Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acido Ascorbico
Acido Ascorbico
Uploaded by
paulette machucaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acido Ascorbico
Acido Ascorbico
Uploaded by
paulette machucaCopyright:
Available Formats
Ascorbic acid EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 8.
Specific optical rotation (2.2.7) : + 20.5 to + 21.5.
Dissolve 2.50 g in water R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same
solvent.
Impurity E : maximum 0.2 per cent.
Test solution. Dissolve 0.25 g in 5 mL of water R. Neutralise
I. methyl 3-amino-4-methylthiophene-2-carboxylate using dilute sodium hydroxide solution R and add 1 mL of
(3-aminoarticaine), dilute acetic acid R and 0.5 mL of calcium chloride solution R.
Reference solution. Dissolve 70 mg of oxalic acid R in water R
and dilute to 500 mL with the same solvent ; to 5 mL of this
solution add 1 mL of dilute acetic acid R and 0.5 mL of calcium
chloride solution R.
Allow the solutions to stand for 1 h. Any opalescence in the
J. methyl 3-[[(2RS)-2-bromopropanoyl]amino]-4- test solution is not more intense than that in the reference
methylthiophene-2-carboxylate (bromo compound). solution.
Related substances. Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare
the solutions immediately before use.
01/2011:0253
Phosphate buffer solution. Dissolve 6.8 g of potassium
dihydrogen phosphate R in water R and dilute to about 175 mL
ASCORBIC ACID with the same solvent. Filter through a membrane filter
Acidum ascorbicum yaozh.com (nominal pore size 0.45 μm) and dilute to 1000 mL with
water R.
Test solution. Dissolve 0.500 g of the substance to be examined
in the mobile phase and dilute to 10.0 mL with the mobile
phase.
Reference solution (a). Dissolve 10.0 mg of ascorbic acid
impurity C CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 5.0 mL with
the mobile phase.
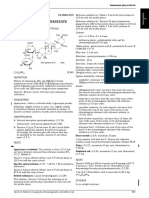
C 6H 8O 6 Mr 176.1
[50-81-7] Reference solution (b). Dissolve 5.0 mg of ascorbic acid
impurity D CRS and 5.0 mg of ascorbic acid CRS in the mobile
DEFINITION phase, add 2.5 mL of reference solution (a) and dilute to
(5R)-5-[(1S)-1,2-Dihydroxyethyl]-3,4-dihydroxyfuran-2(5H)- 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
one. Reference solution (c). Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to
Content : 99.0 per cent to 100.5 per cent. 200.0 mL with the mobile phase. Mix 1.0 mL of this solution
with 1.0 mL of reference solution (a).
CHARACTERS Column :
Appearance : white or almost white, crystalline powder or – size : l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm ;
colourless crystals, becoming discoloured on exposure to air – stationary phase : aminopropylsilyl silica gel for
and moisture. chromatography R (5 μm) ;
Solubility : freely soluble in water, sparingly soluble in ethanol
– temperature : 45 °C.
(96 per cent).
Mobile phase : phosphate buffer solution, acetonitrile R1
mp : about 190 °C, with decomposition.
(25:75 V/V).
IDENTIFICATION Flow rate : 1.0 mL/min.
First identification : B, C. Detection : spectrophotometer at 210 nm.
Second identification : A, C, D. Injection : 20 μL of the test solution and reference solutions (b)
A. Ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrophotometry and (c).
(2.2.25). Run time : 2.5 times the retention time of ascorbic acid.
Test solution. Dissolve 0.10 g in water R and dilute Identification of impurities: use the chromatogram obtained
immediately to 100.0 mL with the same solvent. Add with reference solution (b) to identify the peaks due to
1.0 mL of this solution to 10 mL of 0.1 M hydrochloric acid impurities C and D.
and dilute to 100.0 mL with water R. Relative retention with reference to ascorbic acid
Absorption maximum : at 243 nm, determined immediately (retention time = about 11 min): impurity D = about 0.4 ;
after dissolution. impurity C = about 1.7.
