Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prepare Material, Tools and Equipment For Nursery Work 2 wk3
Prepare Material, Tools and Equipment For Nursery Work 2 wk3
Uploaded by
mervin tomasCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Masturbation Free EbookDocument5 pagesMasturbation Free EbookVishal Pandey75% (4)
- Tle 9 Las Quarter 4 Week 1Document5 pagesTle 9 Las Quarter 4 Week 1Mark Jim Torero100% (1)
- The Woman Speaks To The Man Who Has Employed Her SonDocument3 pagesThe Woman Speaks To The Man Who Has Employed Her SonSerena SulawammotNo ratings yet
- Activity Task Analysis BOW PDFDocument17 pagesActivity Task Analysis BOW PDFMaria Theresa Norada TorresNo ratings yet
- DLL TLE Crop ProductionDocument3 pagesDLL TLE Crop ProductionGinalynMaac100% (2)
- Quarter 2: Week 11 Lo 3. Handle Materials and Equipment TLE-AFAC10CW-11a-e-3Document16 pagesQuarter 2: Week 11 Lo 3. Handle Materials and Equipment TLE-AFAC10CW-11a-e-3Romeo Jr Vicente Ramirez100% (5)
- Technology and Livelihood Education: Agri Crop ProductionDocument23 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education: Agri Crop ProductionMaricris Pamulaklakin Almendras100% (2)
- Agri Crop Production Module 5Document19 pagesAgri Crop Production Module 5Losarim Yoj100% (1)
- DLL Tle - 10Document6 pagesDLL Tle - 10janineNo ratings yet
- DLL AgricultureDocument48 pagesDLL AgricultureElyssaRodriguezDomingoPascua90% (21)
- Prepare Materials, Tools, and Equipment For Nursery Work: Quarter 3-Learning Activity Sheet (LAS) For Grade 9 Week 2Document10 pagesPrepare Materials, Tools, and Equipment For Nursery Work: Quarter 3-Learning Activity Sheet (LAS) For Grade 9 Week 2mervin tomas100% (3)
- Agri-Fishery Arts (Agricultural Crops Production) Quarter4-Learning Activity Sheet (LAS) For Grade 10 Week 1Document8 pagesAgri-Fishery Arts (Agricultural Crops Production) Quarter4-Learning Activity Sheet (LAS) For Grade 10 Week 1mervin tomas100% (4)
- Infectious Disease Naplex QuestionsDocument3 pagesInfectious Disease Naplex QuestionsSARANYA0% (1)
- MPI Painting CodeDocument28 pagesMPI Painting CodeGhayas JawedNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing PDFDocument18 pagesFundamentals of Nursing PDFJamaica Manuel Iglesias100% (6)
- Enverzo, Jelyn / SV 1: Agricultural Crop Production NC IDocument3 pagesEnverzo, Jelyn / SV 1: Agricultural Crop Production NC IRomeo Jr Vicente Ramirez100% (1)
- Tle Afa Agriculture9 Pov q3 Las 3Document10 pagesTle Afa Agriculture9 Pov q3 Las 3Yves Kim Casido Cabanting100% (1)
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in TLE - 8Document2 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in TLE - 8Leah Pinili Blanco0% (1)
- DLL Tle - 10Document6 pagesDLL Tle - 10janineNo ratings yet
- TVL - Afa (Agricultural Crop Production NC I) : Activity Sheet Quarter 3 - C3.1-3 Handling Materials and EquipmentDocument11 pagesTVL - Afa (Agricultural Crop Production NC I) : Activity Sheet Quarter 3 - C3.1-3 Handling Materials and EquipmentBai MonNo ratings yet
- Grade Level: Grade 9/10 Subject: TLE (Agri Crop Production NC II)Document8 pagesGrade Level: Grade 9/10 Subject: TLE (Agri Crop Production NC II)Jane AlbaniaNo ratings yet
- Agri Crop Nine ThreeDocument4 pagesAgri Crop Nine ThreeRhylyahnaraRhon Palla PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Pest and Pathogens Final 2Document3 pagesLesson Plan For Pest and Pathogens Final 2api-317146092100% (2)
- Q3-Tle-Agri-9-Week-1-2 Final EditedDocument11 pagesQ3-Tle-Agri-9-Week-1-2 Final EditedJay Aldin RoseteNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work For Work Agricultural Crop Production Components Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) No. Ofdays TaughtDocument3 pagesBudget of Work For Work Agricultural Crop Production Components Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) No. Ofdays TaughtRonald CortezanoNo ratings yet
