Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Section 2 Duties
Section 2 Duties
Uploaded by
UmaibalanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Medcert CentrelinkDocument1 pageMedcert Centrelinkshane johnsonNo ratings yet
- Weld SurveillanceDocument33 pagesWeld SurveillancecanakyuzNo ratings yet
- WMS JOB Procedure FOR PIPING WORKDocument9 pagesWMS JOB Procedure FOR PIPING WORKsatyamech1_395565923No ratings yet
- CV of Welding InspectorDocument4 pagesCV of Welding Inspectorramesh77c100% (2)
- Industrial Applications of Infrared Thermography: How Infrared Analysis Can be Used to Improve Equipment InspectionFrom EverandIndustrial Applications of Infrared Thermography: How Infrared Analysis Can be Used to Improve Equipment InspectionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- ASTM D 6083-97aDocument6 pagesASTM D 6083-97aJOsé Ratónciitop R Gil0% (1)
- Duties of A Weld InspectorDocument2 pagesDuties of A Weld Inspectorshanebowen31No ratings yet
- Welding InspectorDocument2 pagesWelding Inspectorrahul063No ratings yet
- Welding Inspection CourseDocument23 pagesWelding Inspection CoursepouyaNo ratings yet
- Duties of Welding InspectorDocument3 pagesDuties of Welding InspectorSalman SyedNo ratings yet
- Shaik Yousufuddin (Welding Inspector)Document3 pagesShaik Yousufuddin (Welding Inspector)Mohamed AdelNo ratings yet
- Quality Management System SystemDocument4 pagesQuality Management System SystemMario YañezNo ratings yet
- Faizur Rahman CVDocument6 pagesFaizur Rahman CVmuneeshwaraperumalNo ratings yet
- Document Purpose & Personnel ResponsibilityDocument3 pagesDocument Purpose & Personnel ResponsibilityIlkin hasanovNo ratings yet
- Dutyies of Welding InspectorDocument30 pagesDutyies of Welding InspectorMorg Actus100% (1)
- Resume of Qaqc Mech InspectorDocument5 pagesResume of Qaqc Mech InspectorMohammed IlliasuddinNo ratings yet
- QAQC References 2Document138 pagesQAQC References 2Mohd SharainiNo ratings yet
- Welding Inspection ProcedureDocument5 pagesWelding Inspection ProcedurePugalNo ratings yet
- Baraneedharan Raju CV UpdatedDocument7 pagesBaraneedharan Raju CV UpdatedBaraneedharanNo ratings yet
- Welding InspectionDocument7 pagesWelding Inspectionzahid_497100% (1)
- Inspection Test Procedure ModelDocument8 pagesInspection Test Procedure ModelMahesh SuthaNo ratings yet
- Shortcut To A WPSDocument18 pagesShortcut To A WPSCepi Sindang Kamulan100% (1)
- Specific Requirements Regarding Welding: CPTP-Volume I - Chapter VDocument10 pagesSpecific Requirements Regarding Welding: CPTP-Volume I - Chapter VHaythem Ben ZidNo ratings yet
- CV Aravind API InspectorDocument12 pagesCV Aravind API Inspectorநான் மகான் அல்லNo ratings yet
- Construction ProcedureDocument36 pagesConstruction ProcedureJagdish Busa100% (2)
- Muhammed Thanzeel QC Mechanical Inspector: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesMuhammed Thanzeel QC Mechanical Inspector: ObjectivesMuhammed ThanzeelNo ratings yet
- British Standard 5289: 1976: Visual InspectionDocument10 pagesBritish Standard 5289: 1976: Visual InspectionMarcelo Rodriguez FujimotoNo ratings yet
- QC Questionery. PIPINGDocument6 pagesQC Questionery. PIPINGMd Sharique100% (3)
- Piping Work Method For Fuel Oil Pipe Fabrication Installation and TestingDocument7 pagesPiping Work Method For Fuel Oil Pipe Fabrication Installation and Testingsamsul maarif100% (1)
- Piping QC Inspector Resume 2020Document5 pagesPiping QC Inspector Resume 2020Omprakash Yadav100% (1)
- Section 1 Duties & ResponsiblitiesDocument8 pagesSection 1 Duties & ResponsiblitiesS GoudaNo ratings yet
- Duties Before WeldingDocument1 pageDuties Before WeldingMuhammed ThanzeelNo ratings yet
- QUALITY INSPECTOR (Welding Inspector) : Basic FunctionDocument1 pageQUALITY INSPECTOR (Welding Inspector) : Basic FunctionEdy AlamNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Aqib: Inspection TechnicianDocument4 pagesMuhammad Aqib: Inspection Technicianusama666No ratings yet
