Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Voyage Through Equations O4i2ny
A Voyage Through Equations O4i2ny
Uploaded by
Joel VillegasCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- UL Standard 181B Standard For Closure Systems For Use With Flexible Air Ducts and Air ConnectorsDocument12 pagesUL Standard 181B Standard For Closure Systems For Use With Flexible Air Ducts and Air ConnectorsALI MAKRINo ratings yet
- 7 Weird Tips To Boost Your TestosteroneDocument22 pages7 Weird Tips To Boost Your Testosteronekyo4life67% (3)
- Mass To Mass Stoichiometry ProblemsDocument2 pagesMass To Mass Stoichiometry ProblemsEaEamNo ratings yet
- Concentration PracticeDocument2 pagesConcentration PracticeEaEamNo ratings yet
- Mole 1 + AkDocument2 pagesMole 1 + AkEaEamNo ratings yet
- Percent, Actual, and Theoretical Yield: © 2000 Cavalcade Publishing - All Rights ReservedDocument3 pagesPercent, Actual, and Theoretical Yield: © 2000 Cavalcade Publishing - All Rights ReservedEaEamNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument1 pagePeriodic TableEaEamNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument2 pagesChromatographyEaEamNo ratings yet
- Moles Worksheet: © 2000 Cavalcade Publishing - All Rights ReservedDocument2 pagesMoles Worksheet: © 2000 Cavalcade Publishing - All Rights ReservedEaEamNo ratings yet
- Metals, Metalloids, and Nonmetals: All Rights ReservedDocument2 pagesMetals, Metalloids, and Nonmetals: All Rights ReservedEaEamNo ratings yet
- Igcse 4420 Revision QuestionsanswersDocument9 pagesIgcse 4420 Revision QuestionsanswersEaEamNo ratings yet
- Aim: To Find The Centre of Mass of An Irregular-Shaped Lamina PDFDocument1 pageAim: To Find The Centre of Mass of An Irregular-Shaped Lamina PDFEaEamNo ratings yet
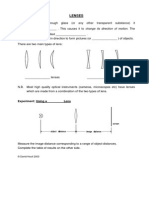
- Lenses: Experiment: Using A LensDocument2 pagesLenses: Experiment: Using A LensEaEamNo ratings yet
- Questions About Motion: © David Hoult 2003Document1 pageQuestions About Motion: © David Hoult 2003EaEamNo ratings yet
- Questions About Density and The Principle of Archimedes: Area 30000cmDocument1 pageQuestions About Density and The Principle of Archimedes: Area 30000cmEaEamNo ratings yet
- Thermocouple Color CodesDocument8 pagesThermocouple Color CodesMohsin ShaukatNo ratings yet
- Physical Metallurgy of Ti-Ni-basedDocument168 pagesPhysical Metallurgy of Ti-Ni-basedHossein FallahiNo ratings yet
- Biological Importance of Carbonyls & NitrosylsDocument7 pagesBiological Importance of Carbonyls & NitrosylsRidoyNo ratings yet
- Acido Citrico HPLCDocument12 pagesAcido Citrico HPLCGustavo RuizNo ratings yet
- Flange PDFDocument13 pagesFlange PDFEsteban Calderón Navarro100% (1)
- Solutions of Optional AssignmentDocument4 pagesSolutions of Optional AssignmentVaibhav BacchavNo ratings yet
- Work Exp 2. Relianc e Industr Ies 3. Bhilosa Ind. PVT - Ltd. Silvassa (D&NH)Document4 pagesWork Exp 2. Relianc e Industr Ies 3. Bhilosa Ind. PVT - Ltd. Silvassa (D&NH)AtharvaNo ratings yet
- BHEL - Material SpecsDocument22 pagesBHEL - Material Specssandy kulkarniNo ratings yet
- T o X I C o L o G yDocument7 pagesT o X I C o L o G yDennis ValdezNo ratings yet
- API 650 (US) EN 14015 (Europe) GOST 31385-2016 (Russia, CIS) X - Tick As NecessaryDocument3 pagesAPI 650 (US) EN 14015 (Europe) GOST 31385-2016 (Russia, CIS) X - Tick As NecessaryBilel NajjarNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 Chemical Reaction ReviewerDocument4 pagesLESSON 2 Chemical Reaction Reviewerjohnromar VilasNo ratings yet
