Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cardio Patho
Cardio Patho
Uploaded by
CG Patron Bambo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views11 pagesThis document contains questions and answers related to cardiovascular system. It provides feedback for 39 multiple choice questions on topics like coronary arteries, risk factors for heart disease, signs of unstable angina, venous disorders, causes of hypertension, clinical manifestations of conditions like Raynaud's disease and deep vein thrombosis. For each question, it indicates whether the selected answer is right or wrong and provides the correct answer.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains questions and answers related to cardiovascular system. It provides feedback for 39 multiple choice questions on topics like coronary arteries, risk factors for heart disease, signs of unstable angina, venous disorders, causes of hypertension, clinical manifestations of conditions like Raynaud's disease and deep vein thrombosis. For each question, it indicates whether the selected answer is right or wrong and provides the correct answer.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views11 pagesCardio Patho
Cardio Patho
Uploaded by
CG Patron BamboThis document contains questions and answers related to cardiovascular system. It provides feedback for 39 multiple choice questions on topics like coronary arteries, risk factors for heart disease, signs of unstable angina, venous disorders, causes of hypertension, clinical manifestations of conditions like Raynaud's disease and deep vein thrombosis. For each question, it indicates whether the selected answer is right or wrong and provides the correct answer.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 11
1.This artery supplies the walls of the left atrium and left ventricle.. Single choice.
posterior interventricular artery
marginal artery
circumflex artery
anterior interventricular artery
Your answer to question 1 is wrong. Correct answers: circumflex artery
4.Select all the modifiable risk factors.. Multiple choice.
DM
Age
African American ethnicity
HTN
Depression
Your answer to question 4 is wrong. Correct answers: DM, HTN, Depression
6.This artery supplies the ventricular walls.. Multiple choice.
posterior interventricular artery
marginal artery
circumflex artery
anterior interventricular artery
Your answer to question 6 is wrong. Correct answers: posterior interventricular artery, anterior
interventricular artery
7.Select the atypical signs and symptoms of unstable angina.. Multiple choice.
chest pain
jaw pain
fatigue
nausea
heartburn
breathlessness
Your answer to question 7 is wrong. Correct answers: fatigue, nausea, breathlessness
8.Select the chronic venous disorders from the choices below:. Multiple choice.
varicose veins
thrombophlebitis
venous stasis ulceration
chronic venous insufficiency
superficial thrombophlebitis
DVT
Your answer to question 8 is wrong. Correct answers: varicose veins, venous stasis ulceration, chronic
venous insufficiency
9.The following are primary causes of acute heart failure except:. Single choice.
Acute MI
Valvular disorder
Dysrhytmias
Hypertensive crisis
Ventricular septal defects
Myocarditis
Your answer to question 9 is wrong. Correct answers: Valvular disorder
11.Select all primary causes of hypertension. Multiple choice.
increase SNS activity
congenital narrowing of aorta
vasoconstrictors
hyperaldosteronism
increased sodium intake
use of NSADS, MAOIs, and sympathetic stimulants
DM
excessive alcohol intake
PIH
smoking
Your answer to question 11 is wrong. Correct answers: increase SNS activity, vasoconstrictors,
increased sodium intake, DM, excessive alcohol intake, smoking
12.Select the acute venous disorders from the choices below:. Multiple choice.
varicose veins
thrombophlebitis
venous stasis ulceration
chronic venous insufficiency
superficial thrombophlebitis
DVT
Your answer to question 12 is wrong. Correct answers: thrombophlebitis, superficial
thrombophlebitis, DVT
14.The following are clinical manifestation of chronic venous insufficiency, except.