- Fertilizer LONGDocument6 pagesFertilizer LONGJaideHizoleSapul100% (2)
- Iii - Learning Activities Vocabulary List: MANUAL HANDLING - Worker's Hands Move On Individual Containers ManuallyDocument8 pagesIii - Learning Activities Vocabulary List: MANUAL HANDLING - Worker's Hands Move On Individual Containers ManuallyRomeo Jr Vicente Ramirez100% (2)
- DLP Agriculture-9 Tools, Area.Document12 pagesDLP Agriculture-9 Tools, Area.Jeraldine RepolloNo ratings yet
- Lo 1 - Acp G11Document13 pagesLo 1 - Acp G11Omar Perez Dela Merced100% (2)
- Activity Sheet Quarter 3 - Week 1: Tvl-Afa - (Agricultural Crops Production Ncii)Document8 pagesActivity Sheet Quarter 3 - Week 1: Tvl-Afa - (Agricultural Crops Production Ncii)Ma Luisa Ancog AngsincoNo ratings yet
- LO 4: Clean Up On Completion of Cropping Work According To Company Standard ProceduresDocument37 pagesLO 4: Clean Up On Completion of Cropping Work According To Company Standard ProceduresRizaLeighFiguesNo ratings yet
- Care of SeedlingsDocument20 pagesCare of SeedlingsMJ Hudierez Geal100% (4)
- Agricrop Production-Quarter 2.grade 10Document79 pagesAgricrop Production-Quarter 2.grade 10Henry James Paglinawan Poon100% (1)
- Module 6 Lesson 1Document14 pagesModule 6 Lesson 1Norico Yvonne50% (2)
- TLE 10 May V. OnaDocument4 pagesTLE 10 May V. OnaJoy Alea-Abrenica WalesNo ratings yet
- Summative Test W 3-4.edited - EditedDocument3 pagesSummative Test W 3-4.edited - EditedRomar Santos100% (1)
- DLL COT Fro ObservationDocument12 pagesDLL COT Fro ObservationShirline Salva FabeNo ratings yet
- Technology and Livelihood Education: Quarter 1, Wk.8 - Module 9Document19 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education: Quarter 1, Wk.8 - Module 9Kristel AcordonNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet - 1 - : Learning Area - Grade Level: Date: I. Introductory ConceptDocument10 pagesLearning Activity Sheet - 1 - : Learning Area - Grade Level: Date: I. Introductory ConceptjaslorNo ratings yet
- (Agri-Crop Production NC1) : Technology and Livelihood Education Quarter 4 - Module 1Document3 pages(Agri-Crop Production NC1) : Technology and Livelihood Education Quarter 4 - Module 1Jess Anthony Efondo100% (2)
- All About Seeds: Maiko Gil D. Hiwatig Trainer ACP NC I & IIDocument75 pagesAll About Seeds: Maiko Gil D. Hiwatig Trainer ACP NC I & IIMaiko Gil HiwatigNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Crop Production NC IDocument22 pagesAgricultural Crop Production NC IEJ Atsilab50% (2)
- DLL For Agricultural Crops Production February 5Document3 pagesDLL For Agricultural Crops Production February 5Jayson Balajadia100% (2)
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesA Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanRia LopezNo ratings yet
- Tle10 Afa Agricropprod q4 Mod2 Cleaninguponcompletion of Irrigationactivities v4Document33 pagesTle10 Afa Agricropprod q4 Mod2 Cleaninguponcompletion of Irrigationactivities v4Rene Rulete Mapalad100% (2)
- TLE-AGRI CROP 2Q-WEEK 6-Final (Procedures For Disposal of Wastee Materials)Document11 pagesTLE-AGRI CROP 2Q-WEEK 6-Final (Procedures For Disposal of Wastee Materials)Mary Grace Pesalbo100% (1)
- Technology and Livelihood Education Quarter 1, Wk.4 - Module 4 Afa-Agri Crop Production-Use of PPE in Agricultural CropDocument12 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education Quarter 1, Wk.4 - Module 4 Afa-Agri Crop Production-Use of PPE in Agricultural Cropjose ariel barroa jrNo ratings yet
- Q4 Tle 9 Week 2Document7 pagesQ4 Tle 9 Week 2Mj MartNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Tle-9: I-Objective/Learning CompetenciesDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Tle-9: I-Objective/Learning CompetenciesVal Basil100% (1)
