Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCM 105 Week 11
NCM 105 Week 11
Uploaded by
Hannah Leigh CastilloCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- How To Download Ebook PDF Primary Care of Women 2Nd Edition by Barbara K Hackley Ebook PDF Docx Kindle Full ChapterDocument36 pagesHow To Download Ebook PDF Primary Care of Women 2Nd Edition by Barbara K Hackley Ebook PDF Docx Kindle Full Chaptersteve.books604100% (32)
- Medical Pathology Ii. Pathology of Urinary System Lectuer NotesDocument26 pagesMedical Pathology Ii. Pathology of Urinary System Lectuer Noteseric epahNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Genitourinary DisordersDocument7 pagesPediatric Genitourinary Disorderscayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis Lab Report 2Document7 pagesUrinalysis Lab Report 2salman ahmedNo ratings yet
- NCLEX (Valerie) PDFDocument18 pagesNCLEX (Valerie) PDFValerie Orengo100% (1)
- Genito-Urinary SystemDocument7 pagesGenito-Urinary Systemugaban.rhaine.bNo ratings yet
- Renal System (Output)Document30 pagesRenal System (Output)Tiffy SuarezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Excretory System PDFDocument17 pagesChapter 9 Excretory System PDFErica Ann Ical100% (1)
- Clinical MicrosDocument14 pagesClinical MicrosKRISTINE JOY PANGAHINNo ratings yet
- Final Management of Upper Urinary Tract ObstructionDocument83 pagesFinal Management of Upper Urinary Tract ObstructiondhabeNo ratings yet
- URINALYSISDocument6 pagesURINALYSISmaeNo ratings yet
- A. B. C. A. B. C. D.: Clinical Chemistry II - Prelims (Bandala)Document19 pagesA. B. C. A. B. C. D.: Clinical Chemistry II - Prelims (Bandala)IceNo ratings yet
- Clin Micro - Introduction and UrinalysisDocument2 pagesClin Micro - Introduction and UrinalysisbiancsNo ratings yet
- Aubf ReviewerDocument8 pagesAubf ReviewerAngel Cris Alegado AguirreNo ratings yet
- 1st Week Aubf Mtap and Semr FinalsDocument48 pages1st Week Aubf Mtap and Semr FinalsKrenz CatiboNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Introduction To Urinalysis PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Introduction To Urinalysis PDFJulie Anne Soro ValdezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Urinalysis: Student Notes: AubfDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Urinalysis: Student Notes: AubfMelody Jane PardilloNo ratings yet
- AUBFDocument28 pagesAUBFMichelle San Miguel FeguroNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Investigation of Renal FunctionDocument34 pagesBiochemical Investigation of Renal FunctionUhuebor DavidNo ratings yet
- Final VPhy102 Functional Anatomy of The Urinary SystemDocument23 pagesFinal VPhy102 Functional Anatomy of The Urinary SystemThereza CahigNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4-Renal Function and AbnormalitiesDocument30 pagesLecture 4-Renal Function and AbnormalitiesThe Great AmegboNo ratings yet
- Kidney Disease Basics: Andrew Narva, MD, Fasn & Amy Barton Pai, Pharmd, Mhi, Fasn, FCCP, FNKFDocument75 pagesKidney Disease Basics: Andrew Narva, MD, Fasn & Amy Barton Pai, Pharmd, Mhi, Fasn, FCCP, FNKFDaniel Apuan SalviejoNo ratings yet
- Module 10 - Drugs Affecting The Urinary SystemDocument6 pagesModule 10 - Drugs Affecting The Urinary Systemsammcabico.studentNo ratings yet
- Urinary System Diseases: PathophysiologyDocument31 pagesUrinary System Diseases: Pathophysiologyai nisa hasnasariNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument4 pagesThe Urinary SystemtnorcilleNo ratings yet
- Section D - Work BookDocument69 pagesSection D - Work BookMohamed AbbasNo ratings yet
- Urinary System Diseases: PathophysiologyDocument31 pagesUrinary System Diseases: PathophysiologyMuhammad Wishal KhanNo ratings yet
- 16 - Urinary System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument58 pages16 - Urinary System Anatomy and PhysiologyNickson OnchokaNo ratings yet
- (BIO) Chapter 9 - Excretion in HumansDocument14 pages(BIO) Chapter 9 - Excretion in Humansanya desilvaNo ratings yet
- Renal Function (2)Document20 pagesRenal Function (2)nekemwbnheismwbwoNo ratings yet
- MNT in Diseases of Kidney and UrinaryDocument38 pagesMNT in Diseases of Kidney and UrinaryJosephine A. Bertulfo100% (1)
- Urinalysis Chapter 5Document178 pagesUrinalysis Chapter 5Sanket GuptaNo ratings yet
- RenalSystem Part 1 (Spring2020)Document49 pagesRenalSystem Part 1 (Spring2020)Sahil ParikhNo ratings yet
- L6 - Biochemistry of The Renal SystemDocument10 pagesL6 - Biochemistry of The Renal SystemmujahidatinstituteNo ratings yet
- L2-SCBM 343-2 Urine-WJDocument42 pagesL2-SCBM 343-2 Urine-WJpond_1993No ratings yet
- UrinaryDocument3 pagesUrinaryIYA LABAO100% (1)
- RENAL FUNCTION TESTS (Lecture)Document8 pagesRENAL FUNCTION TESTS (Lecture)mulengaemmanuel350No ratings yet
