Professional Documents
Culture Documents
04 - Network Representations and Topologies
04 - Network Representations and Topologies
Uploaded by
WorldCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- MPLS Interview QuestionsDocument17 pagesMPLS Interview QuestionsSyed100% (1)
- Software-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachFrom EverandSoftware-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Technicolor C2100T ManualDocument4 pagesTechnicolor C2100T ManualTracy RossNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networks - Network Representations and TopologiesDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Networks - Network Representations and Topologiesbeth pelaez ariasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networks - Network Representations and TopologiesDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Networks - Network Representations and TopologiesZulkifliNo ratings yet
- 04 Network Representations and TopologiesDocument8 pages04 Network Representations and TopologiesLicdo Fausto RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 05.3 - Common Types of NetworksDocument2 pages05.3 - Common Types of NetworksWorldNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networks - IntroductionDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Networks - IntroductionZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To Computer Networks: Structure Page NosDocument226 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Computer Networks: Structure Page NosYash AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Tema 2 - Networking EssentialsDocument19 pagesTema 2 - Networking EssentialsDaniel EspadasNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document18 pagesCH 01MuwienNo ratings yet
- 07 - Reliable NetworksDocument2 pages07 - Reliable NetworksWorldNo ratings yet
- 2introduction To Networks - Common Types of Networks-1Document5 pages2introduction To Networks - Common Types of Networks-1ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks and CommunicationDocument25 pagesComputer Networks and CommunicationFirdaus AhmadNo ratings yet
- Networking Technologies ch01Document18 pagesNetworking Technologies ch01api-3754041No ratings yet
- Schema Learning Area 3Document9 pagesSchema Learning Area 3tycoon96No ratings yet
- Data Communications Networks Network Types Protocol LayeringDocument48 pagesData Communications Networks Network Types Protocol LayeringiotNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networks - IntroductionDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Networks - Introductionbeth pelaez ariasNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 - INTRODUCTION TO Computer ApplicationDocument39 pagesUnit-1 - INTRODUCTION TO Computer ApplicationKajal SoniNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 PdsDocument17 pagesUnit 1 PdsAmuthapriyaa GLNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networks - Common Types of NetworksDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Networks - Common Types of Networksbeth pelaez ariasNo ratings yet
- Network Device Drivers in Linux Sub1Document3 pagesNetwork Device Drivers in Linux Sub1hrushiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networks - Network ComponentsDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Networks - Network ComponentsFaical BitamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Networks: Ed T. EspirituDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Computer Networks: Ed T. EspirituMarjhon TubillaNo ratings yet
- Project Report 1Document46 pagesProject Report 1archit garg100% (1)
- Omputer Etworks: S GangulyDocument14 pagesOmputer Etworks: S GangulyApurva JainNo ratings yet
- 02.1 - Cisco IOS AccessDocument2 pages02.1 - Cisco IOS AccessWorldNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document14 pagesUnit 4kehihi3No ratings yet
- Networks Tutorial: by Amritha Bhat (EDTECH 541)Document23 pagesNetworks Tutorial: by Amritha Bhat (EDTECH 541)amritharauNo ratings yet
- Network CC V1.0Document113 pagesNetwork CC V1.0kaushalNo ratings yet
- MI0035 Computer Networks Descriptive QnsDocument48 pagesMI0035 Computer Networks Descriptive QnsCharles LwangaNo ratings yet