- Duties of Welding InspectorDocument1 pageDuties of Welding InspectorJennifer French100% (1)
- Resume of Qaqc Welding-Mechanical InspectorDocument5 pagesResume of Qaqc Welding-Mechanical InspectorMohammed Illiasuddin100% (1)
- Rajendran Updated C.VDocument8 pagesRajendran Updated C.VKannan RajendranNo ratings yet
- ARAMCO Interview 2015 PDFDocument15 pagesARAMCO Interview 2015 PDFm.srinivasanNo ratings yet
- Audit ReportDocument9 pagesAudit ReportVIVEK100% (1)
- Control Procedures For The Calibration and Measurement of The Welding Power Supplies For PDFDocument11 pagesControl Procedures For The Calibration and Measurement of The Welding Power Supplies For PDFNenad NedeljkovicNo ratings yet
- Inspeksi LasDocument83 pagesInspeksi Lassyahrial cahyantoNo ratings yet
- CV SALAH JALLALI - English - Rev.01Document8 pagesCV SALAH JALLALI - English - Rev.01salahjallaliNo ratings yet
- 9 Cswip 3.1 Book 2010 Coloured BookDocument338 pages9 Cswip 3.1 Book 2010 Coloured BookBùi Công LộcNo ratings yet
- Before, During and After Welding.Document2 pagesBefore, During and After Welding.ashwinNo ratings yet
- Welding Personnel ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesWelding Personnel ResponsibilityIlkin hasanovNo ratings yet
- Welding Works RequirementsDocument48 pagesWelding Works RequirementsrogersampaiocostaNo ratings yet
- Welding Quality Contral ChecklistDocument18 pagesWelding Quality Contral ChecklistRamzi BEN AHMED100% (1)
- PWS&PQRDocument1 pagePWS&PQRkuppiliramaNo ratings yet
- APIINSPECTORDocument10 pagesAPIINSPECTORdada khalandarNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineer: Mohd. Layeequr RahmanDocument7 pagesMechanical Engineer: Mohd. Layeequr RahmanmdlayeequeNo ratings yet
- Work Scope - Pelotn Runner Refurbishment !Document3 pagesWork Scope - Pelotn Runner Refurbishment !manikanthNo ratings yet
- Ttransition JointsDocument15 pagesTtransition JointsAdil HasanovNo ratings yet
- Responsibilities of PersonnelDocument2 pagesResponsibilities of PersonnelmazNo ratings yet
- Inspection and Test ProcedureDocument8 pagesInspection and Test Proceduregaehdd1100% (1)
- Duties of A Weld InspDocument1 pageDuties of A Weld InspbassamNo ratings yet
- Fab 01 QA of Welds, ISO 3834, RWC Etc.Document17 pagesFab 01 QA of Welds, ISO 3834, RWC Etc.Raghu vamshiNo ratings yet
- CV - Sqa-UaeDocument13 pagesCV - Sqa-UaeShanmuga Navaneethan100% (1)
- Welding Control ProcedureDocument4 pagesWelding Control Procedurevenkatesh100% (2)
- CSWIP 3.1 - Welding Inspection-WIS5-2006 PDFDocument358 pagesCSWIP 3.1 - Welding Inspection-WIS5-2006 PDFTuan DangNo ratings yet
- Plant InspectorDocument7 pagesPlant Inspectornaveed7861No ratings yet
- Post Weld Heat Treatment PWHT: Standards, Procedures, Applications, and Interview Q&AFrom EverandPost Weld Heat Treatment PWHT: Standards, Procedures, Applications, and Interview Q&ANo ratings yet
- Process Control for Sheet-Metal Stamping: Process Modeling, Controller Design and Shop-Floor ImplementationFrom EverandProcess Control for Sheet-Metal Stamping: Process Modeling, Controller Design and Shop-Floor ImplementationNo ratings yet
- CSWIP QuestionaireDocument158 pagesCSWIP QuestionaireUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Conditions of ContractDocument2 pagesConditions of ContractUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Phased Array: Multi Element Ultrasonic InspectionsDocument2 pagesPhased Array: Multi Element Ultrasonic InspectionsUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Section 22 Weldability SteelDocument15 pagesSection 22 Weldability SteelUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions Given by ManiDocument138 pagesSample Questions Given by ManiUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Site Coatings PPDocument124 pagesSite Coatings PPUmaibalan100% (4)