- BMAT 2004 Section 2Document16 pagesBMAT 2004 Section 2trueflaseNo ratings yet
- STEEL HSS Beam Load Table Bro PDFDocument116 pagesSTEEL HSS Beam Load Table Bro PDFtyger089No ratings yet
- 3.formulation and Evaluation of Poly Herbal Hair Oil An Economical CosmeticDocument5 pages3.formulation and Evaluation of Poly Herbal Hair Oil An Economical CosmetictmlNo ratings yet
- Materials ConcreteDocument3 pagesMaterials ConcreteKarlo BosecNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Biotech 2.1-2018Document82 pagesPharmaceutical Biotech 2.1-2018An Ngoc HoaiNo ratings yet
- Model Questions PRM 2019Document24 pagesModel Questions PRM 2019Haris AyyazNo ratings yet
- 8.desinsectacion Por AnoxiaDocument20 pages8.desinsectacion Por AnoxiaSusanaMariel100% (1)
- Flow Control Devices Standing Valves / Test Tools: Europe Learning Centre WCP Training SchlumbergerDocument12 pagesFlow Control Devices Standing Valves / Test Tools: Europe Learning Centre WCP Training SchlumbergerAli Ali100% (1)
- CFB Thermal HeatDocument9 pagesCFB Thermal HeatbamzNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Assignment BookDocument28 pagesUnit 9 Assignment BookXenability0% (1)
- Gen Bio ReviewerDocument22 pagesGen Bio ReviewerKylle BenitezNo ratings yet
- Types of RockDocument21 pagesTypes of RockFain AloyanNo ratings yet
- f5 Chapter 1 Essay QDocument4 pagesf5 Chapter 1 Essay Qzhen1998No ratings yet
- Salt Analysis Scheme For StudentsDocument11 pagesSalt Analysis Scheme For StudentsTHE MAKER ELECTRONICSNo ratings yet
- GB Programme Chart: H F C J I K L MDocument2 pagesGB Programme Chart: H F C J I K L MJan ZemanNo ratings yet
- TYS Qns ClarificationsDocument4 pagesTYS Qns ClarificationsSharizah Bte Md AminNo ratings yet
- Thermostatic Valve AMOTDocument4 pagesThermostatic Valve AMOTaldino020203100% (1)
A Voyage Through Equations O4i2ny
A Voyage Through Equations O4i2ny
Uploaded by
Joel VillegasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Voyage Through Equations O4i2ny
A Voyage Through Equations O4i2ny
Uploaded by
Joel VillegasCopyright:
Available Formats
A Voyage through Equations
After working on this worksheet, you should be able to do the following:
1) Given an equation, you should be able to tell what kind of reaction it is.
2) Predict the products of a reaction when given the reactants.
Section 1: Identify the type of reaction
For the following reactions, indicate whether the following are examples of
synthesis, decomposition, combustion, single displacement, double
displacement, or acid-base reactions:
1) Na3PO4 + 3 KOH Æ 3 NaOH + K3PO4 _________________________
2) MgCl2 + Li2CO3 Æ MgCO3 + 2 LiCl _________________________
3) C6H12 + 9 O2 Æ 6 CO2 + 6 H2O _________________________
4) Pb + FeSO4 Æ PbSO4 + Fe _________________________
5) CaCO3 Æ CaO + CO2 _________________________
6) P4 + 3 O2 Æ 2 P2O3 _________________________
7) 2 RbNO3 + BeF2 Æ Be(NO3)2 + 2 RbF ________________________
8) 2 AgNO3 + Cu Æ Cu(NO3)2 + 2 Ag ________________________
9) C3H6O + 4 O2 Æ 3 CO2 + 3 H2O _________________________
10) 2 C5H5 + Fe Æ Fe(C5H5)2 _________________________
11) SeCl6 + O2 Æ SeO2 + 3Cl2 _________________________
12) 2 MgI2 + Mn(SO3)2 Æ 2 MgSO3 + MnI4 _________________________
.