- 4.10.3 Networks and The Effects of Using ThemDocument7 pages4.10.3 Networks and The Effects of Using Themzaki544203No ratings yet
- Networking ProjectDocument21 pagesNetworking ProjectArishveer KaurNo ratings yet
- E CONTENTcomputer NetworkDocument26 pagesE CONTENTcomputer NetworkniharikaNo ratings yet
- CN PR9Document6 pagesCN PR9tovev86979No ratings yet
- Computer NetworkingDocument14 pagesComputer NetworkingJOELNo ratings yet
- PROYECTODocument11 pagesPROYECTOAzteca PicksNo ratings yet
- With The Help of This Diagram, Try To Describe The Function of These Components of A Typical Network SystemDocument8 pagesWith The Help of This Diagram, Try To Describe The Function of These Components of A Typical Network Systemjalello1No ratings yet
- Fundamental Concepts of Computer Networks.: Prepared byDocument70 pagesFundamental Concepts of Computer Networks.: Prepared bySf All People faizNo ratings yet
- 30a-Esp8266 Mesh User Guide en PDFDocument19 pages30a-Esp8266 Mesh User Guide en PDFJULIAN DE LA TORRENo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Notes 3 - TutorialsDuniyaDocument146 pagesComputer Networks Notes 3 - TutorialsDuniyaReenaNo ratings yet
- CCN BcaDocument70 pagesCCN Bcajyothi12swaroop10No ratings yet
- Survey of Wireless Sensor Networks Simulation Tools For Demanding ApplicationsDocument5 pagesSurvey of Wireless Sensor Networks Simulation Tools For Demanding ApplicationsChiranjib PatraNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Computer Network SyllabusDocument8 pagesData Communication and Computer Network SyllabusManoj kavediaNo ratings yet
- Networks MergedDocument277 pagesNetworks Mergedsmitianraj2005No ratings yet
- Basiccomputernetworking 2of5 0Document3 pagesBasiccomputernetworking 2of5 0Abhishek ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Information and Communications Technology Academy Digital Arts DepartmentDocument33 pagesInformation and Communications Technology Academy Digital Arts DepartmentVeronica FerrerNo ratings yet
- 2.0 NetworkDocument24 pages2.0 NetworkChinta QaishyNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two (Network Thesis Book)Document16 pagesChapter Two (Network Thesis Book)Latest Tricks100% (1)
- Chapter 1 6Document69 pagesChapter 1 6b.wafiaNo ratings yet
- Networking CH 7Document30 pagesNetworking CH 7AlHusseinAlShukairiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LAN Protocols: Chapter GoalsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To LAN Protocols: Chapter GoalsPrashant TandanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LAN Protocols: Chapter GoalsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To LAN Protocols: Chapter GoalskartheekNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument68 pagesComputer NetworksZahid IqbalNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Tcp/Ip: Computer NetworkingDocument16 pagesAn Introduction To Tcp/Ip: Computer NetworkingPazoNo ratings yet
- Objective Mappings Testout Network Pro Enus 6 - 0 - XDocument85 pagesObjective Mappings Testout Network Pro Enus 6 - 0 - XJared WuerzburgerNo ratings yet
- Telecommunications: Present Status and Future TrendsFrom EverandTelecommunications: Present Status and Future TrendsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- 02.3 - Cisco IOS AccessDocument2 pages02.3 - Cisco IOS AccessWorldNo ratings yet
- WCS - Chapter 07 - Sol HintsDocument7 pagesWCS - Chapter 07 - Sol HintsWorldNo ratings yet
- GNS3 Lab ManualDocument101 pagesGNS3 Lab ManualWorldNo ratings yet
- IOS Navigation: Primary Command ModesDocument2 pagesIOS Navigation: Primary Command ModesWorldNo ratings yet
- Con Gure IP Addressing: Manual IP Address Con Guration For End DevicesDocument2 pagesCon Gure IP Addressing: Manual IP Address Con Guration For End DevicesWorldNo ratings yet
- 02.1 - Cisco IOS AccessDocument2 pages02.1 - Cisco IOS AccessWorldNo ratings yet
- 04 - The Command StructureDocument2 pages04 - The Command StructureWorldNo ratings yet
- 05 - Basic Device ConfigurationDocument2 pages05 - Basic Device ConfigurationWorldNo ratings yet
- 09 - Network SecurityDocument1 page09 - Network SecurityWorldNo ratings yet