- TLE10 - ACP-NC-II - G10 - Q1 - Mod4 - Prepare Production Plan According To Enterprise Requirements - v3Document24 pagesTLE10 - ACP-NC-II - G10 - Q1 - Mod4 - Prepare Production Plan According To Enterprise Requirements - v3carolina lizardo100% (1)
- Module 1Document12 pagesModule 1ashi ravenNo ratings yet
- Crop ProductionDocument3 pagesCrop ProductionArchie Añasco50% (2)
- Tle 9 19Document8 pagesTle 9 19Romeo Jr Vicente RamirezNo ratings yet
- Content and Learning Competencies Based On CGDocument7 pagesContent and Learning Competencies Based On CGAntonio CaballeroNo ratings yet
- SG LO2 Apply Fertilizer (GoldTown)Document2 pagesSG LO2 Apply Fertilizer (GoldTown)Mayiendlesslove WhiteNo ratings yet
- HENJEL - LE TVi - Q4 - Return To Storage Cabin or Dispose The Materials According To Company Standard Procedures and Supervisor's Instruction - 4.1Document9 pagesHENJEL - LE TVi - Q4 - Return To Storage Cabin or Dispose The Materials According To Company Standard Procedures and Supervisor's Instruction - 4.1HENJEL PERALES100% (1)
- Budget of Work: Grade Level: Subject: ComponentDocument10 pagesBudget of Work: Grade Level: Subject: ComponentMarycon Nacito100% (4)
- Methods of Soil SterilizationDocument38 pagesMethods of Soil SterilizationArianneNo ratings yet
- Tle Agriculture 9 3RD Quarter 3 and 4Document3 pagesTle Agriculture 9 3RD Quarter 3 and 4Mark Jim Torero100% (2)
- Demonstrate Care and Management of Seedlings: Lesson 3Document17 pagesDemonstrate Care and Management of Seedlings: Lesson 3Marycon Nacito100% (1)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in AgricultureDocument5 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in AgricultureReajean EscosaisNo ratings yet
- Sdo Aurora Tle10 Afa-Acp q4 m3Document13 pagesSdo Aurora Tle10 Afa-Acp q4 m3miel park100% (1)
- TLE (Agri Crop Production NC II) Grade Level 1 - 4Th QuarterDocument4 pagesTLE (Agri Crop Production NC II) Grade Level 1 - 4Th QuarterPhoebe JaeNo ratings yet
- Tle 9 Las Q3 M1Document21 pagesTle 9 Las Q3 M1Jhon Marvin Arienza100% (1)
- Y4 - Module 6 - Performing Post-Harvest OperationsDocument11 pagesY4 - Module 6 - Performing Post-Harvest OperationsKevin Bermudez AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Personal Protective Equipment: Use, Responsibility, and CostDocument7 pagesChapter 4 - Personal Protective Equipment: Use, Responsibility, and CostGiovanni Paolito YodicoNo ratings yet
- Complete Guide To PPEDocument5 pagesComplete Guide To PPEChiean CalebNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal Relationship and Communication - wk7Document14 pagesInterpersonal Relationship and Communication - wk7mervin tomas100% (1)
- (Demonstrating Correct Manual Handling Procedures & Techniques When Loading and Unloading Materials) Wk4Document8 pages(Demonstrating Correct Manual Handling Procedures & Techniques When Loading and Unloading Materials) Wk4mervin tomas100% (3)
- SAFE, APPROPRIATE & ENVIRONMENTALLY SOUND NURSERY - wk6Document8 pagesSAFE, APPROPRIATE & ENVIRONMENTALLY SOUND NURSERY - wk6mervin tomasNo ratings yet
- COMMON OHS Hazards, Risks, and Its Controls - wk4Document8 pagesCOMMON OHS Hazards, Risks, and Its Controls - wk4mervin tomasNo ratings yet
- Agri-Fishery Arts (Agricultural Crops Production) Quarter 3-Learning Activity Sheet (LAS) For Grade 9Document18 pagesAgri-Fishery Arts (Agricultural Crops Production) Quarter 3-Learning Activity Sheet (LAS) For Grade 9mervin tomasNo ratings yet
- Brief History of The SINHSDocument5 pagesBrief History of The SINHSmervin tomasNo ratings yet
- Module 1o MilDocument10 pagesModule 1o Milmervin tomasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 15 Motion Information and MediaDocument48 pagesLesson 15 Motion Information and Mediamervin tomas90% (10)
