Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Department of Computing: CS 212: Object Oriented Programming
Department of Computing: CS 212: Object Oriented Programming
Uploaded by
Muneeb AsifCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Checkpoint AnswersDocument28 pagesCheckpoint AnswersKristin Dikiciyan50% (4)
- Powershell ScriptingDocument789 pagesPowershell ScriptingMichael100% (4)
- ICP 2019 Assignment SolutionsDocument82 pagesICP 2019 Assignment SolutionsJP PradhanNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Syllabus 2019-20Document2 pagesBasic Electronics Syllabus 2019-20Sushma NageshNo ratings yet
- Java HomeworkDocument8 pagesJava HomeworkSreekanth NaiduNo ratings yet
- STV Lab Manual Viii - SemDocument31 pagesSTV Lab Manual Viii - Semayushgoud1234No ratings yet
- Ujjwal Oops FileDocument53 pagesUjjwal Oops FileFarhan KhanNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document32 pagesLec 2api-3727430No ratings yet
- Java - 16MDocument24 pagesJava - 16M20EUEE053- MADHUBALAN.SNo ratings yet
- JAVA Lab Manual (Vishesh Purkait)Document27 pagesJAVA Lab Manual (Vishesh Purkait)HUNTER RONYNo ratings yet
- Lab5 SE 120L Spring 2024Document7 pagesLab5 SE 120L Spring 2024karamict8No ratings yet
- Oop Assignment 01Document11 pagesOop Assignment 01sadainsikandar506No ratings yet
- UPES OOPS Lab FileDocument77 pagesUPES OOPS Lab Fileangad singhNo ratings yet
- Java Lab Manual Naman Sharma EN19CS301214Document42 pagesJava Lab Manual Naman Sharma EN19CS301214CSD Naman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Java (College File)Document32 pagesJava (College File)CSD Naman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Java Lab IntroductionDocument15 pagesJava Lab IntroductionRadhika VenkateshNo ratings yet
- CS2209 - Oops Lab ManualDocument62 pagesCS2209 - Oops Lab ManualSelva Kanmani100% (1)
- Final - OOPJ Lab ManualDocument36 pagesFinal - OOPJ Lab Manualchavanpraful0525No ratings yet
- Self Exercises 2Document27 pagesSelf Exercises 2budi_putraNo ratings yet
- My Java Practical File-2Document51 pagesMy Java Practical File-2skekheroNo ratings yet
- Dotnet Record New Cse DDocument54 pagesDotnet Record New Cse DKavin MartinNo ratings yet
- Oops RecordDocument46 pagesOops RecordNAGARAJ GNo ratings yet
- PF Lab Manual GoodDocument42 pagesPF Lab Manual GoodKhanNo ratings yet
- Department of Computer Science A.M.U., Aligarh: AssignmentDocument22 pagesDepartment of Computer Science A.M.U., Aligarh: AssignmentSyed Mubashshir AhmadNo ratings yet
- Programs - Java - IMPDocument10 pagesPrograms - Java - IMPHemil ShahNo ratings yet
- Java Lab ManualDocument27 pagesJava Lab ManualDr Narayana Swamy Ramaiah100% (1)
- Information Retrieval Practical: A Project ReportDocument16 pagesInformation Retrieval Practical: A Project Reportsahadev jagdish dhargalkarNo ratings yet
- File Location Link: CCC 101N: Computer Programming 1 Laboratory Activity: Programming BasicsDocument5 pagesFile Location Link: CCC 101N: Computer Programming 1 Laboratory Activity: Programming BasicsGuiaNo ratings yet
- I Am Sharing 'OOP Final' With YouDocument12 pagesI Am Sharing 'OOP Final' With YouRakib Mohammad AmmarNo ratings yet
- 351CS57-Java - Lab (1) FelixDocument22 pages351CS57-Java - Lab (1) FelixFelix MdazepaNo ratings yet
- Information Retrieval PracticalDocument16 pagesInformation Retrieval Practicalsahadev jagdish dhargalkar100% (1)
- ASP Project WorkDocument29 pagesASP Project WorkSamit TandukarNo ratings yet
- Software Technologies Java BasicsDocument50 pagesSoftware Technologies Java BasicsKrasimir AngelovNo ratings yet
- 43 Ce Shreyash Patel 1 3140705 Oop I Lab ManualDocument36 pages43 Ce Shreyash Patel 1 3140705 Oop I Lab ManualShreyash PatelNo ratings yet
- Practice Programs: On A Separate LineDocument8 pagesPractice Programs: On A Separate Linenithya elysiumNo ratings yet
