Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Product: Any Good or Service That Services To Satisfy The Needs or Wants of Customers Product Life Cycle
Product: Any Good or Service That Services To Satisfy The Needs or Wants of Customers Product Life Cycle
Uploaded by
jjkjljCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Core Actual: Unit 4 Product Strategy ProductDocument9 pagesCore Actual: Unit 4 Product Strategy ProductChristina UyNo ratings yet
- MM 1 Session 18 Dr.s.saibabaDocument33 pagesMM 1 Session 18 Dr.s.saibabasovinahalli 1234No ratings yet
- Presentation On: Assigned By:-Presented ByDocument16 pagesPresentation On: Assigned By:-Presented ByJohn22yNo ratings yet
- Siklus Hidup Produk: (Product Life Cycle)Document24 pagesSiklus Hidup Produk: (Product Life Cycle)Nilam SekarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18-The Marketing Mix - Product-PriceDocument67 pagesChapter 18-The Marketing Mix - Product-PriceradhikaiyerNo ratings yet
- With The Name of Almighty Allah, Who Is The Most Beneficent & MercifulDocument44 pagesWith The Name of Almighty Allah, Who Is The Most Beneficent & MercifulALINo ratings yet
- PLC and StrategiesDocument13 pagesPLC and StrategiesMegha RajputNo ratings yet
- Planning Forecasting Marketing of Products of A Company Is Product ManagementDocument24 pagesPlanning Forecasting Marketing of Products of A Company Is Product ManagementAnant MishraNo ratings yet
- Product Life-CycleDocument16 pagesProduct Life-CycleAnjali MithwaniNo ratings yet
- Marketing - Ii Term II - Batch 36 (2019-21) : Faculty: Dr. Satyanarayana RentalaDocument63 pagesMarketing - Ii Term II - Batch 36 (2019-21) : Faculty: Dr. Satyanarayana RentalaMujebu RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: The Marketing Mix: ProductDocument6 pagesChapter 12: The Marketing Mix: ProductNilar WinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 SDocument24 pagesLecture 1 SMarie SarangayaNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle: S. N. ShrivastavaDocument11 pagesProduct Life Cycle: S. N. Shrivastavaspcam-mba marketingNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle (PLC)Document25 pagesProduct Life Cycle (PLC)Shubhranshu ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Product Lifecycle and Marketing StrategiesDocument9 pagesProduct Lifecycle and Marketing StrategiesmoNo ratings yet
- 5.2. New Product DevDocument15 pages5.2. New Product DevJillianne JillNo ratings yet
- 4.5 The Four PS 2022Document47 pages4.5 The Four PS 2022Paula ReinosoNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On Product Life Cycle (PLC) & Marketing Strategies by Dr.J.R.Das Associate Professor SOA UniversityDocument19 pagesA Presentation On Product Life Cycle (PLC) & Marketing Strategies by Dr.J.R.Das Associate Professor SOA UniversitySantosh kumar sahooNo ratings yet
- Lesson Note Product and PLC (Short)Document10 pagesLesson Note Product and PLC (Short)sudhir singhNo ratings yet
- UNIT: 07 "Organizational Structure & Its Planning": PLC: Product Life CycleDocument5 pagesUNIT: 07 "Organizational Structure & Its Planning": PLC: Product Life CycleTabish KhanNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle - BBA - MohanDocument26 pagesProduct Life Cycle - BBA - MohanNeha TimsinaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Product Development &product Life CycleDocument18 pagesUNIT 2 Product Development &product Life Cycletherashijain16No ratings yet
- Product, Services, and Branding Strategies: Chapter 8 & 9Document28 pagesProduct, Services, and Branding Strategies: Chapter 8 & 9Monir HossainNo ratings yet
- Session-7 Product, Brand & Pricing: Dr. Vinith Kumar NairDocument91 pagesSession-7 Product, Brand & Pricing: Dr. Vinith Kumar NairArjun SNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management - II - PPT UNIT 5Document103 pagesMarketing Management - II - PPT UNIT 5Shudhanshu BhattNo ratings yet