Specific absorbance at the absorption maximum : 545 to 585. System suitability :
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24). – resolution : minimum 3.0 between the peaks due to ascorbic
Comparison : ascorbic acid CRS. acid and impurity C in the chromatogram obtained with
C. pH (2.2.3) : 2.1 to 2.6 for solution S (see Tests). reference solution (c);
D. To 1 mL of solution S add 0.2 mL of dilute nitric acid R – signal-to-noise ratio : minimum 20 for the peak due to
and 0.2 mL of silver nitrate solution R2. A grey precipitate impurity C in the chromatogram obtained with reference
is formed. solution (b).
Limits :
TESTS – impurities C, D : for each impurity, not more than 1.5 times
Solution S. Dissolve 1.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram
dilute to 20 mL with the same solvent. obtained with reference solution (b) (0.15 per cent) ;
Appearance of solution. Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not – unspecified impurities : for each impurity, not more than the
more intensely coloured than reference solution BY7 (2.2.2, area of the peak due to ascorbic acid in the chromatogram
Method II). obtained with reference solution (b) (0.10 per cent) ;
1590 See the information section on general monographs (cover pages)
EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 8.0 Ascorbyl palmitate
– total of impurities other than C and D : not more than
twice the area of the peak due to ascorbic acid in the
chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.2 per
cent) ;
– disregard limit : 0.5 times the area of the peak due to D. methyl D-xylo-hex-2-ulosonate (methyl D-sorbosonate),
ascorbic acid in the chromatogram obtained with reference
solution (b) (0.05 per cent).
Copper : maximum 5 ppm.
Atomic absorption spectrometry (2.2.23, Method I).
E. oxalic acid,
Test solution. Dissolve 2.0 g in 0.1 M nitric acid and dilute to
25.0 mL with the same acid.
Reference solutions. Prepare the reference solutions (0.2 ppm,
0.4 ppm and 0.6 ppm) by diluting copper standard solution
(10 ppm Cu) R with 0.1 M nitric acid.
Source : copper hollow-cathode lamp.
F. (5R)-5-[(1R)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-3,4-dihydroxyfuran-
Wavelength : 324.8 nm. 2(5H)-one,
Atomisation device : air-acetylene flame.
Adjust the zero of the apparatus using 0.1 M nitric acid.
Iron : maximum 2 ppm.
yaozh.com
Atomic absorption spectrometry (2.2.23, Method I).
Test solution. Dissolve 5.0 g in 0.1 M nitric acid and dilute to
25.0 mL with the same acid. G. (2R)-2-[(2R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-oxo-2,5-dihydrofuran-2-yl]-
Reference solutions. Prepare the reference solutions (0.2 ppm, 2-hydroxyacetic acid,
0.4 ppm and 0.6 ppm) by diluting iron standard solution
(20 ppm Fe) R with 0.1 M nitric acid.
Source : iron hollow-cathode lamp.
Wavelength : 248.3 nm.
Atomisation device : air-acetylene flame.
Adjust the zero of the apparatus using 0.1 M nitric acid.
H. methyl (2R)-2-[(2R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-oxo-2,5-
Heavy metals (2.4.8) : maximum 10 ppm. dihydrofuran-2-yl]-2-hydroxyacetate.
Dissolve 2.0 g in water R and dilute to 20 mL with the same
solvent. 12 mL of the solution complies with test A. Prepare 04/2013:0807
the reference solution using lead standard solution (1 ppm
Pb) R. ASCORBYL PALMITATE
Sulfated ash (2.4.14) : maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on
1.0 g. Ascorbylis palmitas
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.150 g in a mixture of 10 mL of dilute sulfuric
acid R and 80 mL of carbon dioxide-free water R. Add 1 mL of
starch solution R. Titrate with 0.05 M iodine until a persistent
violet-blue colour is obtained.
1 mL of 0.05 M iodine is equivalent to 8.81 mg of C6H8O6.
C22H38O7 Mr 414.5
STORAGE [137-66-6]
In a non-metallic container, protected from light.
DEFINITION
IMPURITIES (2S)-2-[(2R)-3,4-Dihydroxy-5-oxo-2,5-dihydrofuran-2-yl]-2-
Specified impurities : C, D, E. hydroxyethyl hexadecanoate.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, Content : 98.0 per cent to 100.5 per cent (dried substance).
if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of
CHARACTERS
the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general
acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or Appearance : white or yellowish-white powder.
by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use Solubility : practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in
(2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities ethanol (96 per cent) and in methanol, practically insoluble
for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of in methylene chloride and in fatty oils.
impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use): A, F, G, H.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Specific optical rotation (see Tests).
