Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Total Income - Total Expenses Net Profit
Total Income - Total Expenses Net Profit
Uploaded by
Viñas, Diana L.Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Finance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)From EverandFinance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (32)
- CHAPTER 34 - Biological Assets: Problem 34-1 (IFRS)Document13 pagesCHAPTER 34 - Biological Assets: Problem 34-1 (IFRS)Kimberly Claire Atienza100% (3)
- Case StudyDocument4 pagesCase StudyRomuald KinimoNo ratings yet
- Fabm 2 - Lesson 2 - SCIDocument20 pagesFabm 2 - Lesson 2 - SCIwendell john medianaNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 1Document13 pagesKelompok 1difarafi97No ratings yet
- Statement of Comprehensive IncomeDocument25 pagesStatement of Comprehensive IncomeAngel Nichole ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Three Chapter FiveDocument4 pagesLecture Three Chapter Fivebouchra bouchraNo ratings yet
- finance conceptsDocument15 pagesfinance conceptsgodwillinno1997No ratings yet
- Income StatementsDocument5 pagesIncome StatementsAdetunbi TolulopeNo ratings yet
- RevenueAccountsWithDefinition, TypesAndExamplesIndeed - Comindia 1710866202575Document7 pagesRevenueAccountsWithDefinition, TypesAndExamplesIndeed - Comindia 1710866202575williamseugine2008No ratings yet
- Income StatementDocument36 pagesIncome StatementTiffany VinzonNo ratings yet
- Script For ReportingDocument14 pagesScript For Reportingvelasco.mhervin08No ratings yet
- Importance and Preparation of Income StatementDocument35 pagesImportance and Preparation of Income StatementChristina BinoboNo ratings yet
- How To Prepare A Profit and Loss (Income) Statement: Zions Business Resource CenterDocument16 pagesHow To Prepare A Profit and Loss (Income) Statement: Zions Business Resource CenterSiti Asma MohamadNo ratings yet
- Financing, Securing and Managing It: GROUP 3 (C-S2A1) Abrogar, Ladyville Bulawin, Nelson Estacio, Ella Payao, LilibethDocument20 pagesFinancing, Securing and Managing It: GROUP 3 (C-S2A1) Abrogar, Ladyville Bulawin, Nelson Estacio, Ella Payao, LilibetharzaianNo ratings yet
- Sat Pra 13Document7 pagesSat Pra 13Samyak KalaskarNo ratings yet
- CashflowDocument6 pagesCashflowAizia Sarceda Guzman71% (7)
- What Is RevenueDocument31 pagesWhat Is RevenueLEARN WITH AGALYANo ratings yet
- Learnings ObjectivesDocument5 pagesLearnings Objectivesnavie VNo ratings yet
- Fabm ReviewerDocument2 pagesFabm Reviewer治太宰No ratings yet
- FINFO Week 3 Learner GuideDocument14 pagesFINFO Week 3 Learner GuideAngelica Caballes TabaniaNo ratings yet
- Income StatementDocument3 pagesIncome StatementMamta LallNo ratings yet
- BoS - Helping You Assess Your Business PerformanceDocument33 pagesBoS - Helping You Assess Your Business PerformancegerardkokNo ratings yet
- Cost of Goods Sold and Operating ExpensesDocument4 pagesCost of Goods Sold and Operating ExpensesAna Mae CatubesNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of PTNGN PDFDocument27 pagesFundamentals of PTNGN PDFEdfrance Delos Reyes0% (1)
- RoarDocument19 pagesRoarFrank HernandezNo ratings yet
- 1.forecasting The Revenues of The Business 2.forecasting The Cost To Be IncurredDocument29 pages1.forecasting The Revenues of The Business 2.forecasting The Cost To Be IncurredDimple MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Income StatementDocument4 pagesUnderstanding The Income Statementluvujaya100% (1)
- Notes of Module IIIDocument16 pagesNotes of Module IIIkirtichourasia14No ratings yet
- Accounting For Non - Accountants - Simple - Business OperationsDocument37 pagesAccounting For Non - Accountants - Simple - Business OperationsTesda CACSNo ratings yet
- Fabm1 10Document14 pagesFabm1 10Francis Esperanza0% (1)
- Lesson 6 Business ForecastDocument26 pagesLesson 6 Business ForecastZalamea, RyzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Financial StrategyDocument5 pagesChapter 6 Financial StrategySweta KumariNo ratings yet
