Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module Details Ultrasonic Testing Methods: Name Nominal Duration
Module Details Ultrasonic Testing Methods: Name Nominal Duration
Uploaded by
lamia97Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module Details Ultrasonic Testing Methods: Name Nominal Duration
Module Details Ultrasonic Testing Methods: Name Nominal Duration
Uploaded by
lamia97Copyright:
Available Formats
1.
Module Details
Module name ULTRASONIC TESTING METHODS
Nominal duration One module
It is anticipated that a learner holding the prescribed entry level
skills will achieve the module purpose in 35 to 40 hours
Module Codes EA614
Discipline Code Non-destructive testing (Code to be allocated)
2. Module Purpose To enable learners to describe the principles, procedures and
applications of ultrasonic testing and to undertake ultrasonic testing
of materials, during normal conditions under general supervision.
3. Prerequisites Nil.
4. Relationship to This module meets the training requirements for Level 1
qualifications in ultrasonic testing under AS3998 - 1992 -
competency "Non-destructive Testing - Qualifications and Certification of
standards Personnel - General Engineering".
Currently no competency standards have been established.
However the learning outcomes in this module relate to
ASF level 2-3.
5. Content Properties and behaviour of ultrasound
Frequency, velocity, wavelength, amplitude
Continuous and pulsed waves
Modes of vibrations
Acoustic impedance pressure, energy, intensity
Reflection, refraction and mode conversion
Critical angle and total reflection
Diffraction, dispersion and attenuation
Generation of ultrasound
Piezoelectricity & types of crystals
Construction of ultrasonic search units
Characteristics of search units- frequency - crystal thickness
relationship
Conversion efficiencies of various crystals
Damping and resolutions
Beam intensity characteristics - near field, far field divergence
Normal & angle probes
Flat and contoured probes
Single crystal and twin crystal probes
Fixed and adjustable probes
Care of search units
Ultrasonic Testing Equipment
Description of basic pulse-echo instrument
Time-base (synchroniser) circuit
Pulser circuits
Receiver or echo-amplifier circuit
A-scan display circuit
Linearity, effect of supersession
Types of displays
A-scan display
B-scan display
C-scan display
Monitors and recording devices
Care of equipment
Types of couplants, desirable characteristics
Testing Methods
Contact testing
Straight beam
Angle beam
Surface waves and Lamb waves
Immersion testing
Straight beam
Angle beam
Bubbler technique
Calibration
Types and uses of AS 2083-1981calibration blocks
Determination of probe characteristics
Water distance for immersion technique
Test application
Selection of test parameters
Frequency
Probe size and shape
Scanning speed and index
Thickness testing
Plate testing
Castings
Forgings
Welds
Interpretation of results
Acceptance standards
Location of discontinuities
Recording and reporting
Job records
Routine reports
Codes and standards
Variables affecting Test Results
Instrument performance variables
Transducer performance variables
Inspected part variables
Entry surface conditions
Part size and geometry
Metallurgical structure
Discontinuity variables
Size and geometry
Distance location from entry surface
Orientation to entry surface
TAFE METAL AND ENGINEERING NATIONAL CURRICULUM PROJECT Page 2 of 7
© ACTRAC PRODUCTS
Module: EA614 - Ultrasonic testing Methods - May, 1998
Reflecting characteristics of the discontinuity
6. Assessment Competency based assessment applies. Assessment should be
carried out by gathering evidence using a variety of methods or
strategy instruments that have validity according to the learning being
assessed.
Assessment method Multiple choice and short answer questions.
Written assignments and demonstrated competence through
assigned tasks.
Final assessment will be by a written examination and practical
examination as required by AS3998 for Level 1 Certification.
Conditions of assessment Assessment will be conducted by suitably qualified assessors, as
required by AS3998. The candidate will have access to any
equipment, materials and documentation as required for the
assessment.
7. Learning On completion of this module, the learner will be able to
outcome details
8. Learning outcome 1 Describe the fundamental properties and behaviour of ultrasound.
Assessment criteria .1 Describe the nature of sound
waves as particle motion associated with energy.
