Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Law of Employment Mind Maps
The Law of Employment Mind Maps
Uploaded by
Sanjeev JayaratnaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chra Reviewer 1 PDFDocument9 pagesChra Reviewer 1 PDFKappa Phi Mu Frat and Soro100% (1)
- Labrev Hw2 VillanuevaDocument13 pagesLabrev Hw2 VillanuevaSam VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- I Am Sharing '4-ENTREP-SLM4-QTR2-WK4-Day-13-16-MAKILANG' With YouDocument23 pagesI Am Sharing '4-ENTREP-SLM4-QTR2-WK4-Day-13-16-MAKILANG' With YouqwertyNo ratings yet
- Resistance To Organizational ChangeDocument19 pagesResistance To Organizational ChangeglazingsunnyNo ratings yet
- Rights and CooperativesDocument3 pagesRights and CooperativesFrance Jacob B. EscopeteNo ratings yet
- Termination of Employment GuideDocument11 pagesTermination of Employment GuideNikita AntonovNo ratings yet
- Labor March 22Document8 pagesLabor March 22Angemeir Chloe FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Labor Standards: Managerial EmployeesDocument7 pagesLabor Standards: Managerial EmployeesCatherine juradoNo ratings yet
- Who Is A Worker According To BLA 2006?Document5 pagesWho Is A Worker According To BLA 2006?zakiNo ratings yet
- Sumbitted By: Sumedha Pandey (16IN662)Document11 pagesSumbitted By: Sumedha Pandey (16IN662)MasthanNo ratings yet
- Labour LawDocument20 pagesLabour LawTrina BaruaNo ratings yet
- Uae Labour Law SummaryDocument28 pagesUae Labour Law SummaryJEAN SAGUANNo ratings yet
- Labor Notes Summary Part IDocument8 pagesLabor Notes Summary Part ISheryl SangilanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3-Workers Rights and ResponsibilitiesDocument17 pagesLesson 3-Workers Rights and ResponsibilitiesCrisa Marie Sta. Teresa100% (1)
- Employment Contract - I NYOMAN YUDIANTARADocument13 pagesEmployment Contract - I NYOMAN YUDIANTARABaskoro AjiNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Employment LawDocument7 pagesBangladesh Employment Lawzahir haqueNo ratings yet
- M10 U1 S2 FepmDocument18 pagesM10 U1 S2 FepmFernando Perfecto muñozNo ratings yet
- Ans. Labor Relations Ans. Parental LeaveDocument5 pagesAns. Labor Relations Ans. Parental LeaveNella ToreNo ratings yet
- Employees Old Age Benefits Act 1976Document46 pagesEmployees Old Age Benefits Act 1976Ajwad FarooqNo ratings yet
- Samplex Labstand Finals Per Exam TypeDocument6 pagesSamplex Labstand Finals Per Exam Typelleiryc7100% (1)
- North Eastern Mindanao State University (Nemsu) : Section: HRM3CDocument3 pagesNorth Eastern Mindanao State University (Nemsu) : Section: HRM3CCyril Ann IriberriNo ratings yet
- Labor Standards pt1Document5 pagesLabor Standards pt1GIGI BODONo ratings yet
- Labor Standards Pt1Document5 pagesLabor Standards Pt1GIGI BODONo ratings yet
- Title Ii Wages Preliminary Matters ARTICLE 97. Definitions. - As Used in This TitleDocument12 pagesTitle Ii Wages Preliminary Matters ARTICLE 97. Definitions. - As Used in This Titlemitsudayo_No ratings yet
- Bangladesh Labor LawDocument20 pagesBangladesh Labor Law'Sånjîdå KåBîr'No ratings yet
- Labor Law Review Notes - Poquiz (2023)Document4 pagesLabor Law Review Notes - Poquiz (2023)Shiela May NocedaNo ratings yet
- Labor Shit UsitaDocument11 pagesLabor Shit UsitaRoseanne MateoNo ratings yet
- LC Book 3 Title IIDocument27 pagesLC Book 3 Title IIRyan G. de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- I. Title of Topic: Case Doctrines For Lab Rev 3Document6 pagesI. Title of Topic: Case Doctrines For Lab Rev 3Joanna ReyesNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1Document11 pagesAssessment 1kandiezein88No ratings yet
- Labor Standards ReviewerDocument4 pagesLabor Standards ReviewerJudge NumberFiveNo ratings yet
- LABOR STANDARDS Dean Duka's LectureDocument12 pagesLABOR STANDARDS Dean Duka's LectureEllan Marie CiprianoNo ratings yet
- Legal Opinion - Retrenchment ProvisionsDocument4 pagesLegal Opinion - Retrenchment ProvisionszrqsjmvjftNo ratings yet
- Labor Relations ReviewerDocument5 pagesLabor Relations ReviewerTricia SibalNo ratings yet
- Written Report-Labor StandardsDocument9 pagesWritten Report-Labor StandardsGodwin CabacunganNo ratings yet
- I. Arnold & Q Bar (15pts)Document18 pagesI. Arnold & Q Bar (15pts)Shane SagumNo ratings yet
- Employee Relations Law in Uganda WorkDocument5 pagesEmployee Relations Law in Uganda WorkNAKIBUULE RITAHNo ratings yet
- Ncm-120-Week-14-Topic 8 (F-P) - Nov 8 To 13, 2021Document45 pagesNcm-120-Week-14-Topic 8 (F-P) - Nov 8 To 13, 2021Shaf Abubakar100% (1)
- Labor Review - Notes 2Document29 pagesLabor Review - Notes 2Bhenz Bryle TomilapNo ratings yet
- Decent Work and EmploymentDocument49 pagesDecent Work and EmploymentHannah Duyag100% (1)
- CLM Lesson 5Document2 pagesCLM Lesson 5Gin HuangNo ratings yet
- Maranaw Hotel vs. CA, Nov. 6, 1992Document2 pagesMaranaw Hotel vs. CA, Nov. 6, 1992Ramon T. De VeraNo ratings yet
- Terms and Conditions of Employment in Ghana: Unit 2 SectionDocument6 pagesTerms and Conditions of Employment in Ghana: Unit 2 SectionBabamu Kalmoni JaatoNo ratings yet