- Income Statement, Its Elements, Usefulness and LimitationsDocument5 pagesIncome Statement, Its Elements, Usefulness and LimitationsDipika tasfannum salamNo ratings yet
- Pact Financial Proj B 3Document4 pagesPact Financial Proj B 3Benedict Arcino RodriguezNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate TurnoverDocument10 pagesHow To Calculate TurnoverJayanti International LtdNo ratings yet
- Module7 Forecasting The Revenues of The BusinessDocument55 pagesModule7 Forecasting The Revenues of The BusinessAlejandro Gutierrez AlbaricoNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Analysis, Target Cost, Variable Cost PDFDocument29 pagesCash Flow Analysis, Target Cost, Variable Cost PDFitsmenatoyNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Analysis, Target Cost, Variable CostDocument29 pagesCash Flow Analysis, Target Cost, Variable CostitsmenatoyNo ratings yet
- EntrepDocument33 pagesEntrepArianne TañanNo ratings yet
- FABM 2nd Sem Long QuizzesDocument8 pagesFABM 2nd Sem Long QuizzesJeamie SayotoNo ratings yet
- Guia InglesDocument6 pagesGuia InglesCristian SandovalNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document85 pagesUnit 4Ankush Singh100% (1)
- Financial Accounting & AnalysisDocument11 pagesFinancial Accounting & Analysisheet jainNo ratings yet
- Guia InglesDocument6 pagesGuia InglesCristian SandovalNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Income StatementDocument4 pages5.3 Income StatementHiNo ratings yet
- Statement of Comprehensive IncomeDocument30 pagesStatement of Comprehensive Incomemaligaya evelyn100% (1)
- Summarized Topics in EntrepreneurshipDocument24 pagesSummarized Topics in EntrepreneurshipMarian AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- What is Operating Profit Margin_ - Sage SoftwareDocument6 pagesWhat is Operating Profit Margin_ - Sage SoftwaredatNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five: Special Issues For MerchantsDocument26 pagesChapter Five: Special Issues For Merchantswww_jeffersoncruz008No ratings yet
- Financial Accounting: Salal Durrani 2020Document12 pagesFinancial Accounting: Salal Durrani 2020Rahat BatoolNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Income Statement and Balance SheetDocument5 pagesBusiness Plan Income Statement and Balance Sheetexllctqvf100% (1)
- ENTREPQ2.2.1Document25 pagesENTREPQ2.2.1Juvy Fernandez Abong DejesaNo ratings yet
- An Examination of Accounting Variances Between Servicing and Merchandising BusinessesDocument8 pagesAn Examination of Accounting Variances Between Servicing and Merchandising Businessess.casama.gabrieldeepNo ratings yet
- Multi Step Income Statement For Merchadising BusinessDocument10 pagesMulti Step Income Statement For Merchadising Businessjesi zamoraNo ratings yet
- Statement of Comprehensive IncomeDocument33 pagesStatement of Comprehensive IncomeZalvy Gwen RecimoNo ratings yet
- Computation of Gross ProfitDocument26 pagesComputation of Gross ProfitEhra Mae MagnoNo ratings yet
- Statement of Comprehensive IncomeDocument4 pagesStatement of Comprehensive IncomeBlessylyn AguilarNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting & AnalysisDocument5 pagesFinancial Accounting & AnalysisSourav SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Entrep Q4 M78 NotesDocument8 pagesEntrep Q4 M78 NotesRamien Andrea CagampangNo ratings yet
- Problem and Its Background IDocument3 pagesProblem and Its Background IViñas, Diana L.No ratings yet
- Problem and Its Background IDocument2 pagesProblem and Its Background IViñas, Diana L.No ratings yet
- Colegio de Montalban: Kasiglahan Village, San Jose, Rodriguez, RizalDocument10 pagesColegio de Montalban: Kasiglahan Village, San Jose, Rodriguez, RizalViñas, Diana L.No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1Viñas, Diana L.No ratings yet