- Marketing 18Document13 pagesMarketing 18api-3728497No ratings yet
- Marketing Management: Product Life CycleDocument22 pagesMarketing Management: Product Life CycleKAUSTUBH TARENo ratings yet
- W 9 Driving Growth in Competitive MarketsDocument27 pagesW 9 Driving Growth in Competitive Marketskuy97skuyNo ratings yet
- PLC BasicDocument28 pagesPLC BasicTwinkal chakradhariNo ratings yet
- Module II PBMDocument14 pagesModule II PBMRajesh Kumar NayakNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management: Product Life CycleDocument21 pagesMarketing Management: Product Life Cycleurandom101No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Product ManagementDocument59 pagesLecture 4 - Product ManagementLIN XIAOLINo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 (Strategy)Document15 pagesLecture 9 (Strategy)dilbagsandhu89No ratings yet
- MKG MGT Chapter Eight 4 P'sDocument62 pagesMKG MGT Chapter Eight 4 P'sElias ZeynuNo ratings yet
- New Product Development and Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument24 pagesNew Product Development and Life-Cycle StrategiesTarun UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Managing ProductDocument14 pagesLesson 2 Managing ProductCOCONUTNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document84 pagesUnit 3prasant bashyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document14 pagesChapter 6liniegurlthanarajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document8 pagesChapter 4Bessy BessyNo ratings yet
- BA 104-Marketing Fundamentals and Strategies: Topic - Product Life CycleDocument26 pagesBA 104-Marketing Fundamentals and Strategies: Topic - Product Life Cycles_s_raiNo ratings yet
- Part Three: Business Marketing ProgrammingDocument26 pagesPart Three: Business Marketing ProgrammingCandra GirinataNo ratings yet
- CH 12 - The Marketing Mix ProductDocument25 pagesCH 12 - The Marketing Mix ProductBlack arab GaladimaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document31 pagesChapter 4Marwan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Slides02 StrategyMarketing PARTIDocument20 pagesSlides02 StrategyMarketing PARTIFrancisco Ribeiro e SilvaNo ratings yet
- 4.5 - Mind MapDocument1 page4.5 - Mind MapPravar TrivediNo ratings yet
- Understanding & Dealing With CompetitionDocument18 pagesUnderstanding & Dealing With CompetitionManan AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Product Life Cycle ManagementDocument45 pagesModule 1 - Product Life Cycle ManagementNeha chauhanNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Marketing Mix - ProductDocument25 pages3.3 Marketing Mix - ProductMy worldNo ratings yet
- Session 5 - Product and Brand StrategyDocument30 pagesSession 5 - Product and Brand StrategyMadhav VakhariaNo ratings yet
- Session 5 - Product and Brand StrategyDocument30 pagesSession 5 - Product and Brand StrategySALONI AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Irish A. Flores Charmaine G. Gonzalgo BSA-4Document13 pagesIrish A. Flores Charmaine G. Gonzalgo BSA-4Julie EstopaceNo ratings yet
- CH-6 Product ManagementDocument27 pagesCH-6 Product ManagementSamson HaileyesusNo ratings yet
- Session 7 & 8 - Services BusinessDocument19 pagesSession 7 & 8 - Services BusinessEshan JainNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management - I 2017 - IIIDocument21 pagesMarketing Management - I 2017 - IIIPrakriti Hagar ABSRAINo ratings yet
- The C Programming Language StroustrupDocument7 pagesThe C Programming Language StroustruplejdiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document41 pagesChapter 7Hoàng Ánh MinhNo ratings yet
- New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument28 pagesNew-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategieswaseem483No ratings yet
