Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2020 09 22 24 SPM Week2
2020 09 22 24 SPM Week2
Uploaded by
bitf17m009-ARUBA AKBAR0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views18 pagesThe document discusses software project management. It outlines key learning outcomes which include understanding who does work within an organization, differences between product and software development, and values and problems of software project management. It describes important project management skills and notes that software project management aims to deliver software on time and on budget. Key differences when managing software projects include software being intangible, processes still evolving, and most projects being one-off. The document also discusses interactions with stakeholders on software projects and common problems that can occur.
Original Description:
Original Title
2020-09-22-24-SPM-Week2 (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses software project management. It outlines key learning outcomes which include understanding who does work within an organization, differences between product and software development, and values and problems of software project management. It describes important project management skills and notes that software project management aims to deliver software on time and on budget. Key differences when managing software projects include software being intangible, processes still evolving, and most projects being one-off. The document also discusses interactions with stakeholders on software projects and common problems that can occur.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views18 pages2020 09 22 24 SPM Week2
2020 09 22 24 SPM Week2
Uploaded by
bitf17m009-ARUBA AKBARThe document discusses software project management. It outlines key learning outcomes which include understanding who does work within an organization, differences between product and software development, and values and problems of software project management. It describes important project management skills and notes that software project management aims to deliver software on time and on budget. Key differences when managing software projects include software being intangible, processes still evolving, and most projects being one-off. The document also discusses interactions with stakeholders on software projects and common problems that can occur.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 18
SPM
Software Project Management
2020-09-22&24
Week 2 - Lecture 3&4
Learning Outcomes Week 2
Lecture 3&4
• We will be able to have understanding of
– Who does the work within the organization?
– Product vs Software making.
– Values of Project Management
– Problems associated with SPM
Project Management Skills
• Leadership
• Communications
• Problem Solving
• Negotiating
• Influencing the Organization
• Mentoring
• Process and technical expertise
• Software Project Management
– It aimed to ensure that the software is delivered on
time, within budget and schedule constraints, and
satisfies the requirements of the client
• Management of software projects is different
from other types of management because:
– Software is not tangible
– Software processes are relatively new and still “under
trial”
– Larger software projects are usually “one-off” projects
– Computer technology evolves very rapidly
• Software Projects versus other types of Projects
• Invisibility
– With physical artifacts, measuring progress is easy as it can be
seen/ felt. However with Software, progress is not immediately
visible.
• Complexity
• – Software products are, generally, more complex than
other engineering artifact of same value.
• Flexibility
• - It is easier to change/ modify software systems to meet
changing organizational/ product requirement as compared
to other engineering artifacts; it may not be possible to
modify a physical artifact at all.
Software Project Management
Interactions / Stakeholders
• As a Project Manager (PM), who do you
interact with?
– Internal to Project team – team members
– External to project team but within the same
organization - Project sponsor,
• Executives, Functional Managers
– External to both the project team and the
organization – Customers, Contractors
Project Triangle / tradeoff
• Value of Project Management
– Allows for excellent organization and tracking
– Better control and use of resources
– Reduces complexity of inter-related tasks
– Allows measurement of outcome versus plans
– Early identification of problems and quick
correction
• Ensure meeting the project objectives within the
allocated schedule & budget
– Communication
– Meetings
– Reviews
– Authorization
– Record Keeping
– Monitoring (testing)
– Interface Control
– Not for assigning blame (usually)
Problems with Software Projects
• Manager’s Point of View:
– Poor estimates and plans
– Lack of quality standards and measures
– Lack of guidance about making organizational decisions
– Lack of techniques to make progress visible
– Poor role definition – who does what?
– Incorrect success criteria
• Members’ Point of View:
– Inadequate specification of work
– Management ignorance of IT
– Lack of knowledge of application area
– Lack of standards
Problems Contd.