- JAVA CODING AND C PROGRAMMING EXAMPLES - PROGRAMMING FOR BEGINNERS (BooksRack - Net)Document62 pagesJAVA CODING AND C PROGRAMMING EXAMPLES - PROGRAMMING FOR BEGINNERS (BooksRack - Net)Ivan BenginNo ratings yet
- Java ProgramsDocument26 pagesJava Programs19H51A1211-MARTHULA MADHAN GOPAL B.Tech IT (2019-23)No ratings yet
- BCS181076 Nabil MunirDocument8 pagesBCS181076 Nabil MunirNabil MunirNo ratings yet
- It Object Exercise 2Document14 pagesIt Object Exercise 2CpE LabNo ratings yet
- Java LabDocument50 pagesJava LabAnkit bahugunaNo ratings yet
- File Location Link: CCC 101N: Computer Programming 1 Laboratory Activity: Programming Basics & MethodsDocument4 pagesFile Location Link: CCC 101N: Computer Programming 1 Laboratory Activity: Programming Basics & MethodsGuiaNo ratings yet
- Icse Class X Computer Application ProjectDocument13 pagesIcse Class X Computer Application ProjectRakesh Kumar Agarwal lNo ratings yet
- Oops Lab Java ProgramsDocument12 pagesOops Lab Java ProgramsPrakash PeriyasamyNo ratings yet
- Programming QuestionsDocument12 pagesProgramming QuestionsEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Class Running Notes 12th MayDocument9 pagesClass Running Notes 12th Maynilesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Java Lab 4th SemDocument9 pagesJava Lab 4th SemVenkatadri VemulaNo ratings yet
- Java Notes 2Document33 pagesJava Notes 2AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Java Programming Laboratory Lab ManualDocument27 pagesJava Programming Laboratory Lab ManualM Joshua AlfredNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Cs6461 - Object Oriented Programming Lab: Valliammai Engineering College SRM Nagar, KattankulathurDocument30 pagesLab Manual Cs6461 - Object Oriented Programming Lab: Valliammai Engineering College SRM Nagar, Kattankulathursathyaraj palanisamyNo ratings yet
- Record PgmsDocument48 pagesRecord Pgmsgojothehonouredone99No ratings yet
- TanayDocument28 pagesTanayubutuvaioNo ratings yet
- JAVAnewfileDocument50 pagesJAVAnewfileGurkirat SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Java Program: 10/3/2019 (Sunday, 8.30 Am - 9.30 Am)Document61 pagesIntroduction To Java Program: 10/3/2019 (Sunday, 8.30 Am - 9.30 Am)Mohd Amran Md AliNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 ReportDocument33 pagesLab 7 ReportNIKESH RANABHATNo ratings yet
- 10Document18 pages10ihavedreams2017No ratings yet
- Java FileDocument33 pagesJava Fileakashbaloni10No ratings yet
- Java RecordDocument24 pagesJava RecordkarenNo ratings yet
- Dot NeT TechnologyDocument36 pagesDot NeT TechnologyPrijan KhadNo ratings yet
- Lab7 (Dealing With Polymorphism and Inheritance)Document18 pagesLab7 (Dealing With Polymorphism and Inheritance)Nicole ParallagNo ratings yet
- Python Advanced Programming: The Guide to Learn Python Programming. Reference with Exercises and Samples About Dynamical Programming, Multithreading, Multiprocessing, Debugging, Testing and MoreFrom EverandPython Advanced Programming: The Guide to Learn Python Programming. Reference with Exercises and Samples About Dynamical Programming, Multithreading, Multiprocessing, Debugging, Testing and MoreNo ratings yet
- 04 DLD Lec 04 Number Systems Dated 08 Mar 2021 SlidesDocument12 pages04 DLD Lec 04 Number Systems Dated 08 Mar 2021 SlidesMuneeb AsifNo ratings yet
- Lab-07 Muneeb Asif 334492Document13 pagesLab-07 Muneeb Asif 334492Muneeb AsifNo ratings yet
- Lab12 Voting Machine DesignDocument6 pagesLab12 Voting Machine DesignMuneeb AsifNo ratings yet
- CS212 - Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument30 pagesCS212 - Object Oriented ProgrammingMuneeb AsifNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Assignment 01 Spring 2021Document1 pageEvaluation Assignment 01 Spring 2021Muneeb AsifNo ratings yet
- Error Frame FormatDocument10 pagesError Frame FormatSandSofts CoNo ratings yet
