Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 viewsVerazon, Bsn3a-Myastenia NCP
Verazon, Bsn3a-Myastenia NCP
Uploaded by
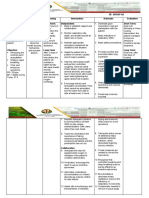
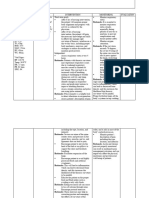
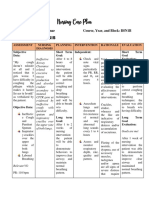
Jaylord Verazon1. The patient has myasthenia gravis, which causes muscle weakness due to antibodies attacking acetylcholine receptors.
2. The nursing plan includes techniques to improve breathing such as deep breathing exercises, incentive spirometry, and diaphragmatic breathing.
3. The short term goals are for the patient to maintain effective breathing patterns and normal respiratory rates and oxygen levels after 8 hours of interventions, and the long term goal is for continued improved breathing after 3 days.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument8 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care Plansmonisha100% (2)
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansjamieboyRN87% (62)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternReichelle Perlas62% (13)
- NCP Multiple SclerosisDocument2 pagesNCP Multiple SclerosisJaylord Verazon100% (2)
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansShaina Fe RabaneraNo ratings yet
- Time Chart: Data Action ResponseDocument2 pagesTime Chart: Data Action ResponseAziil Liiza100% (2)
- Nursing DepartmentDocument15 pagesNursing DepartmentJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Self Liberation by Luis Amann Based On The Teachings of SiloDocument179 pagesSelf Liberation by Luis Amann Based On The Teachings of Silochaitanyasheth100% (2)
- Fairy Tales in Adult Psychotherapy & HypnotherapyDocument15 pagesFairy Tales in Adult Psychotherapy & Hypnotherapyricklff100% (2)
- The Anxiety Workbook For Kids - Take Charge of Fears and Worries Using The Gift of Imagination PDFDocument150 pagesThe Anxiety Workbook For Kids - Take Charge of Fears and Worries Using The Gift of Imagination PDFEduSmile95% (19)
- Management of Pain - Non-Pharmacological Management - Nursing Best Practice GuidelinesDocument2 pagesManagement of Pain - Non-Pharmacological Management - Nursing Best Practice GuidelinesKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationElla EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- NCP Room 303 TelarmaDocument2 pagesNCP Room 303 TelarmaasdasdNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternNicole Genevie MallariNo ratings yet
- Actual - NCP. PT AgnoDocument2 pagesActual - NCP. PT AgnoKate WeyganNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanRachelleNo ratings yet
- Myrna CruzDocument3 pagesMyrna CruzChris Opal NamocatcatNo ratings yet
- Subjective: IndependentDocument2 pagesSubjective: IndependentRea LynNo ratings yet
- Cu 4Document3 pagesCu 4Paul SahagunNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternDocument7 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternDocument8 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument4 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternSeika SouiNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha SuazoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaSofiaLopezNo ratings yet
- Ncp3 CunananDocument2 pagesNcp3 CunananAbbyNo ratings yet
- APOLONIO, Reyjan L. (NCP 1)Document2 pagesAPOLONIO, Reyjan L. (NCP 1)REYJAN APOLONIONo ratings yet
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressDocument2 pagesAsthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressMargarette GeresNo ratings yet
- Copd 2Document3 pagesCopd 2guadalupedeamargaretNo ratings yet
- Case Pres Ncps FinalDocument13 pagesCase Pres Ncps FinalMariejoy YadaoNo ratings yet
- Materi Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageMateri Nursing Care PlanSiti nur Kholifatus samsiyahNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis PneumoniaDocument1 pageNursing Diagnosis PneumoniaPasa ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lipa City CollegesDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lipa City CollegesVincent Maralit MaterialNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJustine Mae A. LoriaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance-Nursing Care Plan For COPDDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance-Nursing Care Plan For COPDRnspeakcom100% (1)
- NCP For CAP TB.Document5 pagesNCP For CAP TB.Cherry Ann BalagotNo ratings yet