- 3.3 - Marketing Mix - IGCSE AIDDocument1 page3.3 - Marketing Mix - IGCSE AIDAdam NoorNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument14 pagesProduct Life CycleSrushti GadgeNo ratings yet
- The Profit Zone (Review and Analysis of Slywotzky and Morrison's Book)From EverandThe Profit Zone (Review and Analysis of Slywotzky and Morrison's Book)No ratings yet
- Total (GDP, GNP, GNI) Number of Population: Measures of Economic ActivityDocument9 pagesTotal (GDP, GNP, GNI) Number of Population: Measures of Economic ActivityjjkjljNo ratings yet
- Biology For The IB Diploma - Option C - Ecology and ConservationDocument75 pagesBiology For The IB Diploma - Option C - Ecology and ConservationjjkjljNo ratings yet
- Business IaDocument3 pagesBusiness IajjkjljNo ratings yet
- Biology For The IB Diploma - Option D - Human PhysiologyDocument57 pagesBiology For The IB Diploma - Option D - Human PhysiologyjjkjljNo ratings yet
- Biology For The IB Diploma - Option B - Biotechnology and BioinformaticsDocument50 pagesBiology For The IB Diploma - Option B - Biotechnology and BioinformaticsjjkjljNo ratings yet
- Promotion: Methods Used by A Business To Create Awareness, Attract Customers & Persuade Them To Buy Its ProductsDocument1 pagePromotion: Methods Used by A Business To Create Awareness, Attract Customers & Persuade Them To Buy Its ProductsjjkjljNo ratings yet
- Biology For The IB Diploma - Option A Neurobiology and BehaviourDocument51 pagesBiology For The IB Diploma - Option A Neurobiology and BehaviourjjkjljNo ratings yet
- Intermediaries (중간의) : Agents or firms that act as a middle person between producer and consumerDocument1 pageIntermediaries (중간의) : Agents or firms that act as a middle person between producer and consumerjjkjljNo ratings yet
- Frankenstein-Ethics, Moral ScienceDocument9 pagesFrankenstein-Ethics, Moral SciencejjkjljNo ratings yet
- Biology HL - Chapter Summaries - Second Edition - Pearson 2014Document34 pagesBiology HL - Chapter Summaries - Second Edition - Pearson 2014jjkjljNo ratings yet
- Iii Iihiiiiiiiiiiii 111111: Does User-Oriented Gas Turbine Research Pay Off?Document7 pagesIii Iihiiiiiiiiiiii 111111: Does User-Oriented Gas Turbine Research Pay Off?Morteza YazdizadehNo ratings yet
- ANALE - Stiinte Economice - Vol 2 - 2014 - FinalDocument250 pagesANALE - Stiinte Economice - Vol 2 - 2014 - FinalmhldcnNo ratings yet
- Teacher Newsletter TemplateDocument1 pageTeacher Newsletter TemplateHart LJNo ratings yet
- Comprehension Toolkit 1Document3 pagesComprehension Toolkit 1api-510893209No ratings yet
- Academic Calendar Fall 19-Spring 20 & Summer 20-Final-1 PDFDocument3 pagesAcademic Calendar Fall 19-Spring 20 & Summer 20-Final-1 PDFAhmadNo ratings yet
- KNX System Specifications: Document OverviewDocument8 pagesKNX System Specifications: Document OverviewGentritNo ratings yet
- Indercos2021 Fulltext Congress BookDocument294 pagesIndercos2021 Fulltext Congress BookDr Sneha's Skin and Allergy Clinic IndiaNo ratings yet
- Cutoff1 101020 0Document3 pagesCutoff1 101020 0ghi98183No ratings yet
- Reply of DV ComplaintDocument17 pagesReply of DV Complaintparveensaini2146No ratings yet
- For Updates Visit orDocument6 pagesFor Updates Visit orJFJannahNo ratings yet
- Home Office and Branch Accounting Agency 1Document20 pagesHome Office and Branch Accounting Agency 1John Stephen PendonNo ratings yet
- 2020 Msce Practical Questions TargetDocument30 pages2020 Msce Practical Questions TargetspinyblessingNo ratings yet
- A320 PedestalDocument14 pagesA320 PedestalAiman ZabadNo ratings yet
- Referee Report TemplateDocument2 pagesReferee Report TemplateAna Jufriani100% (1)
- CAD1501 Notes: Unit 1: What You Can Expect To See in The Summary/Notes For This UnitDocument9 pagesCAD1501 Notes: Unit 1: What You Can Expect To See in The Summary/Notes For This UnitSimone BreetNo ratings yet
