Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Asthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Compress
Asthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Compress
Uploaded by
Margarette Geres0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
390 views2 pages1. The nursing diagnosis was ineffective airway clearance due to possible bronchospasm and increased secretions.
2. Nursing interventions included assessing respiratory status hourly, assisting with positioning, encouraging breathing exercises, increasing fluid intake, administering medications, and monitoring outcomes.
3. The goals were for the client to demonstrate clear airway and adequate oxygen exchange within 3 days and identify factors that could improve or maintain airway clearance.
Original Description:
gfhsksnkjshfhc,n,mxnc
Original Title
Asthma Nursing Care Plan Ncp Ineffective Airway Clearance Compress
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The nursing diagnosis was ineffective airway clearance due to possible bronchospasm and increased secretions.
2. Nursing interventions included assessing respiratory status hourly, assisting with positioning, encouraging breathing exercises, increasing fluid intake, administering medications, and monitoring outcomes.
3. The goals were for the client to demonstrate clear airway and adequate oxygen exchange within 3 days and identify factors that could improve or maintain airway clearance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
390 views2 pagesAsthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Compress
Asthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Compress
Uploaded by
Margarette Geres1. The nursing diagnosis was ineffective airway clearance due to possible bronchospasm and increased secretions.
2. Nursing interventions included assessing respiratory status hourly, assisting with positioning, encouraging breathing exercises, increasing fluid intake, administering medications, and monitoring outcomes.
3. The goals were for the client to demonstrate clear airway and adequate oxygen exchange within 3 days and identify factors that could improve or maintain airway clearance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
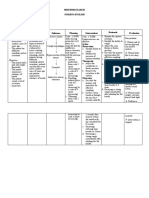
Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Nursing Diagnosis: Goals/ Objectives: Nursing Actions Outcome
Ineffective Airway Short term goal: 1. Some degree in Criteria:
Clearance Client will demonstrate 1. Assess respiratory status bronchospasm is present Client will
every hour during acute with obstruction in
signs of patent airway verbalize
Possible Etiologies: phase: lung sounds, airway and may be
(Related to) and adequate oxygen respiratory rate and depth, manifested with reduction or
• Bronchospasm exchange within 3 days. presence and severity of wheezing or absent absence in
• Increased production Long term goal: wheezing, breathing pattern, breath sounds in severe difficulty in
of secretions; retained Client will demonstrate use of accessory muscles. asthma. Tachypnea is breathing and
secretions; thick, behaviours to improve 2. Assist patient to assume to usually present to some feeling of chest
viscous secretions or maintain airway comfortable position, i.e. degree and respiratory constriction,
• Decreased energy/ elevate head of bed, have dysfunction is variable
clearance and identify respiration and
fatigue client lean on over bed table depending on underlying
potential complications or sit on the edge of bed. process such as allergic cardiac rate
and initiate appropriate 3. Keep environmental reaction. within normal
Defining characteristics:
actions. pollution to a minimum 2. Elevation of head of the range, absence or
(Evidenced by)
according to individual bed facilitates respiratory reduction of
• Statement of difficulty
situation. function by use of inspiratory and
in breathing
4. Encourage and assist gravity, however client in expiratory
• Feeling of chest abdominal and pursed – lip distress may seek
constriction wheezing, and
breathing exercises. position that most eases
• Changes in depth/ rate 5. Increase fluid intake to breathing. ability to resume
of respiration; 3000ml/ day within cardiac 3. Precipitators of allergic to activities.
tachypnea tolerance. type of respiratory Client will be
• Tachycardia 6. Provide warm liquids and reactions that can trigger able to identify
• Use of accessory recommend intake of fluids or exacerbate onset of and avoid
muscles or marked between meals, instead of acute episode. potential
respiratory effort during meals. 4. Provides some means to
7. Administer medications as cope with or control allergens or
• Abnormal breath
indicated. dyspnea and reduce air stimuli that would
sound, inspiratory and
expiratory wheezing 8. Monitor side effects of trapping. trigger asthma
• Cough (persistent), bronchodilator (tremors/ 5. Hydration helps thin attack and be able
without sputum tachycardia). secretions, facilitating to handle
production 9. Provide supplemental expectoration and using symptoms if
• Prolonged expiration humidification, e.g., warm liquids may
recurrence comes,
neutralizer in respiratory decrease bronchospasm.
treatments. 6. Fluids during meals can prompt follow up
10. Monitor ABGs, pulse increase gastric checkup and to
oximetry, chest x- ray. distension and pressure always bring or
on the diaphragm.
have the
7. Anticholinergic
medications are the first prescribed
line drugs for clients with medication/s on
this condition. hand in case
8. Humidity helps reduce asthma occurs.
viscosity of secretions,
facilitating expectoration
and may.
