Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ineffective Tissue Perfusion
Ineffective Tissue Perfusion
Uploaded by
Mary Hope BacutaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ineffective Tissue Perfusion
Ineffective Tissue Perfusion
Uploaded by
Mary Hope BacutaCopyright:
Available Formats
Ineffective Tissue Perfusion
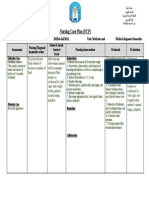
Nursing Diagnosis
Ineffective Tissue Perfusion
Related to:
Excessive blood loss
Possibly evidenced by:
ADVERTISEMENTS
Loss of blood
FHR pattern
Altered BP compared to baseline
Altered PR Severe abdominal pain and rigidity
Pallor
Changes in LOC
Decrease urine output
Edema
Delay in wound healing
Positive Homan’s sign
Skin temperature changes
Desired outcome:
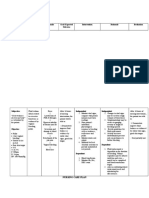
Nursing Interventions Rationale
Assess patient’s vital signs, O2 saturation, and For baseline data.
skin color.
Monitor for restlessness, anxiety, hunger and These conditions may indicate
changes in LOC decreased cerebral perfusion
Monitor accurately I&O To obtain data about renal
perfusion and function and the
extent of blood loss.
Monitor FHT continuously To provide information regarding
fetal distress and/or worsening
of condition
Assess uterine irritability, abdominal pain and To determine the severity of the
rigidity. placental abruptio and bleeding
Assess skin color, temperature, moisture, turgor, To determine peripheral tissue
capillary refill perfusion like hypervolemia.
Elevate extremity above the level of the heart Helps promote circulation.
Teach patient not to apply uterine pressure Uterine pressure can cause
pooling of venous blood in lower
extremities
Instruct patient and/or SO to report immediately To immediately provide
signs and symptoms of thrombosis: (1) pain in leg, additional interventions
groin (2) unilateral leg swelling (3) pale skin
You might also like
- Mrs. Bagent 1-9 BWAKANANG SHETDocument5 pagesMrs. Bagent 1-9 BWAKANANG SHETaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Mi Case StudyDocument27 pagesMi Case StudyMary Hope BacutaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Care PlanDocument4 pagesNutrition Care PlanMary Hope Bacuta100% (1)
- Clinical Reasoning Questions - CollaborationDocument4 pagesClinical Reasoning Questions - CollaborationMohammad OmarNo ratings yet
- 1 Ineffective Peripheral Tissue PerfusionDocument1 page1 Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusionjean_fabulaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 6Document4 pagesCase Study 6Mary Hope Bacuta0% (2)
- Postpartal Thrombophlebitis: Client Assessment Data Base Activity/RestDocument8 pagesPostpartal Thrombophlebitis: Client Assessment Data Base Activity/RestLei OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Group 6 Group Case Study DONEDocument5 pagesGroup 6 Group Case Study DONEE.R.ONo ratings yet
- NCP Gastric CancerDocument6 pagesNCP Gastric Cancerhayascent hilarioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (NCP) : Patient & Family Centered (In Priority Order)Document1 pageNursing Care Plan (NCP) : Patient & Family Centered (In Priority Order)WorodNo ratings yet
- Ariane NCP 1Document2 pagesAriane NCP 1Kristian Ray EraulaNo ratings yet
- NCP Acitivity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesNCP Acitivity IntolerancegizelleNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPNefre Dayap DarrocaNo ratings yet
- NCP Meningitis Sure NaniDocument2 pagesNCP Meningitis Sure NaniARISNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nsg. Diagnosis Sci. Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment Nsg. Diagnosis Sci. Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationRoMarie AbainzaNo ratings yet
- Bisacodyl (Dulcolax)Document1 pageBisacodyl (Dulcolax)ENo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Cardiopulmonary PerfusionDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Cardiopulmonary PerfusionjamiemapanaoNo ratings yet
- Levemir Product Insert PDFDocument11 pagesLevemir Product Insert PDFDegee O. GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Jacildo LT Module 6 TCNDocument2 pagesJacildo LT Module 6 TCNMeryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- NCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsDocument9 pagesNCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsAngie Mandeoya100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyJanina Patricia BuddleNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute Pain FractureDocument1 pageNCP Acute Pain FractureAi RouNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Tetralogy of FallotDocument2 pagesConcept Map Tetralogy of FallotKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- NCP On DyspneaDocument5 pagesNCP On DyspneaDizzy BualanNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPNichole Audrey SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDa NicaNo ratings yet
- Drug PepcidDocument2 pagesDrug PepcidSrkocher0% (1)
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPMcmc Ryan Ferdinand GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Case Study Scenario # 1 Congestive Heart Failure (Mojica)Document10 pagesCase Study Scenario # 1 Congestive Heart Failure (Mojica)Noah Kent MojicaNo ratings yet
- LeopoldsDocument2 pagesLeopoldsMhianne SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance NCPDocument1 pageIneffective Airway Clearance NCPBenz ParCoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease CanDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease Canrix07No ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Core CompetenciesDocument13 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Core CompetenciesMina RacadioNo ratings yet