- FJC PQTDocument2 pagesFJC PQTUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Operating Procedure Castoro8Document12 pagesOperating Procedure Castoro8UmaibalanNo ratings yet
- NDT - Magnetic ParticleDocument73 pagesNDT - Magnetic ParticleUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- QMS Auditor/ Lead Auditor: Pre-Course NotesDocument34 pagesQMS Auditor/ Lead Auditor: Pre-Course NotesUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- NDT - Liquid Penetrant InspectionDocument38 pagesNDT - Liquid Penetrant InspectionUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- NDT - Ultrasonic TestingDocument263 pagesNDT - Ultrasonic TestingUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- SAIPEM Book RT enDocument158 pagesSAIPEM Book RT enUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Asnt-Ut Training ProgramDocument136 pagesAsnt-Ut Training ProgramUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- WIS10 M.TestDocument46 pagesWIS10 M.TestUmaibalan100% (1)
- Cswip 3.2.2 Preparatory Material Yr 2020Document12 pagesCswip 3.2.2 Preparatory Material Yr 2020Umaibalan100% (1)
- Bgas CSWIP Coating.Document180 pagesBgas CSWIP Coating.UmaibalanNo ratings yet
- 226NDocument2 pages226NUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- RT Question AnswersDocument65 pagesRT Question AnswersUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Site Coatings PPDocument124 pagesSite Coatings PPUmaibalan100% (4)
- 226N MSDSDocument6 pages226N MSDSUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Paper 6Document14 pagesPaper 6UmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Paper 4Document10 pagesPaper 4UmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Paper 9Document14 pagesPaper 9UmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document6 pagesPaper 1Umaibalan100% (1)
- Paper 3Document10 pagesPaper 3Umaibalan100% (2)
- Paper 5Document14 pagesPaper 5UmaibalanNo ratings yet
- First Five Pages FinalDocument8 pagesFirst Five Pages FinalPankil ShahNo ratings yet
- ASM-AWG08: AWG08-001 Audio Warning GeneratorDocument41 pagesASM-AWG08: AWG08-001 Audio Warning GeneratorAlexNo ratings yet
- Boiler Design: Heat Recovery Steam GeneratorDocument2 pagesBoiler Design: Heat Recovery Steam Generator郑裕 鸿No ratings yet
- Dutch and British Colonial Intervention in Sri Lanka, 1780-1815 (2007)Document289 pagesDutch and British Colonial Intervention in Sri Lanka, 1780-1815 (2007)Bollox62No ratings yet
- Maruti SuzukiDocument30 pagesMaruti SuzukiChaitanya KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Prashant Jain PJ Sir COMPLETE MATHS PYQ PDF PYQ's ExportDocument20 pagesPrashant Jain PJ Sir COMPLETE MATHS PYQ PDF PYQ's ExportSourabh Singh100% (1)
- New DataDocument10 pagesNew DataVikram GuptaNo ratings yet
- Maruti 110306013819 Phpapp02Document148 pagesMaruti 110306013819 Phpapp02NishantShah0% (1)
- Regression After Midterm 5Document80 pagesRegression After Midterm 5NataliAmiranashviliNo ratings yet
- Casting, Forming and Joining: 14 January 2016Document23 pagesCasting, Forming and Joining: 14 January 2016Bhargav ParsaNo ratings yet
- Online Class Activity Work No1-Ged0011Document2 pagesOnline Class Activity Work No1-Ged0011Khristian SorianoNo ratings yet
- SQL FunctionsDocument42 pagesSQL FunctionssmithaNo ratings yet
- Work Energy ProblemsDocument1 pageWork Energy ProblemsIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- Annexure-2 LOPA - WorksheetDocument19 pagesAnnexure-2 LOPA - Worksheetshantanubiswas1No ratings yet
- Influence Without Authority PresentationDocument18 pagesInfluence Without Authority Presentationatroutt100% (1)
- 2011 P6 Math CA1 AiTongDocument30 pages2011 P6 Math CA1 AiTongandrewsumyw3345No ratings yet