- Tubular Reabsorption TestDocument2 pagesTubular Reabsorption TestFait HeeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Foundation: Mrs. Neha Babru Asst - ProfessorDocument29 pagesNursing Foundation: Mrs. Neha Babru Asst - ProfessorSharon LawrenceNo ratings yet
- L. Genitourinary ImagingDocument36 pagesL. Genitourinary ImagingkamariahsamahNo ratings yet
- Clinical Micrsocopy 1.2Document5 pagesClinical Micrsocopy 1.2monzon.mika1801No ratings yet
- Anaphy FinalDocument22 pagesAnaphy FinalMa Sofiya Yazmin OroñaNo ratings yet
- Intro To UrinalysisDocument25 pagesIntro To Urinalysisp6hccq6jd7No ratings yet
- Renal PPT RevisedDocument101 pagesRenal PPT RevisedPatricia Mag-akatNo ratings yet
- AP15 UrinaryDocument10 pagesAP15 UrinaryPay per PrintNo ratings yet
- Lab 8 Anatomy Physiology of Urinary System - TaggedDocument27 pagesLab 8 Anatomy Physiology of Urinary System - TaggedSaraNo ratings yet
- 8 HAPN23A Genitourinary SystemDocument30 pages8 HAPN23A Genitourinary SystemJezebel MolinoNo ratings yet
- Hepatobiliary-Dr - Kim-Shi-Tan (2022)Document9 pagesHepatobiliary-Dr - Kim-Shi-Tan (2022)rmt_01No ratings yet
- Pathophys UrinaryDocument31 pagesPathophys UrinaryDr Anais AsimNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument50 pagesThe Urinary SystemDasari PrasadNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of The Urine Production (2021)Document80 pagesThe Physiology of The Urine Production (2021)Shelly NobelNo ratings yet
- Renal or Urinary Tract DisorderDocument6 pagesRenal or Urinary Tract DisorderMarcel Quario OrinaNo ratings yet
- Liver Function (1)Document16 pagesLiver Function (1)nekemwbnheismwbwoNo ratings yet
- Kidney FunctionDocument64 pagesKidney FunctionVincent LivandyNo ratings yet
- Posterior Urethral Valves and VURDocument56 pagesPosterior Urethral Valves and VURdhabeNo ratings yet
- Aubf Lab Transes 1Document3 pagesAubf Lab Transes 1Princess Eve OlowanNo ratings yet
- Continence Problem at HomeDocument71 pagesContinence Problem at HomeZayar HmunNo ratings yet
- SEHH2234 2021 S2 Ch16 Urinary System StudentsDocument58 pagesSEHH2234 2021 S2 Ch16 Urinary System Studentsmiki leeNo ratings yet
- Aubf Prelim 1Document59 pagesAubf Prelim 1Kat JornadalNo ratings yet
- Bio 208 Urinary SystemDocument121 pagesBio 208 Urinary SystemNazir RabiuNo ratings yet
- 2 Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument9 pages2 Fluids and ElectrolytesHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Real World Ready Program Suplemental Study Guide September NCM 105-Fluid & ElectrolytesDocument8 pagesReal World Ready Program Suplemental Study Guide September NCM 105-Fluid & ElectrolytesHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument6 pagesWeek 1 Fluids and ElectrolytesHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Background Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument9 pagesBackground Fluids and ElectrolytesHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Week 1: Future Ready Future Smart ProgramDocument10 pagesStudy Guide Week 1: Future Ready Future Smart ProgramHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- "Pediatrics 103" Assignment No. 2: What Are Stages of Cognitive Development by Jean Fiaget?Document4 pages"Pediatrics 103" Assignment No. 2: What Are Stages of Cognitive Development by Jean Fiaget?Hannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Geria Part 1Document16 pagesGeria Part 1Hannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Leopold'S Maneuver: Position & PresentationDocument23 pagesLeopold'S Maneuver: Position & PresentationHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Healthcare TeamDocument20 pagesGeriatric Healthcare TeamHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- "Volleyball": CASTILLO, Hannah Leigh RDocument43 pages"Volleyball": CASTILLO, Hannah Leigh RHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- "Pediatrics Week 1": CASTILLO, Hannah Leigh R. ALHP 2-0 1. What Is Growth and Development?Document4 pages"Pediatrics Week 1": CASTILLO, Hannah Leigh R. ALHP 2-0 1. What Is Growth and Development?Hannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4:: Entrepreneurs and Social EntrepreneurshipDocument24 pagesLesson 4:: Entrepreneurs and Social EntrepreneurshipHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Skills Laboratory NCM 103: Prof. Michael H. EsmillaDocument30 pagesSkills Laboratory NCM 103: Prof. Michael H. EsmillaHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- NSTP 2:Cwts/Lts Curricular ProgramDocument32 pagesNSTP 2:Cwts/Lts Curricular ProgramHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Perineal Care: Michael H. Esmilla, RN, MANDocument15 pagesPerineal Care: Michael H. Esmilla, RN, MANHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- 11.7 Worksheet 1Document4 pages11.7 Worksheet 1Amrita MallickNo ratings yet
