Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Capacitance
What Is Capacitance
Uploaded by
Sakinah Kamal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesCapacitance refers to a component's ability to store an electrical charge. Capacitors consist of conductive plates separated by an insulator and are used to store energy. As current flows through a circuit, the plates of a capacitor collect equal and opposite charges. The capacitor then retains the stored energy when the circuit is turned off, though some leakage may occur. Capacitance is measured in Farads and depends on factors like the distance between and size of the plates and the insulating quality of the dielectric material between the plates.
Original Description:
notes
Original Title
What is capacitance
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCapacitance refers to a component's ability to store an electrical charge. Capacitors consist of conductive plates separated by an insulator and are used to store energy. As current flows through a circuit, the plates of a capacitor collect equal and opposite charges. The capacitor then retains the stored energy when the circuit is turned off, though some leakage may occur. Capacitance is measured in Farads and depends on factors like the distance between and size of the plates and the insulating quality of the dielectric material between the plates.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesWhat Is Capacitance
What Is Capacitance
Uploaded by
Sakinah KamalCapacitance refers to a component's ability to store an electrical charge. Capacitors consist of conductive plates separated by an insulator and are used to store energy. As current flows through a circuit, the plates of a capacitor collect equal and opposite charges. The capacitor then retains the stored energy when the circuit is turned off, though some leakage may occur. Capacitance is measured in Farads and depends on factors like the distance between and size of the plates and the insulating quality of the dielectric material between the plates.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
What is capacitance?
Capacitance is the ability of a component or circuit to collect and store energy in
the form of an electrical charge.
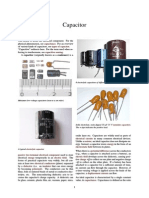
Capacitors are energy-storing devices available in many sizes and shapes. They
consist of two plates of conducting material (usually a thin metal) sandwiched
between an insulator made of ceramic, film, glass or other materials, even air.
The insulator is also known as a dielectric, and it boosts a capacitor's charging
capacity. Capacitors are sometimes called condensers in the automotive, marine
and aviation industries.
The internal plates are wired to two external terminals, which sometimes are long
and thin and can resemble tiny metallic antennae or legs. These terminals can be
plugged into a circuit.
Capacitors and batteries both store energy. While batteries release energy
gradually, capacitors discharge it quickly.
How does a capacitor work?
A capacitor collects energy (voltage) as current flows through an electrical
circuit. Both plates hold equal charges, and as the positive plate collects a charge,
an equal charge flows off the negative plate.
When the circuit is switched off, a capacitor retains the energy it has gathered,
though slight leakage usually occurs.
A variety of capacitors (shown in colour) in circuit board.
Capacitance is expressed as the ratio of the electric charge on each conductor to
the potential difference (i.e., voltage) between them.
The capacitance value of a capacitor is measured in farads (F), units named for
English physicist Michael Faraday (1791–1867).
A farad is a large quantity of capacitance. Most household electrical devices
include capacitors that produce only a fraction of a farad, often a thousandth of a
farad (or microfarad, µF) or as small as a picofarad (a trillionth, pF).
Supercapacitors, meanwhile, can store very large electrical charges of thousands
of farads.
How to increase capacitance
Capacitance can be increased when:
A capacitor's plates (conductors) are positioned closer together.
Larger plates offer more surface area.
The dielectric is the best possible insulator for the application.