- NCP 2 CabalunaDocument7 pagesNCP 2 CabalunaIrene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- CHD With NCPDocument10 pagesCHD With NCPJohanna Kirsten F. DaguioNo ratings yet
- NCP 4Document1 pageNCP 4marohunkNo ratings yet
- MGH 8 - Ihd - NCPDocument12 pagesMGH 8 - Ihd - NCPSesinando Niez Quilao Jr.100% (1)
- NCP Deficit Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesNCP Deficit Fluid VolumeKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- NCP Sensory PerceptionDocument2 pagesNCP Sensory PerceptionGina TangneneiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Acute Pain Related To Inflammatory Response Secondary To InfectionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Acute Pain Related To Inflammatory Response Secondary To InfectionTammy De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionDiane ReyNo ratings yet
- Problem Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Plan Intervention Evaluation Subjective Data: "Masakit Po Yung Sa Short Term: IndependentDocument2 pagesProblem Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Plan Intervention Evaluation Subjective Data: "Masakit Po Yung Sa Short Term: IndependentkyawNo ratings yet
- NCP (Postpartum Hemmorhage)Document3 pagesNCP (Postpartum Hemmorhage)Anne DyNo ratings yet
- NCP Episiotomy WoundDocument3 pagesNCP Episiotomy WoundJP2001No ratings yet
- Impaired Tissue Perfusion Related To The Weakening / Decreased Blood Flow To The Area of Gangrene Due To Obstruction of Blood VesselsDocument3 pagesImpaired Tissue Perfusion Related To The Weakening / Decreased Blood Flow To The Area of Gangrene Due To Obstruction of Blood VesselsKat AlaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans For Activity IntoleranceDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plans For Activity IntolerancethebigtwirpNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical MobilityfionalausNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: STO: Within 4 Hour of DX: DX: Sto: Goal MetDocument5 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: STO: Within 4 Hour of DX: DX: Sto: Goal MetRussel SantosNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument6 pagesNCP Risk For InfectionCazze SunioNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired ComfortDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired ComfortGia P. de VeyraNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageActivity IntoleranceAndrea Francesca SantosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis For CholecystectomyDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis For CholecystectomyMiguel VillacarlosNo ratings yet
- NCP Draft - Ectopic PregnancyDocument7 pagesNCP Draft - Ectopic PregnancyD CNo ratings yet
- NCP CSDocument7 pagesNCP CSTwobee Kriz LeghidNo ratings yet
- NCP PlanningDecreased in Cardiac Output Related To Low Hemoglobin and Hematocrit CountDocument6 pagesNCP PlanningDecreased in Cardiac Output Related To Low Hemoglobin and Hematocrit CountMabelle SorianoNo ratings yet
- Revised NCPDocument8 pagesRevised NCPKryza Dale Bunado BaticanNo ratings yet
- Impaired Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesImpaired Tissue PerfusionLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- Group1 HTP Dengue-FinalDocument9 pagesGroup1 HTP Dengue-FinalCHRISTINE GRACE ELLONo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Abruptio Placenta NCPDocument5 pagesAbruptio Placenta NCPTinNo ratings yet
- Postpartal HemorrhageDocument12 pagesPostpartal Hemorrhagenursereview100% (3)
- Prenatal Hemorrhage: Client Assessment Data Base: General Findings CirculationDocument11 pagesPrenatal Hemorrhage: Client Assessment Data Base: General Findings CirculationLei OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Position Pt. in Supine With Hips Elevated If Ordered or Left Lateral PositionDocument2 pagesPosition Pt. in Supine With Hips Elevated If Ordered or Left Lateral PositionNicole ArandingNo ratings yet
- Importance of ExerciseDocument2 pagesImportance of ExerciseMary Hope Bacuta100% (1)
- Importance of Co-Education: Gender DiscriminationDocument2 pagesImportance of Co-Education: Gender DiscriminationMary Hope BacutaNo ratings yet
- Importance of Co EducationDocument2 pagesImportance of Co EducationMary Hope Bacuta100% (1)
- Coding ManualDocument1 pageCoding ManualMary Hope BacutaNo ratings yet
- Kindness Always WinsDocument1 pageKindness Always WinsMary Hope BacutaNo ratings yet
- NCP For PostpartumDocument1 pageNCP For PostpartumMary Hope BacutaNo ratings yet
- Infant Attachment NCPDocument2 pagesInfant Attachment NCPMary Hope BacutaNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 - Case StudyDocument2 pagesActivity 5 - Case StudyMary Hope BacutaNo ratings yet
- Barangay Visayas Western Visayas (Region VI) Capiz PanayDocument4 pagesBarangay Visayas Western Visayas (Region VI) Capiz PanayMary Hope BacutaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document1 pageAssignment 3Mary Hope BacutaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMary Hope BacutaNo ratings yet
- Name: Alfredo Biclar Sex: Male Address: Binatu-An Panay, Capiz Race/Ethnicity: Hiligaynon Age: 83 Marital Status: MarriedDocument1 pageName: Alfredo Biclar Sex: Male Address: Binatu-An Panay, Capiz Race/Ethnicity: Hiligaynon Age: 83 Marital Status: MarriedMary Hope BacutaNo ratings yet
- Pastoral Letter: Strength Against RacismDocument1 pagePastoral Letter: Strength Against RacismMary Hope BacutaNo ratings yet
- ClinicalDocument5 pagesClinicalMary Hope BacutaNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Activity NutritionDocument1 pageWeek 4 Activity NutritionMary Hope BacutaNo ratings yet