- Mouly TestPlan TexilaDocument11 pagesMouly TestPlan TexilaSatheesh ManiNo ratings yet
- ITEC003 - Basic Programming (BSIT)Document3 pagesITEC003 - Basic Programming (BSIT)Harold LuceroNo ratings yet
- Samp LogDocument61 pagesSamp Logtamazi.imedashviliNo ratings yet
- Super Premium: February 2 0 1 7Document2 pagesSuper Premium: February 2 0 1 7Siddharth SanghaviNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis Using Python (Python For Beginners) - CloudxLabDocument152 pagesData Analysis Using Python (Python For Beginners) - CloudxLabGizliustaNo ratings yet
- AIASDocument5 pagesAIASAVMNo ratings yet
- TOTOLINK A3300R AccessPointDocument6 pagesTOTOLINK A3300R AccessPointIyan Yames BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Cruise Control Using Model Predictive ControllerDocument3 pagesAdaptive Cruise Control Using Model Predictive ControllerInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Adsp 01 Introduction PDFDocument11 pagesAdsp 01 Introduction PDFvondutchlgNo ratings yet
- Modular Alarm Platform 5000 Expert Training 2019 en v1Document77 pagesModular Alarm Platform 5000 Expert Training 2019 en v1nurkas999No ratings yet
- Karmani AghaDocument9 pagesKarmani Agha1hh2No ratings yet
- XVR User Manual V6.1.49.4Document80 pagesXVR User Manual V6.1.49.4Martín MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Utc Tda2030l Datasheet - RetroamplisDocument14 pagesUtc Tda2030l Datasheet - Retroamplisnanodocl5099No ratings yet
- Getting Started With Test Driven Development SlidesDocument20 pagesGetting Started With Test Driven Development Slidesadc 9No ratings yet
- Cambium Networks Learning3Document1 pageCambium Networks Learning3Leandro Jakko AyalaNo ratings yet
- Research On The Information Management System of University Student Status ArchivesDocument4 pagesResearch On The Information Management System of University Student Status ArchivesThea ToñacaoNo ratings yet
- USB 3.2 Revision 1.1Document569 pagesUSB 3.2 Revision 1.1szhouNo ratings yet
- Chapter-10 Parallel Programming Models, Languages and CompilersDocument5 pagesChapter-10 Parallel Programming Models, Languages and Compilersshamsiya saNo ratings yet
- Oose 6Document83 pagesOose 6Habtamu YihuneNo ratings yet
- Mapp100.200-Eng V2 50Document654 pagesMapp100.200-Eng V2 50IvailoNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics - ExcelDocument8 pagesBusiness Analytics - ExcelFERRY SIGNNo ratings yet
- Week 7&8Document8 pagesWeek 7&8setawo8674No ratings yet
- Purdue AI and ML Dual Master Program SlimUpDocument27 pagesPurdue AI and ML Dual Master Program SlimUpnancy_007No ratings yet
- AWS+Slides+Ch+03 FinalizedDocument80 pagesAWS+Slides+Ch+03 FinalizedAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- CIE-3 Alina DocumentationDocument33 pagesCIE-3 Alina DocumentationBTechMag comNo ratings yet
- Doc1 Thesis-1Document86 pagesDoc1 Thesis-1khayee661No ratings yet
- BACnet-modeling A Physical Device in BACnet ObjectsDocument4 pagesBACnet-modeling A Physical Device in BACnet ObjectsAliNo ratings yet
Department of Computing: CS 212: Object Oriented Programming
Department of Computing: CS 212: Object Oriented Programming
Uploaded by
Muneeb AsifOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Department of Computing: CS 212: Object Oriented Programming
Department of Computing: CS 212: Object Oriented Programming
Uploaded by
Muneeb AsifCopyright:
Available Formats
Department of Computing
CS 212: Object Oriented Programming
Class: BESE-11AB
Lab03: Flow Control [Loops, Decisions & Arrays]
Date: 24th March, 2021
Time: 2:00pm- 4:50pm,
09:00am-11:50 am
Instructor:
Ms. Hania Aslam
CS 212: Object Oriented Programming Page 1
Learning Objectives
The objective of this lab is to introduce the concepts of relational operators, if conditions, loops
and arrays. In particular, the students are assumed to have basic understanding of these concepts.