- Colegio de Montalban: Kasiglahan Village, San Jose, Rodriguez, RizalDocument11 pagesColegio de Montalban: Kasiglahan Village, San Jose, Rodriguez, RizalViñas, Diana L.No ratings yet
- Colegio de Montalban: The Problem and Its BackgroundDocument10 pagesColegio de Montalban: The Problem and Its BackgroundViñas, Diana L.No ratings yet
- Colegio de Montalban: Presentation, Analysis and Interpretation of DataDocument15 pagesColegio de Montalban: Presentation, Analysis and Interpretation of DataViñas, Diana L.No ratings yet
- Ang Guro Kong Di Marunong MagbasaDocument3 pagesAng Guro Kong Di Marunong MagbasaViñas, Diana L.No ratings yet
- Bonus ConceptDocument2 pagesBonus ConceptViñas, Diana L.No ratings yet
- Philippine Politics Governance MODULE 9&10 WEEK1&2Document11 pagesPhilippine Politics Governance MODULE 9&10 WEEK1&2Viñas, Diana L.No ratings yet
- Managerial Economics in A Global Economy, 5th Edition by Dominick SalvatoreDocument21 pagesManagerial Economics in A Global Economy, 5th Edition by Dominick SalvatoreIsmail WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Chicken RunDocument6 pagesChicken RunshazlianahashimNo ratings yet
- 5 Perspectives of Quality by Garvin: A Product Perspective On Total Data Quality ManagementDocument3 pages5 Perspectives of Quality by Garvin: A Product Perspective On Total Data Quality ManagementTracy Mae DanghilNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management: Presented By:-Priyanka Deshpande - 02 Nishant Tiwari - 07 Prerna Jhawar - 14Document41 pagesMarketing Management: Presented By:-Priyanka Deshpande - 02 Nishant Tiwari - 07 Prerna Jhawar - 14Prerna JhawarNo ratings yet
- Branch Home PuzzleDocument12 pagesBranch Home PuzzleDainika ShettyNo ratings yet
- Under Armour's Case AnalysisDocument5 pagesUnder Armour's Case AnalysisericNo ratings yet
- Brief Exercise 255Document2 pagesBrief Exercise 255Sadile May KayeNo ratings yet
- Kotler 2017Document3 pagesKotler 2017irfan widyantoNo ratings yet
- Coke Mini-CaseDocument2 pagesCoke Mini-CaseKing CheungNo ratings yet
- Case Study Tesco: Corporate Level and Business Level StrategiesDocument38 pagesCase Study Tesco: Corporate Level and Business Level StrategiesAhdel GirlisonfireNo ratings yet
- Quiz #1Document6 pagesQuiz #1Ioana Stroica100% (3)
- SOAL UAS Akuntansi Berbasis Komputer 2022Document4 pagesSOAL UAS Akuntansi Berbasis Komputer 2022Laksmi Banowati Sadmoko HadiNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Strategic Cost Management Master BudgetDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Strategic Cost Management Master BudgetNCTNo ratings yet
- Module - 2 Informal Risk Capital & Venture CapitalDocument26 pagesModule - 2 Informal Risk Capital & Venture Capitalpvsagar2001No ratings yet
- Aue3702 2020 TL 103 3 eDocument11 pagesAue3702 2020 TL 103 3 e44v8ct8cdyNo ratings yet
- Analysis Competitors in MarketingDocument15 pagesAnalysis Competitors in MarketingkhaledNo ratings yet
- Quiz: What Is Entrepreneurship?: Show MoreDocument4 pagesQuiz: What Is Entrepreneurship?: Show MoreAbyssNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis SAPDocument2 pagesCase Analysis SAPSandeep GangulyNo ratings yet
- FM Study Notes AugustDocument226 pagesFM Study Notes Augustsahil thakurNo ratings yet
- Basic Features of BondsDocument1 pageBasic Features of Bondspmaina100% (1)
- Market Identification and AnalysisDocument29 pagesMarket Identification and AnalysisJerNo ratings yet
- Ch02 P21 Build A ModelDocument3 pagesCh02 P21 Build A ModelFelipe WeulerNo ratings yet
- Session 5 Job CostingDocument58 pagesSession 5 Job CostingJoeyNo ratings yet
- Ford Motor and Quality Tool (Case Study)Document10 pagesFord Motor and Quality Tool (Case Study)Arousha SultanNo ratings yet
- CFAS Questions Chaps 1 and 2Document13 pagesCFAS Questions Chaps 1 and 2King SigueNo ratings yet
- Economics 1 - F6 - 2013Document2 pagesEconomics 1 - F6 - 2013nalompaNo ratings yet
- Reliance Eqity FundDocument27 pagesReliance Eqity FundMohamed SharifNo ratings yet