(SATA). Multiple choice.
shiny skin
chronically swollen legs
unilateral chronic leg swelling
thick, coarse, brownish skin around the ankles
venous stasis ulceration
itchy skin
rest pain
scaly skin
Your answer to question 14 is wrong. Correct answers: shiny skin, unilateral chronic leg swelling, rest
pain
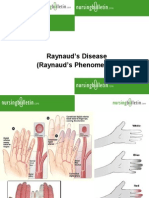
15.Select all the clinical manifestations of Raynaud's disease.. Multiple choice.
bilateral or symmetrical involvement
pain
classic color changes in hands
digital ulcerations as manifested by color or temperature changes in the fingers
gangrene limited to the tips of the digits
cold sensitivity
claudication type of pain at the arch of the foot
pulsations in posterior tibialis and dorsalis pedis are weak and absent
intermittent attacks of pallor or cyanosis
Your answer to question 15 is wrong. Correct answers: bilateral or symmetrical involvement, classic
color changes in hands, gangrene limited to the tips of the digits, intermittent attacks of pallor or
cyanosis
16.Select all the clinical manifestations related to deep vein thrombosis. Multiple
choice.
redness, induration, warmth, and tenderness along a vein
discomfort relieved by applying heat
usually asymptomatic
activity is encouraged
unilateral leg swelling
low grade fever
Your answer to question 16 is wrong. Correct answers: usually asymptomatic, unilateral leg swelling,
low grade fever
17.Select all the clinical manifestations of Buerger's disease.. Multiple choice.
bilateral or symmetrical involvement
pain
classic color changes in hands
digital ulcerations as manifested by color or temperature changes in the fingers
gangrene limited to the tips of the digits
cold sensitivity
claudication type of pain at the arch of the foot
pulsations in posterior tibialis and dorsalis pedis are weak and absent
intermittent attacks of pallor or cyanosis
Your answer to question 17 is wrong. Correct answers: pain, digital ulcerations as manifested by color
or temperature changes in the fingers, cold sensitivity, claudication type of pain at the arch of the
foot, pulsations in posterior tibialis and dorsalis pedis are weak and absent
18.The following are included in the endothelial control of the coronary vascular
tone. Select all that applies.. Multiple choice.
Fatty acids
Endothelial cells
Aerobic metabolism
Anaerobic metabolism
Anti-thrombogenic properties
Your answer to question 18 is wrong. Correct answers: Endothelial cells, Anti-thrombogenic
properties
19.This artery supplies the walls of the right atrium and right ventricle.. Single
choice.
posterior interventricular artery
marginal artery
circumflex artery
anterior interventricular artery
Your answer to question 19 is wrong. Correct answers: marginal artery
20.Select all the criteria for diagnosing primary Raynaud's disease. Multiple
choice.
manifestation for at least 2 years
cold sensitivity
intermittent attacks of pallor or cyanosis of digits
bilateral involvement
ulcerations in digits
no evidence of occlusive disease
gangrene limited to the skin of tips of the digits
Your answer to question 20 is wrong. Correct answers: manifestation for at least 2 years, intermittent
attacks of pallor or cyanosis of digits, bilateral involvement, no evidence of occlusive disease,
gangrene limited to the skin of tips of the digits
21.The following are primary causes of chronic heart failure, except:. Single
choice.
CAD
HTN
PE
Congenital heart disease
Cor Pulmonale
Your answer to question 21 is wrong. Correct answers: PE
24.The following are the clinical manifestations in an abdominal aortic aneurysm.
Select all that applies.. Multiple choice.
pulsating mass in the abdomen
groin pain
abdominal rigidity
flank pain
bruits sounds heard over aneurysm
mottling of the extremities
severe pain
Your answer to question 24 is wrong. Correct answers: pulsating mass in the abdomen, groin pain,
flank pain, bruits sounds heard over aneurysm, mottling of the extremities
25.Vasospastic Raynaud's syndrome includes the following, except:. Multiple
choice.
cold
scleroderma
nicotine
caffeine
rheumatoid arthritis
stress
SLE
Your answer to question 25 is wrong. Correct answers: scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis, SLE
26.This is also known as postphlebitic syndrome.. Single choice.