9. Breathing exercises help
enhance diffusion,
nebulizer medications
can reduce
bronchospasm and
stimulate expectoration.
10. Establishes baseline for
monitoring progression/
regression of disease
process.
You might also like
- JHA - General Electrical WorkDocument7 pagesJHA - General Electrical WorkEL Mer96% (49)
- Unit IG2: Risk Assessment Part 1: BackgroundDocument17 pagesUnit IG2: Risk Assessment Part 1: BackgroundStven Smith100% (6)
- Functional Movement Disorder: Kathrin Lafaver Carine W. Maurer Timothy R. Nicholson David L. Perez EditorsDocument455 pagesFunctional Movement Disorder: Kathrin Lafaver Carine W. Maurer Timothy R. Nicholson David L. Perez Editors李世民100% (3)
- NCP BronchopneumoniaDocument8 pagesNCP BronchopneumoniaCrisantaCasliNo ratings yet
- SP CSDocument4 pagesSP CSKhan HansNo ratings yet
- Cu 4Document3 pagesCu 4Paul SahagunNo ratings yet
- Date/ Time/ Shift Cues Need Nursing Diagnosis With Rationale Objectives of Care Nursing Interventions With Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesDate/ Time/ Shift Cues Need Nursing Diagnosis With Rationale Objectives of Care Nursing Interventions With Rationale EvaluationPauleen Trisha SamparaniNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Case Pres Ncps FinalDocument13 pagesCase Pres Ncps FinalMariejoy YadaoNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance CareplanDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance CareplanderreshaNo ratings yet
- Peritonsillar AbscessDocument2 pagesPeritonsillar AbscessKevin Leo Lucero AragonesNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument6 pagesNCP PTBJay Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planapi-309251523No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyNeri ChavezNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageNCP Ineffective Airway Clearancejae_007No ratings yet
- Laryngeal Cancer Concept MapDocument1 pageLaryngeal Cancer Concept MapTessa Claire JaranowskiNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Oxy. Online BasedDocument5 pagesAssignment For Oxy. Online BasedNurhassem Nor AkangNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPneumoniaPia MedinaNo ratings yet
- CARE PLAN For BRONCHIECTASISDocument8 pagesCARE PLAN For BRONCHIECTASISCecil MonteroNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Objectives of Care Intervention Rationale Evaluation Difficulty of Breathing (Rapid and Shallow)Document1 pageAssessment Diagnosis Objectives of Care Intervention Rationale Evaluation Difficulty of Breathing (Rapid and Shallow)Jamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- NCP Micu Hascvd Cad - RioDocument5 pagesNCP Micu Hascvd Cad - RioRio BonifacioNo ratings yet
- NCP Cough PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNCP Cough PneumoniaAirme Raz AlejandroNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPVince John SevillaNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument3 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliNo ratings yet
- MCN NCPDocument4 pagesMCN NCPPEARL CHRISTINE CUDALNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective: Nabalaka Ko Short Term: Independent: Goal Met Short TermDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective: Nabalaka Ko Short Term: Independent: Goal Met Short Termgeng gengNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- Wk2 NCP Edited2012Document6 pagesWk2 NCP Edited2012Jessely Caling SalasNo ratings yet
- NCP Fever: Read Books, Audiobooks, and More Scribd, IncDocument10 pagesNCP Fever: Read Books, Audiobooks, and More Scribd, IncEricsonMitraNo ratings yet
- NCP ProperDocument5 pagesNCP ProperRustan FrozenNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermGensen Cu RoxasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - MCNDocument2 pagesChapter 6 - MCNPrincess Queenie OlarteNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageNursing Care PlanMikki lor PuaganNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit BatuDocument2 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Batumecz26No ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceEmirose Fatima TagabNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To Acute Pain As Evidence by Increased RespirationDocument6 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To Acute Pain As Evidence by Increased RespirationCamille T. SanchezNo ratings yet