- Anthony Brain Bumiller: UltravisiónDocument2 pagesAnthony Brain Bumiller: UltravisiónMaria Fernanda Camacho TorresNo ratings yet
Total Income - Total Expenses Net Profit
Total Income - Total Expenses Net Profit
Uploaded by
Viñas, Diana L.Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Total Income - Total Expenses Net Profit
Total Income - Total Expenses Net Profit
Uploaded by
Viñas, Diana L.Copyright:
Available Formats
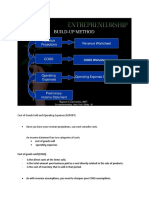
What is a business profit?
Business profit refers to the excess of the business’
total income less all expenses within the accounting period, which may be
presented monthly, quarterly or annually. However, please be informed that a
loss, instead of a profit, will be the result if the total expenses exceed the total
income of the business. For all business owners, profits are important in order
for their business to survive. In the first place, unless you’re in to charity, do
you know anyone who wants to conduct business without making profits?
As business owner, you must have a good understanding of your business’
financial statements. If you’re not, you may need a professional help from
people whom you can get a good accounting and financial advice – they are
generally referred to as Accountants. They can review your financial
statements and can also provide valuable advice on how to improve your
accounting records.
So how do you compute your business profit? The simplest formula is:
Total Income – Total Expenses = Net Profit
• Total income generally includes revenues or sales of goods or services to
customers. It may also include income from deposits, investments and any
other revenue sources such as interest, royalties, dividends, and gains on
exchange of properties.
• Total expenses includes all costs or expenses related to the sale
transactions such as production costs, marketing and all other cost and
expenses related to your business operations including depreciation, losses,
taxes, and interest on debt.
In simple term, profits are all the incomes you earned from your business less
all the expenses you’ve incurred to run the business.
Take note the difference between income, revenue, and gain. You may also
read our post about the difference between cost and expense.
In addition, for presentation purposes, I would like to emphasize three
presentations on how to calculate profit based on the three types of business.
In general, there are three common types of businesses based on their
operation in the market, namely, service business, merchandising business,
and manufacturing business.
Computation of profit on service businesses
Service firms are businesses that provide services instead of product to its
customers. Computation for its profit is simpler because it is known that
service type business does not carry inventory, thus, it does not have a
computation for cost of goods sold. The following is a sample outline for the
computation of the profit of a service business.
*Other operating expenses can be further classified as general and
administrative expenses. They are the expenses incurred by the business
during the accounting period which are not directly related to the service
income earned, such as income taxes.
Computation of profit on merchandising businesses
Merchandising businesses are businesses that enter into retail and trading of
its products. One characteristic of this type of business operation is that they
don’t produce or manufacture their own products to sell. Instead, they
purchase its products from other business and then sell it to customers with a
mark-up from its purchase price. As such, it will be observed that the
computation of its profit involves calculation for its cost of goods sold but do
not compute for the cost of goods manufactured. Below is a sample
computation of net profit or net income of a merchandising business.