- Edo Mite GenealogiesDocument23 pagesEdo Mite GenealogiesPeace Matasavaii LeifiNo ratings yet
- The 40 Verse Hanuman Chalisa English Translation - From Ajit Vadakayil BlogDocument4 pagesThe 40 Verse Hanuman Chalisa English Translation - From Ajit Vadakayil BlogBharat ShahNo ratings yet
- Question Bank FormatDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank Formatmahidpr18No ratings yet
- Present Continuous - Present Simple Vs Present ContinuousDocument2 pagesPresent Continuous - Present Simple Vs Present ContinuouseewuanNo ratings yet
- Affidavit - ERRONEOUS ENTRY - Alzate 2Document1 pageAffidavit - ERRONEOUS ENTRY - Alzate 2Diaz Law OfficeNo ratings yet
- The Quiescent Benefits and Drawbacks of Coffee IntakeDocument6 pagesThe Quiescent Benefits and Drawbacks of Coffee IntakeVikram Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- AUDCISE Unit 3 Worksheets Agner, Jam Althea ODocument3 pagesAUDCISE Unit 3 Worksheets Agner, Jam Althea OdfsdNo ratings yet
- CONSTITUTIONAL - CHANGES - TO - BE - MADE - pdf-SOME IMPORTANT CHANGES TO BE MADE IN THE LANKAN PDFDocument32 pagesCONSTITUTIONAL - CHANGES - TO - BE - MADE - pdf-SOME IMPORTANT CHANGES TO BE MADE IN THE LANKAN PDFThavam RatnaNo ratings yet
- Schedule CDocument273 pagesSchedule CAzi PaybarahNo ratings yet
- Human Rights in IslamDocument22 pagesHuman Rights in IslamNoor AliNo ratings yet
- Commerce: Paper 7100/01 Multiple ChoiceDocument7 pagesCommerce: Paper 7100/01 Multiple Choicemstudy123456No ratings yet
- Gentrification in Color and TimeDocument38 pagesGentrification in Color and TimeBNo ratings yet
- A GUIDE TO TRULY RICH CLUB by BO SANCHEZDocument4 pagesA GUIDE TO TRULY RICH CLUB by BO SANCHEZRaymunda Rauto-avilaNo ratings yet
- Alaina Dauscher - Career Journal #01Document2 pagesAlaina Dauscher - Career Journal #01Alaina DauscherNo ratings yet
- Metaverse Report - Thought Leadership 1Document17 pagesMetaverse Report - Thought Leadership 1Tejas KNo ratings yet
Product: Any Good or Service That Services To Satisfy The Needs or Wants of Customers Product Life Cycle
Product: Any Good or Service That Services To Satisfy The Needs or Wants of Customers Product Life Cycle
Uploaded by
jjkjljOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Product: Any Good or Service That Services To Satisfy The Needs or Wants of Customers Product Life Cycle
Product: Any Good or Service That Services To Satisfy The Needs or Wants of Customers Product Life Cycle
Uploaded by
jjkjljCopyright:
Available Formats
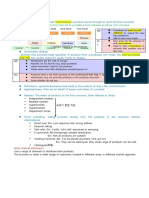
Product: Any good or service that services to satisfy the needs or wants of customers
Product life cycle: The different stages that a product is likely to go through from its initial design and launch to its decline
R&D stage: Designing & Testing the product
- Companies invest a lot of money developing a
new idea into a product (high costs)
- No sales revenue
- High R&D costs
- Prototypes(시제품)&test markets are used
PLC stage Investment level Profit Cash flow
R&D Very high None High
Launch
Launch Very highto market
stage: Product introduced Growth
Little, if any stage: Sees salesNegative
revenue increasing
Growth - High
Sales slowly increase - More consumer awareness
Yes, rising Positive increases sales quickly
Maturity- Less
Extensive promotion - Increase
High, little/no growththe distribution
Positive
Decline - Not profitable Little, if any Yes, falling
- Strong profits Positive, falling
- Objective is to move to growth stage as quickly - More competitors
and become market leader - Product differentiation
- Innovators buy the product - Early adopters(사용자) buy the product
Extension strategy: Maintain sales revenue in the maturity phases
Maturity stage: Sales revenue increase, slowly Decline stage: final stage of PLC
- Sales increasing (slower rate) & peaks - Consumer tastes have changed or
- Economics of scale product becomes old
- Sales start to fall