- Valerie G. Vergara BSN-3-2Document4 pagesValerie G. Vergara BSN-3-2Valerie VergaraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisDocument19 pagesNursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisRiza Angela BarazanNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageIneffective Airway ClearanceFreisanChenMandumotanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument18 pagesNursing Care PlanLayo, Ivy L.No ratings yet
- DULNUANDocument2 pagesDULNUANJB tindonganNo ratings yet
- Problem 3Document2 pagesProblem 3Janah PagayNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjectivecammel ramos100% (1)
- Intervensi Ispa Dan Oma FixDocument5 pagesIntervensi Ispa Dan Oma FixRizki ArifNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing ActualDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing ActualArian May Marcos100% (1)
- Assessment Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation: Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesAssessment Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation: Nursing DiagnosisLovely CacapitNo ratings yet
- Lumunok at Huminga, Nabibilaukan Din Ako Madalas" AsDocument4 pagesLumunok at Huminga, Nabibilaukan Din Ako Madalas" AsPatricia Ortega100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPLP Benoza100% (2)
- Asuhan Keperawatan Pada Bayi S Dengan Asfeksia BeratDocument5 pagesAsuhan Keperawatan Pada Bayi S Dengan Asfeksia BeratGrimmboyYTNo ratings yet
- Case Study:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCase Study:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharlynne AraojoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan in Pedia Ward: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan in Pedia Ward: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharlynne AraojoNo ratings yet
- NCP NutriDocument3 pagesNCP NutricelestirolNo ratings yet
- Assessment Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationIrish Jane GalloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cystic FibrosisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cystic FibrosisYael EzraNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationYzel Vasquez AdavanNo ratings yet
- Lung Cancer N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesLung Cancer N C P BY BHERU LALBheru Lal100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective BreathingDocument6 pagesNCP Ineffective BreathingCuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process Care Plan For Ineffective Breathing Pattern Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation EvaluationDocument19 pagesNursing Process Care Plan For Ineffective Breathing Pattern Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation EvaluationZIANAH JOY FAMYNo ratings yet
- University of Cordilleras College of Nursing NCP: Mycobacterium TuberculosisDocument3 pagesUniversity of Cordilleras College of Nursing NCP: Mycobacterium TuberculosisLyn MhoreNo ratings yet
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument3 pagesSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- GROUP 8 NCP Patient FDocument12 pagesGROUP 8 NCP Patient FasdasdNo ratings yet
- NCP SciDocument3 pagesNCP SciJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Assesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha Suazo100% (1)
- The Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessFrom EverandThe Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessNo ratings yet
- Evidence-Based Respiratory MedicineFrom EverandEvidence-Based Respiratory MedicinePeter G. GibsonNo ratings yet
- JSVFDocument1 pageJSVFJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- AsncudDocument2 pagesAsncudJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 Paper Work The Influence of Cultural and Health Belief System On Health Care PracticesDocument4 pagesActivity 4 Paper Work The Influence of Cultural and Health Belief System On Health Care PracticesJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Journal Making 2 CFE 106 2 Term: Title of The Journal Biblical Passage ContextDocument2 pagesJournal Making 2 CFE 106 2 Term: Title of The Journal Biblical Passage ContextJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Nursing DepartmentDocument14 pagesNursing DepartmentJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- In Partial Fulfillment: Small Study Group (SSG)Document9 pagesIn Partial Fulfillment: Small Study Group (SSG)Jaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Nursing DepartmentDocument29 pagesNursing DepartmentJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- NCP - Major Depressive DisorderDocument7 pagesNCP - Major Depressive DisorderJaylord Verazon100% (1)