- Gujarat Cancer and Research Institute RatesDocument33 pagesGujarat Cancer and Research Institute RatesNimhans HospitalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project 2021-2022Document19 pagesChemistry Project 2021-2022Rudra SathwaraNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Facebook Usage On Academic PerformanceDocument2 pagesThe Impact of Facebook Usage On Academic PerformanceChristine Tabada PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Interactive Effect of Caste and Disability: An AnalysisDocument8 pagesInteractive Effect of Caste and Disability: An AnalysisIJELS Research JournalNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Lymph SystemDocument7 pagesPhysiology of Lymph SystemMwangi NyawiraNo ratings yet
- PintoDocument18 pagesPintosinagadianNo ratings yet
- Pro 3 Mplusdevipplus 07Document6 pagesPro 3 Mplusdevipplus 07daylavianNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry HomeworkDocument3 pagesInorganic Chemistry HomeworkAlpNo ratings yet
- Criticism Herzberg TheoryDocument3 pagesCriticism Herzberg TheoryCaroline NerbasNo ratings yet
- Dec. 4 2021 Bldg. Tech ReviewDocument58 pagesDec. 4 2021 Bldg. Tech Reviewadyjoy antonioNo ratings yet
- Background of The StudyDocument13 pagesBackground of The Studyjeffrey rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Social Studies jss2 First Term EXAMSDocument5 pagesSocial Studies jss2 First Term EXAMSalmightyfavouriteNo ratings yet
- Walking AidsDocument2 pagesWalking AidsSofia P. PanlilioNo ratings yet
- Covalence S1301-M Epoxy Primer: DescriptionDocument4 pagesCovalence S1301-M Epoxy Primer: DescriptionJuan Carlos Contreras CherresNo ratings yet
- Food and Nutrition Multiple Choice Questions With AnswersDocument6 pagesFood and Nutrition Multiple Choice Questions With AnswersMark Busalpa40% (5)
- Cp1018 Boric Acid MsdsDocument6 pagesCp1018 Boric Acid MsdsPanneer SelvamNo ratings yet
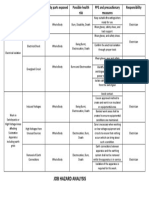
- Job Hazard AnalysisDocument1 pageJob Hazard AnalysisZaul tatingNo ratings yet
- PhilRice - Fertilizer CalculationDocument21 pagesPhilRice - Fertilizer CalculationMichelle Ann SoledadNo ratings yet
- 956-0302 Onan DFE Operator's and Parts Manual (4-1977)Document54 pages956-0302 Onan DFE Operator's and Parts Manual (4-1977)appplesNo ratings yet
- Thesis Van Ende FinalDocument277 pagesThesis Van Ende FinalArtem KravchenkoNo ratings yet
- XT Mobile Shear: Reference GuideDocument12 pagesXT Mobile Shear: Reference GuidePrudzNo ratings yet
- Case Study On A Highway Project: Environmental Impact AssesmentDocument10 pagesCase Study On A Highway Project: Environmental Impact AssesmentSRUTHI FRANCIS M.Tech Environmental Engineering 2020-2022No ratings yet
- Barcode v1Document31 pagesBarcode v1Desinta OctavianiNo ratings yet
- Neon NagaramDocument235 pagesNeon NagaramShammeer0% (1)
- Acceptance Criteria of Weld Defects As Per Different CodesDocument17 pagesAcceptance Criteria of Weld Defects As Per Different CodesMidhun K Chandrabose96% (25)
Prepare Material, Tools and Equipment For Nursery Work 2 wk3
Prepare Material, Tools and Equipment For Nursery Work 2 wk3
Uploaded by
mervin tomasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prepare Material, Tools and Equipment For Nursery Work 2 wk3
Prepare Material, Tools and Equipment For Nursery Work 2 wk3
Uploaded by
mervin tomasCopyright:
Available Formats
Name of Learner:_______________________________________________________________________
Grade Level:___________________________________________________________________________
Section:_______________________________________________________________________________
Date:_________________________________________________________________________________