- A Step by Step Guide For Conducting A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis With Simulation DataDocument9 pagesA Step by Step Guide For Conducting A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis With Simulation DataIlmiatus QoyimahNo ratings yet
- Lizo ForceDocument3 pagesLizo ForcegkvanuNo ratings yet
- 11.2 Baseline Medical Surveillance ProcedureDocument18 pages11.2 Baseline Medical Surveillance ProcedureaceNo ratings yet
- Atlas of ECGDocument162 pagesAtlas of ECGMiuschaNo ratings yet
- SpIn SnOutDocument1 pageSpIn SnOutAj GenoNo ratings yet
- Hypovolamic HypernatremiaDocument9 pagesHypovolamic Hypernatremiaharsh singhviNo ratings yet
- Finals TFN ReviewerDocument5 pagesFinals TFN ReviewerNicole Faith L. NacarioNo ratings yet
- DementiaDocument874 pagesDementiaKoko Riko100% (3)
- Med Surg: GI - Gastrointestinal: PathophysiologyDocument1 pageMed Surg: GI - Gastrointestinal: PathophysiologyTori RolandNo ratings yet
- Week 6-MCQ in EBP-1Document36 pagesWeek 6-MCQ in EBP-1Hasan KhawaldehNo ratings yet
- Tamwed - Mooligai Thottam Project Evaluation JANUARY 2012Document11 pagesTamwed - Mooligai Thottam Project Evaluation JANUARY 2012Manigandan BalajiNo ratings yet
- Molecular Genetics and Metabolism Reports: Case ReportDocument4 pagesMolecular Genetics and Metabolism Reports: Case ReportLeidy Paola Gamboa GamboaNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityLouie Danielle SegarraNo ratings yet
- Frenle Revie Np3 and Np4-1Document49 pagesFrenle Revie Np3 and Np4-1erjen gamingNo ratings yet
- Phylum: Apicomplexa (Because The Apical Point of The Parasite Complex) (Blood and Tissue SporozoaDocument34 pagesPhylum: Apicomplexa (Because The Apical Point of The Parasite Complex) (Blood and Tissue Sporozoaammar amerNo ratings yet
- Precociou S Puberty: BY Vishnupriya Ravimohandoss Year-6 Group-1Document31 pagesPrecociou S Puberty: BY Vishnupriya Ravimohandoss Year-6 Group-1Priya RaviNo ratings yet
- Life Span Development 16th Edition Santrock Test BankDocument31 pagesLife Span Development 16th Edition Santrock Test Bankbrandoncoletjaxprigfm100% (40)
- Name: Vivienne Gaille O. Aguarille Section: NGDocument2 pagesName: Vivienne Gaille O. Aguarille Section: NGvivienne gailleNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology Ii MCQ:: Prepared By: Srey Viso, Pharmd Medical Biologist & Microbiology, DMM For Pharmacy ClassDocument21 pagesBacteriology Ii MCQ:: Prepared By: Srey Viso, Pharmd Medical Biologist & Microbiology, DMM For Pharmacy ClassPiseth VichhekaNo ratings yet
- JatamansiDocument2 pagesJatamansiDinesh Joshi100% (1)
- Hyperbaric Oxygen TherapyDocument147 pagesHyperbaric Oxygen TherapyDavid Omar Navarro LeijaNo ratings yet
- Fact Lym Eng Final Ver4 16nov07Document3 pagesFact Lym Eng Final Ver4 16nov07luthfiana syarifahNo ratings yet
- Composition About The HolidaysDocument1 pageComposition About The HolidaysIssufoAbdalaNo ratings yet
- Head Boy 0-36Document1 pageHead Boy 0-36Almira ClaraNo ratings yet
- Computation For Health Prioritization: Mabini Colleges IncorporatedDocument6 pagesComputation For Health Prioritization: Mabini Colleges IncorporatedGrascia SchneiderNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Destroy - UpsellDocument23 pagesDiabetes Destroy - UpsellSofy AndersonNo ratings yet
- Heath Assessment ToolDocument8 pagesHeath Assessment ToolHouda Hayek100% (1)
NCM 105 Week 11
NCM 105 Week 11
Uploaded by
Hannah Leigh CastilloOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCM 105 Week 11
NCM 105 Week 11
Uploaded by
Hannah Leigh CastilloCopyright:
Available Formats
MRE-COL-SG-WK1
REAL WORLD READY PROGRAM
SUPLEMENTAL STUDY GUIDE
Subject NCM 105- FLUIDS & ELECTROLYTES
Topic Urinary System
Course/Year BSN – 3rd Year
Week Week 11
School Year 1st Semester/AY 2020-2021
I. Objectives
• Recall anatomy of Urinary System
• Identify drugs affecting Nephron activity & Diagnostic Test used to
determine problem in the urinary system
• Enumerate Common Disorder in the Urinary System, identify its causes,
sign & symptoms and appropriate management.
II. Discussion
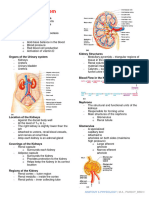
Normal Functions:
- Upper Urinary Tract
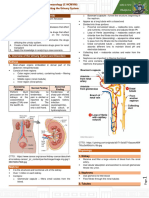
• Kidney functional unit is Nephron
*Ultrafiltration of blood
* Maintenance of H20 & electrolyte hemeostasis
- Lower urinary Tract
• Pelvicalyceal – urine collection
• Ureters – transportation of urine
• Bladder & Urethra – storage & voiding of urine
- Glomerulus
*Filter fluids at a rate of 180L/day
©2020 Good Samaritan Colleges
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including Page1 of 12
photocopying, recording, or other electronic or mechanical methods, without the prior written permission of the Good Samaritan Colleges.