However, more focus is put on implementing these constructs in the Java language.
Activity #1.
Your first activity will be to test the if statements, relational and equality operators in Java.
Test the following program:
// Compare integers using if statements, relational operators
// and equality operators.
import java.util.Scanner; // program uses class Scanner
public class Comparison {
// main method begins execution of Java application
public static void main( String[] args )
{
// create Scanner to obtain input from command line
Scanner input = new Scanner( System.in );
int number1; // first number to compare
int number2; // second number to compare
System.out.print( "Enter first integer: " ); // prompt
number1 = input.nextInt(); // read first number from user
System.out.print( "Enter second integer: " ); // prompt
number2 = input.nextInt(); // read second number from user
if ( number1 == number2 )
System.out.printf( "%d == %d\n", number1, number2 );
if ( number1 != number2 )
System.out.printf( "%d != %d\n", number1, number2 );
if ( number1 < number2 )
System.out.printf( "%d < %d\n", number1, number2 );
if ( number1 > number2 )
System.out.printf( "%d > %d\n", number1, number2 );
if ( number1 <= number2 )
System.out.printf( "%d <= %d\n", number1, number2 );
if ( number1 >= number2 )
System.out.printf( "%d >= %d\n", number1, number2 );
CS 212: Object Oriented Programming Page 2
} // end method main
} // end class Comparison
Activity #2.
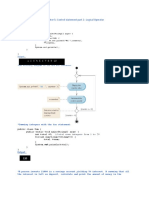
Do as directed in the comments at the start of Calculate class.
public class Calculate {
/**
* There is a mysterious error in this program. Identify this error.
* Is this a syntax error? or a logical one.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum;
int x;
x = 1; // initialize x to 1 for counting
sum = 0; // initialize sum to 0 for totaling
System.out.printf( "Going to calculate the sum" );
while ( x <= 10 ) // while x is less than or equal to 10
{
sum += x; // add x to sum
} // end while
System.out.printf( "The sum is: %d\n", sum );
}
}
Activity #3.
What does the following program print? Predict the output, before you actually try this program.
public class Mystery
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
int y;
int x = 1;
int total = 0;
while ( x <= 10 )
{
y = x * x;
System.out.println( y );
total += y;
++x;
} // end while
System.out.printf( "Total is %d\n", total );
} // end main
CS 212: Object Oriented Programming Page 3
} // end class Mystery
Activity #4.
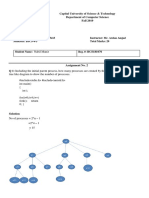
Try the following program and pay special attention to how arrays are created/used in Java.
What is the output of this program? How else can you use this program? Think!!
public class Cards {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String [] suit = { "Clubs", "Diamonds", "Hearts", "Spades"};
String [] rank =
{
"2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "10", "Jack", "Queen", "King", "Ace"
};
String [] deck = new String [suit.length * rank.length];
for (int i = 0; i < suit.length; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < rank.length; j++)
deck [rank.length * i + j] = rank [j] + " of " + suit[i];
for (int k = 0; k < (suit.length * rank.length); k++)
System.out.println(deck[k]);
}
}
Describe the outcome of the above code?
CS 212: Object Oriented Programming Page 4
Task #1:
Body Mass Index Calculator: The formula for calculating BMI is
Weight
BMI =
Height ∗ Height
Create a BMI calculator that reads the user’s weight in kilograms and height in meters, then
calculates and displays the user’s body mass index. Also, display the following information, using
control structures, so that the user can evaluate his/her BMI.
BMI VALUES:
Underweight: less than 18.5
Normal: between 18.5 and 24.9
Overweight: between 25 and 29.9
Obese: 30 or greater
Task #2:
Drivers are concerned with the mileage their automobiles get. One driver has kept track of several
trips by recording the kilometers driven and liters used for each tankful.