Prepare Materials, Tools, and
Equipment for Nursery Work
(Selecting and checking the suitable personal
protective equipment)
Quarter 3- Learning Activity Sheet
(LAS) for Grade 9
Week 3
Crop Production
Prepare Materials, Tools, and Equipment for Nursery Work.
Name of Learner:_______________________________________________________________________
Grade Level:___________________________________________________________________________
Section:_______________________________________________________________________________
Date:_________________________________________________________________________________
LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET IN TECHNOLOGY AND LIVELIHOOD EDUCATION-9
I. Background Information for Learners:
In the previous topic, we discussed the following: You were able to describe/explain how
to avoid a manual handling injury when lifting.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal protective equipment (PPE) can reduce the number and severity of farm work related
injuries and illnesses. Personal protective equipment not only helps protect people but also improves
productivity and profits. Farmers and ranchers can share in these benefits by using the appropriate
protective equipment for themselves, family members and employees when the job and its potential
hazards call for it.
• Protect your head with a hard hat when performing construction work, trimming trees, repairing
machinery, and doing other jobs with head injury risks
• Use a sun safety hat (one with a wide brim and neck protection) to assist in the prevention of skin
cancer.
• Protect your vision with appropriate safety eyewear (safety glasses, goggles, face-shields) when
applying pesticides, fertilizers, working in the shop, or in heavy dust conditions.
• Protect your hearing with acoustic earmuffs or plugs when operating noisy equipment such as grain
dryers, feed grinders, older tractors, chain saws, etc.
Prepare Materials, Tools, and Equipment for Nursery Work.
•Protect your lungs with the correct respiratory equipment (dust masks, cartridge respirators, gas masks,
air packs) when working in dusty or moldy conditions, spray painting, applying chemicals, working in
bins, tanks, silos, and manure storage place.
Use, Responsibility, and Cost
Protection for head, eyes, ears, skin, feet, hands, respiratory system, or body is necessary under
certain hazardous working conditions to be in compliance with appropriate state safety laws. A general
rule to follow is “use of personal protective equipment is required when there is a reasonable probability
that injury or illness can be prevented by such equipment.”
Reasonable engineering controls, such as increased ventilation, are preferable to personal protective
equipment. Where employees are required to wear personal protective equipment, the cost of the
equipment should be considered a departmental expense.
Supervisors or instructors should consult with Occupational Health and Safety (OH&S) or
another qualified person to assess hazards in the areas where their employees work, to determine which
of these areas may require the use of personal protective equipment, and to select the type and quality
of the necessary equipment. It is the responsibility of all employees to wear personal protective
equipment if it has been determined that its use is required. It is also the supervisor or instructor’s
responsibility to ensure that workers, students, and visitors wear the protective equipment as specified.
Training
It is the responsibility of supervisors to provide training to their employees on identifying when
the selected personal protective equipment is necessary, on how to use the equipment, and on proper
care and maintenance of it.