- Employee Should Receive at The Very Least The Minimum Wage For That DayDocument12 pagesEmployee Should Receive at The Very Least The Minimum Wage For That DayArellano AureNo ratings yet
- 2 The Workers Basic RightsDocument21 pages2 The Workers Basic RightsApril Angel Mateo MaribbayNo ratings yet
- Annual Remuneration: The First SRX (6) Months of This Agreement Will Be Set As A Period of ProbationDocument18 pagesAnnual Remuneration: The First SRX (6) Months of This Agreement Will Be Set As A Period of ProbationahmedNo ratings yet
- A Handbook of Major Kuwaiti Corporations: 15Th EditionDocument3 pagesA Handbook of Major Kuwaiti Corporations: 15Th EditionTrafficked_by_ITTNo ratings yet
- Labor Relations Notes - Security of TenureDocument17 pagesLabor Relations Notes - Security of TenureKimberly Mae LugoNo ratings yet
- Phr222-Content-Module 2Document14 pagesPhr222-Content-Module 2Peybi Lazaro ChamchamNo ratings yet
- NCM120Document6 pagesNCM120Mae Arra Lecobu-anNo ratings yet
- Employer Responsibilities and Employee RightsDocument12 pagesEmployer Responsibilities and Employee RightsJhazielle DolleteNo ratings yet
- December 2019Document4 pagesDecember 2019AziraNo ratings yet
- Labor Law - Leave Benefits - Comparison Labor Law and CSC LawDocument15 pagesLabor Law - Leave Benefits - Comparison Labor Law and CSC LawApple LavarezNo ratings yet
- Title I Termination OF Employment Art 279. Security of TenureDocument7 pagesTitle I Termination OF Employment Art 279. Security of Tenuresweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- Labor Standards (Transcriptions - Edited)Document14 pagesLabor Standards (Transcriptions - Edited)Antonina ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Module 10Document4 pagesModule 10Angela DucusinNo ratings yet
- B3 - International Catholic vs. NLRC, GR No. 72222Document1 pageB3 - International Catholic vs. NLRC, GR No. 72222Luds OretoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document46 pagesChapter 11arantonizhaNo ratings yet
- Work Immersion Module 3Document4 pagesWork Immersion Module 3pattiffanylorenzo278No ratings yet
- WAGES and LEAVESDocument23 pagesWAGES and LEAVESDiego DuroyNo ratings yet
- THE LABOUR LAW IN UGANDA: [A TeeParkots Inc Publishers Product]From EverandTHE LABOUR LAW IN UGANDA: [A TeeParkots Inc Publishers Product]No ratings yet
- Textbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 15, Human Resources Overview: Key Labor and Employment IssuesFrom EverandTextbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 15, Human Resources Overview: Key Labor and Employment IssuesNo ratings yet
- Administering Questionnaires: Different Types Design Questionnaires Cross-CulturalDocument10 pagesAdministering Questionnaires: Different Types Design Questionnaires Cross-CulturalSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 11 - Measurement of VariablesDocument3 pagesChapter - 11 - Measurement of VariablesSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Data Collection Methods: ObservationDocument9 pagesData Collection Methods: ObservationSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Interviews: Personal Interview. Advantages and Disadvantages Business Is Largely A Social PhenomenonDocument8 pagesInterviews: Personal Interview. Advantages and Disadvantages Business Is Largely A Social PhenomenonSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Scientific Investigation: Hallmarks of Scientific Research Hypothetico-Deductive ResearchDocument3 pagesScientific Investigation: Hallmarks of Scientific Research Hypothetico-Deductive ResearchSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 - Theoretical Framework & Hypothesis DevelopmentDocument10 pagesChapter - 5 - Theoretical Framework & Hypothesis DevelopmentSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Critical Literature Review The Critical ReviewDocument10 pagesCritical Literature Review The Critical ReviewSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Kotler, Bowen & Makens CH 19Document10 pagesKotler, Bowen & Makens CH 19Sanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Defining and Refining The ProblemDocument13 pagesDefining and Refining The ProblemSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Research Definition ResearchDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Research Definition ResearchSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- MHT CH 01Document9 pagesMHT CH 01Sanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Kotler, Bowen & Makens CH 12Document9 pagesKotler, Bowen & Makens CH 12Sanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Kotler, Bowen & Makens CH 11Document8 pagesKotler, Bowen & Makens CH 11Sanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Kotler, Bowen & Makens CH 14Document7 pagesKotler, Bowen & Makens CH 14Sanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Kotler, Bowen & Makens CH 06Document8 pagesKotler, Bowen & Makens CH 06Sanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Kotler, Bowen & Makens CH 04Document7 pagesKotler, Bowen & Makens CH 04Sanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Summarising Analysing DataDocument19 pagesSummarising Analysing DataSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Job, Batch