• Beginning Inventory – inventories you have in your business at the beginning
of the period that are available for sale.
• Purchases – inventories you bought during the current period.
• Direct costs – costs incurred that can be directly identified or attributed to the
merchandising of the product such as freight-in and inventory storage costs.
• Ending Inventory – inventories you have in your business at the end of the
period that has not yet been sold to customers.
Computation of profit on a manufacturing business
Manufacturing businesses are those that produce or make their own products
then sell it to their customers. The computation of their profit is the same with
merchandising type of business operation. However, the cost of goods sold
section for a manufacturing business is more complicated. The major
difference here is obviously in the need to know how to compute cost of goods
manufactured. Furthermore, the manufacturing type of business operation’s
inventory that is sold is called finished goods rather than being called simply
an inventory and cost of goods manufactured has replaced inventory
purchases. The following is the format of computing the net profit or net
income of a manufacturing business:
Whenever you manufacture your own product, additional elements are
entered into the cost. You’ll have material costs, direct labor, and some
overhead costs to convert raw materials to finished goods. A manufacturing
company has three inventories namely raw materials, work in process
inventory, and finished goods inventory.
• Raw materials consist of all the materials you bought to make your products.
• Work in process is all your products that you are in the middle of making at
the end of the period.
• Finished goods inventory is the value of all completed products that are not
yet sold to customers
https://businesstips.ph/how-to-compute-your-business-profit/
feb. 28,2019
What it is:
Profit is the positive gain remaining for a business after all costs and expenses
have been deducted from total sales. Profit is also referred to as the bottom line,
net profit or net earnings.
How it works (Example):
The formula for profit is:
Total Sales - Total Expenses = Profit
Here is some information about Company XYZ for last year:
Using the formula and the information above, we can calculate that Company
XYZ's profit was:
$2,000,000 - $1,000,000 - $50,000 - $95,000 = $855,000
Why it Matters:
Profit is one of the most important measurements in determining the health and
success of a business. However, the measurement of profit can vary and should
be considered with other factors.
For example, profit varies greatly from company to company and from industry to
industry. Because companies vary in size, it is often more appropriate to consider
profit as a percentage of sales (profit margin) when comparing one company to
another. As well, varying accountingmethods can greatly influence profit, and
these changes may have little to do with a company's actual operations.
Changes in profit are the subject of much analysis. In general, high or rising
profits are indicative of a successful business while low profits could suggest a
myriad of problems, including inadequacies in customer or expense
management.
https://investinganswers.com/financial-dictionary/businesses-corporations/profit-2042
feb. 28, 2019
You might also like
- Finance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)From EverandFinance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (32)
- CHAPTER 34 - Biological Assets: Problem 34-1 (IFRS)Document13 pagesCHAPTER 34 - Biological Assets: Problem 34-1 (IFRS)Kimberly Claire Atienza100% (3)
- Case StudyDocument4 pagesCase StudyRomuald KinimoNo ratings yet