- Nursing DepartmentDocument10 pagesNursing DepartmentJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical Mobility Related To Application of Traction or Cast As Evidenced by AssessmentDocument13 pagesImpaired Physical Mobility Related To Application of Traction or Cast As Evidenced by AssessmentJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- NCP SciDocument3 pagesNCP SciJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- NCP GbsDocument2 pagesNCP GbsJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome EtiologyDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome EtiologyJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Pathophysiology/ Scientific Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Pathophysiology/ Scientific Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Hip Fracture Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Goal & Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For Hip Fracture Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Goal & Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationJaylord Verazon100% (1)
- Comprehensive Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesComprehensive Nursing Care PlanJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Ancheta Et Al Handwashing - Chap4Document53 pagesAncheta Et Al Handwashing - Chap4Jaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic EvaluationDocument29 pagesDiagnostic EvaluationJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy PPTDocument58 pagesChemotherapy PPTJaylord Verazon100% (1)
- NCP Escaran.Document3 pagesNCP Escaran.Roswell Almodiel EscaranNo ratings yet
- ASALEXU Volume 21 Issue 2 Pages 69-82Document14 pagesASALEXU Volume 21 Issue 2 Pages 69-82احمد العايديNo ratings yet
- Brain TapDocument4 pagesBrain TapAnandSindhu100% (1)
- Cognitve Behavioral Therapy Training in Core Skills Presentation NASBHCDocument41 pagesCognitve Behavioral Therapy Training in Core Skills Presentation NASBHCNadiaNo ratings yet
- Time Management GuideDocument99 pagesTime Management GuideRacso ZamboangaNo ratings yet
- 10 Simple Solutions To Worry Gyoerkoe en 10802Document5 pages10 Simple Solutions To Worry Gyoerkoe en 10802talalNo ratings yet
- 9 Anger Dealing With Anger and ImpulsivityDocument2 pages9 Anger Dealing With Anger and ImpulsivityChatura UdharaNo ratings yet
- Session 16 Evoe Spring Spa A Positioning DilemmaDocument13 pagesSession 16 Evoe Spring Spa A Positioning DilemmaharshkarNo ratings yet
- KNGF Guideline: Cardiac RehabilitationDocument2 pagesKNGF Guideline: Cardiac RehabilitationsilkofosNo ratings yet
- Depression Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesDepression Cheat Sheetsaphal sapkotaNo ratings yet
- Stress ManagementDocument71 pagesStress ManagementHardik Patel100% (1)
- Shibashi Set 2 HandoutDocument8 pagesShibashi Set 2 HandoutBambang SudarmadiNo ratings yet
- NCP Pain Post CsDocument1 pageNCP Pain Post Csrholiboi50% (2)
- Games For Accelerating Learning ManualDocument196 pagesGames For Accelerating Learning Manualmasterjyotish100% (17)
- Monologue: How To Improve Your Health: Speaking Practice Tests English C1Document3 pagesMonologue: How To Improve Your Health: Speaking Practice Tests English C1Zuk V CastilloNo ratings yet
- Ndnyt SyllabusDocument32 pagesNdnyt SyllabusVedic Yog Peeth100% (1)
- Oyster Spa Brochure 2022Document28 pagesOyster Spa Brochure 2022Oyster WellnessNo ratings yet
- Hypnosis For BeginnersDocument76 pagesHypnosis For Beginnersrizal paluNo ratings yet
- APA Style NDocument21 pagesAPA Style NZainab SheikhNo ratings yet
- 479 Initial 2-Page Reflection PaperDocument4 pages479 Initial 2-Page Reflection Paperapi-678203412No ratings yet
- Your Blueprint To No ContactDocument40 pagesYour Blueprint To No Contacttobascodudepro100% (3)
- Terra Rosa Emagazine Issue 1Document45 pagesTerra Rosa Emagazine Issue 1Terra RosaNo ratings yet
- Strtess Management TextbookDocument52 pagesStrtess Management TextbookYanti HarjonoNo ratings yet
- Six Ways of Parenting Under StressDocument33 pagesSix Ways of Parenting Under StressCute Aaliya100% (1)
- Mindfulness: Activating The Parasympathetic Wing of Your Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesMindfulness: Activating The Parasympathetic Wing of Your Nervous SystemTereNo ratings yet
Verazon, Bsn3a-Myastenia NCP
Verazon, Bsn3a-Myastenia NCP
Uploaded by
Jaylord Verazon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views5 pages1. The patient has myasthenia gravis, which causes muscle weakness due to antibodies attacking acetylcholine receptors.
