Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology Notebook: 01.02A The Chemistry of Life Honors: Key Questions and Terms Notes
Biology Notebook: 01.02A The Chemistry of Life Honors: Key Questions and Terms Notes
Uploaded by
Chelsea DanteCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Week 2 Lab ReportDocument11 pagesWeek 2 Lab ReportTina VargheseNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Module 2 Combined-1Document14 pagesUnit 2 Module 2 Combined-1api-2930012170% (2)
- Tutorial Study Guide: NSC 1110 - BiologyDocument14 pagesTutorial Study Guide: NSC 1110 - BiologyKalinda MondeNo ratings yet
- Chap5 ChemcomposeDocument20 pagesChap5 ChemcomposeatynzatyNo ratings yet
- CH 3 NotesDocument40 pagesCH 3 Notesbaileigh5995No ratings yet
- Biomolecules ReadingDocument4 pagesBiomolecules Readingandrea dyanne AzoresNo ratings yet
- AP Review Organic CompoundsDocument72 pagesAP Review Organic Compounds둡챙브로No ratings yet
- Worksheet Fleming 2Document5 pagesWorksheet Fleming 2Dominique BoncalesNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE BiomoleculesDocument4 pagesSCIENCE Biomoleculeskimtaemin1997.stageNo ratings yet
- Biomolecule Review WorksheetDocument5 pagesBiomolecule Review WorksheetJeromeNo ratings yet
- Macromolecule (Biomolecule) Review Worksheet: CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesMacromolecule (Biomolecule) Review Worksheet: CarbohydratesArnel MonellonNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document7 pagesActivity 2Adrian Manguiat GaaNo ratings yet
- Bio Molecule Review WorksheetDocument6 pagesBio Molecule Review WorksheetMari LouNo ratings yet
- Study Notes - Topic 2 Q'sDocument4 pagesStudy Notes - Topic 2 Q'sJenniffer SmithNo ratings yet
- Biomolekul-Farmasi.240224Document71 pagesBiomolekul-Farmasi.240224qarirahkhansa03No ratings yet
- MODULE 2-BIOMOLECULES PETA-WORKSHEET-answer KeyDocument4 pagesMODULE 2-BIOMOLECULES PETA-WORKSHEET-answer Keyromavin guillermoNo ratings yet
- Matter 2 Biological Molecules PDQDocument2 pagesMatter 2 Biological Molecules PDQFlvcko SlimNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculeReviewWorksheet KEY 27ee7mmDocument5 pagesBiomoleculeReviewWorksheet KEY 27ee7mmmyeshia raginNo ratings yet
- Bio Molecule Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesBio Molecule Review WorksheetBianca BiancaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet BIO 101 - MSFPDocument11 pagesTutorial Sheet BIO 101 - MSFPhopekingbwalya23No ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 MODULE FOURTH QUARTER Week 3 4 BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesSCIENCE 10 MODULE FOURTH QUARTER Week 3 4 Biomoleculesizi iordeinNo ratings yet
- Enhancement WorksheetDocument5 pagesEnhancement WorksheetEmelinda CruzNo ratings yet
- Water PH and Biological MoleculesDocument39 pagesWater PH and Biological MoleculesSrdjanNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 W 6-8Document38 pagesGeneral Biology 1 W 6-8Emily Munsad AntolijaoNo ratings yet
- Ap Bio Review Unit 1 BiochemistryDocument8 pagesAp Bio Review Unit 1 Biochemistryapi-210373179No ratings yet
- Structures and Functions of Biological MoleculesDocument2 pagesStructures and Functions of Biological MoleculesKoalaNo ratings yet
- BiomolBil - Kel.8 - Makalah LipidDocument23 pagesBiomolBil - Kel.8 - Makalah LipidTitin Evania ManaluNo ratings yet
- Kul2 BioMoleculesDocument72 pagesKul2 BioMoleculessoraya rahmanisaNo ratings yet
- CH3 Biological MoleculesDocument15 pagesCH3 Biological MoleculesAniqa NaseemNo ratings yet
- M4 BiomoleculesDocument41 pagesM4 BiomoleculesStephanie TamayuzaNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules - For K 12 TrainingDocument185 pagesBiological Molecules - For K 12 TrainingVj RanchesNo ratings yet
- AP BioDocument15 pagesAP BioFatma AyadNo ratings yet
- Jose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolDocument8 pagesJose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolEricha SolomonNo ratings yet
- Read Through Each Section and Answer The Following QuestionsDocument4 pagesRead Through Each Section and Answer The Following QuestionsAngelica Calamba CalicaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Online Act PDFDocument3 pagesGen Bio 1 Online Act PDFRiza CatubigNo ratings yet
- Bchem 153 2017 NewDocument454 pagesBchem 153 2017 Newappiadu paulNo ratings yet