- Arithmetic - Time and DistanceDocument2 pagesArithmetic - Time and DistanceVenkateswararao BuridiNo ratings yet
- Sencha Advance CheatSheetDocument43 pagesSencha Advance CheatSheetkokareom2977No ratings yet
- Sociotropy, Autonomy, and Self-CriticismDocument10 pagesSociotropy, Autonomy, and Self-Criticismowilm892973100% (1)
- Krishna File 2Document18 pagesKrishna File 2Ali AhmadNo ratings yet
- American Wheatley Price List 2011Document48 pagesAmerican Wheatley Price List 2011francisb65No ratings yet
- F-Ratio Table 2005Document5 pagesF-Ratio Table 2005ElmowantNo ratings yet
- Metal-Organic Frameworks and Their Postsynthetic ModificationDocument60 pagesMetal-Organic Frameworks and Their Postsynthetic ModificationDean HidayatNo ratings yet
- Research On Layout Design of Main InterfaceDocument12 pagesResearch On Layout Design of Main InterfaceAndrea Mata CelisNo ratings yet
- JTM English Proficiency Test) Jept (Score Description: B Y English Language Cluster General Studies Committee IljtmDocument4 pagesJTM English Proficiency Test) Jept (Score Description: B Y English Language Cluster General Studies Committee IljtmSanjay VengatravanaNo ratings yet
- Ingenieur+vol 87+July-Sept2021+Vol+87+2021Document85 pagesIngenieur+vol 87+July-Sept2021+Vol+87+2021rayan alnoaimiNo ratings yet
- 10th Reflection and Refraction of Light Cbse Test Paper Solved-4Document4 pages10th Reflection and Refraction of Light Cbse Test Paper Solved-4ashokNo ratings yet
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation Class 12 Notes Biology - myCBSEguideDocument15 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance and Variation Class 12 Notes Biology - myCBSEguideShireen SuhailNo ratings yet
Section 2 Duties
Section 2 Duties
Uploaded by
UmaibalanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Section 2 Duties
Section 2 Duties
Uploaded by
UmaibalanCopyright:
Available Formats
THE WELDING INSTITUTE
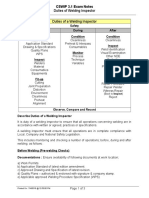
Duties of a Welding Inspector:
It is the duty of a welding inspector to ensure that all operations concerning welding are
carried out in strict accordance with written, or agreed practices, or specifications.
This will include monitoring or checking a number of operations including:
Before welding:
Safety:
Ensure that all operations are carried out in complete compliance with local, company, or
National safety legislation (i.e. permits to work are in place).
Documentation:
Specification. (Year and revision)
Drawings. (Correct revisions)
Welding procedure specifications and welder approvals.
Calibration certification. (Welding equipment/ancillaries and all inspection instruments)
Material and consumable certification
Welding Process and ancillaries:
Welding equipment and all related ancillaries. (Cables, regulators, ovens, quivers etc.)
Incoming Consumables:
All pipe/plate and welding consumables for Size, Type and Condition.
Marking out preparation & set up:
Correct method of cutting weld preparations. (Pre-Heat for thermal cutting if applicable)
Correct preparation. (Relevant bevel angles, root face, root gap, root radius, land, etc.)
Correct pre-welding distortion control. (Tacking, bridging, jigs, line up clamps, etc.)
Correct pre heat applied prior to tack welding.
All tack welding to be monitored and inspected
Welding Inspection – Duties of a Welding Inspector 2.1 Rev 09-09-02
Copyright 2002 TWI Ltd
THE WELDING INSTITUTE
During welding:
Pre-heat values. (Heating method, location and control)
In-process distortion control. (Sequence or balanced welding)
Consumable control. (Specification, size, condition, and any special treatments)
Process type and all related variable parameters. (Voltage, amperage, travel speed)
Purging gases. (Type, pressure/flow and control method)
Welding conditions for root run/hot pass and all subsequent run, and inter-run cleaning.