and Service CostingDocument22 pagesJob, Batch and Service CostingSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Kotler, Bowen & Makens CH 08Document8 pagesKotler, Bowen & Makens CH 08Sanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Kotler, Bowen & Makens CH 05Document8 pagesKotler, Bowen & Makens CH 05Sanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Tute 01 - The Law of ContractDocument38 pagesTute 01 - The Law of ContractSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- The Law of Contract Mind MapsDocument8 pagesThe Law of Contract Mind MapsSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument24 pagesStandard Costing and Variance AnalysisSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Short-Term Decision MakingDocument26 pagesShort-Term Decision MakingSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Sip Report of Planman HR (Temp Staffing)Document51 pagesSip Report of Planman HR (Temp Staffing)Chinmoy MahapatraNo ratings yet
- Acemoglu e Johnson 2023 Rebalancing AIDocument4 pagesAcemoglu e Johnson 2023 Rebalancing AIpatriciovergaraNo ratings yet
- Big BazaarDocument23 pagesBig BazaarSHOAIB MEMONNo ratings yet
- PUA Updated Operating Instructions and Reporting ChangesDocument62 pagesPUA Updated Operating Instructions and Reporting ChangesAdam HarringtonNo ratings yet
- Kaizen: - A Term PaperDocument2 pagesKaizen: - A Term PaperChiil AnnNo ratings yet
- Kasambahay HandbookDocument59 pagesKasambahay HandbookwapbytezNo ratings yet
- Maury County BusinessDocument54 pagesMaury County BusinessJournal CommunicationsNo ratings yet
- Empathy MapDocument10 pagesEmpathy MapPlyers100% (1)
- Difference Between A CV and ResumeDocument3 pagesDifference Between A CV and ResumeSabari MajumderNo ratings yet
- Accenture Digital Adoption ReportDocument25 pagesAccenture Digital Adoption ReportgasibuteaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Personnel Administration Pad254Document20 pagesAssignment Personnel Administration Pad254greeny83100% (1)
- FlexiEle Hire To ExitDocument22 pagesFlexiEle Hire To ExitSachinNo ratings yet
- Labour Market and Income Distribution: The Effects of Education and The Gig-EconomyDocument19 pagesLabour Market and Income Distribution: The Effects of Education and The Gig-EconomyHarry SinghNo ratings yet
- "Work Life Balance of Employees in Selected Hotels in Cagayan de Oro City and Iligan City During Covid 19"-Jamon, Ligtas, VillarDocument84 pages"Work Life Balance of Employees in Selected Hotels in Cagayan de Oro City and Iligan City During Covid 19"-Jamon, Ligtas, VillarJoe Andrei LigtasNo ratings yet
- PAYSLIPDocument11 pagesPAYSLIPSaran ManiNo ratings yet
- A Case Study For Compre MaedDocument2 pagesA Case Study For Compre MaedJL D. BusiaNo ratings yet
- ParticipativemanagementDocument24 pagesParticipativemanagementSarathBabuNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - StressDocument8 pagesUnit 1 - StressJORGE ARRUÉNo ratings yet
- Skill Shift Automation and The Future of The WorkforceDocument2 pagesSkill Shift Automation and The Future of The WorkforcejordybeltNo ratings yet
- Intro To Business Chapter 7 NotesDocument8 pagesIntro To Business Chapter 7 Notesapi-526065196No ratings yet
- Staffing&SchedulingDocument14 pagesStaffing&SchedulingKrishnaveni MurugeshNo ratings yet
- TM1 PresentationDocument33 pagesTM1 PresentationJas Sofia90% (10)
- Robert Wilson - Annotated BibliographyDocument5 pagesRobert Wilson - Annotated Bibliographyapi-557627314No ratings yet
- Market Strikes BackDocument12 pagesMarket Strikes BackAshraf AhmedNo ratings yet
- Graduate CV TemplateDocument2 pagesGraduate CV TemplateFrankie NguyenNo ratings yet
- Barriers To Strategic Human Resource ManagementDocument59 pagesBarriers To Strategic Human Resource ManagementMadhukar Saxena100% (1)
- Staffing Organizations 9th Edition Heneman Test BankDocument12 pagesStaffing Organizations 9th Edition Heneman Test Bankmarkgordonxqaifpntwd100% (18)
- Importance of A Job TitleDocument2 pagesImportance of A Job TitleLORAINENo ratings yet
The Law of Employment Mind Maps
The Law of Employment Mind Maps
Uploaded by
Sanjeev JayaratnaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Law of Employment Mind Maps
The Law of Employment Mind Maps
Uploaded by
Sanjeev JayaratnaCopyright:
Available Formats
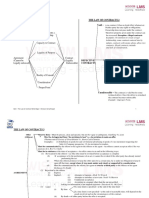
EMPLOYMENT 1
Within 2 months of commencing employment, the employer must give the employee a written statement of prescribed
particulars of his employment. Exceptions: Merchant seamen and those working outside the UK. The statement
should include the following. The names of the employer and employee, date of commencement of employment,
Express pay-scale/rate and intervals, hours of work, holiday pay, sick pay, leave entitlement, pension, length of notice of
termination, job title, disciplinary procedures and grievance procedures.
Changes – Must be given to the employee in writing, within one month of the change
Pay and sick pay - as agreed or reasonable pay; in case of sickness first 8 weeks paid by the employer,
thereafter recovered from the National Insurance Contribution.