DVT
Varicose veins
Chronis Venous Insufficiency
Venous Stasis Ulceration
Your answer to question 26 is wrong. Correct answers: Chronis Venous Insufficiency
27.Which of the following statements are not correct with regards to Venous
stasis ulceration?. Single choice.
Prolonged venous pressure slows nutrient blood flow.
Skin of the lower leg ulcerates, causing a stasis ulcer.
Compression devices are indicated.
End-stage of chronic venous insufficiency.
Your answer to question 27 is wrong. Correct answers: Compression devices are indicated.
28.This is a key factor in atherosclerosis.. Single choice.
Inflammation
Fat deposits
Narrowing of lumen
Hypoxia
Your answer to question 28 is wrong. Correct answers: Inflammation
31.Most common type of cardiomyopathy.. Single choice.
dilated CM
restrictive CM
asymmetric septal hypertrophy (hypertrophic CM)
symmetric hypertrophy (hypertrophic CM)
Your answer to question 31 is wrong. Correct answers: dilated CM
33.Select all the precipitating causes of heart failure. Multiple choice.
anemia
acute MI
infection
thyrotoxicosis
rupture of papillary muscle
cardiomyopathy
hypervolemia
Option 8
Your answer to question 33 is wrong. Correct answers: anemia, infection, thyrotoxicosis,
hypervolemia
34.Receptors found in the aortic arch and carotid artery that causes an increase in
the heart rate.. Single choice.
baroreceptor
chemoreceptor
nociceptor
None of the above
Your answer to question 34 is wrong. Correct answers: chemoreceptor
35.The following events are included in the metabolic syndrome, select all that
applies.. Multiple choice.
Increased levels of C-reactive protein
Hyperlipidemia
Insulin Resistance
Central Obesity
Diabetes Mellitus
Depression
Dyslipidemia
Prothrombic state
BP persistently > 130/85 mmHg
Your answer to question 35 is wrong. Correct answers: Increased levels of C-reactive protein, Insulin
Resistance, Central Obesity, Dyslipidemia, Prothrombic state, BP persistently > 130/85 mmHg
36.Select all the clinical manifestations related to superficial thrombophlebitis..
Multiple choice.
redness, induration, warmth, and tenderness along a vein
discomfort relieved by applying heat
asymptomatic
activity is encouraged
unilateral leg swelling
low grade fever
Your answer to question 36 is wrong. Correct answers: redness, induration, warmth, and tenderness
along a vein, discomfort relieved by applying heat, activity is encouraged
37.This is characterized by an impaired ventricular filling due to an abnormally
stiff ventricle.. Single choice.
dilated CM
restrictive CM
hypertrophic CM
CM in general
Your answer to question 37 is wrong. Correct answers: restrictive CM
39.Select all the characteristic of an arterial ulcer.. Multiple choice.
occurs in the toes or foot
occurs in the malleolus or metatarsal
slopped edges
irregular shape
cold
warm
present sensations
absent pulses
variable pain
collapsed veins
dilated veins, varicosities, edema
severe pain
Your answer to question 39 is wrong. Correct answers: occurs in the toes or foot, cold, absent pulses,
collapsed veins, severe pain
40.The concern of this type of cardiomyopathy is power failure. Single choice.
dilated CM
restrictive CM
asymmetric septal hypertrophy (hypertrophic CM)
apical hypertrophy (hypertrophic CM)
Your answer to question 40 is wrong. Correct answers: dilated CM
41.Obstructive Raynaud's syndrome includes the following, except:. Multiple
choice.
cold
scleroderma
nicotine
caffeine
rheumatoid arthritis
stress
SLE
Your answer to question 41 is wrong. Correct answers: cold, nicotine, caffeine, stress
42.This is a peripheral artery disorder in which clients have rest pain in the
forefoot and toes. There may be calf muscle atrophy, loss of hair on the dorsum
of the foot, and shiny, scaly skin.. Single choice.