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison : ascorbyl palmitate CRS.
A. 2-furaldehyde,
C. Dissolve about 10 mg in 5 mL of methanol R. The solution
decolourises dichlorophenolindophenol standard solution R.
TESTS
Solution S. Dissolve 2.50 g in methanol R and dilute to
C. D-xylo-hex-2-ulosonic acid (D-sorbosonic acid), 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
General Notices (1) apply to all monographs and other texts 1591
You might also like
- Citroen C-Elysee - Peugeot 301 (2012-2017) Service ManualDocument2,104 pagesCitroen C-Elysee - Peugeot 301 (2012-2017) Service ManualHector Alfonso100% (1)
- ASTM E1527 Downloaded 2014-04-14Document47 pagesASTM E1527 Downloaded 2014-04-14thescubatater100% (3)
- European Pharmacopoeia 8.0, Vol. 2 - Европейская Фармакопея 8.0, Том 2 (PDFDrive)Document2,133 pagesEuropean Pharmacopoeia 8.0, Vol. 2 - Европейская Фармакопея 8.0, Том 2 (PDFDrive)YuNo ratings yet
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Acid AscorbicDocument2 pagesAcid AscorbicIli MarinaNo ratings yet
- ZopicloneDocument2 pagesZopicloneaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- Ep7.0 02 1504Document2 pagesEp7.0 02 1504Sidahmed SiDo BouchenakNo ratings yet
- Apomorphine Hydrochloride HemihydrateDocument2 pagesApomorphine Hydrochloride HemihydrateNguyen Van ThaoNo ratings yet
- AdrenalineDocument2 pagesAdrenalinehailagarciaramirez8No ratings yet
- European Pharm. IbuprofenDocument3 pagesEuropean Pharm. IbuprofenMeuthia Sharah AyuninNo ratings yet
- Isoprenaline HydrochlorideDocument2 pagesIsoprenaline HydrochloridesofianesedkaouiNo ratings yet
- SORBITOLDocument2 pagesSORBITOLUrsula Rodrigues CabralNo ratings yet
- Amisulpride EP 11.0Document2 pagesAmisulpride EP 11.0noschNo ratings yet
- Propyl ParahydroxybenzoateDocument2 pagesPropyl ParahydroxybenzoateNam NguyenNo ratings yet
- Felodipine: FelodipinumDocument2 pagesFelodipine: FelodipinumIoana-Alexandra Lungu-NastaseNo ratings yet
- Peroxido Benzoila EP11.1Document2 pagesPeroxido Benzoila EP11.1Lucélia ScachetiNo ratings yet
- Quinine Hydrochloride 0018eDocument2 pagesQuinine Hydrochloride 0018eMark GoldbergNo ratings yet
- Carbidopa EP11.0Document3 pagesCarbidopa EP11.0hoangthingocanh1886No ratings yet
- Acetylsalicylic AcidDocument2 pagesAcetylsalicylic AcidkimberlydamarisNo ratings yet
- DexpanthenolDocument2 pagesDexpanthenolArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Chloroquine Sulfate: Chloroquini SulfasDocument2 pagesChloroquine Sulfate: Chloroquini SulfasEmna ToujaniNo ratings yet
- Sulpiride MonographieDocument3 pagesSulpiride MonographieMohamed DahmaneNo ratings yet
- Ep 8.0Document2 pagesEp 8.0Duyên PhạmNo ratings yet
- Sodium BenzoateDocument2 pagesSodium BenzoateUrsula Rodrigues CabralNo ratings yet
- Prednisone: PrednisonumDocument3 pagesPrednisone: PrednisonumMarcosNo ratings yet
- 2465e-Irbesartan E.PDocument2 pages2465e-Irbesartan E.PRyk BelNo ratings yet
- Zinc ChlorideDocument2 pagesZinc ChlorideAlexi Del Castillo MustaineNo ratings yet
- CHLORTALIDONEDocument2 pagesCHLORTALIDONEartemNo ratings yet
- BarbitalDocument2 pagesBarbitalOrlando David Medinueta De AvilaNo ratings yet
- Chloramphenicol EP 6.0Document2 pagesChloramphenicol EP 6.0calvin fabianusNo ratings yet