Employer’s Holiday and holiday pay – employees with 3 months continuous employment are entitled to this
duties Working hours - Maximum 48 hours a week
Pay slips – employees who work 8 hours a week or more must be given an itemized pay slip, showing
gross pay, deductions and net pay.
Indemnity – must reimburse expenses incurred by the employee in the performance of his duties.
Provision of work- the employer has no duty to provide work for his employee, provided the agreed
wages are paid.
TERMS Exceptions: Where the total remuneration depends on the amount of works done (E.g.
OF Commission), where the employee’s standing and reputation depends on active work (E.g.
CONTRACT actor or pilot)
References – the employer has no duty to provide a reference; if he does so and it is wrong, he can
be liable for defamation of the employee or misrepresentation to the third party.
Health and safety – must provide a safe and healthy system of work and take reasonable care of his
employees. Under the PUBLIC INTEREST DISCLOSURE ACT 1998, whistle
blowers cannot be victimized for exposing malpractice, injustice or health and safety
dangers. Health and safety representatives must be given reasonable paid time to
perform their functions.
Faithful Service Hivac Ltd Vs. Park Royal Scientific Instruments Ltd.
Reasonable competence
Obedience to lawful orders unless they expose him to persons danger Ottoman Bank Ltd. Vs
Chakkarian
Must account for all money and property received during the course of his employment
Implied Employee’s Boston Deep Sea Fishing And Ice Co Vs Ansell
duties Personal service – must not delegate his duties without the employer’s express or implied consent
BA4 The Law of Employment Mind Maps - Dhanan Senathirajah 1
EMPLOYMENT 2
TERMS Collective terms – As negotiated between a trade union and the employer/trade association. Must be reasonable,
OF known to the employee and negotiated agreement.
CONTRACT
Wages - WAGES ACT 1986 - the employer cannot make any deductions from wages except where
they are authorized by statute (tax and NIC), contract (union dues) or agreement in writing (staff loan
recovery)
Maternity leave - Ordinary maternity leave of 26 weeks; a woman who has been continuously employed
For 26 weeks has a right to additional maternity leave of a further 26 weeks. (Total
statutory maternity leave of 52 weeks). She is also entitled to take time off during
working hours for ante-natal care. During ordinary maternity leave Statuary Maternity
Pay is paid (first 6 weeks, 90% of salary and for the remainder, the lower of £100 per
week or 90% of salary). Additional maternity leave is unpaid.
Paternity leave - The employee must be the biological father of the child or the mother’s husband or
partner and must have at least 26 weeks of continuous service. They are entitled to 2
weeks paid leave. The leave must be completed within 56 days of the child’s birth.
Adoptive parents - They are entitled to 26 weeks of ordinary adoption leave and additional adoption
leave of another 26 weeks.
Implied Trade union officials – with pay, to carry out trade union duties relevant to industrial
relations between employer and employees
Time off Trade union members – without pay, for trade union activities
work Employees who have been given notice of dismissal for redundancy, to look for work or
retraining
Magistrate or jury duty
Statutory
terms Health and Safety - See diagram 4.
BA4 The Law of Employment Mind Maps - Dhanan Senathirajah 2
EMPLOYMENT 3
EQUAL PAY ACT 1970 - The employment terms given to a man or woman should at least be as favorable as
those given to an employee of the opposite sex
Sex SEX DISCRIMINATION ACT 1975 - Prohibits discrimination on the grounds of gender in the recruitment,
Promotion, training, benefits or dismissal of employees - Prohibits even indirect
discrimination Price Vs Civil Service Commission
SEX DISCRIMINATION ACT 1986 – Prohibits different retirement ages for males and females. Extends
the 1975 Act to private house holds and concerns employing less than 5 people. Exception:
Genuine Occupational Qualification (GOQ). Sexual harassment is also prohibited
DISCRIMINATION
AT Marital Status - SEX DISCRIMINATION ACT 1986 – It is unlawful to discriminate against married
WORK people in any way
Racial – RACE RELATIONS ACT 1976 - Prohibits discrimination on the grounds of race, religion, colour of
skin, nationality, etc, in the recruitment, promotion, training, benefits or dismissal of employees.
Exceptions: Authenticity in entertainment, art or photography; personal services; maintaining
ethnic authenticity in a bar or restaurant
Disability – DISABILITY DISCRIMINATION ACT 1995 – Gives disabled people similar rights to those
enjoyed in relation to sex and race. Failure by the employer to make “reasonable adjustments”
without justification is classed as discrimination
Tarling Vs. Wisdom Toothbrushes Ltd. O’ Neils Vs Symm & Co. Ltd.
Religion or belief –THE EMPLOYMENT EQUALITY (RELIGION OR BELIEF) REGULATIONS
2003 – Prohibits direct or indirect discrimination, victimization and harassment
Sexual orientation - THE EMPLOYMENT EQUALITY (SEXUAL ORENTATION)
REGULATIONS 2003 - Prohibits direct or indirect discrimination, victimization
and harassment
Age - Prevents unjustified age discrimination in employment and training; prevents employers
from requiring employees to retire at 65; removes upper limits for unfair dismissal and
redundancy rights; removes lower age limits for workers.
BA4 The Law of Employment Mind Maps - Dhanan Senathirajah 3
EMPLOYMENT 4
THE HEALTH AND SAFETY AT WORK ACT 1974 - It is the duty of every employer, to ensure the health, safety
and welfare of all his employees, as far is practicable. He should:
(i) Provide and maintain plant and systems of work which are safe and without risk.