• Lack of up-to-date documentation
• Preceding activities not completed on time – including late delivery of
equipment
• Lack of communication between users and technicians
• Lack of communication leading to duplication of work
• Lack of commitment – especially when a project is tied to one person who
then moves
• Narrow scope of technical expertise
• Changing statutory requirements
• Changing software environment
• Deadline pressure
• Lack of quality control
• Remote management
• Lack of training
• Q&A
You might also like
- Cpe - Eee241-Dld Lab ManualDocument117 pagesCpe - Eee241-Dld Lab ManualmbaNo ratings yet
- Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)Document16 pagesSimple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)elly-naike nkya100% (1)
- Unit 1 - History of E-Commerce PDFDocument25 pagesUnit 1 - History of E-Commerce PDFAishath ZindhNo ratings yet
- State Bank of India Digital Save Solution CSP Form PDFDocument6 pagesState Bank of India Digital Save Solution CSP Form PDFBUBAI MANDAL50% (2)
- SPM Session 11Document27 pagesSPM Session 11Suresh Nanda KumarNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 Introduction Software Project ManagementDocument38 pagesUNIT-1 Introduction Software Project ManagementNikhil Saraogi 21MCA1080100% (1)
- Chapter 3-Project Management ConceptDocument31 pagesChapter 3-Project Management ConceptDanica de Guzman100% (1)
- IT/Software Project Management: Kamran Dahri)Document26 pagesIT/Software Project Management: Kamran Dahri)علی احمدNo ratings yet
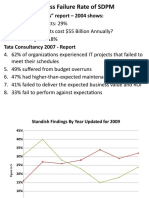
- The Standish "Chaos" Report - 2004 ShowsDocument18 pagesThe Standish "Chaos" Report - 2004 ShowsAKHIL JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- Dr.A.P.Sastri: Software Project Management Bob Hughes and Mike Cotterell: Book 1 Unit - 1 Page Nos: 1-36Document30 pagesDr.A.P.Sastri: Software Project Management Bob Hughes and Mike Cotterell: Book 1 Unit - 1 Page Nos: 1-36Dr. A. Pathanjali Sastri0% (1)
- Software Project Management: Dr. Raghuraj Singh Professor, Computer Science & Engineering Department H.B.T.I., KanpurDocument55 pagesSoftware Project Management: Dr. Raghuraj Singh Professor, Computer Science & Engineering Department H.B.T.I., KanpurIncord HbtiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1pdfDocument141 pagesUnit 1pdfRAVURI VENKATASIVANAGAABHIRAMKUMAR (RA2011032010057)No ratings yet
- SDLC and Software QualityDocument101 pagesSDLC and Software QualityAshar KizakiNo ratings yet
- SDLC and Software QualityDocument112 pagesSDLC and Software QualityAshar KizakiNo ratings yet
- SPM L1Document11 pagesSPM L1saurabh JhaNo ratings yet
- 8-Module 2 - Planning-23-01-2024Document34 pages8-Module 2 - Planning-23-01-2024aryanrathore040No ratings yet
- Unit - I IntroductionDocument141 pagesUnit - I IntroductionRAVURI VENKATASIVANAGAABHIRAMKUMAR (RA2011032010057)No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument9 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionAnas AzeemNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Software Project Management: Topic 1 Waqas Zyad Spring 2020Document28 pagesIntroduction To Software Project Management: Topic 1 Waqas Zyad Spring 2020rana mustafaNo ratings yet
- Software EngineeringDocument194 pagesSoftware EngineeringPALASH KHARE100% (1)
- Software EngineeringDocument194 pagesSoftware EngineeringPALASH KHARENo ratings yet
- Software Project Management: Lecturer: Ushna Khalil Department: Computer Science & ITDocument32 pagesSoftware Project Management: Lecturer: Ushna Khalil Department: Computer Science & ITAbdullah JuttNo ratings yet
- Software Project Management: Project Lifecycle and OrganizationDocument50 pagesSoftware Project Management: Project Lifecycle and Organizationعلی احمدNo ratings yet
- 1 Project ManagementDocument14 pages1 Project Managementyaswanth119No ratings yet
- BSGDocument14 pagesBSGsri_sriNo ratings yet
- Unit3 MU Newpdf 2024 01 23 08 44 49Document51 pagesUnit3 MU Newpdf 2024 01 23 08 44 49nagabe8303No ratings yet
- Software Engineering - 1: Lecture #1Document14 pagesSoftware Engineering - 1: Lecture #1Enggielita FitriNo ratings yet
- ASE S-ProcessDocument28 pagesASE S-ProcessQudoos KhanNo ratings yet
- Software Project Management Lecture TwoDocument18 pagesSoftware Project Management Lecture TwoMilkiyas Jc100% (1)