Minimum, or maximum inter-pass temperature. (Temperature and controlling method)
Compliance with all other variables stated on the approved welding procedure.
After welding:
Visual inspection of the welded joint. (Including dimensional aspects)
NDT requirements. (Method and qualification of operator, and execution)
Identify repairs from assessment of visual or NDT reports. (Refer to repairs below)
Post weld heat treatment (PWHT) (Heating method and temperature recording system)
Re-inspect with visual/NDT after PWHT. (If applicable)
Hydrostatic test procedures. (For pipelines or pressure vessels)
Repairs:
Excavation procedure. (Approval and execution)
Approval of the NDT procedures (For assessment of complete defect removal)
Repair procedure. (Approval of re-welding procedures and welder approval)
Execution of approved re-welding procedure. (Compliance with repair procedure)
Re-inspect the repair area with visual inspection and approved NDT method.
Submission of inspection reports, and all related documents to the Q/C department.
Welding Inspection – Duties of a Welding Inspector 2.2 Rev 09-09-02
Copyright 2002 TWI Ltd
THE WELDING INSTITUTE
Responsibilities of a Welding Inspector:
To Observe
To observe all relevant actions related to weld quality throughout production.
This will include a final visual inspection of the weld area.
To Record
To record, or log all production inspection points relevant to quality, including a final
map and report sheet showing all identified welding imperfections.
To Compare
To compare all reported information with the acceptance levels/criteria and clauses
within the applied application standard.
Submit a final inspection report of your findings to the QA/QC department for
analysis and any remedial actions.
Welding Inspection – Duties of a Welding Inspector 2.3 Rev 09-09-02
Copyright 2002 TWI Ltd
You might also like
- Medcert CentrelinkDocument1 pageMedcert Centrelinkshane johnsonNo ratings yet
- Weld SurveillanceDocument33 pagesWeld SurveillancecanakyuzNo ratings yet
- WMS JOB Procedure FOR PIPING WORKDocument9 pagesWMS JOB Procedure FOR PIPING WORKsatyamech1_395565923No ratings yet
- CV of Welding InspectorDocument4 pagesCV of Welding Inspectorramesh77c100% (2)
- Industrial Applications of Infrared Thermography: How Infrared Analysis Can be Used to Improve Equipment InspectionFrom EverandIndustrial Applications of Infrared Thermography: How Infrared Analysis Can be Used to Improve Equipment InspectionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- ASTM D 6083-97aDocument6 pagesASTM D 6083-97aJOsé Ratónciitop R Gil0% (1)
- Duties of A Weld InspectorDocument2 pagesDuties of A Weld Inspectorshanebowen31No ratings yet
- Welding InspectorDocument2 pagesWelding Inspectorrahul063No ratings yet
- Welding Inspection CourseDocument23 pagesWelding Inspection CoursepouyaNo ratings yet
- Duties of Welding InspectorDocument3 pagesDuties of Welding InspectorSalman SyedNo ratings yet
- Shaik Yousufuddin (Welding Inspector)Document3 pagesShaik Yousufuddin (Welding Inspector)Mohamed AdelNo ratings yet
- Quality Management System SystemDocument4 pagesQuality Management System SystemMario YañezNo ratings yet
- Faizur Rahman CVDocument6 pagesFaizur Rahman CVmuneeshwaraperumalNo ratings yet
- Document Purpose & Personnel ResponsibilityDocument3 pagesDocument Purpose & Personnel ResponsibilityIlkin hasanovNo ratings yet
- Dutyies of Welding InspectorDocument30 pagesDutyies of Welding InspectorMorg Actus100% (1)
- Resume of Qaqc Mech InspectorDocument5 pagesResume of Qaqc Mech InspectorMohammed IlliasuddinNo ratings yet
- QAQC References 2Document138 pagesQAQC References 2Mohd SharainiNo ratings yet
- Welding Inspection ProcedureDocument5 pagesWelding Inspection ProcedurePugalNo ratings yet