Apparel
The purpose of protective apparel is to provide protection for the body from chemical
exposure, temperature extremes, and injury from sharp objects. Lab coats, chemical resistant
aprons, and disposable suits are examples of protective apparel. Proper selection should be based
on intended use.
Foot Protection
Appropriate footwear that is effective in preventing or limiting injury shall be worn where
employees are exposed to conditions which may cause foot injuries. As a rule, low-heeled, closed-
toe shoes shall be worn in all laboratory operations where there is a likelihood of exposure to spilled
chemicals. Where it is determined by a supervisor and OH&S that employees are exposed to a
moderate risk of foot injuries from falling objects or crushing actions, employees will be required
to wear safety-toe footwear.
Eye Protection
Eye injuries can translate into pain, loss of time, money and even your eyesight. Even a
slight loss or impairment of your vision is a tremendous price to pay for a moment of carelessness.
It is a dreadful reminder of what taking a risk can mean. Wear proper eye protection where eye
protection hazards are apparent and use common sense. Become acquainted with proper first aid
treatment for eye injuries and seek medical attention if there is an eye injury.
Prepare Materials, Tools, and Equipment for Nursery Work.
Causes of Eye Injuries
Spray cans are an increasing source of chemical eye injury, compounded by the force of
contact. Whether containing caustics or irritants, spray cans must be carefully used and kept away
from children.
Particles of rocks, soil, crop material or other foreign objects thrown from farm equipment
that chop or grinds can cause unexpected eye injury to the operator or bystander. Keep machinery
properly shielded. Keep away from the discharge path.
Eye injuries are more likely to occur when servicing farm equipment than when operating it. Simple
hand tools can cause severe eye injuries. Wear industrial strength eye protection when using hand
tools. Select the right tool for the job.
Eye Protection
Protective eyewear should be carefully selected, fitted, and cleaned. Protective eyewear
should be reasonably comfortable and fit snugly without interfering with the movements or vision
of the wearer. Protective eyewear should be durable, easily cleaned, and capable of being
disinfected. It should be kept clean and in good repair. To shield eyes from flying particles and
objects, wear industrial-rated glasses or sunglasses and flexible or cushion-fitting ventilated plastic
goggles that fit over ordinary eyeglasses. Adding side shields increases protection. Wear splash
goggles when handling and applying agricultural chemicals. Employees can also wear welding
goggles to protect their eyes from intense light and sparks. Full-face shields are another option for
eye protection and can be worn comfortably. Store eye protection in clean, dust-proof containers.
Safety Glasses and Goggles Appropriate eye protection shall be provided to and worn by
employees whose jobs expose them to eye hazards. Impact and/or chemical resistant goggles or
face shields provide additional protection and should be worn over normal corrective lenses unless
prescription safety glasses are worn.
To obtain prescription safety glasses an employee should follow this procedure:
Basic First Aid (Eye Injuries)
Proper first aid for eye injuries is critical. The method of first aid needed depends upon the
type of injury sustained. Let natural tears wash out specks or particles in the eye. Try not to rub the
eyes if possible. If this does not work, see a physician. For blows to the eye, apply cold compresses
for 15 minutes and again each hour as needed to reduce pain and swelling. If the blow were hard
enough to cause discoloration, see a physician. Internal damage could have occurred. For cuts and
punctures to the eye, do not do anything to the eye but bandage it lightly and seek a physician at
once.
Chemical burns on the eyes can be minor to very serious. Fresh water should be available
for irrigating eyes anywhere chemicals are used. If the eye comes in contact with any chemical, it
should be continuously flooded with water for at least 15 minutes. Do not put anything else in the
eye. See a physician and take the label or container of the chemical involved.
Prepare Materials, Tools, and Equipment for Nursery Work.