- Full Chapter Including Nucleic AcidsDocument99 pagesFull Chapter Including Nucleic AcidsDaran RungwattanasophonNo ratings yet
- Kul 2 Biomolekul-Farmasi.240224Document71 pagesKul 2 Biomolekul-Farmasi.240224soraya rahmanisaNo ratings yet
- Lipids+ +S10+ +PDF+Document29 pagesLipids+ +S10+ +PDF+9jgq6spb4rNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Carbon Compounds: Unit 3: BiochemistryDocument21 pages3.1 Carbon Compounds: Unit 3: Biochemistryapi-520057338No ratings yet
- Marites PPT Demo Final....Document52 pagesMarites PPT Demo Final....Marites B. MartinNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules PDFDocument55 pagesBiomolecules PDFmikaelajulianaedenNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry ReviewerDocument2 pagesBiochemistry ReviewerCAJES NOLINo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Study Guide - Fall 2021Document3 pagesChapter 2 Study Guide - Fall 2021pcNo ratings yet
- 16.3 The Chemistry of LifeDocument64 pages16.3 The Chemistry of LifeDaud KhanNo ratings yet
- Reviewing The ChapterDocument4 pagesReviewing The ChapterMyca NealonNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Lipids Lesson 2: The Energy-Storage and Membrane LipidsDocument10 pagesUnit 3 Lipids Lesson 2: The Energy-Storage and Membrane LipidsValenzuela Allene GraceNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules: The Building Blocks of LifeDocument66 pagesBiological Molecules: The Building Blocks of Life:Y FrankNo ratings yet
- SHS Spec Subj STEM Gen Chem1 SIPack W6Document14 pagesSHS Spec Subj STEM Gen Chem1 SIPack W6Glexis TiamsonNo ratings yet
- Biomacromolecules JigsawDocument3 pagesBiomacromolecules JigsawCarmen CheahNo ratings yet
- Bio 102 Assign 3Document3 pagesBio 102 Assign 3arica foxNo ratings yet
- With Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2016Document2 pagesWith Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2016Catherine Villaruz100% (1)
- Bio MoleculesDocument64 pagesBio MoleculesCharles Dexter FuentesNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry I IntroductionDocument19 pagesBiochemistry I IntroductionCaamir Dek HaybeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Review - BiochemistryDocument3 pagesUnit 1 Review - Biochemistrylillian.albassamNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesActivity 2 CarbohydratesPreiy Julian De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Biochem Semester 1Document8 pagesStudy Guide For Biochem Semester 1Leigh-Ann AmorosoNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument7 pagesBio Moleculesmarkkevingonzales1235No ratings yet
- Biology Notebook: 01.03A Earth's Early Atmosphere Honors: Key Questions and Terms NotesDocument3 pagesBiology Notebook: 01.03A Earth's Early Atmosphere Honors: Key Questions and Terms NotesChelsea DanteNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Lab ReportDocument3 pagesCell Transport Lab ReportChelsea DanteNo ratings yet
- Practice Writing A Lab ReportDocument2 pagesPractice Writing A Lab ReportChelsea DanteNo ratings yet
- Ramadan Mubarak Ramadan Mubarak: 7521 Shore Acres St. 7521 Shore Acres STDocument1 pageRamadan Mubarak Ramadan Mubarak: 7521 Shore Acres St. 7521 Shore Acres STChelsea DanteNo ratings yet
Biology Notebook: 01.02A The Chemistry of Life Honors: Key Questions and Terms Notes
Biology Notebook: 01.02A The Chemistry of Life Honors: Key Questions and Terms Notes
Uploaded by
Chelsea DanteOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology Notebook: 01.02A The Chemistry of Life Honors: Key Questions and Terms Notes
Biology Notebook: 01.02A The Chemistry of Life Honors: Key Questions and Terms Notes
Uploaded by
Chelsea DanteCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology Notebook: 01.
02A The Chemistry of Life Honors
Objectives:
Explain how molecular diversity is based on the properties of carbon
Recognize the structural importance of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins
Explain the functions of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins
Recognize and interpret the chemical formula for the organic compounds: carbohydrates,
lipids, and proteins
Key Questions and Terms Notes
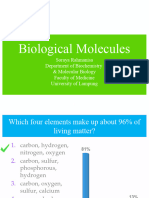
What type of molecules makes up life on
Earth?
What unique ability does carbon have?
