Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study - Morphine (Sulfate)
Drug Study - Morphine (Sulfate)
Uploaded by
Kian Herrera100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
8K views3 pagesThis document summarizes information about the drug morphine, including its indications, dosages, mechanisms of action, contraindications, side effects, and nursing considerations. Morphine is an opioid analgesic used to relieve moderate to severe acute or chronic pain. It works by binding to opioid receptors in the central nervous system. Common side effects include sedation, decreased blood pressure, nausea, vomiting, and constipation. Nurses should monitor vital signs and assess for side effects after administration and encourage deep breathing exercises for patients with pulmonary impairment.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes information about the drug morphine, including its indications, dosages, mechanisms of action, contraindications, side effects, and nursing considerations. Morphine is an opioid analgesic used to relieve moderate to severe acute or chronic pain. It works by binding to opioid receptors in the central nervous system. Common side effects include sedation, decreased blood pressure, nausea, vomiting, and constipation. Nurses should monitor vital signs and assess for side effects after administration and encourage deep breathing exercises for patients with pulmonary impairment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
8K views3 pagesDrug Study - Morphine (Sulfate)
Drug Study - Morphine (Sulfate)
Uploaded by
Kian HerreraThis document summarizes information about the drug morphine, including its indications, dosages, mechanisms of action, contraindications, side effects, and nursing considerations. Morphine is an opioid analgesic used to relieve moderate to severe acute or chronic pain. It works by binding to opioid receptors in the central nervous system. Common side effects include sedation, decreased blood pressure, nausea, vomiting, and constipation. Nurses should monitor vital signs and assess for side effects after administration and encourage deep breathing exercises for patients with pulmonary impairment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
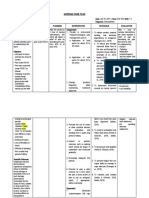
DRUG STUDY
NAME OF ROUTE, DOSAGE AND MECHANISM SIDE EFFECTS/ NURSING
INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION
DRUG FREQUENCY OF ACTION ADVERSE EFFECTS CONSIDERATIONS
Generic Name: Angina: Binds with opioid Relief of moderate Contraindications: Possible Side Effects: Observe the patient’s 10
Morphine PO (Immediate-Release): receptors within to severe, acute, or All Formulations: rights of medication
Ambulatory pts, pts not
(Sulphate) Adults, Elderly: 10–30 mg CNS, inhibiting chronic pain; Hypersensitivity to administration
in severe pain may
q4h as needed. (Solution): 10– ascending pain analgesia during morphine. Acute or severe
experience nausea,
Brand Name: 20 mg q4h as needed. pathways. labor, pain due to asthma, GI obstruction, Baseline Assessment:
vomiting more
Duramorph, (Tablet): 15–30 mg q4h as MI, dyspnea from known or suspected Pt should be in recumbent
frequently than pts in
Infumorph, needed. Therapeutic pulmonary edema paralytic ileus, severe position before drug is given
supine position or who
Roxanol Children 6 Months of Age Effect: Alters not resulting from hepatic/renal impairment, by parenteral route.
have severe pain
and Older Weighing 50 kg or pain perception, chemical severe respiratory Assess onset, type, location,
Classification: Greater: emotional respiratory irritant. depression. duration of pain.
Frequent:
Pharmaco- 15–20 mg q3–4h as needed. response to pain. Obtain vital signs before
Sedation
therapeutic: Children 6 Months of Age Infumorph: Use in Extended-Release: giving medication. If
Opioid and Older Weighing Less devices for GI obstruction, acute Decreased B/P
(including orthostatic respirations are 12/min or
agonist Than 50 kg: managing postoperative pain, less (20/min or less in
(Schedule II). 0.2–0.5 mg/kg q3–4h as intractable chronic hypercarbia hypotension)
children), withhold
needed. pain. Diaphoresis
medication, contact
Clinical: Children Younger Than 6 Injection: Facial flushing
physician.