.2 1.2 Describe the
relationship between velocity, frequency and wavelength.
.3
.4 1.3 Outline the
difference between compression, shear, surface and plate or Lamb
waves.
.5
.6 1.4 Describe the
behaviour of sound as it strikes an interface between two mediums
resulting in reflection, refraction and mode conversion.
.7
.8 1.5 Define "Acoustic
Impedance" and state its importance in ultrasonic testing.
.9
.10 1.6 Appreciate critical
angle and its significance.
.11
.12 1.7 List the factors
that affect attenuation of ultrasonic energy as it passes through a
medium and the practical outcome of attenuation.
.13
Learning outcome 2 Describe how ultrasonic waves are generated and detected.
TAFE METAL AND ENGINEERING NATIONAL CURRICULUM PROJECT Page 3 of 7
© ACTRAC PRODUCTS
Module: EA614 - Ultrasonic testing Methods - May, 1998
Assessment criteria 2.1 Define Piezo electricity and the type of crystals.
2.2 Describe briefly the components in the construction of an
ultrasonic transducer.
2.3 Describe the characteristics of transducers, such as
frequency - crystal thickness relationship, conversion efficiencies of
various crystals, damping and resolution, beam intensity
characteristics, near field, far field and beam divergence.
2.4 List desirable steps for the care of transducers.
Learning outcome 3 Describe the basic parts of pulse-echo instrument and the functions
of various controls.
Assessment criteria 3.1 Describe the functions of the various parts and demonstrate
how the various controls can be used to calibrate and operate the
equipment for optimum performance.
3.2 Outline the various presentations including automatic
recording systems in ultrasonic testing.
3.3 Describe different couplants used and desirable
characteristics for ultrasonic testing and list their advantages and
limitations.
3.4 Demonstrate ability to work competently with A-scan
display unit.
Learning outcome 4 Describe various ultrasonic Testing Methods.
Assessment criteria 4.1 Describe contact testing techniques using.
- straight beam
- angle beam
- surface waves and
- Lamb waves.
4.2 Describe Immersion testing techniques. using.
- straight beam
- angle beam
- bubbler technique
4.3 State advantages, limitations and applications of various
techniques.
Learning Outcome 5 Calibrate ultrasonic test equipment using standard calibration
blocks and determine system parameters using standard blocks.
TAFE METAL AND ENGINEERING NATIONAL CURRICULUM PROJECT Page 4 of 7
© ACTRAC PRODUCTS
Module: EA614 - Ultrasonic testing Methods - May, 1998
Assessment criteria 5.1 Demonstrate competency in calibrating ultrasonic flaw
detection and thickness testing equipment using standard calibration
blocks and in accordance with national standards
.
5.2 Demonstrate ability in the selection of test parameters
including
- frequency, transducer size and type
- scanning speed and index
Learning outcome 6 Demonstrate proficiency in carrying out thickness testing of various
materials in the wrought and cast condition.
Assessment criteria 6.1 Describe the various applications of ultrasonic testing.
6.2 Demonstrate competency in thickness testing of various
materials.
6.3 Show basic understanding in setting up test equipment for
flaw detection in wrought materials, castings, forgings, and welded
assemblies.
6.4 Follow instructions and procedures for the ultrasonic
inspection of selected materials and components.
6.5 Prepare preliminary test reports on ultrasonic inspection of
selected materials and components.
Learning outcome 7 Show awareness of various variables affecting the test results.
Assessment criteria 7.1 Describe the briefly instrument performance variables and
their effect on the CRC display.
7.2 Describe briefly transducer performance variables and their
effect on the CRC display.
7.3 Describe briefly the inspected part variables and their effect
on test results.
7.4 Describe briefly the discontinuity variables and their effect
on test results.
8. Delivery of the This module may be taught by active participation, illustration,
demonstration and description. This module is practical in nature
module and theoretically integrated to complement the acquisition of
practical skills.