- Arginine AspartateDocument2 pagesArginine AspartateNguyen Van ThaoNo ratings yet
- AciclovirDocument2 pagesAciclovirTina BasarNo ratings yet
- Aminocaproic Acid: Acidum AminocaproicumDocument1 pageAminocaproic Acid: Acidum AminocaproicumArtem KulikovNo ratings yet
- Cefotaxime Sodium Eur - PHDocument3 pagesCefotaxime Sodium Eur - PHinha_azzahRaNo ratings yet
- PhenylbutazoneDocument3 pagesPhenylbutazoneThiago FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Zoledronic acid monohydrateDocument2 pagesZoledronic acid monohydrateaymenbiogalenicNo ratings yet
- 1611 - DiosminaDocument2 pages1611 - DiosminaGrenfell VPKNo ratings yet
- Enalapril MaleateDocument3 pagesEnalapril MaleateMulayam Singh YadavNo ratings yet
- Zinc AcexamateDocument2 pagesZinc AcexamateAlexi Del Castillo MustaineNo ratings yet
- Sodium CyclamateDocument2 pagesSodium Cyclamatemoriz52No ratings yet
- CBD PH - Eur MonographDocument3 pagesCBD PH - Eur MonographCecilia MonroyNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone Sodium PhosphateDocument4 pagesDexamethasone Sodium PhosphateMulayam Singh YadavNo ratings yet
- Potassium Chloride EPDocument1 pagePotassium Chloride EPASHOK KUMAR LENKANo ratings yet
- Atorvastatin Calcium Trihydrate Farmacopea BPDocument3 pagesAtorvastatin Calcium Trihydrate Farmacopea BPGuadalupe EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Ammonium GlycyrrhizateDocument2 pagesAmmonium GlycyrrhizateGopalaKrishnan SivaramanNo ratings yet
- Cetirizine DihydrochlorideDocument3 pagesCetirizine DihydrochloridePRADIKA HANDIWIANTANo ratings yet
- Enrofloxacin For Veterinary UseDocument3 pagesEnrofloxacin For Veterinary Usenguyentuanson167No ratings yet
- Ep5.0 02 609Document2 pagesEp5.0 02 609FaisalNo ratings yet
- Fosfomycin EP PDFDocument2 pagesFosfomycin EP PDFASHOK KUMAR LENKA100% (2)
- Fosfomycin EPDocument2 pagesFosfomycin EPASHOK KUMAR LENKANo ratings yet
- Esomeprazole Magnesium Dihydrate EP 11.0Document3 pagesEsomeprazole Magnesium Dihydrate EP 11.0noschNo ratings yet
- Betahistine MesilateDocument2 pagesBetahistine MesilateJuwita Permata SariNo ratings yet
- 2,4 Dichlorobenzyl AlcoholDocument2 pages2,4 Dichlorobenzyl AlcoholsamanehNo ratings yet
- Sodium Hydrogen Chloride EPDocument2 pagesSodium Hydrogen Chloride EPASHOK KUMAR LENKANo ratings yet
- PHE MonographieDocument3 pagesPHE Monographiebalkis hciniNo ratings yet
- Ziprasidone Hydrochloride MonohydrateDocument3 pagesZiprasidone Hydrochloride MonohydrateTiago Luiz TortellaNo ratings yet
- Ammonium GlycyrrhizateDocument2 pagesAmmonium GlycyrrhizateAndré C. de PaulaNo ratings yet
- PH - Eur. Acid UrsodeoxycolicDocument2 pagesPH - Eur. Acid UrsodeoxycolicGrigoras InaNo ratings yet
- Ciclamato de Sodio BPDocument4 pagesCiclamato de Sodio BPGerson Fernandez ChambiNo ratings yet
- Beta CaroteneDocument2 pagesBeta CaroteneValeria MarcuțăNo ratings yet
- GlycerolDocument2 pagesGlycerolUrsula Rodrigues CabralNo ratings yet
- Macrogol EPDocument3 pagesMacrogol EPASHOK KUMAR LENKANo ratings yet
- Literature Synopsis:: Brain-Based LearningDocument7 pagesLiterature Synopsis:: Brain-Based LearningJega SkyNo ratings yet
- Petron Plustm Formula 7 Diesel Engine ConditionerDocument2 pagesPetron Plustm Formula 7 Diesel Engine ConditionerwellblablablaNo ratings yet
