Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ibt Reviewer
Ibt Reviewer
Uploaded by
Hannah RodulfoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ibt Reviewer
Ibt Reviewer
Uploaded by
Hannah RodulfoCopyright:
Available Formats
International business refers to the trade of goods, 3.
Exchange- the activity that requires any
services, technology, capital and/or knowledge transfer of money or trading of products
across national borders and at a global or between buyers and sellers in a marketplace.
transnational scale.
4. Consumption- the end phase of any economic
It involves cross-border transactions of activity, which involves the utilization of goods
goods and services between two or more and services to provide satisfaction to people.
countries.
International business is also known as Economic Resources- are the inputs or resources
globalization. used in the productions of goods and services.
It is also known as FACTORS OF PRODUCTION.
Symbol of Export in Economics= X
Symbol of Import in Economics= M Categories include in Economic Resources
Symbol for Income in Economics = Y 1. Land- the physical space or are which production
takes place. It includes economy's natural
Trade- exchange of goods and services resources. Like trees, farmland, water resources,
gold and oil deposits.
2 Classifications of Trade 2. Labor- the time physical and mental skills that
1. Foreign Trade or International Trade- Theory of people contributed in producing goods and
comparative advantage (states that the country services. Like farmer, teacher, nurse, carpenter and
should export the products on which the country call center representative.
has the greatest advantage and import the product 3. Capital- the tools and other productive
on which it has the greatest disadvantages.) equipment utilized in producing consumer
2. Local or Domestic Trade- exchange of goods goods and services. Like plant, money, machine,
and services within the country, industrial robots and computer.
INTERNATIONAL TRADE- allows countries to 4. Entrepreneurship- a human resource responsible
expand their markets and access goods and fir combining or organizing the land, labor and
services that otherwise may not have been capital resources into a good or services. Like
available domestically. CEO, manager, entrepreneur, company president
and product innovator.
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS relates to any
situation where the production or distribution of 2 types of income
goods or services, exchange or consumption 1. Salary (white color jobs- professional level)
crosses country borders.
2. Wages (blue color jobs)
Phases of Economic Activities:
3 considered capitals in Economics
1. Production- the first phase of economic activities
that involves the transformation of diff inputs so that 1. Tools
the inputs might be converted to final products.
2. Equipment
2. Distribution- this is the systematic way to
process on how commodities and income are 3. Machine
properly allocated among the economic
Capital in Finance- Money
resources owners.
Capital in Accounting- Assets
Objectives of international business
Entrepreneurship- is a humorous human resource
possible for combining and organizing the land, 1. Social and cultural exchange -between one
labor and capital resources into good resources. country to another.
People who manage and control the business and 2. To help and assist developing countries in their
the objective of entrepreneurship is to MAXIMIZE economic in terms of industrial growth.
PROFIT.
3. To assure sustainable managements of the
resources globally.
FORMULA OF PROFIT:
Total Revenue (sale) minus Total cost (expenses)= 3 classifications of countries:
Profit
1. LDC- less developed countries or under
TR- TC= PROFIT developed or a third world countries.
2. IMC- intermediate countries
Resources can be classified into 3:
3. HDC- highly developed countries is always there
1. Human Resources to help the under developed countries in terms of
doing the expansions of the industrial and
2. Manmade Resources technology and markets.
3. Natural Resources Features of international trade
FACTORS THAT CAUSE SCARCITY OF
RESOURCES (limited) GLOBALIZATION
1. Supply induced Globalization means the speed up of
2. Demand induced movement and the exchange of human
3. Structural Scarcity being goods and services, capital,
4. No effective substitutes
technological or cultural practices.
Globalization is the new big word of the
EXCHANGE- is the activity that requires any
day because -----------
transfers of money or trading between buyers and
sellers in the market.
Effects of Globalization
Phase of economic activities- it involves the
utilization of goods and services to provide Promotes and increases interaction
satisfactions to people. between different regions and population
around the world.
2 fundamental economic problems
1. Unlimited Satisfaction (in order to solve Impacts of Globalization
fundamental economic problems we need to erase
letter u and letter n) 1. Economic Impact- is the improvement of the
standard of living, increase completion
2. Limited Resources (we should allocate the among nations and the widening gap
economic resources) it includes economy’s natural between the rich and poor countries.
resources.
2. Increase of awareness of foreign culture-
aware of diff. culture
3. Environmental impact- includes 1. Economic Globalization- development trade
deforestation and related problems (global system between corporations of a certain
warming and environmental managements different regions and countries.