Develop a Java application that will input the kilometers driven and liters used (both as integers)
for each trip. The program should calculate and display the kilometers per liter obtained for each
trip and print the combined kilometers per liter obtained for all trips up to this point, as well.
All averaging calculations should produce floating-point results. Use class Scanner and sentinel-
controlled repetition to obtain the data from the user.
CS 212: Object Oriented Programming Page 5
Hand in
Hand in the source code from this lab at the appropriate location on the LMS system.
To Receive Credit
1. Comment your program heavily. Intelligent comments and a clean, readable formatting of
your code account for 20% of your grade.
2. The lab time is not intended as free time for working on other assignments.
CS 212: Object Oriented Programming Page 6
You might also like
- Checkpoint AnswersDocument28 pagesCheckpoint AnswersKristin Dikiciyan50% (4)
- Powershell ScriptingDocument789 pagesPowershell ScriptingMichael100% (4)
- ICP 2019 Assignment SolutionsDocument82 pagesICP 2019 Assignment SolutionsJP PradhanNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Syllabus 2019-20Document2 pagesBasic Electronics Syllabus 2019-20Sushma NageshNo ratings yet
- Java HomeworkDocument8 pagesJava HomeworkSreekanth NaiduNo ratings yet
- STV Lab Manual Viii - SemDocument31 pagesSTV Lab Manual Viii - Semayushgoud1234No ratings yet
- Ujjwal Oops FileDocument53 pagesUjjwal Oops FileFarhan KhanNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document32 pagesLec 2api-3727430No ratings yet
- Java - 16MDocument24 pagesJava - 16M20EUEE053- MADHUBALAN.SNo ratings yet
- JAVA Lab Manual (Vishesh Purkait)Document27 pagesJAVA Lab Manual (Vishesh Purkait)HUNTER RONYNo ratings yet
- Lab5 SE 120L Spring 2024Document7 pagesLab5 SE 120L Spring 2024karamict8No ratings yet
- Oop Assignment 01Document11 pagesOop Assignment 01sadainsikandar506No ratings yet
- UPES OOPS Lab FileDocument77 pagesUPES OOPS Lab Fileangad singhNo ratings yet
- Java Lab Manual Naman Sharma EN19CS301214Document42 pagesJava Lab Manual Naman Sharma EN19CS301214CSD Naman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Java (College File)Document32 pagesJava (College File)CSD Naman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Java Lab IntroductionDocument15 pagesJava Lab IntroductionRadhika VenkateshNo ratings yet
- CS2209 - Oops Lab ManualDocument62 pagesCS2209 - Oops Lab ManualSelva Kanmani100% (1)
- Final - OOPJ Lab ManualDocument36 pagesFinal - OOPJ Lab Manualchavanpraful0525No ratings yet
- Self Exercises 2Document27 pagesSelf Exercises 2budi_putraNo ratings yet
- My Java Practical File-2Document51 pagesMy Java Practical File-2skekheroNo ratings yet
- Dotnet Record New Cse DDocument54 pagesDotnet Record New Cse DKavin MartinNo ratings yet
- Oops RecordDocument46 pagesOops RecordNAGARAJ GNo ratings yet
- PF Lab Manual GoodDocument42 pagesPF Lab Manual GoodKhanNo ratings yet
- Department of Computer Science A.M.U., Aligarh: AssignmentDocument22 pagesDepartment of Computer Science A.M.U., Aligarh: AssignmentSyed Mubashshir AhmadNo ratings yet
- Programs - Java - IMPDocument10 pagesPrograms - Java - IMPHemil ShahNo ratings yet
- Java Lab ManualDocument27 pagesJava Lab ManualDr Narayana Swamy Ramaiah100% (1)
- Information Retrieval Practical: A Project ReportDocument16 pagesInformation Retrieval Practical: A Project Reportsahadev jagdish dhargalkarNo ratings yet
- File Location Link: CCC 101N: Computer Programming 1 Laboratory Activity: Programming BasicsDocument5 pagesFile Location Link: CCC 101N: Computer Programming 1 Laboratory Activity: Programming BasicsGuiaNo ratings yet
- I Am Sharing 'OOP Final' With YouDocument12 pagesI Am Sharing 'OOP Final' With YouRakib Mohammad AmmarNo ratings yet