2. The nursing plan includes techniques to improve breathing such as deep breathing exercises, incentive spirometry, and diaphragmatic breathing.
3. The short term goals are for the patient to maintain effective breathing patterns and normal respiratory rates and oxygen levels after 8 hours of interventions, and the long term goal is for continued improved breathing after 3 days.
Original Description:
Gg
Original Title
VERAZON, BSN3A-MYASTENIA NCP
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The patient has myasthenia gravis, which causes muscle weakness due to antibodies attacking acetylcholine receptors.
2. The nursing plan includes techniques to improve breathing such as deep breathing exercises, incentive spirometry, and diaphragmatic breathing.
3. The short term goals are for the patient to maintain effective breathing patterns and normal respiratory rates and oxygen levels after 8 hours of interventions, and the long term goal is for continued improved breathing after 3 days.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views5 pagesVerazon, Bsn3a-Myastenia NCP
Verazon, Bsn3a-Myastenia NCP
Uploaded by
Jaylord Verazon1. The patient has myasthenia gravis, which causes muscle weakness due to antibodies attacking acetylcholine receptors.
2. The nursing plan includes techniques to improve breathing such as deep breathing exercises, incentive spirometry, and diaphragmatic breathing.
3. The short term goals are for the patient to maintain effective breathing patterns and normal respiratory rates and oxygen levels after 8 hours of interventions, and the long term goal is for continued improved breathing after 3 days.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
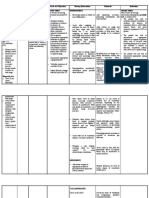
VERAZON, JAYLORD B.
BSN 3A MYASTENIA GRAVIS NCP
ASSESSMENT NURSING SCIENTIFIC PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS EXPLANATION/
PATHOPHYSIOLOG
Y
SUBJECTIVE DATA: "INEFECTIVE SHORT TERM 1. Place patient with 1. A sitting position SHORT TERM
NONE BREATHING Thymus gland stay OBJECTIVE: proper body alignment permits maximum lung OBJECTIVE
PATTERN RELATED large and develops After 8hours of for maximum excursion and chest After 8hours of
OBJECTIVE DATA: TO RESPIRATORY tumors in adult. Nursing Intervention breathing pattern. expansion. Nursing Intervention
-Tachypnea MUSCLE the patient will able to 2. Encourage sustained 2. These techniques the patient will able to
-Presence of crackles WEAKNESS" * maintains an deep breaths by: promotes deep * maintained an
on both lung field Thymus erroneously effective breathing Using demonstration: inspiration, which effective breathing
upon auscultation causes immune cells to pattern, as evidenced highlighting slow increases oxygenation pattern, as evidenced
-use of accesory produce antibodies that by relaxed breathing at inhalation, holding end and prevents by relaxed breathing at
muscle when breathing attacks the receptor normal rate and depth inspiration for a few atelectasis. Controlled normal rate and depth
-orthopnea sites on the voluntary and absence of seconds, and passive breathing methods and absence of
-cyanosis muscle neuromuscular dyspnea. exhalation may also aid slow dyspnea.
junction. * the respiratory rate • respirations in patients * established a good
remains within Utilizing who are tachypneic. respiratory rate within
VITAL SIGN established limits. incentive spirometer Prolonged expiration limits
-Respiratory rate- Antibodies produce by * the ABG levels • prevents air trapping. * established a good
28cpm thymus will bind to the return to and remain Requiring the 3. This method relaxes ABG level within
nicotinic acetylcholine within established patient to yaw muscles and increases limits
receptors in muscle limits. 3. Encourage the patient’s oxygen * indicates either
fibers. * indicates, either diaphragmatic level. verbally or through
verbally or through breathing for patients 4. This training behavior, feeling
behavior, feeling with chronic disease. improves conscious comfortable when
Blocking the receptors comfortable when 4. Evaluate the control of respiratory breathing.