Opioid Months: Extended-release: HF due to lung disease; Constipation
Effect of medication is
analgesic. (Oral solution): 0.08–0.1 Use only when arrhythmias, head injury, Dizziness reduced if full pain recurs
mg/kg q3–4h as needed repeated doses for seizures, acute alcoholism. Drowsiness before next dose.
extended periods of Labor when premature Nausea
PO (Extended-Release): time are required birth expected. Increased Vomiting. Intervention:
Adults, Elderly: Dosage around the clock. intracranial pressure Monitor vital signs 5–10 min
requirement should be after IV administration, 15–
established using prompt- Immediate-Release: Occasional:
Allergic reaction 30 min after SQ, IM.
release formulations and is Hypercarbia
(rash, pruritus) Be alert for decreased
based on total daily dose.
Dyspnea respirations, B/P.
Avinza: AVINza is given once Extreme Cautions:
Confusion Check for adequate voiding.
daily only. COPD, cor pulmonale,
Kadian: Dose is given once hypoxia, hypercapnia, Palpitations Monitor daily pattern of
daily or divided and given preexisting respiratory Tremors bowel activity, stool
q12h. depression, head injury, Urinary retention consistency; avoid
constipation.
MS Contin: Daily dose is increased ICP, severe Abdominal cramps
divided and given q8h or q12h. hypotension. Initiate deep breathing,
Vision changes
coughing exercises,
Dry mouth
IV: Cautions: particularly in those with
Adults, Elderly: 2.5–5 mg q3– Biliary tract disease, Headache pulmonary impairment.
4h as needed. Note: Repeated pancreatitis, Addison’s Decreased appetite Assess for clinical
doses (e.g., 1–2 mg) may be disease, cardiovascular Pain/burning at improvement; record onset of
given more frequently (e.g., disease, morbid obesity, injection site pain relief.
every hr) if needed. Children adrenal insufficiency, Consult physician if pain
50 kg or Greater: elderly, hypothyroidism, Rare: relief is not adequate.
Initially, 2–5 mg q2–4h as urethral stricture, prostatic Paralytic ileus
needed. hyperplasia, debilitated Patient/Family Teaching:
Children Weighing Less pts, pts with CNS Adverse effect: Discomfort may occur with
Than 50 kg: depression, toxic Overdose results in: injection.
Initially, 0.05 mg/kg. Range: psychosis, seizure o Respiratory Change positions slowly to
0.1–0.2 mg/kg q2– 4h as disorders, alcoholism. depression avoid orthostatic
needed. Neonates: Initially, o Skeletal muscle hypotension.
0.05–0.1 mg/kg/dose q4–6h as Avoid tasks that require
flaccidity
needed. alertness, motor skills until
o Cold/ clammy skin
o Cyanosis response to drug is
IV Continuous Infusion: established.
Adults, Elderly: 0.8–10 o Extreme drowsiness
progressing to Avoid alcohol, CNS
mg/hr. Range: Titrate up to 80 depressants.
mg/hr. seizures
o Stupor Tolerance, dependence may
Children Weighing 50 kg or
o Coma occur with prolonged use of
Greater:
high doses.
1.5 mg/hr. Tolerance to
analgesic effect Report ineffective pain
Children Weighing Less
(Physical dependence control, constipation,
Than 50 Kg:
may occur with urinary retention.
Initially, 0.01 mg/kg/hr.
Range: 0.01–0.04 mg/kg/hr repeated use)
(10–40 mcg/ kg/hr). Prolonged duration of
NEONATES: Initially, 0.01 action, cumulative
mg/kg/hr (10 mcg/kg/hr). effect may occur in
Maximum: 0.015–0.02 those with
mg/kg/hr. Note: IM injection hepatic/renal
not recommended impairment.
Antidote: Naloxone
IM:
Adults, Elderly: 5–10 mg q3–
4h as needed. Children: 0.1–
0.2 mg/kg q3–4h as needed.