- 351CS57-Java - Lab (1) FelixDocument22 pages351CS57-Java - Lab (1) FelixFelix MdazepaNo ratings yet
- Information Retrieval PracticalDocument16 pagesInformation Retrieval Practicalsahadev jagdish dhargalkar100% (1)
- ASP Project WorkDocument29 pagesASP Project WorkSamit TandukarNo ratings yet
- Software Technologies Java BasicsDocument50 pagesSoftware Technologies Java BasicsKrasimir AngelovNo ratings yet
- 43 Ce Shreyash Patel 1 3140705 Oop I Lab ManualDocument36 pages43 Ce Shreyash Patel 1 3140705 Oop I Lab ManualShreyash PatelNo ratings yet
- Practice Programs: On A Separate LineDocument8 pagesPractice Programs: On A Separate Linenithya elysiumNo ratings yet
- JAVA CODING AND C PROGRAMMING EXAMPLES - PROGRAMMING FOR BEGINNERS (BooksRack - Net)Document62 pagesJAVA CODING AND C PROGRAMMING EXAMPLES - PROGRAMMING FOR BEGINNERS (BooksRack - Net)Ivan BenginNo ratings yet
- Java ProgramsDocument26 pagesJava Programs19H51A1211-MARTHULA MADHAN GOPAL B.Tech IT (2019-23)No ratings yet
- BCS181076 Nabil MunirDocument8 pagesBCS181076 Nabil MunirNabil MunirNo ratings yet
- It Object Exercise 2Document14 pagesIt Object Exercise 2CpE LabNo ratings yet
- Java LabDocument50 pagesJava LabAnkit bahugunaNo ratings yet
- File Location Link: CCC 101N: Computer Programming 1 Laboratory Activity: Programming Basics & MethodsDocument4 pagesFile Location Link: CCC 101N: Computer Programming 1 Laboratory Activity: Programming Basics & MethodsGuiaNo ratings yet
- Icse Class X Computer Application ProjectDocument13 pagesIcse Class X Computer Application ProjectRakesh Kumar Agarwal lNo ratings yet
- Oops Lab Java ProgramsDocument12 pagesOops Lab Java ProgramsPrakash PeriyasamyNo ratings yet
- Programming QuestionsDocument12 pagesProgramming QuestionsEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Class Running Notes 12th MayDocument9 pagesClass Running Notes 12th Maynilesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Java Lab 4th SemDocument9 pagesJava Lab 4th SemVenkatadri VemulaNo ratings yet
- Java Notes 2Document33 pagesJava Notes 2AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Java Programming Laboratory Lab ManualDocument27 pagesJava Programming Laboratory Lab ManualM Joshua AlfredNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Cs6461 - Object Oriented Programming Lab: Valliammai Engineering College SRM Nagar, KattankulathurDocument30 pagesLab Manual Cs6461 - Object Oriented Programming Lab: Valliammai Engineering College SRM Nagar, Kattankulathursathyaraj palanisamyNo ratings yet
- Record PgmsDocument48 pagesRecord Pgmsgojothehonouredone99No ratings yet
- TanayDocument28 pagesTanayubutuvaioNo ratings yet
- JAVAnewfileDocument50 pagesJAVAnewfileGurkirat SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Java Program: 10/3/2019 (Sunday, 8.30 Am - 9.30 Am)Document61 pagesIntroduction To Java Program: 10/3/2019 (Sunday, 8.30 Am - 9.30 Am)Mohd Amran Md AliNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 ReportDocument33 pagesLab 7 ReportNIKESH RANABHATNo ratings yet
- 10Document18 pages10ihavedreams2017No ratings yet
- Java FileDocument33 pagesJava Fileakashbaloni10No ratings yet
- Java RecordDocument24 pagesJava RecordkarenNo ratings yet
- Dot NeT TechnologyDocument36 pagesDot NeT TechnologyPrijan KhadNo ratings yet
- Lab7 (Dealing With Polymorphism and Inheritance)Document18 pagesLab7 (Dealing With Polymorphism and Inheritance)Nicole ParallagNo ratings yet
- Python Advanced Programming: The Guide to Learn Python Programming. Reference with Exercises and Samples About Dynamical Programming, Multithreading, Multiprocessing, Debugging, Testing and MoreFrom EverandPython Advanced Programming: The Guide to Learn Python Programming. Reference with Exercises and Samples About Dynamical Programming, Multithreading, Multiprocessing, Debugging, Testing and MoreNo ratings yet