MRE-COL-SG-WK1
*Act as a bulk filter to pass along protein-free & RBC free filtered
- Proximal Tubule
*Has freely permeable cell membrane
* Re absorb most electrolytes, glucose, urea & amino acid
*Carries large amounts of H20 with electrolytes back to circulation
*Reduces H20 content of filtrate by 70%
- Loop of Henle
*Contains a high concentration of salts, mostly Na
*Pulls Cl & Na out of filtrate without H20 & re absorb them in ascending limb
*Causes filtrate to become more dilute as it moves into distal tubules
- Distal Tubule
*Reabsorb H20 & concentrate urine as a result of antidiuretic hormone action
*Reabsorb Na & H20
*Secretes K as a result of aldosterone action
- Collecting Duct
* Has ADH which reabsorb H20
* Absorbs or secrete K,Na, Urea, hydrogen ions & ammonia according to the
body needs
Promotion of Normal Urinary Functions:
• Adults
-Adequate hydration
-Activity
-Regular Habits
• Children
Proper Toilet Training:
-2 ½ -3 ½ years old – bladder reflex control
-3 years old - regular voiding habits
- 4 years old - independent bathroom activities
- 5 years old - nighttime control
Drugs Affecting Nephron Activity:
1. Dopamine
2. Carbonic anhydrase inghibitors
3. K-sparing diuretics
©2020 Good Samaritan Colleges
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including Page2 of 12
photocopying, recording, or other electronic or mechanical methods, without the prior written permission of the Good Samaritan Colleges.
MRE-COL-SG-WK1
4. Thiazide diuretics
5. Metazolone
6. Mannitol
7. Loop Diuretics
Diagnostic Studies:
• Urinalysis
• Urine Culture & Sensitivity
• Cystometrogram
• Creatine clearance
• BUN
• Cystoscopy
• Cystourethrogram
• Intravenous Pyelogram
• Renal Scan
• Ultrasound
• Renal Biopsy
• Schilling Test
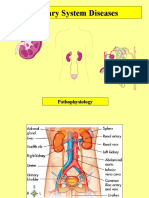
Common Disorder in the Urinary System:
Congenital Malformations of the Urinary System
- Epispadias – Urethral opening on dorsal surface of the penis
- Hypospadias- Male urethral opening on the ventral surface of penis or female
urethral opening in vagina
- Bladder Exstrophy- Posterior & lateral surfaces of the bladder are exposed
Management:
• Surgical Correction
• Reconstructive surgery
Enuresis
- Bed wetting in a child over 4 years old
- Usually have small bladder capacity
- More common in males
- Tend to be deep sleeper
©2020 Good Samaritan Colleges
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including Page3 of 12
photocopying, recording, or other electronic or mechanical methods, without the prior written permission of the Good Samaritan Colleges.
MRE-COL-SG-WK1
Urinary Tract Infection
- is a microbial invasion of the kidneys, ureters, bladder or urethra
Causes:
• Incomplete bladder emptying
• Irritation by bubble baths
• Poor hygiene
• Reflux
Sign & Symptoms:
- Cloudy & foul- smelling urine
- Low grade fever
- Lethargy
- Hematuria
- Abdominal pain
- Enuresis
- Poor feeding pattern
- Frequent urges to void
Treatment:
- Force fluids
- Cranberry Juice
- Assess toileting habits
- Proper perineal hygiene
- Antibiotics
Renal & Urethral Stones
- Mineral crystallization form around organic matter
Types:
• Urolithiasis
-Urinary stones
• Nephrolithiasis
-Kidney Stone
Kidney Stone
- A hard mass developed from crystals that separate from the urine & build up
on the inner surface of the kidney
- Made of salts & mineral
Common Cause:
• Inadequate fluid replacement
• Medical condition
• Family history
©2020 Good Samaritan Colleges
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including Page4 of 12
photocopying, recording, or other electronic or mechanical methods, without the prior written permission of the Good Samaritan Colleges.
MRE-COL-SG-WK1
Predisposing Factors:
- UTI
- DHN
- Hypercalcemia
- Urinary Stasis
- Obstruction
- Genetics
Risk Factor:
• Men at age 40’s-70’s
• Women at age 50’s
• Diet
Food rich in Vitamin C & D
Foods rich in protein, Na, Ca, Oxalate rich foods
• Weight gain
• High BMI
• Large waist size
• Inactive person
• Some medicine
Sign & Symptoms:
- Excruciating pain in the lower back and/or side, groin, abdiomen
- Fever & chills
- Nausea & Vomiting
- Hematuria
- Diaphoresis
- Low grade fever
Diagnostic Test:
• Helical CT Scan
• Ultrasound
Management:
• Monitor I & O
• Force fluid
• Strain urine
• Monitor temperature
• Pain Management
• Diet
-Low Ca
-Low Protein
- Low Na
-Low in Uric acid
-Low in oxalates
©2020 Good Samaritan Colleges
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including Page5 of 12
photocopying, recording, or other electronic or mechanical methods, without the prior written permission of the Good Samaritan Colleges.