13) O3 Æ O + O2 _________________________
14) 2 NO2 Æ 2 O2 + N2_________________________
WKS001x002 © 2000 Cavalcade Publishing (http://www.cavalcadepublishing.com) All Rights Reserved
Section 2: Practicing equation balancing
Before you can write a balanced equation for a problem which asks you to
predict the products of a reaction, you need to know how to balance an equation.
Because some of you may not fully remember how to balance an equation, here
are some practice problems:
1) __ C6H6 + __ O2 Æ __ H2O + __ CO2
2) __ NaI + __ Pb(SO4)2 Æ __ PbI4 + __ Na2SO4
3) __ NH3 + __ O2 Æ__ NO + __ H2O
4) __ Fe(OH)3 Æ __ Fe2O3 + __ H2O
5) __ HNO3 + __ Mg(OH)2 Æ __H2O + __ Mg(NO3)2
6) __ H3PO4 + __ NaBr Æ __ HBr + __ Na3PO4
7) __ C + __ H2 Æ __ C3H8
8) __ CaO + __ MnI4 Æ __ MnO2 + __ CaI2
9) __ Fe2O3 + __ H2O Æ __ Fe(OH)3
10) __ C2H2 + __ H2 Æ __ C2H6
11) __ VF5 + __ HI Æ __ V2I10 + __ HF
12) __ OsO4 + __ PtCl4 Æ __ PtO2 + __ OsCl8
13) __ CF4 + __ Br2 Æ __ CBr4 + __ F2
14) __ Hg2I2 + __ O2 Æ __ Hg2O + __ I2
15) __ Y(NO3)2 + __ GaPO4 Æ __ YPO4 + __ Ga(NO3)2
WKS001x002 © 2000 Cavalcade Publishing (http://www.cavalcadepublishing.com) All Rights Reserved
Section 3: Predicting the products of chemical reactions
Predict the products of the following reactions:
1) __ Ag + __CuSO4 Æ
Type:___________________________
2) __ NaI + __ CaCl2 Æ
Type:___________________________
3) __ O2 + __ H2 Æ
Type:___________________________
4) __ HNO3 + __ Mn(OH)2 Æ
Type:___________________________
5) __ AgNO2 + __ BaSO4 Æ
Type:___________________________
6) __ HCN + __ CuSO4 Æ
Type:___________________________
7) __ H2O + __ AgI Æ
Type:___________________________
8) __ HNO3 + __Fe(OH)3 Æ
Type:___________________________
9) __ LiBr + __ Co(SO3)2 Æ
Type:___________________________
10) __ LiNO3 + __Ag Æ
Type:___________________________
WKS001x002 © 2000 Cavalcade Publishing (http://www.cavalcadepublishing.com) All Rights Reserved
11) __ N2 + __ O2 Æ
Type:___________________________
12) __ H2CO3 Æ
Type:___________________________
13) __ AlCl3 + __ Cs Æ
Type:___________________________
14) __ Al(NO3)3 + __ Ga Æ
Type:___________________________
15) __ H2SO4 + __ NH4OH Æ
Type:___________________________
16) __ CH3COOH + __ O2 Æ
Type:___________________________
17) __ C4H8 + __ O2 Æ
Type:___________________________
18) __ KCl + __ Mg(OH)2 Æ
Type:___________________________
19) __ Zn + __ Au(NO2)2 Æ
Type:___________________________
20) __ KOH + __ H2SO4 Æ
Type:___________________________
21) __ BaS + __ PtCl2 Æ
Type:___________________________
22) __ Na2O Æ
Type:___________________________
WKS001x002 © 2000 Cavalcade Publishing (http://www.cavalcadepublishing.com) All Rights Reserved