sites of acetylcholine breathing. appropriateness of muscles and * reports feeling rested
produce by the nerve * reports feeling rested inspiratory muscle inspiratory muscle each day.
that is made up of each day. training. strength. * performed
cholinergic fibers. * performs 5. Provide respiratory 5. Beta-adrenergic diaphragmatic pursed-
diaphragmatic pursed- medications and agonist medications lip breathing.
lip breathing. oxygen, per doctor’s relax airway smooth * demonstrated a
VERAZON, JAYLORD B. BSN 3A MYASTENIA GRAVIS NCP
* demonstrates orders. muscles and cause maximum lung
Less acetylcholine is maximum lung 6. Avoid high bronchodilation to expansion with
absorbed by the muscle expansion with concentration of open air passages. adequate ventilation.
fiber. Plus, more adequate ventilation. oxygen in patients 6. Hypoxia triggers the * carried out ADLs,
acetylcholine is being * carries out ADLs, with COPD. drive to breathe in the breathing pattern
digest by the enzyme breathing pattern 7. Maintain a clear chronic CO2 retainer remains normal.
acetylcholinesterase. remains normal. airway by encouraging patient. When LONG TERM
patient to mobilize administering oxygen, OBJECTIVE
LONG TERM own secretions with close monitoring is After 3 days of
Muscle weakness in OBJECTIVE successful coughing. very important to Nursing intervertion,
voluntary muscle such After 3 days of nursing 8. Suction secretions, avoid uncertain risings the patient shall have
respiratory muscle. intervention, the as necessary. in the patient’s PaO2, applied techniques that
patient would be able 9. Stay with the patient which could lead to improved breathing
to apply techniques during acute episodes apnea. pattern and be free
that would improve of respiratory distress 7. This facilitates from signs and
breathing pattern and 10. Ambulate patient adequate clearance of symptoms of
be free from signs and as tolerated with secretions respiratory distrees and
symptoms of doctor’s order three 8. This facilitates AEB respiratory rate
respiratory distress. times daily. adequate clearance of within normal range,
11. Encourage secretions. absence of cyanosis,
frequent rest periods 9. This is to clear effective breathing and
and teach patient to blockage in airway. minimal use of
pace activity. 10. This will reduce accesorry muscle
12. Consult dietitian the patient’s anxiety,
for dietary thereby reducing
modifications oxygen demand.
13. Encourage small 11. Ambulation can
frequent meals. further break up and
14. Help patient with move secretions that
ADLs, as necessary. block the airways.
15. Avail a fan in the 12. Extra activity can
room worsen shortness of
16. Encourage social breath. Ensure the
VERAZON, JAYLORD B. BSN 3A MYASTENIA GRAVIS NCP
interactions with patient rests between
others that have strenuous activities.
medical diagnoses of 13. COPD may cause
ineffective breathing malnutrition which can
pattern. affect breathing
17. Educate patient or pattern. Good nutrition
significant other can strengthen the
proper breathing, functionality of
coughing, and respiratory muscles.
splinting methods. 14. This prevents
18. Educate patient crowding of the
about medications: diaphragm.
indications, dosage, 15. This conserves
frequency, and energy and avoids
possible side effects. overexertion and
Incorporate review of fatigue.
metered-dose inhaler 16. Moving air can
and nebulizer decrease feelings of air
treatments, as needed. hunger.