- Fabm 2 - Lesson 2 - SCIDocument20 pagesFabm 2 - Lesson 2 - SCIwendell john medianaNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 1Document13 pagesKelompok 1difarafi97No ratings yet
- Statement of Comprehensive IncomeDocument25 pagesStatement of Comprehensive IncomeAngel Nichole ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Three Chapter FiveDocument4 pagesLecture Three Chapter Fivebouchra bouchraNo ratings yet
- finance conceptsDocument15 pagesfinance conceptsgodwillinno1997No ratings yet
- Income StatementsDocument5 pagesIncome StatementsAdetunbi TolulopeNo ratings yet
- RevenueAccountsWithDefinition, TypesAndExamplesIndeed - Comindia 1710866202575Document7 pagesRevenueAccountsWithDefinition, TypesAndExamplesIndeed - Comindia 1710866202575williamseugine2008No ratings yet
- Income StatementDocument36 pagesIncome StatementTiffany VinzonNo ratings yet
- Script For ReportingDocument14 pagesScript For Reportingvelasco.mhervin08No ratings yet
- Importance and Preparation of Income StatementDocument35 pagesImportance and Preparation of Income StatementChristina BinoboNo ratings yet
- How To Prepare A Profit and Loss (Income) Statement: Zions Business Resource CenterDocument16 pagesHow To Prepare A Profit and Loss (Income) Statement: Zions Business Resource CenterSiti Asma MohamadNo ratings yet
- Financing, Securing and Managing It: GROUP 3 (C-S2A1) Abrogar, Ladyville Bulawin, Nelson Estacio, Ella Payao, LilibethDocument20 pagesFinancing, Securing and Managing It: GROUP 3 (C-S2A1) Abrogar, Ladyville Bulawin, Nelson Estacio, Ella Payao, LilibetharzaianNo ratings yet
- Sat Pra 13Document7 pagesSat Pra 13Samyak KalaskarNo ratings yet
- CashflowDocument6 pagesCashflowAizia Sarceda Guzman71% (7)
- What Is RevenueDocument31 pagesWhat Is RevenueLEARN WITH AGALYANo ratings yet
- Learnings ObjectivesDocument5 pagesLearnings Objectivesnavie VNo ratings yet
- Fabm ReviewerDocument2 pagesFabm Reviewer治太宰No ratings yet
- FINFO Week 3 Learner GuideDocument14 pagesFINFO Week 3 Learner GuideAngelica Caballes TabaniaNo ratings yet
- Income StatementDocument3 pagesIncome StatementMamta LallNo ratings yet
- BoS - Helping You Assess Your Business PerformanceDocument33 pagesBoS - Helping You Assess Your Business PerformancegerardkokNo ratings yet
- Cost of Goods Sold and Operating ExpensesDocument4 pagesCost of Goods Sold and Operating ExpensesAna Mae CatubesNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of PTNGN PDFDocument27 pagesFundamentals of PTNGN PDFEdfrance Delos Reyes0% (1)
- RoarDocument19 pagesRoarFrank HernandezNo ratings yet
- 1.forecasting The Revenues of The Business 2.forecasting The Cost To Be IncurredDocument29 pages1.forecasting The Revenues of The Business 2.forecasting The Cost To Be IncurredDimple MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Income StatementDocument4 pagesUnderstanding The Income Statementluvujaya100% (1)
- Notes of Module IIIDocument16 pagesNotes of Module IIIkirtichourasia14No ratings yet
- Accounting For Non - Accountants - Simple - Business OperationsDocument37 pagesAccounting For Non - Accountants - Simple - Business OperationsTesda CACSNo ratings yet
- Fabm1 10Document14 pagesFabm1 10Francis Esperanza0% (1)
- Lesson 6 Business ForecastDocument26 pagesLesson 6 Business ForecastZalamea, RyzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Financial StrategyDocument5 pagesChapter 6 Financial StrategySweta KumariNo ratings yet
- Income Statement, Its Elements, Usefulness and LimitationsDocument5 pagesIncome Statement, Its Elements, Usefulness and LimitationsDipika tasfannum salamNo ratings yet
- Pact Financial Proj B 3Document4 pagesPact Financial Proj B 3Benedict Arcino RodriguezNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate TurnoverDocument10 pagesHow To Calculate TurnoverJayanti International LtdNo ratings yet