A Voyage through Equations ANSWER KEY
Section 1: Identify the type of reaction
1) Na3PO4 + 3 KOH Æ 3 NaOH + K3PO4 DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT
2) MgCl2 + Li2CO3 Æ MgCO3 + 2 LiCl DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT
3) C6H12 + 9 O2 Æ 6 CO2 + 6 H2O COMBUSTION
4) Pb + FeSO4 Æ PbSO4 + Fe SINGLE DISPLACEMENT
5) CaCO3 Æ CaO + CO2 DECOMPOSITION
6) P4 + 3 O2 Æ 2 P2O3 SYNTHESIS
7) 2 RbNO3 + BeF2 Æ Be(NO3)2 + 2 RbF DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT
8) 2 AgNO3 + Cu Æ Cu(NO3)2 + 2 Ag SINGLE DISPLACEMENT
9) C3H6O + 4 O2 Æ 3 CO2 + 3 H2O COMBUSTION
10) 2 C5H5 + Fe Æ Fe(C5H5)2 SYNTHESIS
11) SeCl6 + O2 Æ SeO2 + 3Cl2 SINGLE DISPLACEMENT
12) 2 MgI2 + Mn(SO3)2 Æ 2 MgSO3 + MnI4 DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT
.
13) O3 Æ O + O2 DECOMPOSITION
14) 2 NO2 Æ 2 O2 + N2 DECOMPOSITION
Section 2: Practicing equation balancing
1) 2 C6H6 + 15 O2 Æ 6 H2O + 12 CO2
2) 4 NaI + 1 Pb(SO4)2 Æ 1 PbI4 + 2 Na2SO4
3) 2 NH3 + 2 O2 Æ 1 NO + 3 H2O
4) 2 Fe(OH)3 Æ 1 Fe2O3 + 3 H2O
5) 2 HNO3 + 1 Mg(OH)2 Æ 2 H2O + 1 Mg(NO3)2
6) 1 H3PO4 + 3 NaBr Æ 3 HBr + 1 Na3PO4
7) 3 C + 4 H2 Æ 1 C3H8
8) 2 CaO + 1 MnI4 Æ 1 MnO2 + 2 CaI2
9) 1 Fe2O3 + 3 H2O Æ 2 Fe(OH)3
10) 1 C2H2 + 2 H2 Æ 1 C2H6
WKS001x002 © 2000 Cavalcade Publishing (http://www.cavalcadepublishing.com) All Rights Reserved
11) 2 VF5 + 10 HI Æ 1 V2I10 + 10 HF
12) 1 OsO4 + 2 PtCl4 Æ 2 PtO2 + 1 OsCl8
13) 1 CF4 + 2 Br2 Æ 1 CBr4 + 2 F2
14) 2 Hg2I2 + 1 O2 Æ 2 Hg2O + 2 I2
15) 1 Y(NO3)2 + 1 GaPO4 Æ 1 YPO4 + 1 Ga(NO3)2
Section 3: Predicting the products of chemical reactions
1) 2 Ag + 1 CuSO4 Æ 1 Ag2SO4 + 1 Cu Type: Single Displacement
2) 2 NaI + 1 CaCl2 Æ 2 NaCl + 1 CaI2 Type: Double Displacement
3) 1 O2 + 1 H2 Æ 2 H2O Type: Synthesis
4) 2 HNO3 + 1 Mn(OH)2 Æ 2 H2O + 1 Mn(NO3)2 Type: Acid-Base
5) 2 AgNO2 + 1 BaSO4 Æ 1 Ag2SO4 + 1 Ba(NO2)2 Type: Double Displacement
6) 2 HCN + 1 CuSO4 Æ 1 H2SO4 + 1 Cu(CN)2 Type: Double Displacement
7) 1 H2O + 1 AgI Æ 1 HI + 1 AgOH Type: Double Displacement
8) 3 HNO3 + 1 Fe(OH)3 Æ 3 H2O + 1 Fe(NO3)3 Type: Acid-Base
9) 4 LiBr + 1 Co(SO3)2 Æ 2 Li2SO3 + 1 CoBr4 Type: Double Displacement
10) 1 LiNO3 + 1 Ag Æ 1 AgNO3 + 1 Li Type: Single Displacement
11) 1 N2 + 2 O2 Æ 2 NO2 Type: Synthesis
12) 1 H2CO3 Æ 1 CO2 + 1 H2O Type: Decomposition
13) 1 AlCl3 + 3 Cs Æ 3 CsCl + 1 Al Type: Single Displacement
14) 1 Al(NO3)3 + 1 Ga Æ 1 Ga(NO3)3 + 1 Al Type: Single Displacement
15) 1 H2SO4 + 2 NH4OH Æ 2 H2O + 1 (NH4)2SO4 Type: Acid-Base
16) 1 CH3COOH + 1 O2 Æ 1 CO2 + 2 H2O Type: Combustion
17) 1 C4H8 + 6 O2 Æ 4 CO2 + 4 H2O Type: Combustion
18) 2 KCl + 1 Mg(OH)2 Æ 2 KOH + 1 MgCl2 Type: Double Displacement
19) 1 Zn + 1 Au(NO2)2 Æ 1 Zn(NO2)2 + 1 Au Type: Single Displacement