19. Teach patient 17. Talking to others
about: with similar conditions
pursed-lip breathing can help to ease
abdominal breathing anxiety and increase
performing relaxation coping skills.
technique 18. These allow
performing relaxation sufficient mobilization
techniques of secretions.
taking prescribed 19. This information
medications (ensuring promotes safe and
accuracy of dose and effective medication
frequency and administration.
monitoring adverse 20. These measures
effects) allow patient to
VERAZON, JAYLORD B. BSN 3A MYASTENIA GRAVIS NCP
scheduling activities to participate in
avoid fatigue and maintaining health
provide for rest period status and improve
20. Refer patient for ventilation.
evaluation of exercise 21. Exercise promotes
potential and conditioning of
development of respiratory muscles
individualized exercise and patient’s sense of
program. well-being
Establishes arousal
ability or level of
consciousness.
This activity will
further increase
intracranial pressure.
The medication such
as Dextromethorphan
will act to the brain to
reduce the urge to
VERAZON, JAYLORD B. BSN 3A MYASTENIA GRAVIS NCP
cough.
You might also like
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument8 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care Plansmonisha100% (2)
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansjamieboyRN87% (62)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternReichelle Perlas62% (13)
- NCP Multiple SclerosisDocument2 pagesNCP Multiple SclerosisJaylord Verazon100% (2)
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansShaina Fe RabaneraNo ratings yet
- Time Chart: Data Action ResponseDocument2 pagesTime Chart: Data Action ResponseAziil Liiza100% (2)
- Nursing DepartmentDocument15 pagesNursing DepartmentJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Self Liberation by Luis Amann Based On The Teachings of SiloDocument179 pagesSelf Liberation by Luis Amann Based On The Teachings of Silochaitanyasheth100% (2)
- Fairy Tales in Adult Psychotherapy & HypnotherapyDocument15 pagesFairy Tales in Adult Psychotherapy & Hypnotherapyricklff100% (2)
- The Anxiety Workbook For Kids - Take Charge of Fears and Worries Using The Gift of Imagination PDFDocument150 pagesThe Anxiety Workbook For Kids - Take Charge of Fears and Worries Using The Gift of Imagination PDFEduSmile95% (19)
- Management of Pain - Non-Pharmacological Management - Nursing Best Practice GuidelinesDocument2 pagesManagement of Pain - Non-Pharmacological Management - Nursing Best Practice GuidelinesKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationElla EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- NCP Room 303 TelarmaDocument2 pagesNCP Room 303 TelarmaasdasdNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternNicole Genevie MallariNo ratings yet
- Actual - NCP. PT AgnoDocument2 pagesActual - NCP. PT AgnoKate WeyganNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanRachelleNo ratings yet
- Myrna CruzDocument3 pagesMyrna CruzChris Opal NamocatcatNo ratings yet
- Subjective: IndependentDocument2 pagesSubjective: IndependentRea LynNo ratings yet
- Cu 4Document3 pagesCu 4Paul SahagunNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternDocument7 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternDocument8 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Breathing PatternJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument4 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternSeika SouiNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha SuazoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaSofiaLopezNo ratings yet
- Ncp3 CunananDocument2 pagesNcp3 CunananAbbyNo ratings yet
- APOLONIO, Reyjan L. (NCP 1)Document2 pagesAPOLONIO, Reyjan L. (NCP 1)REYJAN APOLONIONo ratings yet
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressDocument2 pagesAsthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressMargarette GeresNo ratings yet
- Copd 2Document3 pagesCopd 2guadalupedeamargaretNo ratings yet
- Case Pres Ncps FinalDocument13 pagesCase Pres Ncps FinalMariejoy YadaoNo ratings yet
- Materi Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageMateri Nursing Care PlanSiti nur Kholifatus samsiyahNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis PneumoniaDocument1 pageNursing Diagnosis PneumoniaPasa ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lipa City CollegesDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lipa City CollegesVincent Maralit MaterialNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJustine Mae A. LoriaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance-Nursing Care Plan For COPDDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance-Nursing Care Plan For COPDRnspeakcom100% (1)