- Baraneedharan Raju CV UpdatedDocument7 pagesBaraneedharan Raju CV UpdatedBaraneedharanNo ratings yet
- Welding InspectionDocument7 pagesWelding Inspectionzahid_497100% (1)
- Inspection Test Procedure ModelDocument8 pagesInspection Test Procedure ModelMahesh SuthaNo ratings yet
- Shortcut To A WPSDocument18 pagesShortcut To A WPSCepi Sindang Kamulan100% (1)
- Specific Requirements Regarding Welding: CPTP-Volume I - Chapter VDocument10 pagesSpecific Requirements Regarding Welding: CPTP-Volume I - Chapter VHaythem Ben ZidNo ratings yet
- CV Aravind API InspectorDocument12 pagesCV Aravind API Inspectorநான் மகான் அல்லNo ratings yet
- Construction ProcedureDocument36 pagesConstruction ProcedureJagdish Busa100% (2)
- Muhammed Thanzeel QC Mechanical Inspector: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesMuhammed Thanzeel QC Mechanical Inspector: ObjectivesMuhammed ThanzeelNo ratings yet
- British Standard 5289: 1976: Visual InspectionDocument10 pagesBritish Standard 5289: 1976: Visual InspectionMarcelo Rodriguez FujimotoNo ratings yet
- QC Questionery. PIPINGDocument6 pagesQC Questionery. PIPINGMd Sharique100% (3)
- Piping Work Method For Fuel Oil Pipe Fabrication Installation and TestingDocument7 pagesPiping Work Method For Fuel Oil Pipe Fabrication Installation and Testingsamsul maarif100% (1)
- Piping QC Inspector Resume 2020Document5 pagesPiping QC Inspector Resume 2020Omprakash Yadav100% (1)
- Section 1 Duties & ResponsiblitiesDocument8 pagesSection 1 Duties & ResponsiblitiesS GoudaNo ratings yet
- Duties Before WeldingDocument1 pageDuties Before WeldingMuhammed ThanzeelNo ratings yet
- QUALITY INSPECTOR (Welding Inspector) : Basic FunctionDocument1 pageQUALITY INSPECTOR (Welding Inspector) : Basic FunctionEdy AlamNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Aqib: Inspection TechnicianDocument4 pagesMuhammad Aqib: Inspection Technicianusama666No ratings yet
- Duties of Welding InspectorDocument1 pageDuties of Welding InspectorJennifer French100% (1)
- Resume of Qaqc Welding-Mechanical InspectorDocument5 pagesResume of Qaqc Welding-Mechanical InspectorMohammed Illiasuddin100% (1)
- Rajendran Updated C.VDocument8 pagesRajendran Updated C.VKannan RajendranNo ratings yet
- ARAMCO Interview 2015 PDFDocument15 pagesARAMCO Interview 2015 PDFm.srinivasanNo ratings yet
- Audit ReportDocument9 pagesAudit ReportVIVEK100% (1)
- Control Procedures For The Calibration and Measurement of The Welding Power Supplies For PDFDocument11 pagesControl Procedures For The Calibration and Measurement of The Welding Power Supplies For PDFNenad NedeljkovicNo ratings yet
- Inspeksi LasDocument83 pagesInspeksi Lassyahrial cahyantoNo ratings yet
- CV SALAH JALLALI - English - Rev.01Document8 pagesCV SALAH JALLALI - English - Rev.01salahjallaliNo ratings yet
- 9 Cswip 3.1 Book 2010 Coloured BookDocument338 pages9 Cswip 3.1 Book 2010 Coloured BookBùi Công LộcNo ratings yet
- Before, During and After Welding.Document2 pagesBefore, During and After Welding.ashwinNo ratings yet
- Welding Personnel ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesWelding Personnel ResponsibilityIlkin hasanovNo ratings yet
- Welding Works RequirementsDocument48 pagesWelding Works RequirementsrogersampaiocostaNo ratings yet
- Welding Quality Contral ChecklistDocument18 pagesWelding Quality Contral ChecklistRamzi BEN AHMED100% (1)
- PWS&PQRDocument1 pagePWS&PQRkuppiliramaNo ratings yet
- APIINSPECTORDocument10 pagesAPIINSPECTORdada khalandarNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineer: Mohd. Layeequr RahmanDocument7 pagesMechanical Engineer: Mohd. Layeequr RahmanmdlayeequeNo ratings yet