You might also like
- Open System (1) ThermodynamicDocument38 pagesOpen System (1) ThermodynamicSakinah KamalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Capacitors: Tutorial 1 of 9Document37 pagesIntroduction To Capacitors: Tutorial 1 of 9Noli LlaneraNo ratings yet
- Capacitor DocumentationDocument2 pagesCapacitor DocumentationMidde ShekarNo ratings yet
- What Is Capacitance?Document2 pagesWhat Is Capacitance?Whiteshop PhNo ratings yet
- Philippine Electrical CodeDocument8 pagesPhilippine Electrical CodeAngel19No ratings yet
- Bản Tiếng Anh: I-Capacitor's Concept, structures and symbolsDocument3 pagesBản Tiếng Anh: I-Capacitor's Concept, structures and symbolslinh nguyễn thuỳNo ratings yet
- Capacitors Are Energy Storage Devices Which Have The Ability To Store AnDocument2 pagesCapacitors Are Energy Storage Devices Which Have The Ability To Store AnNeha GoyalNo ratings yet
- A CapacitorDocument1 pageA Capacitorrbharti59No ratings yet
- CapasitorDocument21 pagesCapasitorayu widiana putriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Capacitors and InductorsDocument16 pagesLesson 4 Capacitors and InductorsBlueprint MihNo ratings yet
- CapacitorsDocument13 pagesCapacitorsMelody Bagani FernandezNo ratings yet
- CapacitorDocument1 pageCapacitorVadim GoykhmanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Capacitors, Capacitance and ChargeDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Capacitors, Capacitance and ChargeZeeshan KhanNo ratings yet
- CapacitorsDocument17 pagesCapacitorsWani SageerNo ratings yet
- Grey Minimalist Business Project PresentationDocument19 pagesGrey Minimalist Business Project PresentationBeaver OrealNo ratings yet
- Capacitors: Widely Used in Many LanguagesDocument1 pageCapacitors: Widely Used in Many LanguagesmihikaNo ratings yet
- Pajaczarina e Ia 104 HandoutsDocument8 pagesPajaczarina e Ia 104 Handoutsjeanilauliga30No ratings yet
- Individual Presentation 1 Capasitor: Ceramic CapacitorsDocument6 pagesIndividual Presentation 1 Capasitor: Ceramic CapacitorsRifky OfficialNo ratings yet
- Capacitance: The Components of A CapacitorDocument7 pagesCapacitance: The Components of A CapacitorNaveenNo ratings yet
- Capacitors Capacitance: Electrical CircuitsDocument4 pagesCapacitors Capacitance: Electrical CircuitsVivek PatelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Capacitors: Electronics Tutorial About CapacitorsDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Capacitors: Electronics Tutorial About CapacitorsVenkatesh VenkiNo ratings yet
- Capacitors: Available Online atDocument21 pagesCapacitors: Available Online atOwen LuzNo ratings yet
- Capaciter Working PrincipalDocument2 pagesCapaciter Working PrincipalSanjivee SachinNo ratings yet
- Construction: 'Dielectric' InsulatorDocument4 pagesConstruction: 'Dielectric' InsulatorMinorNo ratings yet
- Idea of Capacitance & CapicitorDocument7 pagesIdea of Capacitance & CapicitoradimeghaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 đọc dịchDocument11 pagesUNIT 2 đọc dịchLê Công ThànhNo ratings yet
- Individual Presentation 1 Capasitor: Ceramic CapacitorsDocument3 pagesIndividual Presentation 1 Capasitor: Ceramic CapacitorsChoiril AthoNo ratings yet
- CapacitorsDocument3 pagesCapacitorsAteek PatilNo ratings yet
- What Is Capacitor and Capacitance - Types of Capacitors - Electrical4uDocument8 pagesWhat Is Capacitor and Capacitance - Types of Capacitors - Electrical4uteju2812No ratings yet
- BasementDocument19 pagesBasementProxima YusNo ratings yet
- Energy Electric Field Polarized Glass Ceramic Plastic Film Paper Mica Oxide LayersDocument6 pagesEnergy Electric Field Polarized Glass Ceramic Plastic Film Paper Mica Oxide LayersFariz Aditya PutraNo ratings yet
- Super Capacitors ConstructionDocument7 pagesSuper Capacitors ConstructionVivek BavdhaneNo ratings yet