TAFE METAL AND ENGINEERING NATIONAL CURRICULUM PROJECT Page 5 of 7
© ACTRAC PRODUCTS
Module: EA614 - Ultrasonic testing Methods - May, 1998
Delivery strategy This module may be taught and assessed on or off-the-job.
The module has a high practical content. Theory and practice will
be taught concurrently. There will be a range of learning activities
including modified lectures, practical work and project work.
Resource requirements Human resources
• trainer/teacher/mentor
•Physical resources
• appropriately equipped training room
• relevant equipment and information
• legislative and regulatory documents
•
Major texts and references Ultrasonic Testing, Drury
Ultrasonic Testing - P.A. Sheedy (In preparation. Pub. Technical
Secretarial Service)
Ultrasonic Testing (Directed Private Study Notes) - Cheema &
Neasbey (from Sydney Institute of Technology)
Ultrasonic Testing Programmed Instruction Handbook -
ASNT/General Dynamics (Available from AINDT)
Occupational health and Learners and/or employees undertaking this module should have
safety requirements demonstrated competencies as defined in the Metal & Engineering
Industry Standards Unit No 1.2F - Apply principles of OH&S in the
work environment. This would apply in the classroom, practical
room or workplace.
TAFE METAL AND ENGINEERING NATIONAL CURRICULUM PROJECT Page 6 of 7
© ACTRAC PRODUCTS
Module: EA614 - Ultrasonic testing Methods - May, 1998
You might also like
- ASTM-E-1742-Radiographic - Examination-Eddy Current TestingDocument14 pagesASTM-E-1742-Radiographic - Examination-Eddy Current TestingVysakh Vasudevan100% (1)
- Astm e 1001Document9 pagesAstm e 1001KEN KNo ratings yet
- E1901 PDFDocument7 pagesE1901 PDFNorman ricardo100% (1)
- FORM QC MRI AcceptTesting 0604Document4 pagesFORM QC MRI AcceptTesting 0604Yuda FhunkshyangNo ratings yet
- Intro To Basic UTDocument41 pagesIntro To Basic UTgirish310100% (1)
- CSWIP Welding Inspection Notes and QuestionsDocument133 pagesCSWIP Welding Inspection Notes and Questionslram70100% (20)
- OBE SYLLABUS IN SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY and SOCIETYDocument15 pagesOBE SYLLABUS IN SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY and SOCIETYchris ian100% (7)
- Bangladesh Navy College Dhaka: Academic TranscriptDocument1 pageBangladesh Navy College Dhaka: Academic Transcript188-B-9 EshraqNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Final Exam Timetable 2015 CapsDocument3 pagesGrade 12 Final Exam Timetable 2015 CapsJamesNo ratings yet
- UT Outline Training LV IIIDocument4 pagesUT Outline Training LV IIITrung Tinh HoNo ratings yet
- Visual Testing Topical Outline: FundamentalsDocument2 pagesVisual Testing Topical Outline: FundamentalsGaurav ChopraNo ratings yet
- T-03 - TP-04 - Data Gathering Non Destructive Testing and Destructive Testing Procedures For Structural EngineersDocument57 pagesT-03 - TP-04 - Data Gathering Non Destructive Testing and Destructive Testing Procedures For Structural EngineersLimar SetstraNo ratings yet
- Advanced NDE Lesson 1Document190 pagesAdvanced NDE Lesson 1N Dhanunjaya Rao BorraNo ratings yet
- Use of The Ultrasonic Time of Flight Diffraction (TOFD) TechniqueDocument12 pagesUse of The Ultrasonic Time of Flight Diffraction (TOFD) TechniqueDavidMontillaNo ratings yet
- Astm A e 2373Document12 pagesAstm A e 2373leonciomavarez100% (1)