Intermittent Claudication
Rest Pain syndrome
CLTI
Acute arterial occlusion
Your answer to question 42 is wrong. Correct answers: CLTI
44.Select all the characteristic of an venous ulcer.. Multiple choice.
occurs in the toes or foot
occurs in the malleolus or metatarsal
slopped edges
irregular shape
cold
warm
present sensations
absent pulses
variable pain
collapsed veins
dilated veins, varicosities, edema
Your answer to question 44 is wrong. Correct answers: occurs in the malleolus or metatarsal, slopped
edges, irregular shape, warm, present sensations, variable pain, dilated veins, varicosities, edema
49.In arterial disorders, non-atherosclerotic origins cause the following, except:.
Single choice.
medial necrosis
atheroma build-up
vasospastic condition
arteritis
Your answer to question 49 is wrong. Correct answers: atheroma build-up
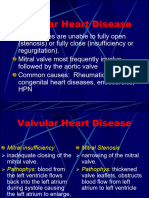
50.Select all predisposing factors for infectious and valvular heart diseases..
Multiple choice.
history of valvular heart disease
RHD
open heart surgeries
prosthetic valve replacement
GU/OB surgeries
IV drug abuse
dental surgery
dental extraction
prolonged antibiotic therapy
2.Trace the pathophysiology of Thomboangitis Obliterans. .
Correct answers: inflammation and irritation of vessels, vasospasms causing pain, increase lesion formation in arterial
walls, impaired functioning of arteries, thrombus formation, chronic occlusive disease causing ischemia, necrosis,
sepsis and bacteremia, septic shock, death
3.Trace the pathophysiology of myocardial ischemia. .
Correct answers: plaques increase in size partially occluding the vessel lumen, some unstable plaques are prone to
ulceration and rupture, underlying tissues of the vessel are exposed to platelet adhesion and thrombus formation,
suddenly cut-off blood supply to heart muscles, acute MI, progression to infarction if vessel obx cannot be reversed
rapidly, myocardial oxygen deficit
5.Trace the pathophysiology of Raynaud's phenomenon.. .
1Correct answers: arterial spasm causing pallor, increase resistance to blood flow, decrease blood flow and perfusion
(cyanosis), ischemia, necrosis, increase in bacterial growth, sepsis and bacteremia , septic shock, death
10.Trace the pathophysiology of myocarditis.. .
Correct answers: myocardial lesion, enlargement of muscle layers, hypertrophy, loss of contractility, heart failure,
death
13.Trace the pathophysiology of varicose veins. .
1
Correct answers: virchow's triad, increase resistance to venous outflow from lower extremities, impaired venous
emptying, backflow or regurgitation, increase venous blood volume with mmHg, veins distended when venous mmHg
is constantly elevated, dilatation and distention, congestion
22.Trace the pathophysiology of a transient ischemic attack. .
Correct answers: reversible cellular changes, anaerobic metabolism, increase in lactic acid level, altered ventricular
compliance, decrease in stroke volume , decrease in cardiac output and coronary vessel perfusion, cardiogenic shock,
death
23.Trace the pathophysiology of angina pectoris starting from its systemic
response.. .
Correct answers: migration of WBC, platelets, and leukocytes to site, excessive release of thromboxanes by blood
platelets, coronary arterial spasm, stimulation of pain nerve endings, carried by sensory nerve endings to thoracic
nerve, chest pain
29.Trace the pathophysiology of MI (>20 mins). .
Correct answers: lack of response to electrical impulse, arrythmia, reduced myocardial contractility, impaired cardiac
pumping, heart failure, death
30.Trace the pathophysiology of chronic venous insufficiency.. .
Correct answers: persistent obstructive thrombus coupled with valvular damage, post-thrombotic syndrome,
inadequate expulsion of venous blood, stasis, venous HTN, superficial tissue becomes edematous and
hyperpigmented, fibrosis compromises tissue oxygenation, stasis ulceration, rupture of small veins
32.Trace the SNS stimulation in the compensatory mechanism during heart
failure.. .