MRE-COL-SG-WK1
Treatment:
• Lithotripsy
• Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy
Prevention:
Drink 10 glass of H20 per day
Cystitis
- Inflammation of the bladder
Predisposing factor:
• More prone in female
• Catheterization, instrumention
• Nosocomial infection
• Kidney infection
• Pregnancy
• Sexual intercourse
• Stagnation of urine in the bladder
• Radiation
• Incorrect perineal hygiene
• Obstruction of the urethra
• Kidney infection
Sign & symptoms:
-Urgency
-Frequency
- Burning during radiation
- Low grade fever
- Suprapubic/flank tenderness
- Pus/blood in urine
Diagnostic Test:
• Cystoscopy
• Urine C & S
Nursing Management:
-Force Fluids to 3000ml/d
-Antibiotic therapy
-Encourage drinking cranberry juice
-Discourage caffeine
-Teach females to avoid following intercourse
-Clean properly after defecation
-Obtain clean-catch midstream urine specimen for urinalysis, C& S,
colony count & possible gram stain
©2020 Good Samaritan Colleges
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including Page6 of 12
photocopying, recording, or other electronic or mechanical methods, without the prior written permission of the Good Samaritan Colleges.
MRE-COL-SG-WK1
Medication:
-Antibiotics
-Urinary Tract analgesic
- Antipyretic
Acute Glomerulonephritis
- Primary or secondary autoimmune renal disease involving the glomerulus in
the kidney
Causes:
-Bacterial
-Viral
-Parasitic Pathogen
Sign & Symptoms:
• Oliguria
• Hematuria
• Fever & chills
• Anorexia
• Nausea & Vomiting
• Abdominal/flank pain
• Periorbital/facial/generalized edema
• Moderate-severe HTN
Management:
-Restrict H20 if Oliguria
-Restrict Na intake
-Daily weights
-Monitor I & O
-Bedrest
-High-calorie, low protein diet
-Medications:
Antibiotics
Corticosteroid
Antihypertensive
Immunosuppressive agent
- Dialysis/Plasma electrophoreses if renal failure develops
Acute Tubular Necrosis
- Medical condition involving the death of tubular cells that form the tubule
that transports urine to the ureters while reabsorbing 99% of the H20
Causes:
-Poisons
-Drugs
-Heavy Metals
©2020 Good Samaritan Colleges
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including Page7 of 12
photocopying, recording, or other electronic or mechanical methods, without the prior written permission of the Good Samaritan Colleges.
MRE-COL-SG-WK1
-Molecules
-Organic solvents
Hydronephrosis
- Renal Colic
- Distention & dilation of the renal pelvis, usually caused by obstruction of the
free flow of urine from the kidney leading to tissue destruction & renal failure
Assessment:
• Pain
• Nausea & Vomiting
• S/S of UTI
• Abdominal Muscle spasm
Management:
-Bedrest
-Antibiotics
-Catheterization
-Force fluids to 300ml/d
-Urinary diversion
Surgical Corre tion
Strain all urine
Nephrosis
-Nephrotic Syndrome
-Idiopathic syndrome characterized by proteinuria & hypoalbuminemia
Types:
• Congenital Nephrotic syndrome
• Secondary Nephrotic syndrome
• Idiopathic Nephrotic syndrome
Sign & Symptoms:
-Edema
-Pallor
-Lethargy
-Oliguria
-Dark, frothy urine
-Decrease serum protein
-Increased serum Cholesterol & plasma lipids
Nursing Management:
-Steroids & antibiotic therapy
- Monitor for infection
- Bedrest
- Fluid restriction
©2020 Good Samaritan Colleges
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including Page8 of 12
photocopying, recording, or other electronic or mechanical methods, without the prior written permission of the Good Samaritan Colleges.
MRE-COL-SG-WK1
-I & O
-High protein, low Na, high Caloric diet
Pyelonephritis
- Urinary/ chronic infection & inflammation of the kidney or renal pelvis
Predisposing factor:
• Pregnancy
• Urinary Obstruction
• Metabolic Disorder
• Trauma
• Obstruction
• UTI
• Bacterial Infection
Sign & Symptoms;
-Chills
-Fever
-General malaise
-Pyuria
-Flank pain/Back pain
Nursing Management:
-Serial urine culture
-Periodic blood test
-Bedrest
-Antibiotic therapy
Urinary Retention
- Also known as Ischuria
- Lack of ability to urinate
Causes:
• Functional
• Mechanical
Predisposing Factor:
-Bedrest
-Tumors
-Prostatic Hypertrophy
-Decrease Bladder tone
-Bladder/urethral cancer
-Post op effects
-Calculi
-Medications
©2020 Good Samaritan Colleges
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including Page9 of 12
photocopying, recording, or other electronic or mechanical methods, without the prior written permission of the Good Samaritan Colleges.
MRE-COL-SG-WK1
Clinical Manifestation:
• Voiding at frequent intervals in small amount
• Suprapubic discomfort & bladder distention
• Appropriate hydration with no urinary output for more than 6 hours
• Specific gravity is elevated
Complications:
-Rupture of bladder
-Infection
-Uremia
Management:
-Stimulate voiding
-Pouring tepid water over perineum
-Positioning
-Catheterization
-Surgery:
* Suprapubic cystostomy
* Surgery for kidney stones
©2020 Good Samaritan Colleges
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including Page10 of
photocopying, recording, or other electronic or mechanical methods, without the prior written permission of the Good Samaritan Colleges.
12
MRE-COL-SG-WK1
III. Learning Rubric
Instruction: Please read carefully and check the corresponding box for your answer.
(Basahin ng mabuti ang bawat tanong at i-tsek ang kahon ng iyong sagot).
Note: Your honest answers will help us gather accurate data to understand and provide
appropriate interventions for the topic discussed. (Ang matapat na pagsagot ay
makapagbibigay ng tumpak na datos upang mas higit na maunawaan at makapagbigay
ng nararapat interbensiyon patungkol sa paksang ito.)