- Principles of Servicing Ultrasound Systems (2.5 Days) : Course OutlineDocument1 pagePrinciples of Servicing Ultrasound Systems (2.5 Days) : Course OutlineMai Thanh SơnNo ratings yet
- RWGWRGDocument24 pagesRWGWRGRajNo ratings yet
- ASNT Nivel III ExaminationDocument6 pagesASNT Nivel III ExaminationjomsedNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing: 1. Module DetailsDocument7 pagesUltrasonic Testing: 1. Module DetailsJimmy JohnNo ratings yet
- Sico Service Catalogue CompressedDocument11 pagesSico Service Catalogue CompressedassurendranNo ratings yet
- Non Destructive TestingDocument24 pagesNon Destructive TestingLipika GayenNo ratings yet
- Use of The Ultrasonic Time of Flight Diffraction (TOFD) TechniqueDocument13 pagesUse of The Ultrasonic Time of Flight Diffraction (TOFD) TechniquevickyNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing Procedure1Document18 pagesUltrasonic Testing Procedure1King Jordan Peralta100% (1)
- NDT Testing of ConcreteDocument55 pagesNDT Testing of ConcreteHVRANANo ratings yet
- E273 Dgyx6217Document4 pagesE273 Dgyx6217benderman1No ratings yet
- Application Note Ultrasonic Weld TestingDocument12 pagesApplication Note Ultrasonic Weld Testingj_carloscoliveira5071No ratings yet
- Astm E1332-01Document5 pagesAstm E1332-01Carlos Raul Caballero LeonNo ratings yet
- Mace S7M - Amndt 2023Document50 pagesMace S7M - Amndt 2023Muhammed MuhsinNo ratings yet
- A 388 - A 388M - 03 - Qtm4oc9bmzg4tqDocument8 pagesA 388 - A 388M - 03 - Qtm4oc9bmzg4tqRod RoperNo ratings yet
- E 1001 - 04 - RtewmdeDocument9 pagesE 1001 - 04 - RtewmdeGopi SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Weld-Solution en LTR 201712 WebDocument8 pagesWeld-Solution en LTR 201712 WebLương Hồ VũNo ratings yet
- 4-5-6. Non Destructive TestingDocument59 pages4-5-6. Non Destructive TestingTEZ ANALYSIS AND STORIES100% (1)
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) in A Nutshell: by MNV Viswanath Scientist - F Quality Assurance Nuclear Fuel ComplexDocument40 pagesNon-Destructive Testing (NDT) in A Nutshell: by MNV Viswanath Scientist - F Quality Assurance Nuclear Fuel ComplexAdhanom G.No ratings yet
- Corrosion InspectionDocument47 pagesCorrosion InspectionMUHAMAD YULIANTONo ratings yet
- Astm-E-2373e2373m-14 TofdDocument13 pagesAstm-E-2373e2373m-14 TofdmajidNo ratings yet
- C 885 - 87 R97 - Qzg4ns04n1i5n0uxDocument6 pagesC 885 - 87 R97 - Qzg4ns04n1i5n0uxÉricka VargasNo ratings yet
- Sonar: Firestone (1940) and Simons (1945)Document9 pagesSonar: Firestone (1940) and Simons (1945)Tom JonesNo ratings yet
- Topic: Advanced Technology in Inspection of Forgings & Capabilities of Midhani QCL Laboratory Presented byDocument79 pagesTopic: Advanced Technology in Inspection of Forgings & Capabilities of Midhani QCL Laboratory Presented byRavikumar KumarNo ratings yet
- ASME BPVC Section V (526-530)Document5 pagesASME BPVC Section V (526-530)Reza Elang HangkosoNo ratings yet
- Ete2033 - Single Phase Wiring Testing - CommDocument21 pagesEte2033 - Single Phase Wiring Testing - CommyammNo ratings yet
- LRGW TR SL 08eDocument5 pagesLRGW TR SL 08eCamilo Godoy VNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Eddy Current TestingDocument113 pagesIntroduction To Eddy Current TestingRanendraNo ratings yet
- Material Integrity Testing MISTDocument2 pagesMaterial Integrity Testing MISTsyafiqNo ratings yet