(ii) Ensure health and safety in relation to the use, handing, storage and transport of articles and
substances
(iii) Provide adequate information, instruction, training and supervision
(iv) Maintain safe places of work with adequate access in and out
(v) Provide a safe and healthy working environment
(vi) Make the premises safe for even visitors
(vii) control or prohibit pollution of the environment
THE FACTORIES ACT 1961- Applies to places where manufacturing or processing work is done. The occupier
has an absolute duty to fence securely all prime movers, all transmission machinery and every dangerous
part of any machinery
THE OFFICE, SHOPS AND RAILWAY PREMISES ACT 1973 - Cover temperature and ventilation of premises,
Safety of floors and stairs, cleanliness of buildings, limits to overcrowding of buildings and fencing
of dangerous machinery on premises
The Health and Safety Commission oversees the system. The Health and Safety Executive
enforces the system
HEALTH Health and Safety Inspectors have the power to enter premises, to investigate and examine,
& to take samples and measurements, to call for documents and other information
SAFETY
Enforcement Improvement notices – minor defects; the business can continue to operate but
the defect must be rectified within a specified time
Notices
Prohibition notices – major defects; the whole or a part of the business will be
closed until the defects are rectified
Any person on whom the notice has been served may appeal to an industrial tribunal which may either
cancel or confirm the notice
Criminal action may be filed against a person who does not discharge his duties relating to Health and
Safety regulations
The employer cannot charge his employees for the cost of safety measures or equipment
BA4 The Law of Employment Mind Maps - Dhanan Senathirajah 4
EMPLOYMENT 5
By Notice- The statutory minimum period is as follows:
(1) Where the employer terminates the contract of employment
(a) An employee with continuous employment of one month or more but less than two
years - at least one week’s notice
(b) An employee with continuous employment of two years or more but less than twelve
Years - at least one week’s notice for each year of employment
(c) An employee with continuous employment of twelve years or more - at least twelve
weeks’ notice
(2) Where the employee terminates the contract of employment
- At least one week’s notice if he had worked for at least one month
TERMINATION
OF Summary dismissal -Where the employer dismisses the employee without notice. This is
EMPLOYMENT justified only if the employee had committed a serious breach of contract
Pepper Vs. Webb; Wilson Vs Racher
Constructive dismissal - Where the employer, although willing to continue the employment,
repudiates some essential term of the contract. E.g. A removal of “interesting and
enjoyable” duties Colman Vs. Baldwin
Death of a personal employer
Employer’s inability Dissolution of partnership
To continue employment
Liquidation of a company
By Beach
Of If the employee resigns or goes on strike or fails to perform
Contract the contract and to observe its conditions, the employer may
dismiss him
Repudiation of the contract
By the employee
Any employee who has worked for a continuous period of at
least two years and has been dismissed. May request the
employer for a written statement of the reasons for his
dismissal. The employer must provide it within fourteen days.
BA4 The Law of Employment Mind Maps - Dhanan Senathirajah 5
EMPLOYMENT 6
Without justification
Definition
Without proper notice
Governed by the Common Law of contracts
WRONGFUL Willful disobedience of a lawful order- if it amounts to willful serious defiance of authority
DISMISSAL Laws Vs London Chronicles
Misconduct – In connection with the business or outside if it is grave. E.g. Making a secret profit, disclosure of
confidential information, assaults on a fellow employee, etc.
Dishonesty – where the employee is in a position of trust
Justification
of dismissal Incompetence or neglect – where the employee lacks or fails to use the skill he professes to have
Gross negligence – depending on the nature of the job e.g. negligently landing an aero plane.
Immorality – If it affects the performance of duties or the reputation of the business
Repeated drunkenness
• The employee’s past record must be taken into account - one failure does not justify summary
dismissal.
Employer’s breach – The employee cam claim for damages for loss of earnings, loss of reputation, humiliation,
Remedies etc
Employee’s breach – recovery of confidential papers, recovery of secret profits made or injunction
BA4 The Law of Employment Mind Maps - Dhanan Senathirajah 6
EMPLOYMENT 7
Exclusions – Persons ordinarily employed outside Great Britain, persons dismissed while taking unofficial
strike action and members of the police and armed forces
Scope
Been in continuous employment for one year, whether full time or part time
Conditions Have been dismissed
Have been unfairly dismissed
Application must be made within 3 months of dismissal
Governed by statute. An unfair dismissal can also be a wrongful dismissal
Actual - usually fairly clear - cut and recognized by the words used by the employer
Dismissal Constructive – a fundamental breach of the employment contract by the employer
Expiry - of a fixed term contract without renewal
Must apply the correct procedure – E.g. disciplinary procedure; independent inquiry; the employee’s side
of the story must be heard, etc.
Reasonableness Must take all circumstances into consideration
UNFAIR Of the employer Warnings must be given along with the penalty. No warning is needed for serious cases Newman Vs.
DISMISSAL T. H. White Motors
Lack of capability or qualification to perform the work
Lewis Shops Group Ltd. Vs Wiggins; International Sports Ltd. Vs
Thomson
Potentially fair reasons Misconduct
Redundancy- selection must be reasonable and if possible alternative
employment must be offered
Justification Other substantial reasons – E.g. marrying a competitor, refusing to
Accept reorganization when a majority has expected.
Dismissal of all strikers
Automatically fair reasons Being a threat to national security
Pregnancy or other maternity related grounds
Trade union membership or activities
Dismissal on transfer of an undertaking
Automatically unfair reasons Taking steps to avert danger to health and safety at work.