Correct answers: cardioregulatory center and chemoreceptor in MO, sympathetic postganglionic neurons release NE,
positive intotropic and chronotropic effect, arterial vasoconstriction, increase in peripheral resistance, compensations
maintain cardiac output, increase in blood volume and blood pressure
38.Trace the pathophysiology of endocarditis.. .
Correct answers: deposition in heart valves and layers, triggers fibrin, platelet, leukocyte, aggregation to site,
engulfment of organism and development of vegetation, adhere to endocardial layers of the heart, leaflet swelling,
erosion of valves and beadlike vegetation, deformity, insufficiency, stenosis, and ulcerations, dysfunction of valve
leaflets, valvular heart disease, heart failure and eventually death
43.Trace the pathophysiology of atherosclerosis. .
Correct answers: endothelial lining damage, accumulation of cholesterol/LDL, cellular waste products, collagen,
oxidation of immune cells and molecules, triggering of more inflammatory response, monocytes enter the site of
injury, macrophages eats and digests cholesterol molecules, foam cells and accumulation causes fatty streaks,
atheroma, fibrous encapsulation of lesion, Atherosclerosis
45.Trace the pathophysiology of pulmonary edema in hypertension. .
Correct answers: increased left myocardial workload, increased left ventricular hypertrophy, dilatation and increased
volume with end diastolic mmHg, regurgitation, development of valvular lesions, increased LA mmHg, increased LA
hypertrophy, increased mmHg in pulmonary and capillary bed, pulmonary congestion
46.Trace the pathophysiology of Aneurysm starting from Medial Necrosis.. .
Correct answers: Medial necrosis, increase mmHg in tunica media, degenerative changes occur, atrophy, weakened
arterial walls, dilatation, development of aneurysm
47.Trace the pathophysiology of tissue scarring and necrosis.. .
Correct answers: increased tendency to form clots, intravascular coagulation, thromboembolic conditions, dislodge
thrombi (emboli), microinfarcts, avascularization of the area, loss of function and heart failure, death
48.Trace the pathophysiology of pericarditis.. .
Correct answers: tissue necrosis, inflammation reaction, irritation of pericardium, exudative thickening of pericardial
layers, influx of neutrophils, increase in pericardial permeability, release of cytokines and fluid shifting causing
pericardial effusion, obliteration of pericardial cavity, prevents diastolic dilatation and decreased movement of
contraction, cardiac tamponade then heart failure then death
You might also like
- Test Bank CardioDocument16 pagesTest Bank CardioLudwigJayBarayuga86% (7)
- Garmin G5000Document382 pagesGarmin G5000孙鹏No ratings yet
- 27 Adbri Masonry Versaloc TechnicalDocument24 pages27 Adbri Masonry Versaloc TechnicalSteveMateNo ratings yet
- 11 KV ArDocument4 pages11 KV ArSathi Reddy ThondapuNo ratings yet
- Oet Listening GraciaDocument9 pagesOet Listening Graciabritfort cochin100% (1)
- CH 30 Online Patho QuizDocument9 pagesCH 30 Online Patho QuizTessa SandyNo ratings yet
- Medicine WardDocument20 pagesMedicine Wardsadiaafrin66523No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular NursingDocument30 pagesCardiovascular NursingAnusha Verghese100% (3)
- Activity On Diseases of The Circulatory SystemDocument11 pagesActivity On Diseases of The Circulatory SystemMarisol Taloza RenonNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disorders 2Document22 pagesCardiovascular Disorders 2Rayan JaafeerNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction and Heart Failure Practice Quiz (70 Questions)Document44 pagesMyocardial Infarction and Heart Failure Practice Quiz (70 Questions)Melodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Stasis Dermatitis and Leg UlcersDocument76 pagesStasis Dermatitis and Leg Ulcersozhan_holmesNo ratings yet