- Heavy promotion to differentiate brands
- Promotional spending is cut
- Product lines extended (more product, versions
- Price, profit↓
(버전) & variations (변화))
- Companies stop production
- Unsuccessful competitors drop from market
- Product is dropped from the market
Reduce price - Target different market segments
Sell existing products into new markets - Develop new promotional strategies
Find new uses for the product - Change product’s packaging
Boston consulting group matrix: Marketing planning tool for product portfolio
AD - Tool used to identify the need to rebalance portfolio
- Can be applied at all levels
Boston Matrix
Dis - Market share does not always translate to profit
- Does not identify root cause of low market share
- Simplifies complex issue of portfolio management
Branding: Differencing a firm’s products from competitors
Sign - Branding can be so influential that is actually alters the consumers feeling & their perception of the product
Symbol
Aspects of branding: Brand awareness
Color scheme ∙ Attracts consumers when they are making buying decisions
Measures the extent to which potential customers or the
Font ∙ Gives the firms a competitive edge over rivals, resulting in
greater market share
public recognizes a particular brand
Design ∙ Develops long-term sales through brand loyalty
Role & Advantages Brand awareness
Brand development
- Differentiation
↓ Marketing process of proving and enlarging the brand
Brand development
- Recognition Helps to extend a product’s life cycle name to boost sales revenue & market share
- Legal instrument Brand loyalty
- Reduces risk Consumer keeps buy a same brand of a product. Have a
- Premium pricing preference of that brand
- Reduce price elasticity of demand Brand value
- Extension Premium that customers are willing to pay for a brand
- Barriers to new competitors name over and above the value of the product itself
Packaging: The ways in which a product is presented to the consumer
Importance:
- Huge impact on customer perceptions of a product or brand
- Differentiates from competitor products
- Protects that product from damage during transportation
- Provides information (law)
- Makes distribution easier
- Used to impulse(충동) buying
- Promote the brand or the business
You might also like
- Core Actual: Unit 4 Product Strategy ProductDocument9 pagesCore Actual: Unit 4 Product Strategy ProductChristina UyNo ratings yet
- MM 1 Session 18 Dr.s.saibabaDocument33 pagesMM 1 Session 18 Dr.s.saibabasovinahalli 1234No ratings yet
- Presentation On: Assigned By:-Presented ByDocument16 pagesPresentation On: Assigned By:-Presented ByJohn22yNo ratings yet
- Siklus Hidup Produk: (Product Life Cycle)Document24 pagesSiklus Hidup Produk: (Product Life Cycle)Nilam SekarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18-The Marketing Mix - Product-PriceDocument67 pagesChapter 18-The Marketing Mix - Product-PriceradhikaiyerNo ratings yet
- With The Name of Almighty Allah, Who Is The Most Beneficent & MercifulDocument44 pagesWith The Name of Almighty Allah, Who Is The Most Beneficent & MercifulALINo ratings yet
- PLC and StrategiesDocument13 pagesPLC and StrategiesMegha RajputNo ratings yet
- Planning Forecasting Marketing of Products of A Company Is Product ManagementDocument24 pagesPlanning Forecasting Marketing of Products of A Company Is Product ManagementAnant MishraNo ratings yet
- Product Life-CycleDocument16 pagesProduct Life-CycleAnjali MithwaniNo ratings yet