- 03 - Network ComponentsDocument2 pages03 - Network ComponentsWorldNo ratings yet
- 07 - Reliable NetworksDocument2 pages07 - Reliable NetworksWorldNo ratings yet
- 05.3 - Common Types of NetworksDocument2 pages05.3 - Common Types of NetworksWorldNo ratings yet
- 02 - Networks Affect Our LivesDocument1 page02 - Networks Affect Our LivesWorldNo ratings yet
- 01 - IntroductionDocument1 page01 - IntroductionWorldNo ratings yet
- Manual NP 301 3one DataDocument30 pagesManual NP 301 3one DataCARLOS IVAN RIOSNo ratings yet
- Docker NetworkingDocument6 pagesDocker Networkingjames.sharma251No ratings yet
- Cisco Aaa Case Study OverviewDocument16 pagesCisco Aaa Case Study OverviewEstuardo Hernández ArguetaNo ratings yet
- KX-TDE100 KX-TDE200 KX-TDE600: Programming Manual For Virtual SIP CO Line CardDocument60 pagesKX-TDE100 KX-TDE200 KX-TDE600: Programming Manual For Virtual SIP CO Line CardJonny TekNo ratings yet
- Setup Huawei ONUDocument2 pagesSetup Huawei ONUfuck youbixNo ratings yet
- Diameter ProtocolDocument14 pagesDiameter ProtocolversatilityNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 Address TranslationDocument16 pagesChapter7 Address TranslationDacaen DanNo ratings yet
- Hikvision 0904848459 Camera TCMDocument1 pageHikvision 0904848459 Camera TCMKs QuốcNo ratings yet
- Aws Architecture GuideDocument84 pagesAws Architecture Guideatlnacional02No ratings yet
- OS6850 Broch 031806rD 07janDocument16 pagesOS6850 Broch 031806rD 07janPrueNo ratings yet
- Network Layer Architecture and Types of ProtocolDocument3 pagesNetwork Layer Architecture and Types of ProtocolSuryanshNo ratings yet
- EDS-405A Series - Moxa-Eds-405a-Series-Firmware-V3.11.rom - Software Release History PDFDocument17 pagesEDS-405A Series - Moxa-Eds-405a-Series-Firmware-V3.11.rom - Software Release History PDFMiroslaw LabudaNo ratings yet
- Cisco 4000 Series ISRs Software Configuration GuideDocument330 pagesCisco 4000 Series ISRs Software Configuration GuideJack NicoleNo ratings yet
- Ethical Hacking Exercises W3-Memo-StM-V1-24082021Document4 pagesEthical Hacking Exercises W3-Memo-StM-V1-24082021BonginkosiNo ratings yet
- DMZDocument31 pagesDMZKarekezi Prudence100% (1)
- Scrip MikrotikDocument16 pagesScrip MikrotikbreaknetcfNo ratings yet
- Notes FinalDocument34 pagesNotes FinalNasir AliNo ratings yet
- Guide Commandes cr2960 PDFDocument994 pagesGuide Commandes cr2960 PDFǾssǿ BelkadiNo ratings yet
- VLSM ActivityDocument15 pagesVLSM ActivitySarah Jane MangenteNo ratings yet
- Radiolinie SIAE ALS ALFO Series 2Document57 pagesRadiolinie SIAE ALS ALFO Series 2Advantec Srl50% (2)
- PaloAltoNetworks Network Design GuideDocument110 pagesPaloAltoNetworks Network Design GuideLiam Cowden100% (1)
- PPPoE-CONF ENCONTRADA NA NETDocument4 pagesPPPoE-CONF ENCONTRADA NA NETFábio FariasNo ratings yet
- Avaya 4500 Seris Config GuideDocument400 pagesAvaya 4500 Seris Config GuideJustin Tompkin-DrewNo ratings yet
- BGP Confederation and Communities LabbDocument11 pagesBGP Confederation and Communities Labbmmihir82100% (1)
- PL NEW ARK 5 Februari 2013Document86 pagesPL NEW ARK 5 Februari 2013Rizhal AdarriyantoNo ratings yet
- Internet Technology Sheet 2Document8 pagesInternet Technology Sheet 2Abdelrahman ElattarNo ratings yet
- VTP Server:: Switch (Config) #Int Range g0/1-2 Switch (Config-If-Range) #Switchport Mode TrunkDocument9 pagesVTP Server:: Switch (Config) #Int Range g0/1-2 Switch (Config-If-Range) #Switchport Mode TrunkSara VananNo ratings yet
- Gazelle S1020i: L2 Manageable Industrial SwitchDocument2 pagesGazelle S1020i: L2 Manageable Industrial SwitchMaz MoektiNo ratings yet
04 - Network Representations and Topologies
04 - Network Representations and Topologies
Uploaded by
WorldOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
04 - Network Representations and Topologies
04 - Network Representations and Topologies
Uploaded by
WorldCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction to Networks v7.0
/ Networking Today / Network Representations and Topologies
Introduction to Networks
1
Network Representations and Topologies
Networking Today
1.0 Introduction 1.3.1
1.0.1 Why should I take this module? Network Representations
What will I learn to do in this
1.0.2
module?