- Administering Enema POWERPOINT GIVING ENEMA TO PATIENT, FOR PATIENT WITH GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS .. LECTURES, PRINCIPLES AND PROCEDURESDocument14 pagesAdministering Enema POWERPOINT GIVING ENEMA TO PATIENT, FOR PATIENT WITH GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS .. LECTURES, PRINCIPLES AND PROCEDURESPb0% (1)
- NCP TBDocument7 pagesNCP TBLorraine CilloNo ratings yet
- 3 NCP AsthmaDocument6 pages3 NCP AsthmajaninenicoleNo ratings yet
- NCP BMDocument1 pageNCP BMSourabh MehraNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPNikki del Rosario100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Sweating Temperature Rigors Nausea Vomiting Diarrhoea Lethargy MalaiseDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Sweating Temperature Rigors Nausea Vomiting Diarrhoea Lethargy Malaise06eltianNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory FailureDocument25 pagesAcute Respiratory FailurejohnleeeNo ratings yet
- Rufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Document6 pagesRufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Knowledge DeficitDocument5 pagesKnowledge DeficitteamstrocaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Planjnx_anonymousNo ratings yet
- Group 6 Group Case Study DONEDocument5 pagesGroup 6 Group Case Study DONEE.R.ONo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: Nursing Care Plan FormDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: Nursing Care Plan FormissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Group 4-Open Wound Head Injury After Debris FallDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Group 4-Open Wound Head Injury After Debris FallNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- NCP Acitivity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesNCP Acitivity IntolerancegizelleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Problem Explanation Goal Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument1 pageNursing Problem Explanation Goal Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveZed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageIneffective Airway ClearanceChristineAlaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument13 pagesNursing Care PlanCris Solis33% (3)
- Problem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Document10 pagesProblem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Raidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia NCPDocument10 pagesPneumonia NCPDIAZ Candy AliahNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Computation 2021Document3 pagesNCM 112 Computation 2021Marie Kelsey Acena Macaraig100% (1)
- NCP DobDocument2 pagesNCP DobPaulo GeneraloNo ratings yet
- Venn Diagram (Nursing Process vs. Education Process)Document2 pagesVenn Diagram (Nursing Process vs. Education Process)Maze Jamela Peñaojas ManlogonNo ratings yet
- Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: IndependentDocument1 pageSubjective Data: Short Term Goal: IndependentVanetNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Assesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha Suazo100% (1)
- DULNUANDocument2 pagesDULNUANJB tindonganNo ratings yet
- APOLONIO, Reyjan L. (NCP 1)Document2 pagesAPOLONIO, Reyjan L. (NCP 1)REYJAN APOLONIONo ratings yet
- LP1ncm109 YboaDocument21 pagesLP1ncm109 YboaMargarette GeresNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Concept of The Community: 1.0 Intended Learning OutcomesDocument9 pagesUnit 1: Concept of The Community: 1.0 Intended Learning OutcomesMargarette GeresNo ratings yet
- LP2 ncm105Document8 pagesLP2 ncm105Margarette GeresNo ratings yet
- GE7 The Contemporary World: Hanna Joyce B. MacawiliDocument15 pagesGE7 The Contemporary World: Hanna Joyce B. MacawiliMargarette Geres100% (1)
- GE7 The Contemporary World: Hanna Joyce B. MacawiliDocument15 pagesGE7 The Contemporary World: Hanna Joyce B. MacawiliMargarette Geres100% (1)
- 3LP 2020ncm105Document7 pages3LP 2020ncm105Margarette GeresNo ratings yet