CONTENT YES MAYBE NO
(2)
(3) (1)
1. I have background knowledge about the topic.
(Mayroon na akong konting kaalaman tungkol sa paksa.)
2. I can analyze the content to deepen my understanding.
(Kaya kong suriing mabuti ang paksa upang mapalawak pa ang
aking kaalaman.)
3. I can give my own examples.
(Kaya kong magbigay ng sarili kong halimbawa.)
4. I can summarize the content and information that I have
learned.
(Kaya kong lagumin ang paksa at ang kaalamang aking
natutunan.)
5. I clearly understood the topic.
(Lubos kong naunawaan ang paksa ng aralin.)
6. I understand the direction of each activity and answered it
correctly.
(Nauunawan ko ang panuto ng bawat gawain at nasagutan ito ng
tama.)
7. I can enumerate the necessary steps and procedures related
to the lesson.
(Kaya kong hanayin ang mga hakbang at proseso na may
kaugnayan sa paksang tinalakay.)
8. I can independently perform the skill, strategy, or process.
(Kaya kong i-apply ang aking natutunan upang magsagawa ng
isang kasanayan, pamamaraan, o proseso.)
9. I can relate the topic to real-life situations.
(Kaya kong iugnay ang paksa sa totoong buhay.)
10. I accomplished the task on time.
(Natapos ko ang mga gawain sa itinakdang oras.)
©2020 Good Samaritan Colleges
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including Page11 of
photocopying, recording, or other electronic or mechanical methods, without the prior written permission of the Good Samaritan Colleges.
12
MRE-COL-SG-WK1
©2020 Good Samaritan Colleges
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including Page12 of
photocopying, recording, or other electronic or mechanical methods, without the prior written permission of the Good Samaritan Colleges.
12
You might also like
- How To Download Ebook PDF Primary Care of Women 2Nd Edition by Barbara K Hackley Ebook PDF Docx Kindle Full ChapterDocument36 pagesHow To Download Ebook PDF Primary Care of Women 2Nd Edition by Barbara K Hackley Ebook PDF Docx Kindle Full Chaptersteve.books604100% (32)
- Medical Pathology Ii. Pathology of Urinary System Lectuer NotesDocument26 pagesMedical Pathology Ii. Pathology of Urinary System Lectuer Noteseric epahNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Genitourinary DisordersDocument7 pagesPediatric Genitourinary Disorderscayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis Lab Report 2Document7 pagesUrinalysis Lab Report 2salman ahmedNo ratings yet
- NCLEX (Valerie) PDFDocument18 pagesNCLEX (Valerie) PDFValerie Orengo100% (1)
- Genito-Urinary SystemDocument7 pagesGenito-Urinary Systemugaban.rhaine.bNo ratings yet
- Renal System (Output)Document30 pagesRenal System (Output)Tiffy SuarezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Excretory System PDFDocument17 pagesChapter 9 Excretory System PDFErica Ann Ical100% (1)
- Clinical MicrosDocument14 pagesClinical MicrosKRISTINE JOY PANGAHINNo ratings yet
- Final Management of Upper Urinary Tract ObstructionDocument83 pagesFinal Management of Upper Urinary Tract ObstructiondhabeNo ratings yet
- URINALYSISDocument6 pagesURINALYSISmaeNo ratings yet
- A. B. C. A. B. C. D.: Clinical Chemistry II - Prelims (Bandala)Document19 pagesA. B. C. A. B. C. D.: Clinical Chemistry II - Prelims (Bandala)IceNo ratings yet
- Clin Micro - Introduction and UrinalysisDocument2 pagesClin Micro - Introduction and UrinalysisbiancsNo ratings yet
- Aubf ReviewerDocument8 pagesAubf ReviewerAngel Cris Alegado AguirreNo ratings yet
- 1st Week Aubf Mtap and Semr FinalsDocument48 pages1st Week Aubf Mtap and Semr FinalsKrenz CatiboNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Introduction To Urinalysis PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Introduction To Urinalysis PDFJulie Anne Soro ValdezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Urinalysis: Student Notes: AubfDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Urinalysis: Student Notes: AubfMelody Jane PardilloNo ratings yet
- AUBFDocument28 pagesAUBFMichelle San Miguel FeguroNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Investigation of Renal FunctionDocument34 pagesBiochemical Investigation of Renal FunctionUhuebor DavidNo ratings yet
- Final VPhy102 Functional Anatomy of The Urinary SystemDocument23 pagesFinal VPhy102 Functional Anatomy of The Urinary SystemThereza CahigNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4-Renal Function and AbnormalitiesDocument30 pagesLecture 4-Renal Function and AbnormalitiesThe Great AmegboNo ratings yet
- Kidney Disease Basics: Andrew Narva, MD, Fasn & Amy Barton Pai, Pharmd, Mhi, Fasn, FCCP, FNKFDocument75 pagesKidney Disease Basics: Andrew Narva, MD, Fasn & Amy Barton Pai, Pharmd, Mhi, Fasn, FCCP, FNKFDaniel Apuan SalviejoNo ratings yet
- Module 10 - Drugs Affecting The Urinary SystemDocument6 pagesModule 10 - Drugs Affecting The Urinary Systemsammcabico.studentNo ratings yet