Advantages of Globalization 2. Financial Globalization- considered as it can
be link a financial system
1. Increase competition- customers looking for
a cheaper of good but there is a better 3. Cultural- different countries to adopt
quality of the products you can survive the cultural system
competition if there is no quality you will not
survive. 4. Political- development of growing influence
by
2. Increase international mobility- it needs
skilled workers 5. Sociological- different information and
events to move into interconnection
3. Lower cost of production- there must be a
quality of products and must have lower 6. Technological- the will of the people are
cost of production. interconnected
4. Improvement of education- interest to 7. Geographical-
spread and improve cultural diversity 8. Ecological-
5. There is a reduction of poverty- because it
leads to more workers
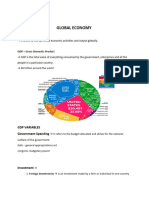
Gross Domestic Product- all about the product in
6. Leads tremendously of the transport
the Philippines
services of the world
Gross National Product (GNP)
Disadvantages of Globalization
is all about export and import
Globalization is the key factor of
international business. This new era of It refers to the total market value of all final
globalization brings competition to goods and services produced by citizen in
international market. There is specialization one (1) year.
and higher level of thinking.
1. Increase commodity price- we cannot 3 approaches of computing gross national product.
control the price of the imported products
1. Gross national product by expenditure
2. Exploitation of lower labor- approach
3. Cost of diseases 2. Gross national product by income approach
4. Increase relative poverty and inequality 3. Gross national product by income approach
5. Increase stability Formula by Expenditure Approach
6. Disparity among people 1. XN= X-M
7. Uneven distribution of goods 2. Ig= IN + CCA (capital consumption
allowances/ depreciation)
Examples of Globalization 3. GNP= c + G + Ig + Xn
Formula by Income Approach
1. To protect newly established domestic
1. CP=UCP+D+ CITX industries from foreign competition.
2. To protect aging and inefficient domestic
CORPORATE PROFIT= industries from foreign competition.
UNDISTRIBUTED CORPORATE PROFIT+ 3. To protect domestic producers from
DIVIDENT+ CORPORATE INCOME “dumping” by foreign companies or
TAXES) governments.
GNP= R+I+W/S+PY+IBTX+CCA+CP 4. To raise revenue
GNP by Industrial origin approach IMPORTANCE OF TARIFFS
1. Agricultural sectors Tariffs have three primary functions:
a) Forestry
b) Fishery 1. to serve as a source of revenue,
2. to protect domestic industries, and
2. Industrial sectors 3. to remedy trade distortions (punitive
function).
a) Mining and Quarrying
b) Construction The revenue function comes from the fact
c) Manufacturing that the income from tariffs provides
d) Electricity governments with a source of funding.
3. Services sectors
NEGATIVE EFFECTS OF TARIFF
a) Transportation and
Communication Negative consequences of the tariffs
b) Ownership and Real Estate increase on the broad economy {including
c) Trade higher prices, lower consumption, reduced
d) Finance business investment, and drops in the
e) Public Services valuations of affected firms.
f) Private Services
TWO DISADVANTAGES OF TARIFFS
TARIFF
Tariffs raise the price of imports. This
impacts consumers in the country applying
it is a political tool that has been used the tariff in the form of costlier imports.
throughout the history to control the amount When trading partners retaliate with their
of imports that flow into a country and to own tariffs, it raises the cost of doing
determine which nations will be granted the business for exporting industries.
most favorable trading conditions.
Tariffs cause a decrease in product
A tariff is a tax or duty imposed by one quality.
nation on the imported goods or services of
another country that serves to increase the
prices and make imports less desirable or ADVANTAGES/ BENEFIT OF TARIFF
atleast competition vs. domestic goods and
services.
Tariffs mainly benefit the importing
countries, as they are the ones setting the
Higher tariffs create protectionism policy and receiving the money. The primary
benefit is that tariffs produce revenue on
goods and services brought into the
TARIFFS ARE GENERALLY IMPOSED FOR: country. Tariffs can also serve as an
opening point for negotiations between two What is an example of a quota?
countries.
A quota is a type of trade restriction where a
How Do Tariffs Affect a Country’s Balance of government imposes a limit on the number
Trade? (Negative) or the value of a product that another
country can import.
Tariffs make imported goods more
expensive, which obviously makes
For example, a government may place a
consumers unhappy if those costs result in
quota limiting a neighboring nation to
higher prices.
importing no more than 10 tons of grain.