- Lecture 01Document18 pagesLecture 01Lakshan KarunarathneNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument88 pagesUnit IDipakNo ratings yet
- CSC577 - Chapter 3 - Project ManagementDocument47 pagesCSC577 - Chapter 3 - Project ManagementZufairi IrfanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Software Project ManagementDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Software Project ManagementjahanzebNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering: Unit - IDocument52 pagesSoftware Engineering: Unit - IDheeraj NaniNo ratings yet
- Se Unit-IDocument14 pagesSe Unit-Isnikhath20No ratings yet
- Software and Software EngineeringDocument33 pagesSoftware and Software Engineeringapi-3843649No ratings yet
- SPM 1Document15 pagesSPM 1Kaushal AnandNo ratings yet
- SW Project ManagementDocument64 pagesSW Project ManagementVignesh DksNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document20 pagesLecture 5Muhammad AdeelNo ratings yet
- UNIT-I: Software Engineering & Process Models: Dual Role of SoftwareDocument4 pagesUNIT-I: Software Engineering & Process Models: Dual Role of SoftwareAnsh GoelNo ratings yet
- Initial Process: BITS PilaniDocument14 pagesInitial Process: BITS PilaniRavi BirhmanNo ratings yet
- 01 - OO OverviewDocument127 pages01 - OO Overviewernestohp7No ratings yet
- Introduction To Project ManagementDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Project ManagementZaman HaiderNo ratings yet
- SPM-B Question BankDocument25 pagesSPM-B Question BankThiyaga RajanNo ratings yet
- SPM and SPM Concepts ADocument15 pagesSPM and SPM Concepts AAhsan ChNo ratings yet
- BN209 MN507 Lecture1Document34 pagesBN209 MN507 Lecture1gauchodepoaNo ratings yet
- Project-Mgmt-Presentation - 9B - Software Project Mng. PlanDocument110 pagesProject-Mgmt-Presentation - 9B - Software Project Mng. PlanMuhammad Talha ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Bab 3Document24 pagesBab 3Jeri Agus RahadianNo ratings yet
- SPM Unit 1Document45 pagesSPM Unit 1Dhivyabharathi ANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Software Project ManagementDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Software Project Managementtpr chanduNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering: Project Management & EstimationDocument61 pagesSoftware Engineering: Project Management & EstimationrizwanNo ratings yet
- 4-Module - 1-02-Dec-2019Material - IV - 02-Dec-2019 - PPT - 4 PDFDocument56 pages4-Module - 1-02-Dec-2019Material - IV - 02-Dec-2019 - PPT - 4 PDFLogic BombNo ratings yet
- Effective Software Project Management Focuses On The Four P's - The People - The Product - The Process - The ProjectDocument49 pagesEffective Software Project Management Focuses On The Four P's - The People - The Product - The Process - The ProjectChotaliya DharmeshNo ratings yet
- Analysis PhaseDocument44 pagesAnalysis PhaseHassam ShahidNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering Revisited: Vu Thi Huong GiangDocument41 pagesSoftware Engineering Revisited: Vu Thi Huong GiangPhạmQuangDuyNo ratings yet
- 12 Project ManagementDocument29 pages12 Project ManagementVEDIKA MALVIYANo ratings yet
- Software Engineering Unit 1Document53 pagesSoftware Engineering Unit 1Zacheous KasondaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 of WCNDocument4 pagesChapter 24 of WCNvishakha_18No ratings yet
- APSI - Week 2Document47 pagesAPSI - Week 2Anindya VaniaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To Software Project ManagementDocument37 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To Software Project Managementjack jackNo ratings yet
- Concept of Project Management: Presented ByDocument30 pagesConcept of Project Management: Presented ByToji ThomasNo ratings yet
- Ch1-Introduction, Fundamentals, Classic MistakesDocument33 pagesCh1-Introduction, Fundamentals, Classic Mistakeslama zaidNo ratings yet
- BPP 3213 Project Estimation and Scheduling: Lecture 1 Fundamentals of Project PlanningDocument42 pagesBPP 3213 Project Estimation and Scheduling: Lecture 1 Fundamentals of Project Planningsaleem_malik786No ratings yet
- Analysis of Algorithms: Dec 07, 2020, Before 8.00pmDocument1 pageAnalysis of Algorithms: Dec 07, 2020, Before 8.00pmbitf17m009-ARUBA AKBARNo ratings yet