Network architects and administrators must be able to show what their networks will look like. They need to be able to easily
see which components connect to other components, where they will be located, and how they will be connected. Diagrams of
1.1 Networks Aect our Lives networks often use symbols, like those shown in the gure, to represent the dierent devices and connections that make up a
network.
1.1.1 Networks Connect Us
Video - The Cisco Networking
1.1.2
Academy Learning Experience
Desktop Computer Laptop Printer
1.1.3 No Boundaries End Devices
1.2 Network Components IP Phone Wireless Tablet TelePresence Endpoint
1.2.1 Host Roles
1.2.2 Peer-to-Peer
Wireless Router LAN Switch Router
Intermediary
1.2.3 End Devices
Devices
1.2.4 Intermediary Devices Multilayer Switch Firewall Appliance
1.2.5 Network Media
Wireless Media
Check Your Understanding -
1.2.6
Network Components
Network Media LAN Media
Network Representations
1.3
and Topologies WAN Media
1.3.1 Network Representations
1.3.2 Topology Diagrams
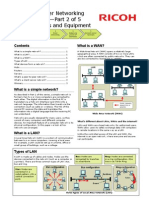
A diagram provides an easy way to understand how devices connect in a large network. This type of “picture” of a network is
known as a topology diagram. The ability to recognize the logical representations of the physical networking components is
Check Your Understanding -
critical to being able to visualize the organization and operation of a network.
1.3.3 Network Representations and
Topologies
In addition to these representations, specialized terminology is used to describe how each of these devices and media connect
to each other:
1.4 Common Types of Networks
Network Interface Card (NIC) - A NIC physically connects the end device to the network.
1.5 Internet Connections Physical Port - A connector or outlet on a networking device where the media connects to an end device or another
networking device.
Interface - Specialized ports on a networking device that connect to individual networks. Because routers connect networks,
1.6 Reliable Networks the ports on a router are referred to as network interfaces.
1.7 Network Trends Note: The terms port and interface are often used interchangeably.
1.8 Network Security
1.3.2
1.9 The IT Professional
1.10 Module Practice and Quiz
Topology Diagrams
Basic Switch and End Device
2 Conguration Topology diagrams are mandatory documentation for anyone working with a network. They provide a visual map of how the
network is connected. There are two types of topology diagrams: physical and logical.
Physical Topology Diagrams
3 Protocols and Models
Physical topology diagrams illustrate the physical location of intermediary devices and cable installation, as shown in the gure.
You can see that the rooms in which these devices are located are labeled in this physical topology.
4 Physical Layer
5 Number Systems
Internet Rm: 2124
Rack 1
6 Data Link Layer Shelf 1 Class 1: Rm: 2125
Server Room: Rm: 2158
Web Server
Rack 2 S3
7 Ethernet Switching Shelf 1
Rack 1 Rack 1 Rack 1
Shelf 2 Shelf 1 Shelf 2 Class 2: Rm: 2126
Email Server
8 Network Layer Rack 2
Shelf 2
S1 R1 S4
Rack 1
9 Address Resolution File Server Shelf 3 Rack 1
Rack 2 Class 3: Rm: 2127
Shelf 3
Shelf 3
S2
10 Basic Router Conguration S5
11 IPv4 Addressing
IT Office: Rm: 2159
12 IPv6 Addressing
Logical Topology Diagrams
13 ICMP
Logical topology diagrams illustrate devices, ports, and the addressing scheme of the network, as shown in the gure. You can
see which end devices are connected to which intermediary devices and what media is being used.
14 Transport Layer
15 Application Layer Internet
Network Security Network Network 192.168.100.0
16 Fundamentals 192.168.10.0
Fa0/1
Web Server S3
17 G0/1
Build a Small Network
G0/0 Network 192.168.101.0
G1/0
Fa0/1
G0/1 G1/1 G0/1 Fa0/1
Email Server Fa0/2
S1 G0/1 R1 G1/2 S4
Fa0/3 G0/2
G0/1 Network 192.168.102.0
File Server
G0/1
S2 Fa0/1
Fa0/1 Fa0/2 S5
Network 192.168.11.0
The topologies shown in the physical and logical diagrams are appropriate for your level of understanding at this point in the
course. Search the internet for “network topology diagrams” to see some more complex examples. If you add the word “Cisco”
to your search phrase, you will nd many topologies using icons that are similar to what you have seen in these gures.