Domestic companies that may rely on
imported materials to produce their goods
could see tariffs reducing their profits and For example, the organization of petroleum
raise prices to make up the difference, exporting countries sets a production quota
which also hurts consumers. for crude oil in order to “maintain” the price
of crude oil in the world market.
POSITIVE NEGATIVE
- Reducing the -make imported Types of quotas
profits goods more
expensive that Absolute quota – a simple physical limit on
makes the the number.
consumers unhappy
-Raises prices to -cost result in higher Tariff rate quota – These allow a certain
make up the prices. number of imports to gain a discount on the
difference usual tariff rate.
Voluntary export restraints (VER) - This is
QUOTA when a government limits the amounts of
exports from one country to another for a
A quota is a government-imposed trade particular type of good.
restriction that limits the number or
monetary value of goods that a country can Effect of import quotas
import or export during a particular period.
Countries use quotas in international trade
to help regulate the volume of trade An import quota is a limit on the amount of
between them and other countries. imports that can be brought into a particular
country.
Countries sometimes impose quotas on
specific products to reduce imports and For example, the US may limit the number
increase domestic production. of Japanese car imports to 2 million per
year.
How do quotas affect businesses?
Quotas will reduce imports, and help Quotas will reduce imports, and help
domestic suppliers. However, they will lead domestic suppliers. However, they will lead
to higher prices for consumers, a decline in to higher prices for consumers, a decline in
economic welfare and could lead to economic welfare and could lead to
retaliation with other countries placing tariffs retaliation with other countries placing tariffs
on our exports. on our exports.
The primary goal of import quotas is to Quotas will lead to lower sales for foreign
reduce imports and increase domestic companies, but it could push up prices and
production. make sales more profitable.
You might also like
- Eticket Receipt: Teklie/Dagmawit Bekele Mrs (Adt)Document3 pagesEticket Receipt: Teklie/Dagmawit Bekele Mrs (Adt)Tarik Kefale100% (3)
- ElectricityDocument1 pageElectricityDarge GmentizaNo ratings yet
- Contempo (1st Year 1st Sem)Document3 pagesContempo (1st Year 1st Sem)John Edward AliponNo ratings yet
- Review-Materials-SOCSCI 2Document5 pagesReview-Materials-SOCSCI 2bgdp8hzbzyNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument61 pagesUntitledCharmaine Mejias SagairanNo ratings yet
- IBT Prelims 1Document8 pagesIBT Prelims 1sah mihNo ratings yet
- Class Notes On GlobalizationDocument6 pagesClass Notes On Globalization마스러버No ratings yet
- I - Learning Objectives: Prelim Week 4Document5 pagesI - Learning Objectives: Prelim Week 4Carmelita VolanteNo ratings yet
- Revisiting Economics As A Social ScienceDocument38 pagesRevisiting Economics As A Social ScienceShirly Sarmiento CañeteNo ratings yet
- Contemp - Post Midterms Lessons SummaryDocument19 pagesContemp - Post Midterms Lessons SummaryibanezlouisemargueriteNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - IbtDocument6 pagesReviewer - IbtChristine Angeli AritaNo ratings yet
- Lesson One Applied EconomicsDocument39 pagesLesson One Applied Economicsanneborja511No ratings yet
- Summary Marketing InterDocument12 pagesSummary Marketing Interasmara.savira1115No ratings yet
- The Contemporary World ReviewerDocument39 pagesThe Contemporary World ReviewerBeverly Ann BotinNo ratings yet
- IBT Lecture PasafdDocument2 pagesIBT Lecture Pasafd132345usdfghjNo ratings yet
- Why Is Global Economy Important?Document2 pagesWhy Is Global Economy Important?Mary Ianne Therese GumabongNo ratings yet
- Igcse Econ 1Document23 pagesIgcse Econ 1Thimani WijepalaNo ratings yet
- Economicactivity 170616135505Document4 pagesEconomicactivity 170616135505somesh dubeyNo ratings yet
- ECONOMY Crux Prelims 88 Pages BY CA Rahul Kumar @upsc ThoughtDocument88 pagesECONOMY Crux Prelims 88 Pages BY CA Rahul Kumar @upsc ThoughtYashwant Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- GE 104 Midterm Reviewer - The Contemporary WorldDocument7 pagesGE 104 Midterm Reviewer - The Contemporary WorldChelden100% (1)
