Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Arco, Brexson - Assign1
Arco, Brexson - Assign1
Uploaded by
Brexson ArcoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Arco, Brexson - Assign1
Arco, Brexson - Assign1
Uploaded by
Brexson ArcoCopyright:
Available Formats
SPI101 ASSIGNMNET 1
BREXSON ARCO 4-12-21
SBIT3Ñ
1. What is sexual harassment?
Sexual Harassment is a behavior. It is defined as unwelcome
behavior of a sexual nature.
Unwelcome Behavior is the critical word. Unwelcome does not
mean "involuntary." A victim may consent or agree to certain
conduct and actively participate in it even though it is offensive
and objectionable.
2. Differentiate Wage and Salary
Wages are the money your employer pays you for the hours you
work each week.
Salary, on the other hand, typically defines a fixed amount your
employer pays you, not necessarily for specific hours worked but
for completing the duties of your job.
3. Types of Wage
Minimum Wage
Minimum wage is the most widely recognized term in the realm of
employee compensation. It is the lowest hourly wage an employer
can pay an employee for work.
Living Wage
Living wage is the lowest wage at which the wage earner and
his/her family can afford the most basic costs of living.
Prevailing Wage
Prevailing wage typically refers to the rate of pay contractors and
vendors must offer their employees when doing business with a
government agency.
Tipped Wage
Tipped wage is a base wage paid to an employee who receives a
substantial portion of his/her compensation from tips.
Fair Wage
By general definition, fair wage is a compilation of company
practices that lead to sustainable wage developments.
4. Factors to Consider in the Formulation of Fair Wages
Ability to Pay
The ability of an industry to pay will influence wage rate to be paid, if the
concern is running into losses, then it may not be able to pay higher wage
rates. A profitable enterprise may pay more to attract good workers.
During the period of prosperity, workers are paid higher wages because
management wants to share the profits with labour.
Demand and Supply
The labour market conditions or demand and supply forces to operate at
the national and local levels and determine the wage rates.
Prevailing Market Rates
No enterprise can ignore prevailing wage rates. The wage rates paid in the
industry or other concerns at the same place will form a base for fixing
wage rates
Cost of Living
In many industries wages are linked to enterprise cost of living which
ensures a fair wages to workers. The wage rates are directly influenced by
cost of living of a place.
Bargaining of Trade Unions
The wage rates are also influenced by the bargaining power of trade
unions.
Productivity
Productivity is the contribution of the workers in order to increase output.
It also measures the contribution of other factors of production like
machines, materials, and management .
Government Regulations
To improve the working conditions of workers, government may pass a
legislation for fixing minimum wages of workers.
Cost of Training
In determining, the wages of the workers, in different occupations,
allowances must be made for all the exercises incurred on training and
time devoted for it.
5. What is Gift giving and Bribery?
A Gift is a thing given willingly to someone without payment; a present.
Give (something) as a gift, especially formally or as a donation or bequest.
Bribery as: the offering, promising, giving, accepting or soliciting of an
advantage as an inducement for an action which is illegal, unethical or a
breach of trust.
6. Factors in Determining the Morality of Gift-Giving
The Value of the Gift.
Purpose of the Gift.
Circumstances under which the Gift was. given or received.
Position between or Relationship of the. Giver and Receiver.
Acceptable Business Practice in the Industry.
Company Policy.
Laws and Regulations.
7. Ethical Advertising?
Ethical advertising is about being truthful concerning the product or
service in question and never exaggerating the capabilities of a
product/service, or hiding its flaws.
8. Define Trade Secret
A trade secret is any practice or process of a company that is generally
not known outside of the company. Information considered a trade
secret gives the company a competitive advantage over its competitors
and is often a product of internal research and development.
9. Ways to Protect Trade Secrets
Restricting access to confidential information physically and electronically
to only those individuals that need to know the information;
Marking documents that they constitute confidential information;
Making use of non-disclosure and confidentiality agreements;
Maintaining information with password protection;
Disposing confidential information by shredding or other means designed
to destroy the information;
Conducting exit interviews with departing employees to ensure the return
of all confidential information in the employee’s possession and to
emphasise confidential obligations;
Ensuring that there are restraint of trade provisions in the employment
contracts;
Establishing due diligence and on-going third party management
procedures;
Instituting and information protection team;
Make trade secret protection a priority
10. Advantages of Trade Secret Protection
Trade secrets involve no registration costs. Obviously there may be costs
associated with the administrative, technical and/or legal barriers the
company puts in place to protect its trade secrets.