- Marketing - Ii Term II - Batch 36 (2019-21) : Faculty: Dr. Satyanarayana RentalaDocument63 pagesMarketing - Ii Term II - Batch 36 (2019-21) : Faculty: Dr. Satyanarayana RentalaMujebu RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: The Marketing Mix: ProductDocument6 pagesChapter 12: The Marketing Mix: ProductNilar WinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 SDocument24 pagesLecture 1 SMarie SarangayaNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle: S. N. ShrivastavaDocument11 pagesProduct Life Cycle: S. N. Shrivastavaspcam-mba marketingNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle (PLC)Document25 pagesProduct Life Cycle (PLC)Shubhranshu ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Product Lifecycle and Marketing StrategiesDocument9 pagesProduct Lifecycle and Marketing StrategiesmoNo ratings yet
- 5.2. New Product DevDocument15 pages5.2. New Product DevJillianne JillNo ratings yet
- 4.5 The Four PS 2022Document47 pages4.5 The Four PS 2022Paula ReinosoNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On Product Life Cycle (PLC) & Marketing Strategies by Dr.J.R.Das Associate Professor SOA UniversityDocument19 pagesA Presentation On Product Life Cycle (PLC) & Marketing Strategies by Dr.J.R.Das Associate Professor SOA UniversitySantosh kumar sahooNo ratings yet
- Lesson Note Product and PLC (Short)Document10 pagesLesson Note Product and PLC (Short)sudhir singhNo ratings yet
- UNIT: 07 "Organizational Structure & Its Planning": PLC: Product Life CycleDocument5 pagesUNIT: 07 "Organizational Structure & Its Planning": PLC: Product Life CycleTabish KhanNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle - BBA - MohanDocument26 pagesProduct Life Cycle - BBA - MohanNeha TimsinaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Product Development &product Life CycleDocument18 pagesUNIT 2 Product Development &product Life Cycletherashijain16No ratings yet
- Product, Services, and Branding Strategies: Chapter 8 & 9Document28 pagesProduct, Services, and Branding Strategies: Chapter 8 & 9Monir HossainNo ratings yet
- Session-7 Product, Brand & Pricing: Dr. Vinith Kumar NairDocument91 pagesSession-7 Product, Brand & Pricing: Dr. Vinith Kumar NairArjun SNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management - II - PPT UNIT 5Document103 pagesMarketing Management - II - PPT UNIT 5Shudhanshu BhattNo ratings yet
- Marketing 18Document13 pagesMarketing 18api-3728497No ratings yet
- Marketing Management: Product Life CycleDocument22 pagesMarketing Management: Product Life CycleKAUSTUBH TARENo ratings yet
- W 9 Driving Growth in Competitive MarketsDocument27 pagesW 9 Driving Growth in Competitive Marketskuy97skuyNo ratings yet
- PLC BasicDocument28 pagesPLC BasicTwinkal chakradhariNo ratings yet
- Module II PBMDocument14 pagesModule II PBMRajesh Kumar NayakNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management: Product Life CycleDocument21 pagesMarketing Management: Product Life Cycleurandom101No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Product ManagementDocument59 pagesLecture 4 - Product ManagementLIN XIAOLINo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 (Strategy)Document15 pagesLecture 9 (Strategy)dilbagsandhu89No ratings yet
- MKG MGT Chapter Eight 4 P'sDocument62 pagesMKG MGT Chapter Eight 4 P'sElias ZeynuNo ratings yet
- New Product Development and Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument24 pagesNew Product Development and Life-Cycle StrategiesTarun UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Managing ProductDocument14 pagesLesson 2 Managing ProductCOCONUTNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document84 pagesUnit 3prasant bashyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document14 pagesChapter 6liniegurlthanarajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document8 pagesChapter 4Bessy BessyNo ratings yet
- BA 104-Marketing Fundamentals and Strategies: Topic - Product Life CycleDocument26 pagesBA 104-Marketing Fundamentals and Strategies: Topic - Product Life Cycles_s_raiNo ratings yet
- Part Three: Business Marketing ProgrammingDocument26 pagesPart Three: Business Marketing ProgrammingCandra GirinataNo ratings yet