- Passive Energy Electrostatically Electric Field Electrical Conductors Dielectric InsulatorDocument3 pagesPassive Energy Electrostatically Electric Field Electrical Conductors Dielectric InsulatorRenielDelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Capacitors: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadDocument27 pagesChapter 10 - Capacitors: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. Boylestadakankshag_13No ratings yet
- Introduction To Capacitors: ResistorDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Capacitors: ResistorDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- CapacitorDocument1 pageCapacitordwarika2006No ratings yet
- CapacitorDocument3 pagesCapacitorSiva KumarNo ratings yet
- Thea Angela Marie M.Garcia SSC X-EinsteinDocument4 pagesThea Angela Marie M.Garcia SSC X-EinsteinThea Angela GarciaNo ratings yet
- CapacitorsDocument86 pagesCapacitorsarunNo ratings yet
- Energy Storage Technology and ManagementDocument35 pagesEnergy Storage Technology and ManagementN.K. ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Capacitor InglesDocument7 pagesCapacitor Inglesguti5717No ratings yet
- Tiger Emt 1Document30 pagesTiger Emt 1CharavanaNo ratings yet
- Uper Capacitor: G.Sujith Reddy 17311A0473 Ece BDocument29 pagesUper Capacitor: G.Sujith Reddy 17311A0473 Ece BSUJITHNo ratings yet
- ComponentsDocument1 pageComponentsRyan TumananNo ratings yet
- Ntroduction To CapacitorsDocument5 pagesNtroduction To CapacitorsJohn Renzo Vibar ToribioNo ratings yet
- Capacitance and Its ApplicationDocument31 pagesCapacitance and Its ApplicationSuardi F. Seiei0% (1)
- EOTDocument57 pagesEOTabcNo ratings yet
- Capacitor - WikipediaDocument210 pagesCapacitor - WikipediaHarshit SaxenaNo ratings yet
- TLE-EPAS 10 WK5 - Name: - DateDocument6 pagesTLE-EPAS 10 WK5 - Name: - DateNoli LlaneraNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Types: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument1 pageCapacitor Types: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaraviNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Capacitors: ResistorDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Capacitors: ResistorsxpNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting CapacitanceDocument5 pagesFactors Affecting CapacitanceKrati PandeyNo ratings yet
- CapacitorDocument21 pagesCapacitordraganscribd12No ratings yet
- Capacitance and Mutual Capacitance, That Are Usually Both Designated by The SameDocument1 pageCapacitance and Mutual Capacitance, That Are Usually Both Designated by The SameAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- CapacitorDocument61 pagesCapacitorAngel Nuñez100% (1)
- Capacitor: 4 Electrolytic Capacitors of Different Voltages and CapacitanceDocument21 pagesCapacitor: 4 Electrolytic Capacitors of Different Voltages and CapacitanceRajat SinghNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentraviNo ratings yet
- 2Document83 pages2Kalyan Reddy AnuguNo ratings yet
- Capacitors: II. CompositionDocument5 pagesCapacitors: II. CompositionJustine jerome FloranteNo ratings yet
- New Rich Text DocumentDocument28 pagesNew Rich Text Documentstephen otienoNo ratings yet
- DJF21012 Sand Casting 1006Document15 pagesDJF21012 Sand Casting 1006Sakinah KamalNo ratings yet
- DJJ30082 Worksheet Milling ReportDocument9 pagesDJJ30082 Worksheet Milling ReportSakinah KamalNo ratings yet
- Djf21012 - Foundry Workshop: Worksheet ReportDocument11 pagesDjf21012 - Foundry Workshop: Worksheet ReportSakinah KamalNo ratings yet
- DJF21012 1006 CastingDocument16 pagesDJF21012 1006 CastingSakinah KamalNo ratings yet
- DJJ2022 - Electrical Technology: LAB 1: Analog MultimeterDocument8 pagesDJJ2022 - Electrical Technology: LAB 1: Analog MultimeterSakinah KamalNo ratings yet