1.3.3
Check Your Understanding - Network Representations
and Topologies
Check your understanding of network representations and topologies by choosing the BEST answer to the
following questions.
1. Which connection physically connects the end device to the network?
Port
NIC
Interface
2. Which connections are specialized ports on a networking device that connect
to individual networks?
Port
NIC
Interface
3. Which type of network topology lets you see which end devices are connected
to which intermediary devices and what media is being used?
Physical topology
Logical topology
4. Which type of network topology lets you see the actual location of intermediary Check
devices and cable installation?
Show Me
Physical topology
Logical topology
Reset
Network Components
1.2 1.4
Common Types of Networks
You might also like
- MPLS Interview QuestionsDocument17 pagesMPLS Interview QuestionsSyed100% (1)
- Software-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachFrom EverandSoftware-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Technicolor C2100T ManualDocument4 pagesTechnicolor C2100T ManualTracy RossNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networks - Network Representations and TopologiesDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Networks - Network Representations and Topologiesbeth pelaez ariasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networks - Network Representations and TopologiesDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Networks - Network Representations and TopologiesZulkifliNo ratings yet
- 04 Network Representations and TopologiesDocument8 pages04 Network Representations and TopologiesLicdo Fausto RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 05.3 - Common Types of NetworksDocument2 pages05.3 - Common Types of NetworksWorldNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networks - IntroductionDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Networks - IntroductionZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To Computer Networks: Structure Page NosDocument226 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Computer Networks: Structure Page NosYash AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Tema 2 - Networking EssentialsDocument19 pagesTema 2 - Networking EssentialsDaniel EspadasNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document18 pagesCH 01MuwienNo ratings yet
- 07 - Reliable NetworksDocument2 pages07 - Reliable NetworksWorldNo ratings yet
- 2introduction To Networks - Common Types of Networks-1Document5 pages2introduction To Networks - Common Types of Networks-1ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks and CommunicationDocument25 pagesComputer Networks and CommunicationFirdaus AhmadNo ratings yet
- Networking Technologies ch01Document18 pagesNetworking Technologies ch01api-3754041No ratings yet
- Schema Learning Area 3Document9 pagesSchema Learning Area 3tycoon96No ratings yet
- Data Communications Networks Network Types Protocol LayeringDocument48 pagesData Communications Networks Network Types Protocol LayeringiotNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networks - IntroductionDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Networks - Introductionbeth pelaez ariasNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 - INTRODUCTION TO Computer ApplicationDocument39 pagesUnit-1 - INTRODUCTION TO Computer ApplicationKajal SoniNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 PdsDocument17 pagesUnit 1 PdsAmuthapriyaa GLNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networks - Common Types of NetworksDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Networks - Common Types of Networksbeth pelaez ariasNo ratings yet
- Network Device Drivers in Linux Sub1Document3 pagesNetwork Device Drivers in Linux Sub1hrushiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networks - Network ComponentsDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Networks - Network ComponentsFaical BitamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Networks: Ed T. EspirituDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Computer Networks: Ed T. EspirituMarjhon TubillaNo ratings yet