- Lesson 1 What Is GlobalizationDocument17 pagesLesson 1 What Is GlobalizationshaylieeeNo ratings yet
- MGT107 IBT Midterm ReviewerDocument15 pagesMGT107 IBT Midterm ReviewerMary Grace AlzateNo ratings yet
- Economics: Is A Study of Social Behavior and Relation of Human Wants, Production and Distribution and AllocationDocument34 pagesEconomics: Is A Study of Social Behavior and Relation of Human Wants, Production and Distribution and AllocationjoycebuquingNo ratings yet
- TNCT 3rd-Periodical-Exam ReviewerDocument2 pagesTNCT 3rd-Periodical-Exam ReviewerCourtney BaguinatNo ratings yet
- Handout For Applied Economics 1st QuarterDocument4 pagesHandout For Applied Economics 1st QuarterNorlie Amor LabradorNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Contemporary WorldDocument3 pagesReviewer in Contemporary WorldBenjo BataoNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Wolrd - Final ReviewerDocument4 pagesContemporary Wolrd - Final ReviewerSherlyn MamacNo ratings yet
- BBC 1200 Lesson 1 What Is GlobalizationDocument17 pagesBBC 1200 Lesson 1 What Is GlobalizationMARIANo ratings yet
- Contemp WorldDocument5 pagesContemp Worldqweyo yhuNo ratings yet
- GLOBALIZATIONDocument4 pagesGLOBALIZATIONMARRIAH ELIZZA FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-The Changing World EconomyDocument19 pagesChapter 2-The Changing World EconomyKhánh NgọcNo ratings yet
- Impact of Globalization On Organization Behavior: Waseem Ahmed Iman Annushree Mohd YaseenDocument23 pagesImpact of Globalization On Organization Behavior: Waseem Ahmed Iman Annushree Mohd YaseenPrincess Shaira FajardoNo ratings yet
- Global EconomyDocument18 pagesGlobal EconomyContillo JessiecaNo ratings yet
- BBC 1200 Lesson 1 What Is Globalization - 398639958Document17 pagesBBC 1200 Lesson 1 What Is Globalization - 398639958Rafael Capunpon VallejosNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 For StudentsDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 1 For StudentsmrolimmakhmudjanovNo ratings yet
- 0 - LTS BepDocument10 pages0 - LTS Bepsharmaji2507No ratings yet
- Hannah OutlineDocument9 pagesHannah OutlineHannah Valiente BasagreNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World PrelimsDocument3 pagesContemporary World PrelimsylananzackNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World NotesDocument3 pagesContemporary World NotesLouis CabaticNo ratings yet
- Micro Econ. 1Document42 pagesMicro Econ. 1ELIANA PAULNo ratings yet
- Building Economics and Sociology: Ix Semester, B.ArchDocument138 pagesBuilding Economics and Sociology: Ix Semester, B.ArchVenkat KiranNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Contemporary WorldDocument3 pagesReviewer in Contemporary WorldCarrie Anne Aquila GarciaNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World ReviewerDocument5 pagesContemporary World ReviewerAugusto RamboyongNo ratings yet
- Change: Chapter 3: Patterns of Development andDocument5 pagesChange: Chapter 3: Patterns of Development andHiền ThảoNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument4 pagesReviewerFerlyn Cariño GundaNo ratings yet
- Global/ Int. Business: Final PaperDocument8 pagesGlobal/ Int. Business: Final PaperHira RazaNo ratings yet
- Econ 1-3Document46 pagesEcon 1-3i'm lightNo ratings yet
- M E-4Document2 pagesM E-4Shaira BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing GlobalizationDocument6 pagesFactors Influencing Globalizationryan bhinog100% (1)
- Report Compilation About GlobalizationDocument14 pagesReport Compilation About GlobalizationRocelle Jewel HufanaNo ratings yet
- Gcworld (Prelims)Document4 pagesGcworld (Prelims)CyberR.DomingoNo ratings yet
- Purcom Reviewer MidtermsDocument16 pagesPurcom Reviewer MidtermsAndrei Yuri DiñoNo ratings yet
- Fria Mae Abellano - International Business and TradeDocument14 pagesFria Mae Abellano - International Business and TradeFria Mae Aycardo AbellanoNo ratings yet
- GE 3 The Contemporary World QUIZ 1Document3 pagesGE 3 The Contemporary World QUIZ 1wzialcitaNo ratings yet