- NCP For CAP TB.Document5 pagesNCP For CAP TB.Cherry Ann BalagotNo ratings yet
- Valerie G. Vergara BSN-3-2Document4 pagesValerie G. Vergara BSN-3-2Valerie VergaraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisDocument19 pagesNursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisRiza Angela BarazanNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageIneffective Airway ClearanceFreisanChenMandumotanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument18 pagesNursing Care PlanLayo, Ivy L.No ratings yet
- DULNUANDocument2 pagesDULNUANJB tindonganNo ratings yet
- Problem 3Document2 pagesProblem 3Janah PagayNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjectivecammel ramos100% (1)
- Intervensi Ispa Dan Oma FixDocument5 pagesIntervensi Ispa Dan Oma FixRizki ArifNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing ActualDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing ActualArian May Marcos100% (1)
- Assessment Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation: Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesAssessment Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation: Nursing DiagnosisLovely CacapitNo ratings yet
- Lumunok at Huminga, Nabibilaukan Din Ako Madalas" AsDocument4 pagesLumunok at Huminga, Nabibilaukan Din Ako Madalas" AsPatricia Ortega100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPLP Benoza100% (2)
- Asuhan Keperawatan Pada Bayi S Dengan Asfeksia BeratDocument5 pagesAsuhan Keperawatan Pada Bayi S Dengan Asfeksia BeratGrimmboyYTNo ratings yet
- Case Study:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCase Study:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharlynne AraojoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan in Pedia Ward: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan in Pedia Ward: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharlynne AraojoNo ratings yet
- NCP NutriDocument3 pagesNCP NutricelestirolNo ratings yet
- Assessment Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationIrish Jane GalloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cystic FibrosisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cystic FibrosisYael EzraNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationYzel Vasquez AdavanNo ratings yet
- Lung Cancer N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesLung Cancer N C P BY BHERU LALBheru Lal100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective BreathingDocument6 pagesNCP Ineffective BreathingCuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process Care Plan For Ineffective Breathing Pattern Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation EvaluationDocument19 pagesNursing Process Care Plan For Ineffective Breathing Pattern Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation EvaluationZIANAH JOY FAMYNo ratings yet
- University of Cordilleras College of Nursing NCP: Mycobacterium TuberculosisDocument3 pagesUniversity of Cordilleras College of Nursing NCP: Mycobacterium TuberculosisLyn MhoreNo ratings yet
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument3 pagesSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- GROUP 8 NCP Patient FDocument12 pagesGROUP 8 NCP Patient FasdasdNo ratings yet
- NCP SciDocument3 pagesNCP SciJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Assesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha Suazo100% (1)
- The Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessFrom EverandThe Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessNo ratings yet
- Evidence-Based Respiratory MedicineFrom EverandEvidence-Based Respiratory MedicinePeter G. GibsonNo ratings yet
- JSVFDocument1 pageJSVFJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- AsncudDocument2 pagesAsncudJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 Paper Work The Influence of Cultural and Health Belief System On Health Care PracticesDocument4 pagesActivity 4 Paper Work The Influence of Cultural and Health Belief System On Health Care PracticesJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Journal Making 2 CFE 106 2 Term: Title of The Journal Biblical Passage ContextDocument2 pagesJournal Making 2 CFE 106 2 Term: Title of The Journal Biblical Passage ContextJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Nursing DepartmentDocument14 pagesNursing DepartmentJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- In Partial Fulfillment: Small Study Group (SSG)Document9 pagesIn Partial Fulfillment: Small Study Group (SSG)Jaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Nursing DepartmentDocument29 pagesNursing DepartmentJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- NCP - Major Depressive DisorderDocument7 pagesNCP - Major Depressive DisorderJaylord Verazon100% (1)