- PlebitisDocument5 pagesPlebitisIndra PutraNo ratings yet
- Oet Listening EugeniuszDocument9 pagesOet Listening Eugeniuszbritfort cochinNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Heart Disease Group 9 ReportDocument68 pagesRheumatic Heart Disease Group 9 Reportbevzie datuNo ratings yet
- Listening 15 2Document12 pagesListening 15 2sulekhaprasadam052No ratings yet
- Prometric 4Document9 pagesPrometric 4ClaiborneRillorta100% (3)
- Day 12 Q - MR JonathanDocument9 pagesDay 12 Q - MR Jonathangeenasajan8No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Question SDocument8 pagesPathophysiology Question SMaryam saleemNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Practice Exam 21 (60 Questions)Document36 pagesNCLEX Practice Exam 21 (60 Questions)Melodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Nursing Exam 16cardiovascular Nursing (60 Items)Document19 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing Exam 16cardiovascular Nursing (60 Items)Heather ClemonsNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine VivasDocument9 pagesInternal Medicine Vivasponcus payNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Fever& IE MCQDocument7 pagesRheumatic Fever& IE MCQLedia EssamNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument16 pagesCardiovascular DiseaseRaf Luis0% (3)
- Text Practice Exam: 1. Which of The Following Arteries Primarily Feeds The Anterior Wall of The Heart?Document20 pagesText Practice Exam: 1. Which of The Following Arteries Primarily Feeds The Anterior Wall of The Heart?Lariza LopegaNo ratings yet
- L 19Document9 pagesL 19Suhail BhattiNo ratings yet
- ZabuDocument8 pagesZabuZabu CastilloNo ratings yet
- جراحة - خالد الهبيل 7Document8 pagesجراحة - خالد الهبيل 7hasan ahmdNo ratings yet
- 60 Item Exam On Cardiovascular DisordersDocument9 pages60 Item Exam On Cardiovascular DisordersAijem RyanNo ratings yet
- EdemaDocument39 pagesEdemaMariyah Qibtiyyah Al JufriNo ratings yet
- 1Document24 pages1Noey TabangcuraNo ratings yet
- OSCE Internal MedicineDocument4 pagesOSCE Internal Medicinemohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular IV and VDocument6 pagesCardiovascular IV and VJessicaNo ratings yet
- Symposium On DipodemDocument25 pagesSymposium On DipodemHemant ShirkeNo ratings yet
- 6th Year Final MCQ Internal Medicine 2009Document9 pages6th Year Final MCQ Internal Medicine 2009Dimsy Flora KpaiNo ratings yet
- Cardio NurseslabsDocument6 pagesCardio Nurseslabsfasantos0217qcNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Rheumatic Fever UmeshDocument4 pagesSeminar On Rheumatic Fever UmeshawasthiphothocopyNo ratings yet
- 100 MCQsDocument35 pages100 MCQsBader AlMajedNo ratings yet
- Raynaud's DiseaseDocument20 pagesRaynaud's Diseaseseigelystic100% (12)
- Arterial InsufficiencyDocument26 pagesArterial InsufficiencyGull gullNo ratings yet
- INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS CPC FINAL SlidesDocument63 pagesINFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS CPC FINAL SlideswaqasNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Pathology QuizDocument8 pagesCardiac Pathology QuizAhmed AlkhaqaniNo ratings yet
- Images of Vascular DisordersDocument47 pagesImages of Vascular DisordersAsiya NoorNo ratings yet
- Quiz Week 2 (Blood Pressure)Document9 pagesQuiz Week 2 (Blood Pressure)María Paula Cristancho GalvisNo ratings yet