Hand Protection
Gloves provide protection for the hands and arms from chemicals, temperature extremes,
and abrasion. Their proper selection and use are vital to their ability to protect. This is especially
true when dealing with potential exposure to chemicals. It is important to remember that both the
thickness and the type of material in the glove affect its ability to serve as a barrier against a specific
chemical. Another factor in the proper selection of gloves is the wearer’s need for dexterity. It is
often advisable to reduce the size and thickness of the glove to allow the user to perform
manipulations safely. Caution is also required in using gloves around moving equipment. Gloves
should not be worn by anyone whose hands are exposed to moving parts in which they could be
caught.
Hearing Protectors
Hearing protectors come in two forms: plugs and muffs. Each has specific advantages based
on wearer comfort, work environment, and cost. Both are designed to reduce the noise to an
acceptable level, although this ability is based on the level and type of noise and on the type of
hearing protector.
Proper selection is important.
It is the responsibility of supervisors to investigate whether their work environments expose
employees to noise above the permissible level.
Nothing shall prevent the employee from wearing hearing protectors for reduction of annoyance
noise or high-level noise of short duration. Hearing protectors should always be considered
“personal” equipment and should not be used by other individuals, except for muffs that are
adequately cleaned and sanitized.
Helmets
Employees working in areas where there is possible danger of head injury from impact,
falling or flying objects, or electrical shock and burns must wear protective helmets. The typical
“hard hat” is the protective helmet of choice in most situations. Hard hats for short-term use can be
obtained from the Facilities Services Tool Room.
Respirators
The ability of respiratory protective equipment to provide adequate protection is based on
proper selection and fit and on training in the use of the respirator. Therefore, respirators which are
intended for protection against harmful dusts, fogs, fumes, mists, gases, smokes, sprays, or vapours
must not be obtained or worn by employees.
Persons should not be assigned to tasks requiring the use of respirators unless it has been
determined that they are physically able to perform the work and use the equipment. The local
physician shall determine what health and physical conditions are pertinent. The respirator user’s
medical status should be reviewed annually.
Prepare Materials, Tools, and Equipment for Nursery Work.
General Fall Protection Recommendations:
The following items are highly recommended to provide maximum protection of workers
and ensure compliance with regulations and standards. All work environments are different, so the
following are guidelines only. When establishing your own fall protection program, choose the
correct system to meet your needs.
Warnings: Always read all instructions and warnings contained on and in the product packaging
before using any fall protection equipment.
Inspection: All fall protection equipment should be inspected prior to use by following procedures
outlined in the manufacturer’s brochure.
Training: All workers shall be trained by a competent person in the proper use of fall protection
products.
Regulations: Understand all Federal, State, Local and Provincial regulations pertaining to fall
protection before using the equipment.
Rescue Pre-Planning: Minimizing the time between a fall occurrence and medical attention of the
workers is vitally important. A thorough rescue program should be established prior to
using fall protection equipment. Employers should provide for a prompt rescue should
a fall occur. Rescue procedures should be reviewed on a regular basis as part of the
company's overall safety training program.
Equipment Preferences: If there are any doubts about which fall protection product to use, choose
the following basic system:
Full-Body Harness with Sliding Back D-Ring Should a fall occur, the body harnesses would
distribute the load throughout the body instead of concentrating the forces on the
abdomen, as is the case with traditional body belts. The sliding back D-Ring will keep
the worker in an upright position in the event of a fall, which allows the worker to remain
as comfortable as possible while awaiting a rescue.
Shock-Absorbing Lanyards with Locking Snap Hooks Lanyards with built-in shock absorbers
reduce fall arresting forces by 65-80% compared to forces generated by traditional lanyards.
Locking snaps feature self-closing, self-locking keepers, which remain closed until unlocked and
pressed open for connection or disconnection.
Reliable Anchorage Points Anchor points or attachments must be capable of supporting 5000 lbs.
per worker. If there is any doubt about the strength of the attachment point -- DO NOT ATTACH.
Search for an alternative anchor point.
Types of PPE and protective clothing
Personal protective equipment and clothing can include:
overalls and protective aprons
headgear - safety helmets, wide brimmed hats to protect against the sun.
safety boots or shoes
safety glasses or goggles
gloves
respirators and masks
earmuffs and earpieces
Prepare Materials, Tools, and Equipment for Nursery Work.