20) 2 KOH + 1 H2SO4 Æ 1 K2SO4 + 2 H2O Type: Acid-Base
21) 1 BaS + 1 PtCl2 Æ 1 BaCl2 + 1 PtS Type: Double Displacement
22) 2 Na2O Æ 4 Na + 1 O2 Type: Decomposition
WKS001x002 © 2000 Cavalcade Publishing (http://www.cavalcadepublishing.com) All Rights Reserved
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- UL Standard 181B Standard For Closure Systems For Use With Flexible Air Ducts and Air ConnectorsDocument12 pagesUL Standard 181B Standard For Closure Systems For Use With Flexible Air Ducts and Air ConnectorsALI MAKRINo ratings yet
- 7 Weird Tips To Boost Your TestosteroneDocument22 pages7 Weird Tips To Boost Your Testosteronekyo4life67% (3)
- Mass To Mass Stoichiometry ProblemsDocument2 pagesMass To Mass Stoichiometry ProblemsEaEamNo ratings yet
- Concentration PracticeDocument2 pagesConcentration PracticeEaEamNo ratings yet
- Mole 1 + AkDocument2 pagesMole 1 + AkEaEamNo ratings yet
- Percent, Actual, and Theoretical Yield: © 2000 Cavalcade Publishing - All Rights ReservedDocument3 pagesPercent, Actual, and Theoretical Yield: © 2000 Cavalcade Publishing - All Rights ReservedEaEamNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument1 pagePeriodic TableEaEamNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument2 pagesChromatographyEaEamNo ratings yet
- Moles Worksheet: © 2000 Cavalcade Publishing - All Rights ReservedDocument2 pagesMoles Worksheet: © 2000 Cavalcade Publishing - All Rights ReservedEaEamNo ratings yet
- Metals, Metalloids, and Nonmetals: All Rights ReservedDocument2 pagesMetals, Metalloids, and Nonmetals: All Rights ReservedEaEamNo ratings yet
- Igcse 4420 Revision QuestionsanswersDocument9 pagesIgcse 4420 Revision QuestionsanswersEaEamNo ratings yet
- Aim: To Find The Centre of Mass of An Irregular-Shaped Lamina PDFDocument1 pageAim: To Find The Centre of Mass of An Irregular-Shaped Lamina PDFEaEamNo ratings yet
- Lenses: Experiment: Using A LensDocument2 pagesLenses: Experiment: Using A LensEaEamNo ratings yet
- Questions About Motion: © David Hoult 2003Document1 pageQuestions About Motion: © David Hoult 2003EaEamNo ratings yet
- Questions About Density and The Principle of Archimedes: Area 30000cmDocument1 pageQuestions About Density and The Principle of Archimedes: Area 30000cmEaEamNo ratings yet
- Thermocouple Color CodesDocument8 pagesThermocouple Color CodesMohsin ShaukatNo ratings yet
- Physical Metallurgy of Ti-Ni-basedDocument168 pagesPhysical Metallurgy of Ti-Ni-basedHossein FallahiNo ratings yet
- Biological Importance of Carbonyls & NitrosylsDocument7 pagesBiological Importance of Carbonyls & NitrosylsRidoyNo ratings yet
- Acido Citrico HPLCDocument12 pagesAcido Citrico HPLCGustavo RuizNo ratings yet