What are organic compounds?
Carbohydrates
What process allows monosaccharides to bond
together to form disaccharides and then large
polysaccharides?
Describe the difference between dehydration
synthesis and hydrolysis?
What accounts for the differences in the
functions and properties of molecules like
starches, glycogen, cellulose and chitin?
What are the functions/properties of starch?
What are the functions/properties of glycogen
What are the functions/properties of cellulose?
What are the functions/properties of chitin?
Lipids
What are some reasons that fatty acids are
important?
Name 2 differences between a saturated and 1.
unsaturated fat. 2.
Why are steroids important to life?
Describe the relationship between cholesterol
and testosterone?
Describe the structure of a phospholipid.
Describe the structure of phospholipids in cell
membranes.
Why are lipids grouped together?
Do cell membranes allow all molecules into
the cell?
Proteins
What are some functions of proteins?
How many different amino acids do cells use
to build proteins?
What are the 4 main components of an amino
acid?
What is a polypeptide bond and does it form?
Describe the shape of a protein molecule.
Why is shape so important?
Sample Question:
The different properties and functions of carbohydrates, and other biological molecules, is due to
what?
A. Their structures.
B. Where they are found.
C. They are inorganic molecules.
D. Their bonds.
You might also like
- Week 2 Lab ReportDocument11 pagesWeek 2 Lab ReportTina VargheseNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Module 2 Combined-1Document14 pagesUnit 2 Module 2 Combined-1api-2930012170% (2)
- Tutorial Study Guide: NSC 1110 - BiologyDocument14 pagesTutorial Study Guide: NSC 1110 - BiologyKalinda MondeNo ratings yet
- Chap5 ChemcomposeDocument20 pagesChap5 ChemcomposeatynzatyNo ratings yet
- CH 3 NotesDocument40 pagesCH 3 Notesbaileigh5995No ratings yet
- Biomolecules ReadingDocument4 pagesBiomolecules Readingandrea dyanne AzoresNo ratings yet
- AP Review Organic CompoundsDocument72 pagesAP Review Organic Compounds둡챙브로No ratings yet
- Worksheet Fleming 2Document5 pagesWorksheet Fleming 2Dominique BoncalesNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE BiomoleculesDocument4 pagesSCIENCE Biomoleculeskimtaemin1997.stageNo ratings yet
- Biomolecule Review WorksheetDocument5 pagesBiomolecule Review WorksheetJeromeNo ratings yet
- Macromolecule (Biomolecule) Review Worksheet: CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesMacromolecule (Biomolecule) Review Worksheet: CarbohydratesArnel MonellonNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document7 pagesActivity 2Adrian Manguiat GaaNo ratings yet
- Bio Molecule Review WorksheetDocument6 pagesBio Molecule Review WorksheetMari LouNo ratings yet
- Study Notes - Topic 2 Q'sDocument4 pagesStudy Notes - Topic 2 Q'sJenniffer SmithNo ratings yet
- Biomolekul-Farmasi.240224Document71 pagesBiomolekul-Farmasi.240224qarirahkhansa03No ratings yet
- MODULE 2-BIOMOLECULES PETA-WORKSHEET-answer KeyDocument4 pagesMODULE 2-BIOMOLECULES PETA-WORKSHEET-answer Keyromavin guillermoNo ratings yet
- Matter 2 Biological Molecules PDQDocument2 pagesMatter 2 Biological Molecules PDQFlvcko SlimNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculeReviewWorksheet KEY 27ee7mmDocument5 pagesBiomoleculeReviewWorksheet KEY 27ee7mmmyeshia raginNo ratings yet
- Bio Molecule Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesBio Molecule Review WorksheetBianca BiancaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet BIO 101 - MSFPDocument11 pagesTutorial Sheet BIO 101 - MSFPhopekingbwalya23No ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 MODULE FOURTH QUARTER Week 3 4 BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesSCIENCE 10 MODULE FOURTH QUARTER Week 3 4 Biomoleculesizi iordeinNo ratings yet
- Enhancement WorksheetDocument5 pagesEnhancement WorksheetEmelinda CruzNo ratings yet
- Water PH and Biological MoleculesDocument39 pagesWater PH and Biological MoleculesSrdjanNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 W 6-8Document38 pagesGeneral Biology 1 W 6-8Emily Munsad AntolijaoNo ratings yet
- Ap Bio Review Unit 1 BiochemistryDocument8 pagesAp Bio Review Unit 1 Biochemistryapi-210373179No ratings yet
- Structures and Functions of Biological MoleculesDocument2 pagesStructures and Functions of Biological MoleculesKoalaNo ratings yet