- Urinary System Diseases: PathophysiologyDocument31 pagesUrinary System Diseases: Pathophysiologyai nisa hasnasariNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument4 pagesThe Urinary SystemtnorcilleNo ratings yet
- Section D - Work BookDocument69 pagesSection D - Work BookMohamed AbbasNo ratings yet
- Urinary System Diseases: PathophysiologyDocument31 pagesUrinary System Diseases: PathophysiologyMuhammad Wishal KhanNo ratings yet
- 16 - Urinary System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument58 pages16 - Urinary System Anatomy and PhysiologyNickson OnchokaNo ratings yet
- (BIO) Chapter 9 - Excretion in HumansDocument14 pages(BIO) Chapter 9 - Excretion in Humansanya desilvaNo ratings yet
- Renal Function (2)Document20 pagesRenal Function (2)nekemwbnheismwbwoNo ratings yet
- MNT in Diseases of Kidney and UrinaryDocument38 pagesMNT in Diseases of Kidney and UrinaryJosephine A. Bertulfo100% (1)
- Urinalysis Chapter 5Document178 pagesUrinalysis Chapter 5Sanket GuptaNo ratings yet
- RenalSystem Part 1 (Spring2020)Document49 pagesRenalSystem Part 1 (Spring2020)Sahil ParikhNo ratings yet
- L6 - Biochemistry of The Renal SystemDocument10 pagesL6 - Biochemistry of The Renal SystemmujahidatinstituteNo ratings yet
- L2-SCBM 343-2 Urine-WJDocument42 pagesL2-SCBM 343-2 Urine-WJpond_1993No ratings yet
- UrinaryDocument3 pagesUrinaryIYA LABAO100% (1)
- RENAL FUNCTION TESTS (Lecture)Document8 pagesRENAL FUNCTION TESTS (Lecture)mulengaemmanuel350No ratings yet
- Tubular Reabsorption TestDocument2 pagesTubular Reabsorption TestFait HeeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Foundation: Mrs. Neha Babru Asst - ProfessorDocument29 pagesNursing Foundation: Mrs. Neha Babru Asst - ProfessorSharon LawrenceNo ratings yet
- L. Genitourinary ImagingDocument36 pagesL. Genitourinary ImagingkamariahsamahNo ratings yet
- Clinical Micrsocopy 1.2Document5 pagesClinical Micrsocopy 1.2monzon.mika1801No ratings yet
- Anaphy FinalDocument22 pagesAnaphy FinalMa Sofiya Yazmin OroñaNo ratings yet
- Intro To UrinalysisDocument25 pagesIntro To Urinalysisp6hccq6jd7No ratings yet
- Renal PPT RevisedDocument101 pagesRenal PPT RevisedPatricia Mag-akatNo ratings yet
- AP15 UrinaryDocument10 pagesAP15 UrinaryPay per PrintNo ratings yet
- Lab 8 Anatomy Physiology of Urinary System - TaggedDocument27 pagesLab 8 Anatomy Physiology of Urinary System - TaggedSaraNo ratings yet
- 8 HAPN23A Genitourinary SystemDocument30 pages8 HAPN23A Genitourinary SystemJezebel MolinoNo ratings yet
- Hepatobiliary-Dr - Kim-Shi-Tan (2022)Document9 pagesHepatobiliary-Dr - Kim-Shi-Tan (2022)rmt_01No ratings yet
- Pathophys UrinaryDocument31 pagesPathophys UrinaryDr Anais AsimNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument50 pagesThe Urinary SystemDasari PrasadNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of The Urine Production (2021)Document80 pagesThe Physiology of The Urine Production (2021)Shelly NobelNo ratings yet
- Renal or Urinary Tract DisorderDocument6 pagesRenal or Urinary Tract DisorderMarcel Quario OrinaNo ratings yet
- Liver Function (1)Document16 pagesLiver Function (1)nekemwbnheismwbwoNo ratings yet
- Kidney FunctionDocument64 pagesKidney FunctionVincent LivandyNo ratings yet
- Posterior Urethral Valves and VURDocument56 pagesPosterior Urethral Valves and VURdhabeNo ratings yet
- Aubf Lab Transes 1Document3 pagesAubf Lab Transes 1Princess Eve OlowanNo ratings yet
- Continence Problem at HomeDocument71 pagesContinence Problem at HomeZayar HmunNo ratings yet
- SEHH2234 2021 S2 Ch16 Urinary System StudentsDocument58 pagesSEHH2234 2021 S2 Ch16 Urinary System Studentsmiki leeNo ratings yet
- Aubf Prelim 1Document59 pagesAubf Prelim 1Kat JornadalNo ratings yet
- Bio 208 Urinary SystemDocument121 pagesBio 208 Urinary SystemNazir RabiuNo ratings yet
- 2 Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument9 pages2 Fluids and ElectrolytesHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Real World Ready Program Suplemental Study Guide September NCM 105-Fluid & ElectrolytesDocument8 pagesReal World Ready Program Suplemental Study Guide September NCM 105-Fluid & ElectrolytesHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument6 pagesWeek 1 Fluids and ElectrolytesHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Background Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument9 pagesBackground Fluids and ElectrolytesHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Week 1: Future Ready Future Smart ProgramDocument10 pagesStudy Guide Week 1: Future Ready Future Smart ProgramHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- "Pediatrics 103" Assignment No. 2: What Are Stages of Cognitive Development by Jean Fiaget?Document4 pages"Pediatrics 103" Assignment No. 2: What Are Stages of Cognitive Development by Jean Fiaget?Hannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Geria