References:
Kizior, R. J. & Hodgson, K. J. (2019). Saunders Nursing Drug Handbook 2019. Elsevier Inc.
You might also like
- Republic of The Philippines Puerto Princesa City: Palawan State UniversityDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Puerto Princesa City: Palawan State UniversityRosemarie EustaquioNo ratings yet
- VancomycinDocument3 pagesVancomycinGwyn Rosales100% (3)
- Purves Neuroscience Website Questions CH 6 AnswersDocument4 pagesPurves Neuroscience Website Questions CH 6 AnswersPK32145987No ratings yet
- NCP (Acute Pain)Document4 pagesNCP (Acute Pain)Kian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studyw dNo ratings yet
- MAALOX (Drug Study)Document3 pagesMAALOX (Drug Study)Kian HerreraNo ratings yet
- BUPIVACAINEDocument1 pageBUPIVACAINEVoid Less0% (2)
- Morphine SulfateDocument2 pagesMorphine SulfateArianne Nicole PinuelaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Morphine SulfateDocument8 pagesDrug Study: Morphine SulfateShara Lailanie A. Azis100% (1)
- 9 PropofolDocument2 pages9 PropofolAbdelhafiz Susmiran100% (3)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyROCHELLE DALIWAN100% (1)
- Midazolam Drug Study SaclotDocument1 pageMidazolam Drug Study SaclotMaybelle Cababat Saclot100% (1)
- Drug Study - MidazolamDocument2 pagesDrug Study - MidazolamKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Dopamine HydrochlorideDocument2 pagesDopamine HydrochlorideNasrah N. MusaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Amiodarone)Document8 pagesDrug Study (Amiodarone)Justine Conui100% (1)
- FentanylDocument3 pagesFentanylDavid Villanueva67% (3)
- Calcium GluconateDocument2 pagesCalcium GluconateMae Ann Bueno Castillon100% (1)
- Morphine SulfateDocument5 pagesMorphine Sulfateapi-3797941100% (4)
- Heparin InjectionDocument2 pagesHeparin InjectiongagandipkSNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - MidazolamDocument8 pagesDrug Study - MidazolamKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Midazolam: RecommendedDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Midazolam: RecommendedShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- Morphine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMorphine Drug StudyNo Vem BerNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Table OkDocument29 pagesDrug Study Table OkRifa'atul Mahmudah100% (1)
- DS PiptazDocument1 pageDS PiptazCristel Z. Gabuco100% (1)
- Morphine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMorphine Drug StudyXerxes Dejito100% (2)
- KetamineDocument2 pagesKetamineyanti anggrenie100% (1)
- DRUG+STUDY PropofolDocument2 pagesDRUG+STUDY PropofolJoevence Gazo Cuaresma100% (2)
- Magnesium SulfateDocument1 pageMagnesium SulfateIvanne Hisoler67% (3)
- Drug Study: Adult: Induction: 40 MGDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Adult: Induction: 40 MGpretty_mary100% (4)
- Amiodarone (PACERONE)Document1 pageAmiodarone (PACERONE)Amanda CoadNo ratings yet
- Amiodarone Drug StudyDocument3 pagesAmiodarone Drug StudyDexter Niel Ortilano CPAC-SNNo ratings yet
- Tapazole and Calcium GluconateDocument3 pagesTapazole and Calcium Gluconatekuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone Drug LiteratureDocument1 pageDexamethasone Drug LiteratureOneForAll :No ratings yet
- MorphineDocument1 pageMorphineKenny Nadela67% (3)
- Generic Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- Casilan, Ynalie Drug Study (Morphine)Document5 pagesCasilan, Ynalie Drug Study (Morphine)Ynalie CasilanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PethidineDocument2 pagesDrug Study Pethidinerica sebabillonesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Format Ready To PrintDocument2 pagesDrug Study Format Ready To Printmay_hisolerNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Dopamine HCLDocument2 pagesDrug Study Dopamine HCLA.No ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY-LidocaineDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY-LidocaineCarissa Mae Tapec Estrada100% (1)