- Module7 Forecasting The Revenues of The BusinessDocument55 pagesModule7 Forecasting The Revenues of The BusinessAlejandro Gutierrez AlbaricoNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Analysis, Target Cost, Variable Cost PDFDocument29 pagesCash Flow Analysis, Target Cost, Variable Cost PDFitsmenatoyNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Analysis, Target Cost, Variable CostDocument29 pagesCash Flow Analysis, Target Cost, Variable CostitsmenatoyNo ratings yet
- EntrepDocument33 pagesEntrepArianne TañanNo ratings yet
- FABM 2nd Sem Long QuizzesDocument8 pagesFABM 2nd Sem Long QuizzesJeamie SayotoNo ratings yet
- Guia InglesDocument6 pagesGuia InglesCristian SandovalNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document85 pagesUnit 4Ankush Singh100% (1)
- Financial Accounting & AnalysisDocument11 pagesFinancial Accounting & Analysisheet jainNo ratings yet
- Guia InglesDocument6 pagesGuia InglesCristian SandovalNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Income StatementDocument4 pages5.3 Income StatementHiNo ratings yet
- Statement of Comprehensive IncomeDocument30 pagesStatement of Comprehensive Incomemaligaya evelyn100% (1)
- Summarized Topics in EntrepreneurshipDocument24 pagesSummarized Topics in EntrepreneurshipMarian AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- What is Operating Profit Margin_ - Sage SoftwareDocument6 pagesWhat is Operating Profit Margin_ - Sage SoftwaredatNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five: Special Issues For MerchantsDocument26 pagesChapter Five: Special Issues For Merchantswww_jeffersoncruz008No ratings yet
- Financial Accounting: Salal Durrani 2020Document12 pagesFinancial Accounting: Salal Durrani 2020Rahat BatoolNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Income Statement and Balance SheetDocument5 pagesBusiness Plan Income Statement and Balance Sheetexllctqvf100% (1)
- ENTREPQ2.2.1Document25 pagesENTREPQ2.2.1Juvy Fernandez Abong DejesaNo ratings yet
- An Examination of Accounting Variances Between Servicing and Merchandising BusinessesDocument8 pagesAn Examination of Accounting Variances Between Servicing and Merchandising Businessess.casama.gabrieldeepNo ratings yet
- Multi Step Income Statement For Merchadising BusinessDocument10 pagesMulti Step Income Statement For Merchadising Businessjesi zamoraNo ratings yet
- Statement of Comprehensive IncomeDocument33 pagesStatement of Comprehensive IncomeZalvy Gwen RecimoNo ratings yet
- Computation of Gross ProfitDocument26 pagesComputation of Gross ProfitEhra Mae MagnoNo ratings yet
- Statement of Comprehensive IncomeDocument4 pagesStatement of Comprehensive IncomeBlessylyn AguilarNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting & AnalysisDocument5 pagesFinancial Accounting & AnalysisSourav SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Entrep Q4 M78 NotesDocument8 pagesEntrep Q4 M78 NotesRamien Andrea CagampangNo ratings yet
- Problem and Its Background IDocument3 pagesProblem and Its Background IViñas, Diana L.No ratings yet
- Problem and Its Background IDocument2 pagesProblem and Its Background IViñas, Diana L.No ratings yet
- Colegio de Montalban: Kasiglahan Village, San Jose, Rodriguez, RizalDocument10 pagesColegio de Montalban: Kasiglahan Village, San Jose, Rodriguez, RizalViñas, Diana L.No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1Viñas, Diana L.No ratings yet
- Colegio de Montalban: Kasiglahan Village, San Jose, Rodriguez, RizalDocument11 pagesColegio de Montalban: Kasiglahan Village, San Jose, Rodriguez, RizalViñas, Diana L.No ratings yet
- Colegio de Montalban: The Problem and Its BackgroundDocument10 pagesColegio de Montalban: The Problem and Its BackgroundViñas, Diana L.No ratings yet