- Project Report 1Document46 pagesProject Report 1archit garg100% (1)
- Omputer Etworks: S GangulyDocument14 pagesOmputer Etworks: S GangulyApurva JainNo ratings yet
- 02.1 - Cisco IOS AccessDocument2 pages02.1 - Cisco IOS AccessWorldNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document14 pagesUnit 4kehihi3No ratings yet
- Networks Tutorial: by Amritha Bhat (EDTECH 541)Document23 pagesNetworks Tutorial: by Amritha Bhat (EDTECH 541)amritharauNo ratings yet
- Network CC V1.0Document113 pagesNetwork CC V1.0kaushalNo ratings yet
- MI0035 Computer Networks Descriptive QnsDocument48 pagesMI0035 Computer Networks Descriptive QnsCharles LwangaNo ratings yet
- 4.10.3 Networks and The Effects of Using ThemDocument7 pages4.10.3 Networks and The Effects of Using Themzaki544203No ratings yet
- Networking ProjectDocument21 pagesNetworking ProjectArishveer KaurNo ratings yet
- E CONTENTcomputer NetworkDocument26 pagesE CONTENTcomputer NetworkniharikaNo ratings yet
- CN PR9Document6 pagesCN PR9tovev86979No ratings yet
- Computer NetworkingDocument14 pagesComputer NetworkingJOELNo ratings yet
- PROYECTODocument11 pagesPROYECTOAzteca PicksNo ratings yet
- With The Help of This Diagram, Try To Describe The Function of These Components of A Typical Network SystemDocument8 pagesWith The Help of This Diagram, Try To Describe The Function of These Components of A Typical Network Systemjalello1No ratings yet
- Fundamental Concepts of Computer Networks.: Prepared byDocument70 pagesFundamental Concepts of Computer Networks.: Prepared bySf All People faizNo ratings yet
- 30a-Esp8266 Mesh User Guide en PDFDocument19 pages30a-Esp8266 Mesh User Guide en PDFJULIAN DE LA TORRENo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Notes 3 - TutorialsDuniyaDocument146 pagesComputer Networks Notes 3 - TutorialsDuniyaReenaNo ratings yet
- CCN BcaDocument70 pagesCCN Bcajyothi12swaroop10No ratings yet
- Survey of Wireless Sensor Networks Simulation Tools For Demanding ApplicationsDocument5 pagesSurvey of Wireless Sensor Networks Simulation Tools For Demanding ApplicationsChiranjib PatraNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Computer Network SyllabusDocument8 pagesData Communication and Computer Network SyllabusManoj kavediaNo ratings yet
- Networks MergedDocument277 pagesNetworks Mergedsmitianraj2005No ratings yet
- Basiccomputernetworking 2of5 0Document3 pagesBasiccomputernetworking 2of5 0Abhishek ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Information and Communications Technology Academy Digital Arts DepartmentDocument33 pagesInformation and Communications Technology Academy Digital Arts DepartmentVeronica FerrerNo ratings yet
- 2.0 NetworkDocument24 pages2.0 NetworkChinta QaishyNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two (Network Thesis Book)Document16 pagesChapter Two (Network Thesis Book)Latest Tricks100% (1)
- Chapter 1 6Document69 pagesChapter 1 6b.wafiaNo ratings yet
- Networking CH 7Document30 pagesNetworking CH 7AlHusseinAlShukairiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LAN Protocols: Chapter GoalsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To LAN Protocols: Chapter GoalsPrashant TandanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LAN Protocols: Chapter GoalsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To LAN Protocols: Chapter GoalskartheekNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument68 pagesComputer NetworksZahid IqbalNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Tcp/Ip: Computer NetworkingDocument16 pagesAn Introduction To Tcp/Ip: Computer NetworkingPazoNo ratings yet
- Objective Mappings Testout Network Pro Enus 6 - 0 - XDocument85 pagesObjective Mappings Testout Network Pro Enus 6 - 0 - XJared WuerzburgerNo ratings yet
- Telecommunications: Present Status and Future TrendsFrom EverandTelecommunications: Present Status and Future TrendsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- 02.3 - Cisco IOS AccessDocument2 pages02.3 - Cisco IOS AccessWorldNo ratings yet
- WCS - Chapter 07 - Sol HintsDocument7 pagesWCS - Chapter 07 - Sol HintsWorldNo ratings yet
- GNS3 Lab ManualDocument101 pagesGNS3 Lab ManualWorldNo ratings yet