- Contemporary WorldDocument7 pagesContemporary WorldZiee KielNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full International Business The Challenges of Globalization 9th Edition Wild Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full International Business The Challenges of Globalization 9th Edition Wild Solutions Manual PDFmorselhurly.qa26100% (11)
- Business Question and AnswersDocument12 pagesBusiness Question and AnswersAbdisamad ElmiNo ratings yet
- Mic CH1 1Document11 pagesMic CH1 1Poona RasanNo ratings yet
- Business Organization and Systems Bba I Semester IDocument65 pagesBusiness Organization and Systems Bba I Semester Idevika7575No ratings yet
- International Business Management - Chapter 1Document3 pagesInternational Business Management - Chapter 1HÂN HUỲNH ĐẶNG BẢONo ratings yet
- Invoice PDFDocument2 pagesInvoice PDFMriganabh ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Elaine Makes Delicious Cupcakes That She Mails To Customers AcrossDocument1 pageElaine Makes Delicious Cupcakes That She Mails To Customers Acrosstrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- 400 Billion: Power Distribution in EuropeDocument26 pages400 Billion: Power Distribution in EuropecokavolitangoNo ratings yet
- Challenges of Multinational Companies A1Document6 pagesChallenges of Multinational Companies A1Glydel Anne C. LincalioNo ratings yet
- EthiopiaDocument46 pagesEthiopiaace187No ratings yet
- Process Download PDFDocument2 pagesProcess Download PDFhitech cityNo ratings yet
- Impact and Challenges of GST in India With Reference To Media Entertainment Sector - An InsightDocument17 pagesImpact and Challenges of GST in India With Reference To Media Entertainment Sector - An InsightHJ ManviNo ratings yet
- Trade Law Unit 2Document9 pagesTrade Law Unit 2Mansi DabasNo ratings yet
- Law of Taxation II - Course ManualDocument17 pagesLaw of Taxation II - Course ManualarshiaNo ratings yet
- Gepco Online BillDocument2 pagesGepco Online Billroyalbutt413No ratings yet
- GMR Hyd Cargo Terminal Handling Charges PDFDocument1 pageGMR Hyd Cargo Terminal Handling Charges PDFSridhar NagavarapuNo ratings yet
- BillDocument1 pageBillNiket KumarNo ratings yet
- 37 - Chevron Philippines vs. CIRDocument2 pages37 - Chevron Philippines vs. CIRLEIGH TARITZ GANANCIALNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - VAT On ImportationDocument5 pagesLesson 3 - VAT On ImportationVince TablacNo ratings yet
- Free Trade AgreementsDocument3 pagesFree Trade AgreementsAditya Pandey100% (1)
- BA223-Module 1-Lesson ProperDocument12 pagesBA223-Module 1-Lesson ProperMark Bryan ComAyaNo ratings yet
- Tax Invoice For LT Current Consumption Charges For The Month of March 2024Document1 pageTax Invoice For LT Current Consumption Charges For The Month of March 2024sudha rathinamNo ratings yet
- ABT - Tariff Explaination With Examples PDFDocument33 pagesABT - Tariff Explaination With Examples PDFDayanandaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Solution Manual For Principles of Corporate Finance 13th by Brealey PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Solution Manual For Principles of Corporate Finance 13th by Brealey PDF Full Chaptercucumisinitial87qlh100% (22)
- Paper-8 Indirect Tax Laws 73366bos59159Document44 pagesPaper-8 Indirect Tax Laws 73366bos59159cadivyaguptaNo ratings yet
- NSS Economics (Book 3) Chapter 16 (Efficiency and Government Intervention)Document16 pagesNSS Economics (Book 3) Chapter 16 (Efficiency and Government Intervention)dizzelNo ratings yet
- Amaron Battery Change InvoiceDocument2 pagesAmaron Battery Change InvoiceShivam MishraNo ratings yet
- WK 9 Elementary Treatment of Fiscal PolicyDocument52 pagesWK 9 Elementary Treatment of Fiscal PolicyGODSTIME EGBO JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- 045 41033974 PDFDocument12 pages045 41033974 PDFDavidNo ratings yet
- Bill of Supply For Electricity: Due DateDocument1 pageBill of Supply For Electricity: Due DatesukantNo ratings yet
- Faisalabad Electric Supply Company: Govt ConnectionDocument2 pagesFaisalabad Electric Supply Company: Govt ConnectionM Aqeel Ahmad KalyarNo ratings yet
- Protectionism EssayDocument3 pagesProtectionism EssayChloe CharlesNo ratings yet
- Lotus Enclave (Phase-Ii) - 2/3 BHK Villas: Preferential Location Charges (PLC)Document2 pagesLotus Enclave (Phase-Ii) - 2/3 BHK Villas: Preferential Location Charges (PLC)SAROJNo ratings yet