- Work Scope - Pelotn Runner Refurbishment !Document3 pagesWork Scope - Pelotn Runner Refurbishment !manikanthNo ratings yet
- Ttransition JointsDocument15 pagesTtransition JointsAdil HasanovNo ratings yet
- Responsibilities of PersonnelDocument2 pagesResponsibilities of PersonnelmazNo ratings yet
- Inspection and Test ProcedureDocument8 pagesInspection and Test Proceduregaehdd1100% (1)
- Duties of A Weld InspDocument1 pageDuties of A Weld InspbassamNo ratings yet
- Fab 01 QA of Welds, ISO 3834, RWC Etc.Document17 pagesFab 01 QA of Welds, ISO 3834, RWC Etc.Raghu vamshiNo ratings yet
- CV - Sqa-UaeDocument13 pagesCV - Sqa-UaeShanmuga Navaneethan100% (1)
- Welding Control ProcedureDocument4 pagesWelding Control Procedurevenkatesh100% (2)
- CSWIP 3.1 - Welding Inspection-WIS5-2006 PDFDocument358 pagesCSWIP 3.1 - Welding Inspection-WIS5-2006 PDFTuan DangNo ratings yet
- Plant InspectorDocument7 pagesPlant Inspectornaveed7861No ratings yet
- Post Weld Heat Treatment PWHT: Standards, Procedures, Applications, and Interview Q&AFrom EverandPost Weld Heat Treatment PWHT: Standards, Procedures, Applications, and Interview Q&ANo ratings yet
- Process Control for Sheet-Metal Stamping: Process Modeling, Controller Design and Shop-Floor ImplementationFrom EverandProcess Control for Sheet-Metal Stamping: Process Modeling, Controller Design and Shop-Floor ImplementationNo ratings yet
- CSWIP QuestionaireDocument158 pagesCSWIP QuestionaireUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Conditions of ContractDocument2 pagesConditions of ContractUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Phased Array: Multi Element Ultrasonic InspectionsDocument2 pagesPhased Array: Multi Element Ultrasonic InspectionsUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Section 22 Weldability SteelDocument15 pagesSection 22 Weldability SteelUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions Given by ManiDocument138 pagesSample Questions Given by ManiUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Site Coatings PPDocument124 pagesSite Coatings PPUmaibalan100% (4)
- FJC PQTDocument2 pagesFJC PQTUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Operating Procedure Castoro8Document12 pagesOperating Procedure Castoro8UmaibalanNo ratings yet
- NDT - Magnetic ParticleDocument73 pagesNDT - Magnetic ParticleUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- QMS Auditor/ Lead Auditor: Pre-Course NotesDocument34 pagesQMS Auditor/ Lead Auditor: Pre-Course NotesUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- NDT - Liquid Penetrant InspectionDocument38 pagesNDT - Liquid Penetrant InspectionUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- NDT - Ultrasonic TestingDocument263 pagesNDT - Ultrasonic TestingUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- SAIPEM Book RT enDocument158 pagesSAIPEM Book RT enUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Asnt-Ut Training ProgramDocument136 pagesAsnt-Ut Training ProgramUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- WIS10 M.TestDocument46 pagesWIS10 M.TestUmaibalan100% (1)
- Cswip 3.2.2 Preparatory Material Yr 2020Document12 pagesCswip 3.2.2 Preparatory Material Yr 2020Umaibalan100% (1)
- Bgas CSWIP Coating.Document180 pagesBgas CSWIP Coating.UmaibalanNo ratings yet
- 226NDocument2 pages226NUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- RT Question AnswersDocument65 pagesRT Question AnswersUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Site Coatings PPDocument124 pagesSite Coatings PPUmaibalan100% (4)
- 226N MSDSDocument6 pages226N MSDSUmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Paper 6Document14 pagesPaper 6UmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Paper 4Document10 pagesPaper 4UmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Paper 9Document14 pagesPaper 9UmaibalanNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document6 pagesPaper 1Umaibalan100% (1)