- What To Study For The ExamsDocument6 pagesWhat To Study For The ExamsvinchandNo ratings yet
- Standard Test Method For Radioscopic Examination of WeldmentsDocument5 pagesStandard Test Method For Radioscopic Examination of WeldmentsWagner Renato AraújoNo ratings yet
- Astm e 1032-06Document6 pagesAstm e 1032-06Renato BarretoNo ratings yet
- How To Choose and Install Instrumentation - Aksan Kawanda PDFDocument95 pagesHow To Choose and Install Instrumentation - Aksan Kawanda PDFRizky Prana AntariksaNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Examination of Weldments: Standard Test Method ForDocument6 pagesRadiographic Examination of Weldments: Standard Test Method ForCaroline SosaNo ratings yet
- E164-97 UT Contact Examination of WeldmentsDocument23 pagesE164-97 UT Contact Examination of WeldmentsALP69No ratings yet
- 3311701basic Instrumentation PDFDocument5 pages3311701basic Instrumentation PDFurvish_soniNo ratings yet
- Nondestructive Evaluation of Wood-Based Flexural Members Using Transverse VibrationDocument8 pagesNondestructive Evaluation of Wood-Based Flexural Members Using Transverse Vibrationasma hamzaNo ratings yet
- Plastics Testing and Characterization: Industrial ApplicationsFrom EverandPlastics Testing and Characterization: Industrial ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Liquid Chromatography - Mass Spectrometry: An IntroductionFrom EverandLiquid Chromatography - Mass Spectrometry: An IntroductionNo ratings yet
- Cavity Ring-Down Spectroscopy: Techniques and ApplicationsFrom EverandCavity Ring-Down Spectroscopy: Techniques and ApplicationsGiel BerdenNo ratings yet
- Radioisotope Gauges for Industrial Process MeasurementsFrom EverandRadioisotope Gauges for Industrial Process MeasurementsNo ratings yet
- Inductively Coupled Plasma Spectrometry and its ApplicationsFrom EverandInductively Coupled Plasma Spectrometry and its ApplicationsSteve J. HillNo ratings yet
- TQIWPJS0ON 9 Aluminium ExtrusionDocument3 pagesTQIWPJS0ON 9 Aluminium Extrusionlamia97No ratings yet
- Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument16 pagesJump To Navigation Jump To Searchlamia97No ratings yet
- Stud And: The MineraDocument172 pagesStud And: The Mineralamia97No ratings yet
- Differences in Densification Behaviour oDocument8 pagesDifferences in Densification Behaviour olamia97No ratings yet
- Quality AssuaranceDocument150 pagesQuality Assuarancelamia97100% (1)
- Procedure Qualification RecordDocument10 pagesProcedure Qualification Recordlamia97No ratings yet
- Coxem CX-200Plus - Operating ManualDocument4 pagesCoxem CX-200Plus - Operating Manuallamia97No ratings yet
- Jubail Industrial College: Dept. of Çáåäïóé Çáãíßçäíßíé Æçáêõäíú / Program Maaden Al/5 Rolling/ExtrusionDocument1 pageJubail Industrial College: Dept. of Çáåäïóé Çáãíßçäíßíé Æçáêõäíú / Program Maaden Al/5 Rolling/Extrusionlamia97No ratings yet
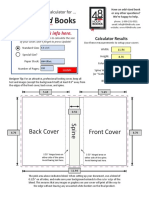
- Case Bound Books: Back Cover Front CoverDocument1 pageCase Bound Books: Back Cover Front Coverlamia97No ratings yet
- Bohr MagnetonsDocument5 pagesBohr Magnetonslamia97No ratings yet
- RaiS2012 PDFDocument21 pagesRaiS2012 PDFlamia97No ratings yet
- 0deec5241b45d2bb69000000 PDFDocument6 pages0deec5241b45d2bb69000000 PDFlamia97No ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Analysis I - TheoryDocument3 pagesPharmaceutical Analysis I - TheoryHarit0% (1)