- 04 DLD Lec 04 Number Systems Dated 08 Mar 2021 SlidesDocument12 pages04 DLD Lec 04 Number Systems Dated 08 Mar 2021 SlidesMuneeb AsifNo ratings yet
- Lab-07 Muneeb Asif 334492Document13 pagesLab-07 Muneeb Asif 334492Muneeb AsifNo ratings yet
- Lab12 Voting Machine DesignDocument6 pagesLab12 Voting Machine DesignMuneeb AsifNo ratings yet
- CS212 - Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument30 pagesCS212 - Object Oriented ProgrammingMuneeb AsifNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Assignment 01 Spring 2021Document1 pageEvaluation Assignment 01 Spring 2021Muneeb AsifNo ratings yet
- Error Frame FormatDocument10 pagesError Frame FormatSandSofts CoNo ratings yet
- Mouly TestPlan TexilaDocument11 pagesMouly TestPlan TexilaSatheesh ManiNo ratings yet
- ITEC003 - Basic Programming (BSIT)Document3 pagesITEC003 - Basic Programming (BSIT)Harold LuceroNo ratings yet
- Samp LogDocument61 pagesSamp Logtamazi.imedashviliNo ratings yet
- Super Premium: February 2 0 1 7Document2 pagesSuper Premium: February 2 0 1 7Siddharth SanghaviNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis Using Python (Python For Beginners) - CloudxLabDocument152 pagesData Analysis Using Python (Python For Beginners) - CloudxLabGizliustaNo ratings yet
- AIASDocument5 pagesAIASAVMNo ratings yet
- TOTOLINK A3300R AccessPointDocument6 pagesTOTOLINK A3300R AccessPointIyan Yames BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Cruise Control Using Model Predictive ControllerDocument3 pagesAdaptive Cruise Control Using Model Predictive ControllerInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Adsp 01 Introduction PDFDocument11 pagesAdsp 01 Introduction PDFvondutchlgNo ratings yet
- Modular Alarm Platform 5000 Expert Training 2019 en v1Document77 pagesModular Alarm Platform 5000 Expert Training 2019 en v1nurkas999No ratings yet
- Karmani AghaDocument9 pagesKarmani Agha1hh2No ratings yet
- XVR User Manual V6.1.49.4Document80 pagesXVR User Manual V6.1.49.4Martín MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Utc Tda2030l Datasheet - RetroamplisDocument14 pagesUtc Tda2030l Datasheet - Retroamplisnanodocl5099No ratings yet
- Getting Started With Test Driven Development SlidesDocument20 pagesGetting Started With Test Driven Development Slidesadc 9No ratings yet
- Cambium Networks Learning3Document1 pageCambium Networks Learning3Leandro Jakko AyalaNo ratings yet
- Research On The Information Management System of University Student Status ArchivesDocument4 pagesResearch On The Information Management System of University Student Status ArchivesThea ToñacaoNo ratings yet
- USB 3.2 Revision 1.1Document569 pagesUSB 3.2 Revision 1.1szhouNo ratings yet
- Chapter-10 Parallel Programming Models, Languages and CompilersDocument5 pagesChapter-10 Parallel Programming Models, Languages and Compilersshamsiya saNo ratings yet
- Oose 6Document83 pagesOose 6Habtamu YihuneNo ratings yet
- Mapp100.200-Eng V2 50Document654 pagesMapp100.200-Eng V2 50IvailoNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics - ExcelDocument8 pagesBusiness Analytics - ExcelFERRY SIGNNo ratings yet
- Week 7&8Document8 pagesWeek 7&8setawo8674No ratings yet
- Purdue AI and ML Dual Master Program SlimUpDocument27 pagesPurdue AI and ML Dual Master Program SlimUpnancy_007No ratings yet
- AWS+Slides+Ch+03 FinalizedDocument80 pagesAWS+Slides+Ch+03 FinalizedAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- CIE-3 Alina DocumentationDocument33 pagesCIE-3 Alina DocumentationBTechMag comNo ratings yet
- Doc1 Thesis-1Document86 pagesDoc1 Thesis-1khayee661No ratings yet
- BACnet-modeling A Physical Device in BACnet ObjectsDocument4 pagesBACnet-modeling A Physical Device in BACnet ObjectsAliNo ratings yet