- Course OutlineDocument8 pagesCourse OutlineclobregasNo ratings yet
- Printed - NCLEX Practice Exam 21Document32 pagesPrinted - NCLEX Practice Exam 21Melodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Printed - NCLEX Practice Exam 21Document32 pagesPrinted - NCLEX Practice Exam 21Melodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Clin Path III Exam 1Document25 pagesClin Path III Exam 1obitajoy06No ratings yet
- Textbook Reference-Unit VI (p449) : Part 1 of 3Document53 pagesTextbook Reference-Unit VI (p449) : Part 1 of 3glenn johnstonNo ratings yet
- Famaily Medicine M3Document9 pagesFamaily Medicine M3Rauof QaziNo ratings yet
- VHD To DVTDocument55 pagesVHD To DVTShiehan Mae ForroNo ratings yet
- Final Medical Examination 4 Year Medical Student:) Select ONE BEST Answer (Document10 pagesFinal Medical Examination 4 Year Medical Student:) Select ONE BEST Answer (Dhanoush MşđNo ratings yet
- 159-Med-Vas-Chronic Leg UlcerDocument3 pages159-Med-Vas-Chronic Leg UlcerqurbanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Rheumatic FeverDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Rheumatic FevergitozsbyNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Patient With Joint DiseaseDocument14 pagesEvaluation of The Patient With Joint Diseaseqayyum consultantfpscNo ratings yet
- 8 CopiesDocument12 pages8 CopiesMuhammad Javed GabaNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic FeverDocument3 pagesRheumatic FeverPanji SaksonoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular ExamDocument24 pagesCardiovascular ExamSteven OdhiamboNo ratings yet
- Nursing Mnemonics: The Ultimate Tips and Notes For NursesFrom EverandNursing Mnemonics: The Ultimate Tips and Notes For NursesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Raynaud’s Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandRaynaud’s Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Anti Inflammatory Diet Cookbook: Inflammation Be Gone! - Complete Clean Eating Meal Plans To Reduce Inflammation and Promote Gut Healing With Healthy Keto Air Fryer RecipesFrom EverandAnti Inflammatory Diet Cookbook: Inflammation Be Gone! - Complete Clean Eating Meal Plans To Reduce Inflammation and Promote Gut Healing With Healthy Keto Air Fryer RecipesNo ratings yet
- Sick Sinus Syndrome, (Sinus Nodal Disorder) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSick Sinus Syndrome, (Sinus Nodal Disorder) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Homeroom Guidance Lda BamboDocument1 pageHomeroom Guidance Lda BamboCG Patron BamboNo ratings yet
- Altered Elimination Multi System ProblemDocument9 pagesAltered Elimination Multi System ProblemCG Patron BamboNo ratings yet
- En Notes EscDocument7 pagesEn Notes EscCG Patron BamboNo ratings yet
- Inspirational Videos On Older Persons 1Document2 pagesInspirational Videos On Older Persons 1CG Patron BamboNo ratings yet
- If Tomorrow Never ComesDocument2 pagesIf Tomorrow Never ComesCG Patron BamboNo ratings yet
- Self Care DeficitDocument2 pagesSelf Care DeficitCG Patron Bambo0% (1)
- Jeremy Bentham & John Stuart MillDocument22 pagesJeremy Bentham & John Stuart MillCG Patron BamboNo ratings yet
- Renal and Urologic DisordersDocument20 pagesRenal and Urologic DisordersCG Patron BamboNo ratings yet
- Reflection - PRINT PDFDocument3 pagesReflection - PRINT PDFCG Patron BamboNo ratings yet
- NCP Chest PainDocument2 pagesNCP Chest PainCG Patron BamboNo ratings yet
- NCP FormDocument4 pagesNCP FormCG Patron BamboNo ratings yet