- Minetruck MT436B 9851 2249 01N tcm835-1540890 PDFDocument4 pagesMinetruck MT436B 9851 2249 01N tcm835-1540890 PDFCristian Cabrera0% (1)
- 80cc (LT80 2002-2006)Document42 pages80cc (LT80 2002-2006)DanyNo ratings yet
- Wax Pattern: Type 1 (Medium Direct IntraoralDocument11 pagesWax Pattern: Type 1 (Medium Direct IntraoralMustafa SaßerNo ratings yet
- Workbook PDFDocument145 pagesWorkbook PDFRecordTrac - City of OaklandNo ratings yet
- SDS Biplas PL 4 MMDocument3 pagesSDS Biplas PL 4 MMAkhilNo ratings yet
- Celebrating The Life Of: Arthur Kinyanjui KimaniDocument32 pagesCelebrating The Life Of: Arthur Kinyanjui KimaniKinuthia MathewNo ratings yet
- HRM IN SERVICE SECTOR AssignmentDocument6 pagesHRM IN SERVICE SECTOR AssignmentANUSREE AnilkumarNo ratings yet
- Zamil Product Brochure PDFDocument30 pagesZamil Product Brochure PDFZameer KhanNo ratings yet
- Glamphouse Tents Brochure DigitalDocument2 pagesGlamphouse Tents Brochure Digitalgatrio2001No ratings yet
- Kemasan HNA NO Produk SyrupDocument2 pagesKemasan HNA NO Produk SyruprianNo ratings yet
- Quality Management Principles For Excellence: by - Sacchidanand Gogawale, Zen International SystemsDocument5 pagesQuality Management Principles For Excellence: by - Sacchidanand Gogawale, Zen International SystemsSanjeevani GogawaleNo ratings yet
- The Yoyo Intermittent Recovery Test in Basketball PlayersDocument7 pagesThe Yoyo Intermittent Recovery Test in Basketball PlayersAldo PrengaNo ratings yet
- BoQ For HVAC Requirement For ZPPLDocument2 pagesBoQ For HVAC Requirement For ZPPLBehram CiodiaNo ratings yet
- Modelling The Human Olfactory Stimulus Response FunctionDocument16 pagesModelling The Human Olfactory Stimulus Response Functionđạt lê tiếnNo ratings yet
- 30-Article Text-59-1-10-20201115Document9 pages30-Article Text-59-1-10-20201115Regita cahyani achmadNo ratings yet
- PolityDocument10 pagesPolityKedar BhasmeNo ratings yet
- Letter To Parents (RVHS Incident)Document2 pagesLetter To Parents (RVHS Incident)dontspreadaboutmeNo ratings yet
- The Challenge of CMC Regulatory Compliance For Biopharmaceuticals 4Th 4Th Edition John Geigert Full Chapter PDFDocument69 pagesThe Challenge of CMC Regulatory Compliance For Biopharmaceuticals 4Th 4Th Edition John Geigert Full Chapter PDFdoryamkoyna100% (3)
- Fundamentals of Freestyle Wrestling v1Document3 pagesFundamentals of Freestyle Wrestling v1keynote76No ratings yet
- Care Instructions Manual &: Induction CooktopDocument13 pagesCare Instructions Manual &: Induction Cooktopgenas7265No ratings yet
- EJMCM - Volume 7 - Issue 11 - Pages 9184-9190Document7 pagesEJMCM - Volume 7 - Issue 11 - Pages 9184-9190Akshay BeradNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportsDocument18 pagesLab ReportsLana RaedNo ratings yet
- 7 - 1 - The - MoleDocument17 pages7 - 1 - The - Molenaziya begumNo ratings yet
- 08 Proceduri de UrgentaDocument9 pages08 Proceduri de UrgentaSorescu Radu VasileNo ratings yet
- Ict - Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesIct - Lesson Planapi-249343709100% (2)
- Homeopathic Remedies For Hydronephrosis - Homeo ExpertDocument7 pagesHomeopathic Remedies For Hydronephrosis - Homeo ExpertDr. Kazy Habibur RahmanNo ratings yet