Trade secret protection does not require disclosure or registration, unlike
for example a patent which becomes public information
Trade secret protection is not limited in time, unlike for example a patent
which only lasts for twenty years;
Trade secrets have immediate effect, unlike for example a patent which
may take a few years to be granted.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5825)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- NLRC Position Paper JOJODocument15 pagesNLRC Position Paper JOJOramszlai100% (8)
- Injury Claim Information-C188Document10 pagesInjury Claim Information-C188Alex KennedyNo ratings yet
- Compensation Bench Marking Survey Questionnaire Final 1Document6 pagesCompensation Bench Marking Survey Questionnaire Final 1Abhi Chatterjee50% (4)
- Case Study: Dreamworld Amusement Park Dreamworld: Initial Years of OperationDocument3 pagesCase Study: Dreamworld Amusement Park Dreamworld: Initial Years of OperationArnav MittalNo ratings yet
- Labour Law 1Document18 pagesLabour Law 1Heena Shaikh100% (1)
- 405 Case Study MrunalDocument2 pages405 Case Study MrunalMrunal KolteNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 185812Document26 pagesG.R. No. 185812Danica GodornesNo ratings yet
- Employee Loyalty, Organizational Performance & Performance Evaluation - A Critical SurveyDocument13 pagesEmployee Loyalty, Organizational Performance & Performance Evaluation - A Critical SurveyMaheswari GopisettiNo ratings yet
- Complete Tds CourseDocument32 pagesComplete Tds CourseAMLANNo ratings yet
- Income From Salaries: Solutions To Assignment ProblemsDocument8 pagesIncome From Salaries: Solutions To Assignment Problemsvineetsharma04No ratings yet
- 10-Practical Questions of Individuals (78-113)Document38 pages10-Practical Questions of Individuals (78-113)Sajid Saith0% (1)
- Slick Line Operator Oil Field Services Interview Questions and Answers 23620Document12 pagesSlick Line Operator Oil Field Services Interview Questions and Answers 23620Ibrahim DidarNo ratings yet
- Beginner - Level - Questions - With TestdataDocument12 pagesBeginner - Level - Questions - With Testdataarunkumars0121No ratings yet
- Maranguinot V NLRC (G.R. No. 120969. January 22, 1998)Document15 pagesMaranguinot V NLRC (G.R. No. 120969. January 22, 1998)Shila Tabanao VisitacionNo ratings yet
- Namrata Sharma (4 9) - 1Document3 pagesNamrata Sharma (4 9) - 1DeepakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Equal Remuneration ActDocument5 pagesChapter 4 - Equal Remuneration ActHyma TennetiNo ratings yet
- Appointment OrdersDocument115 pagesAppointment OrdersM NageshNo ratings yet
- SCDC 2019 AuditDocument192 pagesSCDC 2019 AuditABC News 4No ratings yet
- Shs Perforated Materials Vs DiazDocument4 pagesShs Perforated Materials Vs DiazKarl Marxcuz ReyesNo ratings yet
- Scarsdale Proposed School BudgetDocument160 pagesScarsdale Proposed School BudgetCara MatthewsNo ratings yet
- Main ReportDocument52 pagesMain ReportTmd TanvirNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Circular For FY2020-21Document87 pagesIncome Tax Circular For FY2020-21Kartik DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- 78-A Prime Security Services Inc. v. NationalDocument8 pages78-A Prime Security Services Inc. v. NationalChristine Gel MadrilejoNo ratings yet
- Organizational Development and Change: 03 Year 02 Semester Individual AssignmentDocument15 pagesOrganizational Development and Change: 03 Year 02 Semester Individual AssignmentYeshNo ratings yet
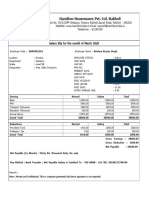
- Hamilton Housewares Pvt. Ltd.-Rakholi: Salary Slip For The Month of March 2020Document1 pageHamilton Housewares Pvt. Ltd.-Rakholi: Salary Slip For The Month of March 2020deepaaithappa020No ratings yet
- Labor Law Cases 2Document10 pagesLabor Law Cases 2Allana Erica CortesNo ratings yet
- Contractor Employee Biographical Data Sheet: 12. Education - Language ProficiencyDocument3 pagesContractor Employee Biographical Data Sheet: 12. Education - Language Proficiencykhanzada akbariNo ratings yet
- Oracle Subqueries Questions McqsDocument42 pagesOracle Subqueries Questions McqsUmer Waqar100% (1)
- IGCSE Business Studies A - Notes C2 People in BusinessDocument21 pagesIGCSE Business Studies A - Notes C2 People in BusinessmohamedNo ratings yet
- Task 1Document4 pagesTask 1malingakalubowilaNo ratings yet