- CH 12 - The Marketing Mix ProductDocument25 pagesCH 12 - The Marketing Mix ProductBlack arab GaladimaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document31 pagesChapter 4Marwan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Slides02 StrategyMarketing PARTIDocument20 pagesSlides02 StrategyMarketing PARTIFrancisco Ribeiro e SilvaNo ratings yet
- 4.5 - Mind MapDocument1 page4.5 - Mind MapPravar TrivediNo ratings yet
- Understanding & Dealing With CompetitionDocument18 pagesUnderstanding & Dealing With CompetitionManan AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Product Life Cycle ManagementDocument45 pagesModule 1 - Product Life Cycle ManagementNeha chauhanNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Marketing Mix - ProductDocument25 pages3.3 Marketing Mix - ProductMy worldNo ratings yet
- Session 5 - Product and Brand StrategyDocument30 pagesSession 5 - Product and Brand StrategyMadhav VakhariaNo ratings yet
- Session 5 - Product and Brand StrategyDocument30 pagesSession 5 - Product and Brand StrategySALONI AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Irish A. Flores Charmaine G. Gonzalgo BSA-4Document13 pagesIrish A. Flores Charmaine G. Gonzalgo BSA-4Julie EstopaceNo ratings yet
- CH-6 Product ManagementDocument27 pagesCH-6 Product ManagementSamson HaileyesusNo ratings yet
- Session 7 & 8 - Services BusinessDocument19 pagesSession 7 & 8 - Services BusinessEshan JainNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management - I 2017 - IIIDocument21 pagesMarketing Management - I 2017 - IIIPrakriti Hagar ABSRAINo ratings yet
- The C Programming Language StroustrupDocument7 pagesThe C Programming Language StroustruplejdiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document41 pagesChapter 7Hoàng Ánh MinhNo ratings yet
- New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument28 pagesNew-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategieswaseem483No ratings yet
- 3.3 - Marketing Mix - IGCSE AIDDocument1 page3.3 - Marketing Mix - IGCSE AIDAdam NoorNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument14 pagesProduct Life CycleSrushti GadgeNo ratings yet
- The Profit Zone (Review and Analysis of Slywotzky and Morrison's Book)From EverandThe Profit Zone (Review and Analysis of Slywotzky and Morrison's Book)No ratings yet
- Total (GDP, GNP, GNI) Number of Population: Measures of Economic ActivityDocument9 pagesTotal (GDP, GNP, GNI) Number of Population: Measures of Economic ActivityjjkjljNo ratings yet
- Biology For The IB Diploma - Option C - Ecology and ConservationDocument75 pagesBiology For The IB Diploma - Option C - Ecology and ConservationjjkjljNo ratings yet
- Business IaDocument3 pagesBusiness IajjkjljNo ratings yet
- Biology For The IB Diploma - Option D - Human PhysiologyDocument57 pagesBiology For The IB Diploma - Option D - Human PhysiologyjjkjljNo ratings yet
- Biology For The IB Diploma - Option B - Biotechnology and BioinformaticsDocument50 pagesBiology For The IB Diploma - Option B - Biotechnology and BioinformaticsjjkjljNo ratings yet
- Promotion: Methods Used by A Business To Create Awareness, Attract Customers & Persuade Them To Buy Its ProductsDocument1 pagePromotion: Methods Used by A Business To Create Awareness, Attract Customers & Persuade Them To Buy Its ProductsjjkjljNo ratings yet
- Biology For The IB Diploma - Option A Neurobiology and BehaviourDocument51 pagesBiology For The IB Diploma - Option A Neurobiology and BehaviourjjkjljNo ratings yet
- Intermediaries (중간의) : Agents or firms that act as a middle person between producer and consumerDocument1 pageIntermediaries (중간의) : Agents or firms that act as a middle person between producer and consumerjjkjljNo ratings yet
- Frankenstein-Ethics, Moral ScienceDocument9 pagesFrankenstein-Ethics, Moral SciencejjkjljNo ratings yet