- Nursing DepartmentDocument10 pagesNursing DepartmentJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical Mobility Related To Application of Traction or Cast As Evidenced by AssessmentDocument13 pagesImpaired Physical Mobility Related To Application of Traction or Cast As Evidenced by AssessmentJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- NCP SciDocument3 pagesNCP SciJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- NCP GbsDocument2 pagesNCP GbsJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome EtiologyDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome EtiologyJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Pathophysiology/ Scientific Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Pathophysiology/ Scientific Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Hip Fracture Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Goal & Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For Hip Fracture Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Goal & Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationJaylord Verazon100% (1)
- Comprehensive Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesComprehensive Nursing Care PlanJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Ancheta Et Al Handwashing - Chap4Document53 pagesAncheta Et Al Handwashing - Chap4Jaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic EvaluationDocument29 pagesDiagnostic EvaluationJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy PPTDocument58 pagesChemotherapy PPTJaylord Verazon100% (1)
- NCP Escaran.Document3 pagesNCP Escaran.Roswell Almodiel EscaranNo ratings yet
- ASALEXU Volume 21 Issue 2 Pages 69-82Document14 pagesASALEXU Volume 21 Issue 2 Pages 69-82احمد العايديNo ratings yet
- Brain TapDocument4 pagesBrain TapAnandSindhu100% (1)
- Cognitve Behavioral Therapy Training in Core Skills Presentation NASBHCDocument41 pagesCognitve Behavioral Therapy Training in Core Skills Presentation NASBHCNadiaNo ratings yet
- Time Management GuideDocument99 pagesTime Management GuideRacso ZamboangaNo ratings yet
- 10 Simple Solutions To Worry Gyoerkoe en 10802Document5 pages10 Simple Solutions To Worry Gyoerkoe en 10802talalNo ratings yet
- 9 Anger Dealing With Anger and ImpulsivityDocument2 pages9 Anger Dealing With Anger and ImpulsivityChatura UdharaNo ratings yet
- Session 16 Evoe Spring Spa A Positioning DilemmaDocument13 pagesSession 16 Evoe Spring Spa A Positioning DilemmaharshkarNo ratings yet
- KNGF Guideline: Cardiac RehabilitationDocument2 pagesKNGF Guideline: Cardiac RehabilitationsilkofosNo ratings yet
- Depression Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesDepression Cheat Sheetsaphal sapkotaNo ratings yet
- Stress ManagementDocument71 pagesStress ManagementHardik Patel100% (1)
- Shibashi Set 2 HandoutDocument8 pagesShibashi Set 2 HandoutBambang SudarmadiNo ratings yet
- NCP Pain Post CsDocument1 pageNCP Pain Post Csrholiboi50% (2)
- Games For Accelerating Learning ManualDocument196 pagesGames For Accelerating Learning Manualmasterjyotish100% (17)
- Monologue: How To Improve Your Health: Speaking Practice Tests English C1Document3 pagesMonologue: How To Improve Your Health: Speaking Practice Tests English C1Zuk V CastilloNo ratings yet
- Ndnyt SyllabusDocument32 pagesNdnyt SyllabusVedic Yog Peeth100% (1)
- Oyster Spa Brochure 2022Document28 pagesOyster Spa Brochure 2022Oyster WellnessNo ratings yet
- Hypnosis For BeginnersDocument76 pagesHypnosis For Beginnersrizal paluNo ratings yet
- APA Style NDocument21 pagesAPA Style NZainab SheikhNo ratings yet
- 479 Initial 2-Page Reflection PaperDocument4 pages479 Initial 2-Page Reflection Paperapi-678203412No ratings yet
- Your Blueprint To No ContactDocument40 pagesYour Blueprint To No Contacttobascodudepro100% (3)
- Terra Rosa Emagazine Issue 1Document45 pagesTerra Rosa Emagazine Issue 1Terra RosaNo ratings yet
- Strtess Management TextbookDocument52 pagesStrtess Management TextbookYanti HarjonoNo ratings yet
- Six Ways of Parenting Under StressDocument33 pagesSix Ways of Parenting Under StressCute Aaliya100% (1)
- Mindfulness: Activating The Parasympathetic Wing of Your Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesMindfulness: Activating The Parasympathetic Wing of Your Nervous SystemTereNo ratings yet