- Paper 3Document10 pagesPaper 3Umaibalan100% (2)
- Paper 5Document14 pagesPaper 5UmaibalanNo ratings yet
- First Five Pages FinalDocument8 pagesFirst Five Pages FinalPankil ShahNo ratings yet
- ASM-AWG08: AWG08-001 Audio Warning GeneratorDocument41 pagesASM-AWG08: AWG08-001 Audio Warning GeneratorAlexNo ratings yet
- Boiler Design: Heat Recovery Steam GeneratorDocument2 pagesBoiler Design: Heat Recovery Steam Generator郑裕 鸿No ratings yet
- Dutch and British Colonial Intervention in Sri Lanka, 1780-1815 (2007)Document289 pagesDutch and British Colonial Intervention in Sri Lanka, 1780-1815 (2007)Bollox62No ratings yet
- Maruti SuzukiDocument30 pagesMaruti SuzukiChaitanya KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Prashant Jain PJ Sir COMPLETE MATHS PYQ PDF PYQ's ExportDocument20 pagesPrashant Jain PJ Sir COMPLETE MATHS PYQ PDF PYQ's ExportSourabh Singh100% (1)
- New DataDocument10 pagesNew DataVikram GuptaNo ratings yet
- Maruti 110306013819 Phpapp02Document148 pagesMaruti 110306013819 Phpapp02NishantShah0% (1)
- Regression After Midterm 5Document80 pagesRegression After Midterm 5NataliAmiranashviliNo ratings yet
- Casting, Forming and Joining: 14 January 2016Document23 pagesCasting, Forming and Joining: 14 January 2016Bhargav ParsaNo ratings yet
- Online Class Activity Work No1-Ged0011Document2 pagesOnline Class Activity Work No1-Ged0011Khristian SorianoNo ratings yet
- SQL FunctionsDocument42 pagesSQL FunctionssmithaNo ratings yet
- Work Energy ProblemsDocument1 pageWork Energy ProblemsIqbal A MirNo ratings yet
- Annexure-2 LOPA - WorksheetDocument19 pagesAnnexure-2 LOPA - Worksheetshantanubiswas1No ratings yet
- Influence Without Authority PresentationDocument18 pagesInfluence Without Authority Presentationatroutt100% (1)
- 2011 P6 Math CA1 AiTongDocument30 pages2011 P6 Math CA1 AiTongandrewsumyw3345No ratings yet
- Arithmetic - Time and DistanceDocument2 pagesArithmetic - Time and DistanceVenkateswararao BuridiNo ratings yet
- Sencha Advance CheatSheetDocument43 pagesSencha Advance CheatSheetkokareom2977No ratings yet
- Sociotropy, Autonomy, and Self-CriticismDocument10 pagesSociotropy, Autonomy, and Self-Criticismowilm892973100% (1)
- Krishna File 2Document18 pagesKrishna File 2Ali AhmadNo ratings yet
- American Wheatley Price List 2011Document48 pagesAmerican Wheatley Price List 2011francisb65No ratings yet
- F-Ratio Table 2005Document5 pagesF-Ratio Table 2005ElmowantNo ratings yet
- Metal-Organic Frameworks and Their Postsynthetic ModificationDocument60 pagesMetal-Organic Frameworks and Their Postsynthetic ModificationDean HidayatNo ratings yet
- Research On Layout Design of Main InterfaceDocument12 pagesResearch On Layout Design of Main InterfaceAndrea Mata CelisNo ratings yet
- JTM English Proficiency Test) Jept (Score Description: B Y English Language Cluster General Studies Committee IljtmDocument4 pagesJTM English Proficiency Test) Jept (Score Description: B Y English Language Cluster General Studies Committee IljtmSanjay VengatravanaNo ratings yet
- Ingenieur+vol 87+July-Sept2021+Vol+87+2021Document85 pagesIngenieur+vol 87+July-Sept2021+Vol+87+2021rayan alnoaimiNo ratings yet
- 10th Reflection and Refraction of Light Cbse Test Paper Solved-4Document4 pages10th Reflection and Refraction of Light Cbse Test Paper Solved-4ashokNo ratings yet
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation Class 12 Notes Biology - myCBSEguideDocument15 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance and Variation Class 12 Notes Biology - myCBSEguideShireen SuhailNo ratings yet