Seeking to enforce rights relating to national minimum wage.
Refusing or opting out of Sunday working in the retail sector
Making a protected disclosure under the PUBLIC INTEREST
DISCLOSURE ACT 1998
BA4 The Law of Employment Mind Maps - Dhanan Senathirajah 7
Re-instatement – To return to the same job without any breach of continuity
Re-engagement – The employee is given new employment with the employer, comparable with the earlier
Job
Basic award
UNFAIR
DISMISSAL
Remedies Compensation Compensatory award - for additional loss of earning, expenses and benefits
Punitive additional award – Where the employer does not comply with an
order for re-instatement or re-engagement
BA4 The Law of Employment Mind Maps - Dhanan Senathirajah 8
You might also like
- Chra Reviewer 1 PDFDocument9 pagesChra Reviewer 1 PDFKappa Phi Mu Frat and Soro100% (1)
- Labrev Hw2 VillanuevaDocument13 pagesLabrev Hw2 VillanuevaSam VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- I Am Sharing '4-ENTREP-SLM4-QTR2-WK4-Day-13-16-MAKILANG' With YouDocument23 pagesI Am Sharing '4-ENTREP-SLM4-QTR2-WK4-Day-13-16-MAKILANG' With YouqwertyNo ratings yet
- Resistance To Organizational ChangeDocument19 pagesResistance To Organizational ChangeglazingsunnyNo ratings yet
- Rights and CooperativesDocument3 pagesRights and CooperativesFrance Jacob B. EscopeteNo ratings yet
- Termination of Employment GuideDocument11 pagesTermination of Employment GuideNikita AntonovNo ratings yet
- Labor March 22Document8 pagesLabor March 22Angemeir Chloe FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Labor Standards: Managerial EmployeesDocument7 pagesLabor Standards: Managerial EmployeesCatherine juradoNo ratings yet
- Who Is A Worker According To BLA 2006?Document5 pagesWho Is A Worker According To BLA 2006?zakiNo ratings yet
- Sumbitted By: Sumedha Pandey (16IN662)Document11 pagesSumbitted By: Sumedha Pandey (16IN662)MasthanNo ratings yet
- Labour LawDocument20 pagesLabour LawTrina BaruaNo ratings yet
- Uae Labour Law SummaryDocument28 pagesUae Labour Law SummaryJEAN SAGUANNo ratings yet
- Labor Notes Summary Part IDocument8 pagesLabor Notes Summary Part ISheryl SangilanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3-Workers Rights and ResponsibilitiesDocument17 pagesLesson 3-Workers Rights and ResponsibilitiesCrisa Marie Sta. Teresa100% (1)
- Employment Contract - I NYOMAN YUDIANTARADocument13 pagesEmployment Contract - I NYOMAN YUDIANTARABaskoro AjiNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Employment LawDocument7 pagesBangladesh Employment Lawzahir haqueNo ratings yet
- M10 U1 S2 FepmDocument18 pagesM10 U1 S2 FepmFernando Perfecto muñozNo ratings yet
- Ans. Labor Relations Ans. Parental LeaveDocument5 pagesAns. Labor Relations Ans. Parental LeaveNella ToreNo ratings yet
- Employees Old Age Benefits Act 1976Document46 pagesEmployees Old Age Benefits Act 1976Ajwad FarooqNo ratings yet
- Samplex Labstand Finals Per Exam TypeDocument6 pagesSamplex Labstand Finals Per Exam Typelleiryc7100% (1)
- North Eastern Mindanao State University (Nemsu) : Section: HRM3CDocument3 pagesNorth Eastern Mindanao State University (Nemsu) : Section: HRM3CCyril Ann IriberriNo ratings yet
- Labor Standards pt1Document5 pagesLabor Standards pt1GIGI BODONo ratings yet
- Labor Standards Pt1Document5 pagesLabor Standards Pt1GIGI BODONo ratings yet
- Title Ii Wages Preliminary Matters ARTICLE 97. Definitions. - As Used in This TitleDocument12 pagesTitle Ii Wages Preliminary Matters ARTICLE 97. Definitions. - As Used in This Titlemitsudayo_No ratings yet
- Bangladesh Labor LawDocument20 pagesBangladesh Labor Law'Sånjîdå KåBîr'No ratings yet
- Labor Law Review Notes - Poquiz (2023)Document4 pagesLabor Law Review Notes - Poquiz (2023)Shiela May NocedaNo ratings yet
- Labor Shit UsitaDocument11 pagesLabor Shit UsitaRoseanne MateoNo ratings yet
- LC Book 3 Title IIDocument27 pagesLC Book 3 Title IIRyan G. de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- I. Title of Topic: Case Doctrines For Lab Rev 3Document6 pagesI. Title of Topic: Case Doctrines For Lab Rev 3Joanna ReyesNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1Document11 pagesAssessment 1kandiezein88No ratings yet
- Labor Standards ReviewerDocument4 pagesLabor Standards ReviewerJudge NumberFiveNo ratings yet
- LABOR STANDARDS Dean Duka's LectureDocument12 pagesLABOR STANDARDS Dean Duka's LectureEllan Marie CiprianoNo ratings yet
- Legal Opinion - Retrenchment ProvisionsDocument4 pagesLegal Opinion - Retrenchment ProvisionszrqsjmvjftNo ratings yet
- Labor Relations ReviewerDocument5 pagesLabor Relations ReviewerTricia SibalNo ratings yet
- Written Report-Labor StandardsDocument9 pagesWritten Report-Labor StandardsGodwin CabacunganNo ratings yet
- I. Arnold & Q Bar (15pts)Document18 pagesI. Arnold & Q Bar (15pts)Shane SagumNo ratings yet
- Employee Relations Law in Uganda WorkDocument5 pagesEmployee Relations Law in Uganda WorkNAKIBUULE RITAHNo ratings yet
- Ncm-120-Week-14-Topic 8 (F-P) - Nov 8 To 13, 2021Document45 pagesNcm-120-Week-14-Topic 8 (F-P) - Nov 8 To 13, 2021Shaf Abubakar100% (1)