- NCM 104 Community Health Nursing 1: Bachelor of Science in NursingDocument8 pagesNCM 104 Community Health Nursing 1: Bachelor of Science in NursingMargarette GeresNo ratings yet
- CHN1 LP 2 QuianoDocument27 pagesCHN1 LP 2 QuianoMargarette GeresNo ratings yet
- More On Mediterranean Diets (Artemis P. Simopoulos, Francesco Visioli) (Z-Library)Document255 pagesMore On Mediterranean Diets (Artemis P. Simopoulos, Francesco Visioli) (Z-Library)qrscentralNo ratings yet
- DR V PendseDocument1 pageDR V PendsePriyansh TanejaNo ratings yet
- Evaluare Pacient - Scor HAS-BLED: H A S B L E DDocument2 pagesEvaluare Pacient - Scor HAS-BLED: H A S B L E Dviorel79No ratings yet
- EUCAST Breakpoints V 2.0 120101Document73 pagesEUCAST Breakpoints V 2.0 120101mermarinarNo ratings yet
- 07-Vaccination Traveller RSUI 2020Document35 pages07-Vaccination Traveller RSUI 2020Eirna Syam Fitri IINo ratings yet
- Surgical Management of Maxillary and Mandibular Fractures in An Eastern Bluetongue Skink, Tiliqua Scincoides ScincoidesDocument5 pagesSurgical Management of Maxillary and Mandibular Fractures in An Eastern Bluetongue Skink, Tiliqua Scincoides ScincoidesAndres ArbelaezNo ratings yet
- PARASITEDocument16 pagesPARASITEMarielle Katherine E. EgamNo ratings yet
- Course Notes - Section 2: 4. What Is Aromatherapy?Document4 pagesCourse Notes - Section 2: 4. What Is Aromatherapy?LisaNo ratings yet
- The Exorcism of Emily Rose ScriptDocument228 pagesThe Exorcism of Emily Rose ScriptRixie MoonNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Mapeh: Lesson 1 (Health)Document7 pagesQuarter 3 Mapeh: Lesson 1 (Health)Jannie SantillanNo ratings yet
- Awareness SurveyDocument6 pagesAwareness Surveyveerasankar123No ratings yet
- MSDS - BeCu AlloyDocument6 pagesMSDS - BeCu AlloyTaherNo ratings yet
- Soal ArithmiaDocument13 pagesSoal Arithmiaeka rahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Sugar BluesDocument16 pagesSugar Bluesrobert desai100% (3)
- A Consideration in The Itchy or Overgrooming Cat: Feline DemodicosisDocument5 pagesA Consideration in The Itchy or Overgrooming Cat: Feline DemodicosisBirdella GwenNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic Management: BleomycinDocument1 pagePharmacologic Management: BleomycinKim ApuradoNo ratings yet
- Teaching Clinical Reasoning To Medical Students: A Case-Based Illness Script Worksheet ApproachDocument7 pagesTeaching Clinical Reasoning To Medical Students: A Case-Based Illness Script Worksheet Approachstarskyhutch0000No ratings yet
- English 102 Reading Writing Module 2Document24 pagesEnglish 102 Reading Writing Module 2Milyn Mae PalganNo ratings yet
- LIST OF DOCUMENTS To Be Submitted To The Notified Body (NB) PCBC For Conformity Assessment of The Medical DeviceDocument5 pagesLIST OF DOCUMENTS To Be Submitted To The Notified Body (NB) PCBC For Conformity Assessment of The Medical DevicegobeliyNo ratings yet
- Ayurvedic Management of Adhd (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) - A Case StudyDocument5 pagesAyurvedic Management of Adhd (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) - A Case StudyNatseenNo ratings yet
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument12 pagesBronchial AsthmaRAMNo ratings yet
- Dilg Doh Jao 2020 0001Document31 pagesDilg Doh Jao 2020 0001Novie FeneciosNo ratings yet
- Youth Leadership Participation and Accountability - The Recommendations 1Document28 pagesYouth Leadership Participation and Accountability - The Recommendations 1Aldren HilaNo ratings yet
- Knowledge and Attitudes Towards Cervical Cancer Screening Among Students Aged 18-30 at Kampala International UniversityDocument10 pagesKnowledge and Attitudes Towards Cervical Cancer Screening Among Students Aged 18-30 at Kampala International UniversityKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- MAPEH ReviewerDocument10 pagesMAPEH ReviewerAlthea Lexine P. CorpusNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Childbirth Postpartum and Newborn Care PDFDocument184 pagesPregnancy Childbirth Postpartum and Newborn Care PDFdiana100% (1)
- Midterm Exam Iii Nursing EnglishDocument3 pagesMidterm Exam Iii Nursing EnglishAlfriedo 008No ratings yet