- Biology HL - Chapter Summaries - Second Edition - Pearson 2014Document34 pagesBiology HL - Chapter Summaries - Second Edition - Pearson 2014jjkjljNo ratings yet
- Iii Iihiiiiiiiiiiii 111111: Does User-Oriented Gas Turbine Research Pay Off?Document7 pagesIii Iihiiiiiiiiiiii 111111: Does User-Oriented Gas Turbine Research Pay Off?Morteza YazdizadehNo ratings yet
- ANALE - Stiinte Economice - Vol 2 - 2014 - FinalDocument250 pagesANALE - Stiinte Economice - Vol 2 - 2014 - FinalmhldcnNo ratings yet
- Teacher Newsletter TemplateDocument1 pageTeacher Newsletter TemplateHart LJNo ratings yet
- Comprehension Toolkit 1Document3 pagesComprehension Toolkit 1api-510893209No ratings yet
- Academic Calendar Fall 19-Spring 20 & Summer 20-Final-1 PDFDocument3 pagesAcademic Calendar Fall 19-Spring 20 & Summer 20-Final-1 PDFAhmadNo ratings yet
- KNX System Specifications: Document OverviewDocument8 pagesKNX System Specifications: Document OverviewGentritNo ratings yet
- Indercos2021 Fulltext Congress BookDocument294 pagesIndercos2021 Fulltext Congress BookDr Sneha's Skin and Allergy Clinic IndiaNo ratings yet
- Cutoff1 101020 0Document3 pagesCutoff1 101020 0ghi98183No ratings yet
- Reply of DV ComplaintDocument17 pagesReply of DV Complaintparveensaini2146No ratings yet
- For Updates Visit orDocument6 pagesFor Updates Visit orJFJannahNo ratings yet
- Home Office and Branch Accounting Agency 1Document20 pagesHome Office and Branch Accounting Agency 1John Stephen PendonNo ratings yet
- 2020 Msce Practical Questions TargetDocument30 pages2020 Msce Practical Questions TargetspinyblessingNo ratings yet
- A320 PedestalDocument14 pagesA320 PedestalAiman ZabadNo ratings yet
- Referee Report TemplateDocument2 pagesReferee Report TemplateAna Jufriani100% (1)
- CAD1501 Notes: Unit 1: What You Can Expect To See in The Summary/Notes For This UnitDocument9 pagesCAD1501 Notes: Unit 1: What You Can Expect To See in The Summary/Notes For This UnitSimone BreetNo ratings yet
- Edo Mite GenealogiesDocument23 pagesEdo Mite GenealogiesPeace Matasavaii LeifiNo ratings yet
- The 40 Verse Hanuman Chalisa English Translation - From Ajit Vadakayil BlogDocument4 pagesThe 40 Verse Hanuman Chalisa English Translation - From Ajit Vadakayil BlogBharat ShahNo ratings yet
- Question Bank FormatDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank Formatmahidpr18No ratings yet
- Present Continuous - Present Simple Vs Present ContinuousDocument2 pagesPresent Continuous - Present Simple Vs Present ContinuouseewuanNo ratings yet
- Affidavit - ERRONEOUS ENTRY - Alzate 2Document1 pageAffidavit - ERRONEOUS ENTRY - Alzate 2Diaz Law OfficeNo ratings yet
- The Quiescent Benefits and Drawbacks of Coffee IntakeDocument6 pagesThe Quiescent Benefits and Drawbacks of Coffee IntakeVikram Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- AUDCISE Unit 3 Worksheets Agner, Jam Althea ODocument3 pagesAUDCISE Unit 3 Worksheets Agner, Jam Althea OdfsdNo ratings yet
- CONSTITUTIONAL - CHANGES - TO - BE - MADE - pdf-SOME IMPORTANT CHANGES TO BE MADE IN THE LANKAN PDFDocument32 pagesCONSTITUTIONAL - CHANGES - TO - BE - MADE - pdf-SOME IMPORTANT CHANGES TO BE MADE IN THE LANKAN PDFThavam RatnaNo ratings yet
- Schedule CDocument273 pagesSchedule CAzi PaybarahNo ratings yet
- Human Rights in IslamDocument22 pagesHuman Rights in IslamNoor AliNo ratings yet
- Commerce: Paper 7100/01 Multiple ChoiceDocument7 pagesCommerce: Paper 7100/01 Multiple Choicemstudy123456No ratings yet
- Gentrification in Color and TimeDocument38 pagesGentrification in Color and TimeBNo ratings yet
- A GUIDE TO TRULY RICH CLUB by BO SANCHEZDocument4 pagesA GUIDE TO TRULY RICH CLUB by BO SANCHEZRaymunda Rauto-avilaNo ratings yet
- Alaina Dauscher - Career Journal #01Document2 pagesAlaina Dauscher - Career Journal #01Alaina DauscherNo ratings yet
- Metaverse Report - Thought Leadership 1Document17 pagesMetaverse Report - Thought Leadership 1Tejas KNo ratings yet