Part 1Document16 pagesGeria Part 1Hannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Leopold'S Maneuver: Position & PresentationDocument23 pagesLeopold'S Maneuver: Position & PresentationHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Healthcare TeamDocument20 pagesGeriatric Healthcare TeamHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- "Volleyball": CASTILLO, Hannah Leigh RDocument43 pages"Volleyball": CASTILLO, Hannah Leigh RHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- "Pediatrics Week 1": CASTILLO, Hannah Leigh R. ALHP 2-0 1. What Is Growth and Development?Document4 pages"Pediatrics Week 1": CASTILLO, Hannah Leigh R. ALHP 2-0 1. What Is Growth and Development?Hannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4:: Entrepreneurs and Social EntrepreneurshipDocument24 pagesLesson 4:: Entrepreneurs and Social EntrepreneurshipHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Skills Laboratory NCM 103: Prof. Michael H. EsmillaDocument30 pagesSkills Laboratory NCM 103: Prof. Michael H. EsmillaHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- NSTP 2:Cwts/Lts Curricular ProgramDocument32 pagesNSTP 2:Cwts/Lts Curricular ProgramHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Perineal Care: Michael H. Esmilla, RN, MANDocument15 pagesPerineal Care: Michael H. Esmilla, RN, MANHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- 11.7 Worksheet 1Document4 pages11.7 Worksheet 1Amrita MallickNo ratings yet
- A Step by Step Guide For Conducting A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis With Simulation DataDocument9 pagesA Step by Step Guide For Conducting A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis With Simulation DataIlmiatus QoyimahNo ratings yet
- Lizo ForceDocument3 pagesLizo ForcegkvanuNo ratings yet
- 11.2 Baseline Medical Surveillance ProcedureDocument18 pages11.2 Baseline Medical Surveillance ProcedureaceNo ratings yet
- Atlas of ECGDocument162 pagesAtlas of ECGMiuschaNo ratings yet
- SpIn SnOutDocument1 pageSpIn SnOutAj GenoNo ratings yet
- Hypovolamic HypernatremiaDocument9 pagesHypovolamic Hypernatremiaharsh singhviNo ratings yet
- Finals TFN ReviewerDocument5 pagesFinals TFN ReviewerNicole Faith L. NacarioNo ratings yet
- DementiaDocument874 pagesDementiaKoko Riko100% (3)
- Med Surg: GI - Gastrointestinal: PathophysiologyDocument1 pageMed Surg: GI - Gastrointestinal: PathophysiologyTori RolandNo ratings yet
- Week 6-MCQ in EBP-1Document36 pagesWeek 6-MCQ in EBP-1Hasan KhawaldehNo ratings yet
- Tamwed - Mooligai Thottam Project Evaluation JANUARY 2012Document11 pagesTamwed - Mooligai Thottam Project Evaluation JANUARY 2012Manigandan BalajiNo ratings yet
- Molecular Genetics and Metabolism Reports: Case ReportDocument4 pagesMolecular Genetics and Metabolism Reports: Case ReportLeidy Paola Gamboa GamboaNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityLouie Danielle SegarraNo ratings yet
- Frenle Revie Np3 and Np4-1Document49 pagesFrenle Revie Np3 and Np4-1erjen gamingNo ratings yet
- Phylum: Apicomplexa (Because The Apical Point of The Parasite Complex) (Blood and Tissue SporozoaDocument34 pagesPhylum: Apicomplexa (Because The Apical Point of The Parasite Complex) (Blood and Tissue Sporozoaammar amerNo ratings yet
- Precociou S Puberty: BY Vishnupriya Ravimohandoss Year-6 Group-1Document31 pagesPrecociou S Puberty: BY Vishnupriya Ravimohandoss Year-6 Group-1Priya RaviNo ratings yet
- Life Span Development 16th Edition Santrock Test BankDocument31 pagesLife Span Development 16th Edition Santrock Test Bankbrandoncoletjaxprigfm100% (40)
- Name: Vivienne Gaille O. Aguarille Section: NGDocument2 pagesName: Vivienne Gaille O. Aguarille Section: NGvivienne gailleNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology Ii MCQ:: Prepared By: Srey Viso, Pharmd Medical Biologist & Microbiology, DMM For Pharmacy ClassDocument21 pagesBacteriology Ii MCQ:: Prepared By: Srey Viso, Pharmd Medical Biologist & Microbiology, DMM For Pharmacy ClassPiseth VichhekaNo ratings yet
- JatamansiDocument2 pagesJatamansiDinesh Joshi100% (1)
- Hyperbaric Oxygen TherapyDocument147 pagesHyperbaric Oxygen TherapyDavid Omar Navarro LeijaNo ratings yet
- Fact Lym Eng Final Ver4 16nov07Document3 pagesFact Lym Eng Final Ver4 16nov07luthfiana syarifahNo ratings yet
- Composition About The HolidaysDocument1 pageComposition About The HolidaysIssufoAbdalaNo ratings yet
- Head Boy 0-36Document1 pageHead Boy 0-36Almira ClaraNo ratings yet
- Computation For Health Prioritization: Mabini Colleges IncorporatedDocument6 pagesComputation For Health Prioritization: Mabini Colleges IncorporatedGrascia SchneiderNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Destroy - UpsellDocument23 pagesDiabetes Destroy - UpsellSofy AndersonNo ratings yet
- Heath Assessment ToolDocument8 pagesHeath Assessment ToolHouda Hayek100% (1)