- Deontological Theory: AristotleDocument32 pagesDeontological Theory: AristotleCG Patron BamboNo ratings yet
- Npi (Schizo)Document31 pagesNpi (Schizo)CG Patron BamboNo ratings yet
- Laboratory and Diagnostic FindingsDocument4 pagesLaboratory and Diagnostic FindingsCG Patron BamboNo ratings yet
- Stratified RocksDocument16 pagesStratified RocksJanuxie ParkNo ratings yet
- Research On Sustainable Development of Textile Industrial Clusters in The Process of GlobalizationDocument5 pagesResearch On Sustainable Development of Textile Industrial Clusters in The Process of GlobalizationSam AbdulNo ratings yet
- Covellite PDFDocument1 pageCovellite PDFRyoga RizkyNo ratings yet
- Q1. As A Production Manager For RMC, What Do You Recommend? Why??Document2 pagesQ1. As A Production Manager For RMC, What Do You Recommend? Why??MUNSIF JAWEEDNo ratings yet
- 2012 Training Materials PDFDocument32 pages2012 Training Materials PDFWisam Ankah100% (1)
- Campbeltown's Kilkerran Gun BatteryDocument2 pagesCampbeltown's Kilkerran Gun BatteryKintyre On RecordNo ratings yet
- XPR 300 Manual HyperthermDocument106 pagesXPR 300 Manual HyperthermDawitt BadilloNo ratings yet
- MESP by Peralta L.J.G. and Ubana P.a.D. of SNHSDocument9 pagesMESP by Peralta L.J.G. and Ubana P.a.D. of SNHSLouise Joseph PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Updating The Canadian Standards Association Offshore Structures CodeDocument6 pagesUpdating The Canadian Standards Association Offshore Structures CodenabiloucheNo ratings yet
- Peavey Xr8000 SCHDocument12 pagesPeavey Xr8000 SCHLisandro Orrego SalvadorNo ratings yet
- AHL Unit Removal For Pre 0305Document4 pagesAHL Unit Removal For Pre 0305Alex PioneerNo ratings yet
- Philips PL - 2016Document52 pagesPhilips PL - 2016Ganesh PonmozhiNo ratings yet
- Asus T12C (X51C) Motherboard Schematic DiagramDocument94 pagesAsus T12C (X51C) Motherboard Schematic DiagramYblis100% (1)
- Quinone-Based Molecular Electrochemistry and Their Contributions To Medicinal Chemistry: A Look at The Present and FutureDocument9 pagesQuinone-Based Molecular Electrochemistry and Their Contributions To Medicinal Chemistry: A Look at The Present and FutureSanti Osorio DiezNo ratings yet
- Journal Malunggay PDFDocument12 pagesJournal Malunggay PDFRochelle Mae Calabazaron Domingo-DuqueNo ratings yet
- Methods?: Condoms Internal Condoms Sexually Transmissible Infections (Stis)Document25 pagesMethods?: Condoms Internal Condoms Sexually Transmissible Infections (Stis)Alecia R. CastilloNo ratings yet
- Artikel Review BiodegradasiDocument6 pagesArtikel Review BiodegradasiEka Ayu NingtyasNo ratings yet
- Poisoning ToxicologyDocument2 pagesPoisoning ToxicologySelena MoonNo ratings yet
- Technical Contractr-60Mvar SVC - Endoks - ModifiedDocument50 pagesTechnical Contractr-60Mvar SVC - Endoks - Modifiedaashish bissaNo ratings yet
- Advanced LWRsDocument4 pagesAdvanced LWRsyaprak dönerNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Orbital Diagrams - TeacherDocument2 pagesWorksheet - Orbital Diagrams - Teacherdela2100% (3)
- Wee1964 N001Document9 pagesWee1964 N001Oliver RubioNo ratings yet
- The Seven Spiritual Laws of Success BIZDocument7 pagesThe Seven Spiritual Laws of Success BIZDeac Roxana100% (2)
- Design of Partition PlateDocument5 pagesDesign of Partition Platepippo2378793No ratings yet
- CPS - Data Intensive Distributed ComputingDocument11 pagesCPS - Data Intensive Distributed ComputingManoj KavediaNo ratings yet
- Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra 5G - Full Phone SpecificationsDocument13 pagesSamsung Galaxy S22 Ultra 5G - Full Phone SpecificationsAb BossNo ratings yet