- 12 Physics EMDocument352 pages12 Physics EMarunkumar.h21426No ratings yet
- 05 Types and Goals of ResearchDocument11 pages05 Types and Goals of ResearchRowena Malabanan MaraquillaNo ratings yet
- HOPE 2 Culminating OutputDocument2 pagesHOPE 2 Culminating OutputArjohn Amoyan100% (1)
- Informal Essay Rubric: Features 4 Expert 3 Accomplished 2 Capable 1 Beginner Quality of WritingDocument2 pagesInformal Essay Rubric: Features 4 Expert 3 Accomplished 2 Capable 1 Beginner Quality of WritingasfdgasdgNo ratings yet
- Reflective Essay Final 1Document3 pagesReflective Essay Final 1api-317997916No ratings yet
- Blood Group Testing - An Experiment To Determine The Blood GroupDocument12 pagesBlood Group Testing - An Experiment To Determine The Blood GroupAbhay Kishore KaulNo ratings yet
- Regulations For The Intercollegiate Membership Examination of The Surgical Royal Colleges of Great Britain and in IrelandDocument10 pagesRegulations For The Intercollegiate Membership Examination of The Surgical Royal Colleges of Great Britain and in IrelandPalwasha MalikNo ratings yet
- BA 631 H4 2018 Syllabus-CADocument7 pagesBA 631 H4 2018 Syllabus-CAKalyan YadavNo ratings yet
- 758 3021 4 PBDocument26 pages758 3021 4 PBAakashNo ratings yet
- Instructions To DOH Deployment Program ApplicantsDocument3 pagesInstructions To DOH Deployment Program ApplicantsRov BillonesNo ratings yet
- Department of Architecture: Deenbandhu Chhotu Ram University of Science and Technology, Murthal (Sonepat)Document42 pagesDepartment of Architecture: Deenbandhu Chhotu Ram University of Science and Technology, Murthal (Sonepat)nikita chawlaNo ratings yet
- Quadrant+SystemDocument34 pagesQuadrant+SystemVM ViKasNo ratings yet
- Documents Required For Non-ECRDocument3 pagesDocuments Required For Non-ECRmep.No ratings yet
- 0500 s09 QP 2Document8 pages0500 s09 QP 2Ali NasrallahNo ratings yet
- Writing A Case Study: Type 1: The Analytical ApproachDocument2 pagesWriting A Case Study: Type 1: The Analytical ApproachPhilip Andrew Briola UndagNo ratings yet
- HPGD2303 Educational Assessment - Esept21 (CS)Document255 pagesHPGD2303 Educational Assessment - Esept21 (CS)ANISAH BINTI ISMAIL STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Transmission Corporation of Telangana Limited Vidyutsoudha::Hyderabad-82Document13 pagesTransmission Corporation of Telangana Limited Vidyutsoudha::Hyderabad-82sydavali.shaikNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal GuidelinesDocument7 pagesProject Proposal GuidelinesAnil MarsaniNo ratings yet
- 2015 Engleza Locala Salaj Clasa A Ixa Sectiunea A SubiectebaremDocument4 pages2015 Engleza Locala Salaj Clasa A Ixa Sectiunea A Subiectebaremmerimeri3No ratings yet
- Moca Vs MMSEDocument2 pagesMoca Vs MMSEYw LiuNo ratings yet
- CLE Syllabus For EvidenceDocument3 pagesCLE Syllabus For EvidencewadzievjNo ratings yet
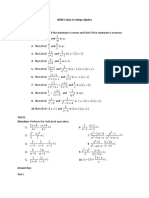
- WEEK 5 Quiz in College AlgebraDocument4 pagesWEEK 5 Quiz in College AlgebraAngelo Rey NavaNo ratings yet
- English I Paper Kc.Document30 pagesEnglish I Paper Kc.srvs1972No ratings yet
- ADocument1 pageAvj_174No ratings yet
- Item AnalysisDocument14 pagesItem Analysisjustin may tuyor100% (1)
- History Code No. 027 Class XI (2021-22) Themes in World HistoryDocument5 pagesHistory Code No. 027 Class XI (2021-22) Themes in World Historysayooj tvNo ratings yet