- BiomolBil - Kel.8 - Makalah LipidDocument23 pagesBiomolBil - Kel.8 - Makalah LipidTitin Evania ManaluNo ratings yet
- Kul2 BioMoleculesDocument72 pagesKul2 BioMoleculessoraya rahmanisaNo ratings yet
- CH3 Biological MoleculesDocument15 pagesCH3 Biological MoleculesAniqa NaseemNo ratings yet
- M4 BiomoleculesDocument41 pagesM4 BiomoleculesStephanie TamayuzaNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules - For K 12 TrainingDocument185 pagesBiological Molecules - For K 12 TrainingVj RanchesNo ratings yet
- AP BioDocument15 pagesAP BioFatma AyadNo ratings yet
- Jose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolDocument8 pagesJose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolEricha SolomonNo ratings yet
- Read Through Each Section and Answer The Following QuestionsDocument4 pagesRead Through Each Section and Answer The Following QuestionsAngelica Calamba CalicaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Online Act PDFDocument3 pagesGen Bio 1 Online Act PDFRiza CatubigNo ratings yet
- Bchem 153 2017 NewDocument454 pagesBchem 153 2017 Newappiadu paulNo ratings yet
- Full Chapter Including Nucleic AcidsDocument99 pagesFull Chapter Including Nucleic AcidsDaran RungwattanasophonNo ratings yet
- Kul 2 Biomolekul-Farmasi.240224Document71 pagesKul 2 Biomolekul-Farmasi.240224soraya rahmanisaNo ratings yet
- Lipids+ +S10+ +PDF+Document29 pagesLipids+ +S10+ +PDF+9jgq6spb4rNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Carbon Compounds: Unit 3: BiochemistryDocument21 pages3.1 Carbon Compounds: Unit 3: Biochemistryapi-520057338No ratings yet
- Marites PPT Demo Final....Document52 pagesMarites PPT Demo Final....Marites B. MartinNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules PDFDocument55 pagesBiomolecules PDFmikaelajulianaedenNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry ReviewerDocument2 pagesBiochemistry ReviewerCAJES NOLINo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Study Guide - Fall 2021Document3 pagesChapter 2 Study Guide - Fall 2021pcNo ratings yet
- 16.3 The Chemistry of LifeDocument64 pages16.3 The Chemistry of LifeDaud KhanNo ratings yet
- Reviewing The ChapterDocument4 pagesReviewing The ChapterMyca NealonNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Lipids Lesson 2: The Energy-Storage and Membrane LipidsDocument10 pagesUnit 3 Lipids Lesson 2: The Energy-Storage and Membrane LipidsValenzuela Allene GraceNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules: The Building Blocks of LifeDocument66 pagesBiological Molecules: The Building Blocks of Life:Y FrankNo ratings yet
- SHS Spec Subj STEM Gen Chem1 SIPack W6Document14 pagesSHS Spec Subj STEM Gen Chem1 SIPack W6Glexis TiamsonNo ratings yet
- Biomacromolecules JigsawDocument3 pagesBiomacromolecules JigsawCarmen CheahNo ratings yet
- Bio 102 Assign 3Document3 pagesBio 102 Assign 3arica foxNo ratings yet
- With Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2016Document2 pagesWith Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2016Catherine Villaruz100% (1)
- Bio MoleculesDocument64 pagesBio MoleculesCharles Dexter FuentesNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry I IntroductionDocument19 pagesBiochemistry I IntroductionCaamir Dek HaybeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Review - BiochemistryDocument3 pagesUnit 1 Review - Biochemistrylillian.albassamNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesActivity 2 CarbohydratesPreiy Julian De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Biochem Semester 1Document8 pagesStudy Guide For Biochem Semester 1Leigh-Ann AmorosoNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument7 pagesBio Moleculesmarkkevingonzales1235No ratings yet
- Biology Notebook: 01.03A Earth's Early Atmosphere Honors: Key Questions and Terms NotesDocument3 pagesBiology Notebook: 01.03A Earth's Early Atmosphere Honors: Key Questions and Terms NotesChelsea DanteNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Lab ReportDocument3 pagesCell Transport Lab ReportChelsea DanteNo ratings yet
- Practice Writing A Lab ReportDocument2 pagesPractice Writing A Lab ReportChelsea DanteNo ratings yet
- Ramadan Mubarak Ramadan Mubarak: 7521 Shore Acres St. 7521 Shore Acres STDocument1 pageRamadan Mubarak Ramadan Mubarak: 7521 Shore Acres St. 7521 Shore Acres STChelsea DanteNo ratings yet