- Medication Indication Pharmacodynamic S Contraindication Common Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesMedication Indication Pharmacodynamic S Contraindication Common Side Effects Nursing Consideration5S CASTILLEJO Danica M.No ratings yet
- MethadoneDocument2 pagesMethadoneIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Promethazine HCLDocument2 pagesPromethazine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (8)
- Fentanyl Drug StudyDocument3 pagesFentanyl Drug StudyAngelica shane Navarro75% (4)
- HydrochlorothiazideDocument2 pagesHydrochlorothiazidekuro hanabusa100% (1)
- DigoxinDocument4 pagesDigoxinJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- BudesonideDocument2 pagesBudesonideDiane Bonita HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug STUDY CefotaximeDocument5 pagesDrug STUDY CefotaximeCrystal Jade100% (1)
- Codeine Phosphate (Drug Study)Document2 pagesCodeine Phosphate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (2)
- KETAMINEDocument2 pagesKETAMINERPh Krishna Chandra JagritNo ratings yet
- AllopurinolDocument1 pageAllopurinolRachel SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate Drug STudyDocument2 pagesAtropine Sulfate Drug STudyLiway100% (1)
- ORDocument7 pagesORMay EvelynNo ratings yet
- Cisplatin Drug StudyDocument1 pageCisplatin Drug StudykyawNo ratings yet
- Ativan (Lorazepam) Drug StudyDocument3 pagesAtivan (Lorazepam) Drug StudyCHERISE CORDOVA100% (2)
- MIDAZOLAM Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMIDAZOLAM Drug StudyEur Miole60% (5)
- Drug Study - MorphineDocument3 pagesDrug Study - MorphineKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- PDF Drug Study Morphine SulfateDocument3 pagesPDF Drug Study Morphine SulfateCrishelNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Propofol: CNS Depressants: AdditiveDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Propofol: CNS Depressants: AdditiveShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- MeperidineDocument3 pagesMeperidineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY Butorphanol LRDR AngelicaRonquilloDocument2 pagesDRUG-STUDY Butorphanol LRDR AngelicaRonquillokarl eiron delos santosNo ratings yet
- Any Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently ReceivingDocument1 pageAny Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently Receivinggeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- Journal ReadingDocument8 pagesJournal ReadingKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading (SICU)Document12 pagesJournal Reading (SICU)Kian HerreraNo ratings yet
- EssayDocument2 pagesEssayKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Sermon: How To Get From Here To There - Joshua 1: I. Receive The Challenge (V. 2)Document3 pagesSermon: How To Get From Here To There - Joshua 1: I. Receive The Challenge (V. 2)Kian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading - Pituitary AdenomasDocument3 pagesJournal Reading - Pituitary AdenomasKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - MorphineDocument3 pagesDrug Study - MorphineKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Tranexamic AcidDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Tranexamic AcidKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (NCP) For A Patient With Angina PectorisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan (NCP) For A Patient With Angina PectorisKian Herrera100% (1)
- Drug Study (Acetaminophen)Document1 pageDrug Study (Acetaminophen)Kian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (NCP) For A Patient With Acute Renal FailureDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan (NCP) For A Patient With Acute Renal FailureKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - MidazolamDocument2 pagesDrug Study - MidazolamKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - AlfuzosinDocument1 pageDrug Study - AlfuzosinKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - ParecoxibDocument2 pagesDrug Study - ParecoxibKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - AmlodipineDocument2 pagesDrug Study - AmlodipineKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - ZolpidemDocument2 pagesDrug Study - ZolpidemKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - MidazolamDocument8 pagesDrug Study - MidazolamKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- BioassayDocument4 pagesBioassayAddictedto Nonsense50% (2)