- IOS Navigation: Primary Command ModesDocument2 pagesIOS Navigation: Primary Command ModesWorldNo ratings yet
- Con Gure IP Addressing: Manual IP Address Con Guration For End DevicesDocument2 pagesCon Gure IP Addressing: Manual IP Address Con Guration For End DevicesWorldNo ratings yet
- 02.1 - Cisco IOS AccessDocument2 pages02.1 - Cisco IOS AccessWorldNo ratings yet
- 04 - The Command StructureDocument2 pages04 - The Command StructureWorldNo ratings yet
- 05 - Basic Device ConfigurationDocument2 pages05 - Basic Device ConfigurationWorldNo ratings yet
- 09 - Network SecurityDocument1 page09 - Network SecurityWorldNo ratings yet
- 03 - Network ComponentsDocument2 pages03 - Network ComponentsWorldNo ratings yet
- 07 - Reliable NetworksDocument2 pages07 - Reliable NetworksWorldNo ratings yet
- 05.3 - Common Types of NetworksDocument2 pages05.3 - Common Types of NetworksWorldNo ratings yet
- 02 - Networks Affect Our LivesDocument1 page02 - Networks Affect Our LivesWorldNo ratings yet
- 01 - IntroductionDocument1 page01 - IntroductionWorldNo ratings yet
- Manual NP 301 3one DataDocument30 pagesManual NP 301 3one DataCARLOS IVAN RIOSNo ratings yet
- Docker NetworkingDocument6 pagesDocker Networkingjames.sharma251No ratings yet
- Cisco Aaa Case Study OverviewDocument16 pagesCisco Aaa Case Study OverviewEstuardo Hernández ArguetaNo ratings yet
- KX-TDE100 KX-TDE200 KX-TDE600: Programming Manual For Virtual SIP CO Line CardDocument60 pagesKX-TDE100 KX-TDE200 KX-TDE600: Programming Manual For Virtual SIP CO Line CardJonny TekNo ratings yet
- Setup Huawei ONUDocument2 pagesSetup Huawei ONUfuck youbixNo ratings yet
- Diameter ProtocolDocument14 pagesDiameter ProtocolversatilityNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 Address TranslationDocument16 pagesChapter7 Address TranslationDacaen DanNo ratings yet
- Hikvision 0904848459 Camera TCMDocument1 pageHikvision 0904848459 Camera TCMKs QuốcNo ratings yet
- Aws Architecture GuideDocument84 pagesAws Architecture Guideatlnacional02No ratings yet
- OS6850 Broch 031806rD 07janDocument16 pagesOS6850 Broch 031806rD 07janPrueNo ratings yet
- Network Layer Architecture and Types of ProtocolDocument3 pagesNetwork Layer Architecture and Types of ProtocolSuryanshNo ratings yet
- EDS-405A Series - Moxa-Eds-405a-Series-Firmware-V3.11.rom - Software Release History PDFDocument17 pagesEDS-405A Series - Moxa-Eds-405a-Series-Firmware-V3.11.rom - Software Release History PDFMiroslaw LabudaNo ratings yet
- Cisco 4000 Series ISRs Software Configuration GuideDocument330 pagesCisco 4000 Series ISRs Software Configuration GuideJack NicoleNo ratings yet
- Ethical Hacking Exercises W3-Memo-StM-V1-24082021Document4 pagesEthical Hacking Exercises W3-Memo-StM-V1-24082021BonginkosiNo ratings yet
- DMZDocument31 pagesDMZKarekezi Prudence100% (1)
- Scrip MikrotikDocument16 pagesScrip MikrotikbreaknetcfNo ratings yet
- Notes FinalDocument34 pagesNotes FinalNasir AliNo ratings yet
- Guide Commandes cr2960 PDFDocument994 pagesGuide Commandes cr2960 PDFǾssǿ BelkadiNo ratings yet
- VLSM ActivityDocument15 pagesVLSM ActivitySarah Jane MangenteNo ratings yet
- Radiolinie SIAE ALS ALFO Series 2Document57 pagesRadiolinie SIAE ALS ALFO Series 2Advantec Srl50% (2)
- PaloAltoNetworks Network Design GuideDocument110 pagesPaloAltoNetworks Network Design GuideLiam Cowden100% (1)
- PPPoE-CONF ENCONTRADA NA NETDocument4 pagesPPPoE-CONF ENCONTRADA NA NETFábio FariasNo ratings yet
- Avaya 4500 Seris Config GuideDocument400 pagesAvaya 4500 Seris Config GuideJustin Tompkin-DrewNo ratings yet
- BGP Confederation and Communities LabbDocument11 pagesBGP Confederation and Communities Labbmmihir82100% (1)
- PL NEW ARK 5 Februari 2013Document86 pagesPL NEW ARK 5 Februari 2013Rizhal AdarriyantoNo ratings yet
- Internet Technology Sheet 2Document8 pagesInternet Technology Sheet 2Abdelrahman ElattarNo ratings yet
- VTP Server:: Switch (Config) #Int Range g0/1-2 Switch (Config-If-Range) #Switchport Mode TrunkDocument9 pagesVTP Server:: Switch (Config) #Int Range g0/1-2 Switch (Config-If-Range) #Switchport Mode TrunkSara VananNo ratings yet
- Gazelle S1020i: L2 Manageable Industrial SwitchDocument2 pagesGazelle S1020i: L2 Manageable Industrial SwitchMaz MoektiNo ratings yet