioex Digestion (Fin)Document12 pagesPhysioex Digestion (Fin)Tisha TuazonNo ratings yet
- Topic 5Document105 pagesTopic 5melyn chiongNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer - Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesScience Reviewer - Digestive SystemCarlieseNo ratings yet
- Biology Revision NotesDocument34 pagesBiology Revision NotesFreakshow38No ratings yet
- Nutrition: VitaminsDocument29 pagesNutrition: Vitaminsrv5bcgywkpNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Human Digestive System: The Mouth and PharynxDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Human Digestive System: The Mouth and Pharynxitachi278No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology DigestiveDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology DigestiveFretzgine Lou ManuelNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument25 pagesBiologycarlotarubioperez123No ratings yet
- The Chemistry of DigestionDocument18 pagesThe Chemistry of DigestionHarsh PatelNo ratings yet
- Yr 10 WK 3 NoteDocument5 pagesYr 10 WK 3 Notesedrick ocheNo ratings yet
- Biology 13A Lab #13: Nutrition and Digestion: Expected Learning OutcomesDocument13 pagesBiology 13A Lab #13: Nutrition and Digestion: Expected Learning Outcomesdavin gunawanNo ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument3 pagesMetabolismAliyu LawalNo ratings yet
- Digestive Sys Lab WorksheetDocument12 pagesDigestive Sys Lab WorksheetedwardNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesLesson PlanMelita-Mely Baco Pallarco100% (2)
- How and Why Wonder Book of The Human BodyDocument50 pagesHow and Why Wonder Book of The Human Bodykett8233100% (3)
- 15 English PPT Nursing 5 ADocument208 pages15 English PPT Nursing 5 ASinta WuLandari100% (1)
- Sci Digest Circ Respir Systems v1Document36 pagesSci Digest Circ Respir Systems v1draganNo ratings yet
- Digestion Exam Style QuestionDocument4 pagesDigestion Exam Style QuestionIkenna UchechukwuNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument26 pagesDigestive Systemshahrulafzanizam79No ratings yet
- Cancer Statistics, 2011: The Impact of Eliminating Socioeconomic and Racial Disparities On Premature Cancer DeathsDocument25 pagesCancer Statistics, 2011: The Impact of Eliminating Socioeconomic and Racial Disparities On Premature Cancer DeathshamzaloNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation On AppendisectomyDocument32 pagesCase Presentation On AppendisectomyUday Kumar100% (1)
- Biology - Course - Haidar RahhalDocument36 pagesBiology - Course - Haidar RahhalFatima SlimNo ratings yet
- Nursing Case Study: UMC OR RotationDocument32 pagesNursing Case Study: UMC OR RotationMaryjoy EstarisNo ratings yet
- CoC - DG - Supplement - Autopsy of A Deep OneDocument2 pagesCoC - DG - Supplement - Autopsy of A Deep Onebobbob24No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 14 The Digestive SystemDocument116 pagesCHAPTER 14 The Digestive Systemteu doongieNo ratings yet
- Science Class 7thDocument298 pagesScience Class 7thbhat.sohail191No ratings yet
- PEMF To Support Heavy Metal Detoxification (Truly Heal)Document50 pagesPEMF To Support Heavy Metal Detoxification (Truly Heal)Vas Ra100% (5)
- CH 18: Nutrients & Digestion: What You Should Read! Chapter 18 Pages 523 - 529Document13 pagesCH 18: Nutrients & Digestion: What You Should Read! Chapter 18 Pages 523 - 529richteremsNo ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument101 pagesDigestion and Absorptionrhansari1616No ratings yet
- Digestive System and NutritionDocument6 pagesDigestive System and NutritionAthena HuynhNo ratings yet
- AP 10th Class Biology Study MaterialDocument212 pagesAP 10th Class Biology Study MaterialPreeti ThakurNo ratings yet
- Ruminant Digestive SystemDocument12 pagesRuminant Digestive SystemMacharia JosephNo ratings yet
- The Role of Enzymes in The Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesThe Role of Enzymes in The Digestive SystemJeanAnzurezNo ratings yet
- COT Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesCOT Digestive SystemMariel Cardenas100% (1)
- Unit 5: Digestive System Test BankDocument8 pagesUnit 5: Digestive System Test Bankjv peridoNo ratings yet
- Radiography of The GI SystemDocument48 pagesRadiography of The GI SystemSherwyn Nueva- LimNo ratings yet
- Class 7 - Nutrition in AnimalsDocument20 pagesClass 7 - Nutrition in AnimalsSMKNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer For Science Quiz Elementary: MatterDocument30 pagesScience Reviewer For Science Quiz Elementary: MatterIan BelgaNo ratings yet
- GRACE 8 Quarter 4 Lesson 1Document32 pagesGRACE 8 Quarter 4 Lesson 1Mary Dianne BelgaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesNutrition Lesson Planapi-281170522No ratings yet