- Drug MetabolismDocument38 pagesDrug MetabolismAamir NawazNo ratings yet
- Fact UrasDocument6 pagesFact UrasRonald Salazar CuzcanoNo ratings yet
- Nanobio Pharmaceutical Technology Elsevier PDFDocument657 pagesNanobio Pharmaceutical Technology Elsevier PDFSelvamani PalanisamyNo ratings yet
- CHF Group 3 Ncmb312 RleDocument39 pagesCHF Group 3 Ncmb312 RleMaica Lectana50% (2)
- Menopause: Cagayan Valley Medical Center Department of Obstetrics and GynecologyDocument37 pagesMenopause: Cagayan Valley Medical Center Department of Obstetrics and GynecologySofia Kezia Apostol CabaroNo ratings yet
- 1899 PDFDocument7 pages1899 PDFNot WestNo ratings yet
- Cancer - GuidelinesDocument119 pagesCancer - GuidelinesChelleyOllitroNo ratings yet
- Master Obat 20211Document90 pagesMaster Obat 20211fiannysjahjadiNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Practice TestDocument4 pagesPsychiatric Practice TestARIS100% (2)
- Bisimilar Final Draft 23-01-2018 PDFDocument59 pagesBisimilar Final Draft 23-01-2018 PDFmailtorubal2573No ratings yet
- Differences Between Generations of CephalosporinsDocument3 pagesDifferences Between Generations of CephalosporinsAnkan PalNo ratings yet
- Lithium NeurotoxicityDocument4 pagesLithium NeurotoxicityKimolli JamesNo ratings yet
- Renal: Est Autoregulatory SystemsDocument12 pagesRenal: Est Autoregulatory SystemsIdrissa ContehNo ratings yet
- Introductory Class For 2024 FPGEEDocument10 pagesIntroductory Class For 2024 FPGEEalihassan.ph40No ratings yet
- THE Check Principle Applied in Pharmacology: Remember To Take Your Tagamet With Meals!Document35 pagesTHE Check Principle Applied in Pharmacology: Remember To Take Your Tagamet With Meals!helloaNo ratings yet
- Reading Synthesis # 2: San Roque Extension, Roxas City, Capiz, Philippines 5800Document15 pagesReading Synthesis # 2: San Roque Extension, Roxas City, Capiz, Philippines 5800Jay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Seizure Disorder Case Study ClinicalDocument5 pagesSeizure Disorder Case Study Clinicalapi-546621912No ratings yet
- 029 Medication TrayDocument3 pages029 Medication TrayS BindhiyaNo ratings yet
- United States Pharmacopeia (USP) PDFDocument229 pagesUnited States Pharmacopeia (USP) PDFHoneyNo ratings yet
- 8 Daftar PustakaDocument6 pages8 Daftar PustakafennykusumaNo ratings yet
- Antifolate Drugs 17970Document19 pagesAntifolate Drugs 17970TES SENNo ratings yet
- Wahyuningrum Indah Saraswati-01206321A - Tugas P.farprak - Penyimpanan ObatDocument50 pagesWahyuningrum Indah Saraswati-01206321A - Tugas P.farprak - Penyimpanan ObatSaraswati Indah ArumNo ratings yet
- The Endocannabinoid System and PainDocument39 pagesThe Endocannabinoid System and PainLevente BalázsNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns of Methicillin Resistant Staphyl - PDF NIHDocument5 pagesAntibiotic Susceptibility Patterns of Methicillin Resistant Staphyl - PDF NIHzia ul RahmanNo ratings yet
- BMJ k1950 FullDocument6 pagesBMJ k1950 FullMUHAMMAD09No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyClau MagahisNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis:Development of New Drugs and Treatment RegimensDocument10 pagesTuberculosis:Development of New Drugs and Treatment RegimensMedylin DualloNo ratings yet
- Cannabinoids: The Separation of Central From Peripheral Effects On A Structural BasisDocument8 pagesCannabinoids: The Separation of Central From Peripheral Effects On A Structural BasisJose Carlos Solis SuarezNo ratings yet