- Flange PDFDocument13 pagesFlange PDFEsteban Calderón Navarro100% (1)
- Solutions of Optional AssignmentDocument4 pagesSolutions of Optional AssignmentVaibhav BacchavNo ratings yet
- Work Exp 2. Relianc e Industr Ies 3. Bhilosa Ind. PVT - Ltd. Silvassa (D&NH)Document4 pagesWork Exp 2. Relianc e Industr Ies 3. Bhilosa Ind. PVT - Ltd. Silvassa (D&NH)AtharvaNo ratings yet
- BHEL - Material SpecsDocument22 pagesBHEL - Material Specssandy kulkarniNo ratings yet
- T o X I C o L o G yDocument7 pagesT o X I C o L o G yDennis ValdezNo ratings yet
- API 650 (US) EN 14015 (Europe) GOST 31385-2016 (Russia, CIS) X - Tick As NecessaryDocument3 pagesAPI 650 (US) EN 14015 (Europe) GOST 31385-2016 (Russia, CIS) X - Tick As NecessaryBilel NajjarNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 Chemical Reaction ReviewerDocument4 pagesLESSON 2 Chemical Reaction Reviewerjohnromar VilasNo ratings yet
- BMAT 2004 Section 2Document16 pagesBMAT 2004 Section 2trueflaseNo ratings yet
- STEEL HSS Beam Load Table Bro PDFDocument116 pagesSTEEL HSS Beam Load Table Bro PDFtyger089No ratings yet
- 3.formulation and Evaluation of Poly Herbal Hair Oil An Economical CosmeticDocument5 pages3.formulation and Evaluation of Poly Herbal Hair Oil An Economical CosmetictmlNo ratings yet
- Materials ConcreteDocument3 pagesMaterials ConcreteKarlo BosecNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Biotech 2.1-2018Document82 pagesPharmaceutical Biotech 2.1-2018An Ngoc HoaiNo ratings yet
- Model Questions PRM 2019Document24 pagesModel Questions PRM 2019Haris AyyazNo ratings yet
- 8.desinsectacion Por AnoxiaDocument20 pages8.desinsectacion Por AnoxiaSusanaMariel100% (1)
- Flow Control Devices Standing Valves / Test Tools: Europe Learning Centre WCP Training SchlumbergerDocument12 pagesFlow Control Devices Standing Valves / Test Tools: Europe Learning Centre WCP Training SchlumbergerAli Ali100% (1)
- CFB Thermal HeatDocument9 pagesCFB Thermal HeatbamzNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Assignment BookDocument28 pagesUnit 9 Assignment BookXenability0% (1)
- Gen Bio ReviewerDocument22 pagesGen Bio ReviewerKylle BenitezNo ratings yet
- Types of RockDocument21 pagesTypes of RockFain AloyanNo ratings yet
- f5 Chapter 1 Essay QDocument4 pagesf5 Chapter 1 Essay Qzhen1998No ratings yet
- Salt Analysis Scheme For StudentsDocument11 pagesSalt Analysis Scheme For StudentsTHE MAKER ELECTRONICSNo ratings yet
- GB Programme Chart: H F C J I K L MDocument2 pagesGB Programme Chart: H F C J I K L MJan ZemanNo ratings yet
- TYS Qns ClarificationsDocument4 pagesTYS Qns ClarificationsSharizah Bte Md AminNo ratings yet
- Thermostatic Valve AMOTDocument4 pagesThermostatic Valve AMOTaldino020203100% (1)