- Food Truck Business Plan ExampleDocument33 pagesFood Truck Business Plan Examplebitf17m009-ARUBA AKBARNo ratings yet
- Ethics MergedDocument338 pagesEthics Mergedbitf17m009-ARUBA AKBARNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: Submitted ToDocument34 pagesEntrepreneurship: Submitted Tobitf17m009-ARUBA AKBARNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Multi-Word Terms and Complex Terms From The Classical Arabic Text of The QuranDocument14 pagesExtraction of Multi-Word Terms and Complex Terms From The Classical Arabic Text of The Quranbitf17m009-ARUBA AKBARNo ratings yet
- CAse StUdyDocument4 pagesCAse StUdybitf17m009-ARUBA AKBARNo ratings yet
- 1 Case Study Chapter 3: Automakers Becomes Software Companies 1. How Is Software Adding Value To Automakers' Products?Document4 pages1 Case Study Chapter 3: Automakers Becomes Software Companies 1. How Is Software Adding Value To Automakers' Products?bitf17m009-ARUBA AKBARNo ratings yet
- SPM MCQsDocument1 pageSPM MCQsbitf17m009-ARUBA AKBARNo ratings yet
- GE Essential Acquisition System Operator ManualDocument284 pagesGE Essential Acquisition System Operator Manualcesmar1992No ratings yet
- Cable Operator Management System (System)Document7 pagesCable Operator Management System (System)sanjaykumarguptaa50% (8)
- GreengateCommissioningTrainingManual1 18 2010 PDFDocument385 pagesGreengateCommissioningTrainingManual1 18 2010 PDFgramirezsalazar@yahoo.com.mxNo ratings yet
- AE 24 LectureDocument12 pagesAE 24 LectureYza GesmundoNo ratings yet
- 20105-AR-GEN-00-004-01 Rev 02Document1 page20105-AR-GEN-00-004-01 Rev 02Bahaa MohamedNo ratings yet
- DeltaVectorControl CatalogDocument16 pagesDeltaVectorControl CatalogGustavo YbañezNo ratings yet
- COMPSTAT 2004 - Proceedings in Computational Statistics - Jaromir Antoch (2004) PDFDocument578 pagesCOMPSTAT 2004 - Proceedings in Computational Statistics - Jaromir Antoch (2004) PDFHaojie LiangNo ratings yet
- Hands On Virtual Computing 9781337101936 1337101931 CompressDocument587 pagesHands On Virtual Computing 9781337101936 1337101931 Compressxinag92686No ratings yet
- 3 DB RDMDocument49 pages3 DB RDMfaisal shahzadNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Deep LearningDocument37 pagesFundamentals of Deep LearningAlejandroHerreraGurideChileNo ratings yet
- Upgrade Fails When User-Defined Field Is Defined On TableDocument3 pagesUpgrade Fails When User-Defined Field Is Defined On TableDant NazarNo ratings yet
- Apd4 T88res Install e RevbDocument54 pagesApd4 T88res Install e RevbMSushi MsushispaNo ratings yet
- Topographic Mapping: John N. HatzopoulosDocument25 pagesTopographic Mapping: John N. HatzopoulosEed RrdNo ratings yet
- E - 20221018 MT940 ConfDocument4 pagesE - 20221018 MT940 ConfCarlos GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Journal - Change of Authorship Form: Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing InstituteDocument3 pagesJournal - Change of Authorship Form: Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing InstituteReynaldo CanahuaNo ratings yet
- Talentnext - 2021 - Learningphase - Mile1 - Mcqs Wipro: Nipoorva YadavDocument3 pagesTalentnext - 2021 - Learningphase - Mile1 - Mcqs Wipro: Nipoorva YadavNipoorva Yadav100% (1)
- Discriminant and RootsDocument2 pagesDiscriminant and RootsCharalampidis DimitrisNo ratings yet
- Oracle Enterprise Project Management: David ChaimsonDocument47 pagesOracle Enterprise Project Management: David Chaimsonice_heatNo ratings yet
- MCS 011Document4 pagesMCS 011kk2760057No ratings yet
- The Bean Validation Reference Implementation. - Hibernate ValidatorDocument4 pagesThe Bean Validation Reference Implementation. - Hibernate ValidatorChandu ChandrakanthNo ratings yet
- How To Choose The Most Efficient Data Type To-Many Associations PDFDocument3 pagesHow To Choose The Most Efficient Data Type To-Many Associations PDFKhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 8Document2 pagesAssignment 8Vikram C KNo ratings yet
- FCM Kao DCS - Rev1Document34 pagesFCM Kao DCS - Rev1Izarulhaq AwangNo ratings yet
- FiltersDocument20 pagesFiltersAllu KhanNo ratings yet
- 03 Instructor's GuideDocument15 pages03 Instructor's GuideRean Joy CalalangNo ratings yet
- Joining Instruction 344Document3 pagesJoining Instruction 344cyrel carl moloNo ratings yet