- Labor Review - Notes 2Document29 pagesLabor Review - Notes 2Bhenz Bryle TomilapNo ratings yet
- Decent Work and EmploymentDocument49 pagesDecent Work and EmploymentHannah Duyag100% (1)
- CLM Lesson 5Document2 pagesCLM Lesson 5Gin HuangNo ratings yet
- Maranaw Hotel vs. CA, Nov. 6, 1992Document2 pagesMaranaw Hotel vs. CA, Nov. 6, 1992Ramon T. De VeraNo ratings yet
- Terms and Conditions of Employment in Ghana: Unit 2 SectionDocument6 pagesTerms and Conditions of Employment in Ghana: Unit 2 SectionBabamu Kalmoni JaatoNo ratings yet
- Employee Should Receive at The Very Least The Minimum Wage For That DayDocument12 pagesEmployee Should Receive at The Very Least The Minimum Wage For That DayArellano AureNo ratings yet
- 2 The Workers Basic RightsDocument21 pages2 The Workers Basic RightsApril Angel Mateo MaribbayNo ratings yet
- Annual Remuneration: The First SRX (6) Months of This Agreement Will Be Set As A Period of ProbationDocument18 pagesAnnual Remuneration: The First SRX (6) Months of This Agreement Will Be Set As A Period of ProbationahmedNo ratings yet
- A Handbook of Major Kuwaiti Corporations: 15Th EditionDocument3 pagesA Handbook of Major Kuwaiti Corporations: 15Th EditionTrafficked_by_ITTNo ratings yet
- Labor Relations Notes - Security of TenureDocument17 pagesLabor Relations Notes - Security of TenureKimberly Mae LugoNo ratings yet
- Phr222-Content-Module 2Document14 pagesPhr222-Content-Module 2Peybi Lazaro ChamchamNo ratings yet
- NCM120Document6 pagesNCM120Mae Arra Lecobu-anNo ratings yet
- Employer Responsibilities and Employee RightsDocument12 pagesEmployer Responsibilities and Employee RightsJhazielle DolleteNo ratings yet
- December 2019Document4 pagesDecember 2019AziraNo ratings yet
- Labor Law - Leave Benefits - Comparison Labor Law and CSC LawDocument15 pagesLabor Law - Leave Benefits - Comparison Labor Law and CSC LawApple LavarezNo ratings yet
- Title I Termination OF Employment Art 279. Security of TenureDocument7 pagesTitle I Termination OF Employment Art 279. Security of Tenuresweetlunacy00No ratings yet
- Labor Standards (Transcriptions - Edited)Document14 pagesLabor Standards (Transcriptions - Edited)Antonina ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Module 10Document4 pagesModule 10Angela DucusinNo ratings yet
- B3 - International Catholic vs. NLRC, GR No. 72222Document1 pageB3 - International Catholic vs. NLRC, GR No. 72222Luds OretoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document46 pagesChapter 11arantonizhaNo ratings yet
- Work Immersion Module 3Document4 pagesWork Immersion Module 3pattiffanylorenzo278No ratings yet
- WAGES and LEAVESDocument23 pagesWAGES and LEAVESDiego DuroyNo ratings yet
- THE LABOUR LAW IN UGANDA: [A TeeParkots Inc Publishers Product]From EverandTHE LABOUR LAW IN UGANDA: [A TeeParkots Inc Publishers Product]No ratings yet
- Textbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 15, Human Resources Overview: Key Labor and Employment IssuesFrom EverandTextbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 15, Human Resources Overview: Key Labor and Employment IssuesNo ratings yet
- Administering Questionnaires: Different Types Design Questionnaires Cross-CulturalDocument10 pagesAdministering Questionnaires: Different Types Design Questionnaires Cross-CulturalSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 11 - Measurement of VariablesDocument3 pagesChapter - 11 - Measurement of VariablesSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Data Collection Methods: ObservationDocument9 pagesData Collection Methods: ObservationSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Interviews: Personal Interview. Advantages and Disadvantages Business Is Largely A Social PhenomenonDocument8 pagesInterviews: Personal Interview. Advantages and Disadvantages Business Is Largely A Social PhenomenonSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Scientific Investigation: Hallmarks of Scientific Research Hypothetico-Deductive ResearchDocument3 pagesScientific Investigation: Hallmarks of Scientific Research Hypothetico-Deductive ResearchSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 - Theoretical Framework & Hypothesis DevelopmentDocument10 pagesChapter - 5 - Theoretical Framework & Hypothesis DevelopmentSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Critical Literature Review The Critical ReviewDocument10 pagesCritical Literature Review The Critical ReviewSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Kotler, Bowen & Makens CH 19Document10 pagesKotler, Bowen & Makens CH 19Sanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Defining and Refining The ProblemDocument13 pagesDefining and Refining The ProblemSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Research Definition ResearchDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Research Definition ResearchSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- MHT CH 01Document9 pagesMHT CH 01Sanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Kotler, Bowen & Makens CH 12Document9 pagesKotler, Bowen & Makens CH 12Sanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Kotler, Bowen & Makens CH 11Document8 pagesKotler, Bowen & Makens CH 11Sanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Kotler, Bowen & Makens CH 14Document7 pagesKotler, Bowen & Makens CH 14Sanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Kotler, Bowen & Makens CH 06Document8 pagesKotler, Bowen & Makens CH 06Sanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Kotler, Bowen & Makens CH 04Document7 pagesKotler, Bowen & Makens CH 04Sanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Summarising Analysing DataDocument19 pagesSummarising Analysing DataSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Job, Batch and Service CostingDocument22 pagesJob, Batch and Service CostingSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Kotler, Bowen & Makens CH 08Document8 pagesKotler, Bowen & Makens CH 08Sanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Kotler, Bowen & Makens CH 05Document8 pagesKotler, Bowen & Makens CH 05Sanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Tute 01 - The Law of ContractDocument38 pagesTute 01 - The Law of ContractSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- The Law of Contract Mind MapsDocument8 pagesThe Law of Contract Mind MapsSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument24 pagesStandard Costing and Variance AnalysisSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Short-Term Decision MakingDocument26 pagesShort-Term Decision MakingSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Sip Report of Planman HR (Temp Staffing)Document51 pagesSip Report of Planman HR (Temp Staffing)Chinmoy MahapatraNo ratings yet
- Acemoglu e Johnson 2023 Rebalancing AIDocument4 pagesAcemoglu e Johnson 2023 Rebalancing AIpatriciovergaraNo ratings yet
- Big BazaarDocument23 pagesBig BazaarSHOAIB MEMONNo ratings yet
- PUA Updated Operating Instructions and Reporting ChangesDocument62 pagesPUA Updated Operating Instructions and Reporting ChangesAdam HarringtonNo ratings yet
- Kaizen: - A Term PaperDocument2 pagesKaizen: - A Term PaperChiil AnnNo ratings yet
- Kasambahay HandbookDocument59 pagesKasambahay HandbookwapbytezNo ratings yet
- Maury County BusinessDocument54 pagesMaury County BusinessJournal CommunicationsNo ratings yet
- Empathy MapDocument10 pagesEmpathy MapPlyers100% (1)
- Difference Between A CV and ResumeDocument3 pagesDifference Between A CV and ResumeSabari MajumderNo ratings yet
- Accenture Digital Adoption ReportDocument25 pagesAccenture Digital Adoption ReportgasibuteaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Personnel Administration Pad254Document20 pagesAssignment Personnel Administration Pad254greeny83100% (1)
- FlexiEle Hire To ExitDocument22 pagesFlexiEle Hire To ExitSachinNo ratings yet
- Labour Market and Income Distribution: The Effects of Education and The Gig-EconomyDocument19 pagesLabour Market and Income Distribution: The Effects of Education and The Gig-EconomyHarry SinghNo ratings yet
- "Work Life Balance of Employees in Selected Hotels in Cagayan de Oro City and Iligan City During Covid 19"-Jamon, Ligtas, VillarDocument84 pages"Work Life Balance of Employees in Selected Hotels in Cagayan de Oro City and Iligan City During Covid 19"-Jamon, Ligtas, VillarJoe Andrei LigtasNo ratings yet
- PAYSLIPDocument11 pagesPAYSLIPSaran ManiNo ratings yet
- A Case Study For Compre MaedDocument2 pagesA Case Study For Compre MaedJL D. BusiaNo ratings yet
- ParticipativemanagementDocument24 pagesParticipativemanagementSarathBabuNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - StressDocument8 pagesUnit 1 - StressJORGE ARRUÉNo ratings yet
- Skill Shift Automation and The Future of The WorkforceDocument2 pagesSkill Shift Automation and The Future of The WorkforcejordybeltNo ratings yet
- Intro To Business Chapter 7 NotesDocument8 pagesIntro To Business Chapter 7 Notesapi-526065196No ratings yet
- Staffing&SchedulingDocument14 pagesStaffing&SchedulingKrishnaveni MurugeshNo ratings yet
- TM1 PresentationDocument33 pagesTM1 PresentationJas Sofia90% (10)
- Robert Wilson - Annotated BibliographyDocument5 pagesRobert Wilson - Annotated Bibliographyapi-557627314No ratings yet
- Market Strikes BackDocument12 pagesMarket Strikes BackAshraf AhmedNo ratings yet
- Graduate CV TemplateDocument2 pagesGraduate CV TemplateFrankie NguyenNo ratings yet
- Barriers To Strategic Human Resource ManagementDocument59 pagesBarriers To Strategic Human Resource ManagementMadhukar Saxena100% (1)
- Staffing Organizations 9th Edition Heneman Test BankDocument12 pagesStaffing Organizations 9th Edition Heneman Test Bankmarkgordonxqaifpntwd100% (18)
- Importance of A Job TitleDocument2 pagesImportance of A Job TitleLORAINENo ratings yet




























































![THE LABOUR LAW IN UGANDA: [A TeeParkots Inc Publishers Product]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/702714789/149x198/ac277f344e/1706724197?v=1)