- Colegio de Montalban: Presentation, Analysis and Interpretation of DataDocument15 pagesColegio de Montalban: Presentation, Analysis and Interpretation of DataViñas, Diana L.No ratings yet
- Ang Guro Kong Di Marunong MagbasaDocument3 pagesAng Guro Kong Di Marunong MagbasaViñas, Diana L.No ratings yet
- Bonus ConceptDocument2 pagesBonus ConceptViñas, Diana L.No ratings yet
- Philippine Politics Governance MODULE 9&10 WEEK1&2Document11 pagesPhilippine Politics Governance MODULE 9&10 WEEK1&2Viñas, Diana L.No ratings yet
- Managerial Economics in A Global Economy, 5th Edition by Dominick SalvatoreDocument21 pagesManagerial Economics in A Global Economy, 5th Edition by Dominick SalvatoreIsmail WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Chicken RunDocument6 pagesChicken RunshazlianahashimNo ratings yet
- 5 Perspectives of Quality by Garvin: A Product Perspective On Total Data Quality ManagementDocument3 pages5 Perspectives of Quality by Garvin: A Product Perspective On Total Data Quality ManagementTracy Mae DanghilNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management: Presented By:-Priyanka Deshpande - 02 Nishant Tiwari - 07 Prerna Jhawar - 14Document41 pagesMarketing Management: Presented By:-Priyanka Deshpande - 02 Nishant Tiwari - 07 Prerna Jhawar - 14Prerna JhawarNo ratings yet
- Branch Home PuzzleDocument12 pagesBranch Home PuzzleDainika ShettyNo ratings yet
- Under Armour's Case AnalysisDocument5 pagesUnder Armour's Case AnalysisericNo ratings yet
- Brief Exercise 255Document2 pagesBrief Exercise 255Sadile May KayeNo ratings yet
- Kotler 2017Document3 pagesKotler 2017irfan widyantoNo ratings yet
- Coke Mini-CaseDocument2 pagesCoke Mini-CaseKing CheungNo ratings yet
- Case Study Tesco: Corporate Level and Business Level StrategiesDocument38 pagesCase Study Tesco: Corporate Level and Business Level StrategiesAhdel GirlisonfireNo ratings yet
- Quiz #1Document6 pagesQuiz #1Ioana Stroica100% (3)
- SOAL UAS Akuntansi Berbasis Komputer 2022Document4 pagesSOAL UAS Akuntansi Berbasis Komputer 2022Laksmi Banowati Sadmoko HadiNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Strategic Cost Management Master BudgetDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Strategic Cost Management Master BudgetNCTNo ratings yet
- Module - 2 Informal Risk Capital & Venture CapitalDocument26 pagesModule - 2 Informal Risk Capital & Venture Capitalpvsagar2001No ratings yet
- Aue3702 2020 TL 103 3 eDocument11 pagesAue3702 2020 TL 103 3 e44v8ct8cdyNo ratings yet
- Analysis Competitors in MarketingDocument15 pagesAnalysis Competitors in MarketingkhaledNo ratings yet
- Quiz: What Is Entrepreneurship?: Show MoreDocument4 pagesQuiz: What Is Entrepreneurship?: Show MoreAbyssNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis SAPDocument2 pagesCase Analysis SAPSandeep GangulyNo ratings yet
- FM Study Notes AugustDocument226 pagesFM Study Notes Augustsahil thakurNo ratings yet
- Basic Features of BondsDocument1 pageBasic Features of Bondspmaina100% (1)
- Market Identification and AnalysisDocument29 pagesMarket Identification and AnalysisJerNo ratings yet
- Ch02 P21 Build A ModelDocument3 pagesCh02 P21 Build A ModelFelipe WeulerNo ratings yet
- Session 5 Job CostingDocument58 pagesSession 5 Job CostingJoeyNo ratings yet
- Ford Motor and Quality Tool (Case Study)Document10 pagesFord Motor and Quality Tool (Case Study)Arousha SultanNo ratings yet
- CFAS Questions Chaps 1 and 2Document13 pagesCFAS Questions Chaps 1 and 2King SigueNo ratings yet
- Economics 1 - F6 - 2013Document2 pagesEconomics 1 - F6 - 2013nalompaNo ratings yet
- Reliance Eqity FundDocument27 pagesReliance Eqity FundMohamed SharifNo ratings yet
- Anthony Brain Bumiller: UltravisiónDocument2 pagesAnthony Brain Bumiller: UltravisiónMaria Fernanda Camacho TorresNo ratings yet