Use of PPE
Key point: When hazards in the workplace cannot be eliminated or reduced by other risk
controls, employers must provide personal protective equipment and clothing (PPE).
Employees must be instructed in how to use PPE and clothing provided by the employer.
They should be told why the use of PPE is necessary before they start the job for which it has been
provided.
Where PPE is provided, you must use it as you have been instructed to do.
Employers should make sure that the PPE they purchase complies with the relevant appropriate
standard.
They must make sure that PPE is stored in a clean and fully operational condition, that it
can be easily found when needed and that it is safe from interference and damage.
PPE should be inspected regularly and before use to make sure it is in good working order.
Damaged or defective PPE must be reported at once. It must be tagged (to prevent its use until it
has been repaired) or thrown away and replaced.
II. Learning Competency with Code: At the end of the lesson the student will be able to:
Identifying the required materials, tools, and equipment based on lists provided and /or
authority’s instructions
III. Directions/Instructions:
• Follow the directions and/or instructions in the activities and exercises diligently and Answer
all the given tests and exercises.
IV. Exercises/Activities:
Exercise #1: Basing on the picture below, identify the different personal protective equipment.
Write your answer on the space provided. 2 points each.
Prepare Materials, Tools, and Equipment for Nursery Work.
Exercise #2: Crossword Puzzle
Exercise #3: Crossword Puzzle
Direction: Answer the puzzle below. Write your answer inside the box.
Prepare Materials, Tools, and Equipment for Nursery Work.
VI. Reflection:
1. I Learned that ….
2. I enjoyed most on …
3. I want to Learn more on …
III. Answer Key:
Exercise #1 (Answers may vary)
Exercise# 2
Exercise#3:
Prepare Materials, Tools, and Equipment for Nursery Work.
IV. References for Learners:
Prepared by:
MERVIN L. TOMAS
Subject Teacher
Prepare Materials, Tools, and Equipment for Nursery Work.
You might also like
- Masturbation Free EbookDocument5 pagesMasturbation Free EbookVishal Pandey75% (4)
- Tle 9 Las Quarter 4 Week 1Document5 pagesTle 9 Las Quarter 4 Week 1Mark Jim Torero100% (1)
- The Woman Speaks To The Man Who Has Employed Her SonDocument3 pagesThe Woman Speaks To The Man Who Has Employed Her SonSerena SulawammotNo ratings yet
- Activity Task Analysis BOW PDFDocument17 pagesActivity Task Analysis BOW PDFMaria Theresa Norada TorresNo ratings yet
- DLL TLE Crop ProductionDocument3 pagesDLL TLE Crop ProductionGinalynMaac100% (2)
- Quarter 2: Week 11 Lo 3. Handle Materials and Equipment TLE-AFAC10CW-11a-e-3Document16 pagesQuarter 2: Week 11 Lo 3. Handle Materials and Equipment TLE-AFAC10CW-11a-e-3Romeo Jr Vicente Ramirez100% (5)
- Technology and Livelihood Education: Agri Crop ProductionDocument23 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education: Agri Crop ProductionMaricris Pamulaklakin Almendras100% (2)
- Agri Crop Production Module 5Document19 pagesAgri Crop Production Module 5Losarim Yoj100% (1)
- DLL Tle - 10Document6 pagesDLL Tle - 10janineNo ratings yet
- DLL AgricultureDocument48 pagesDLL AgricultureElyssaRodriguezDomingoPascua90% (21)
- Prepare Materials, Tools, and Equipment For Nursery Work: Quarter 3-Learning Activity Sheet (LAS) For Grade 9 Week 2Document10 pagesPrepare Materials, Tools, and Equipment For Nursery Work: Quarter 3-Learning Activity Sheet (LAS) For Grade 9 Week 2mervin tomas100% (3)
- Agri-Fishery Arts (Agricultural Crops Production) Quarter4-Learning Activity Sheet (LAS) For Grade 10 Week 1Document8 pagesAgri-Fishery Arts (Agricultural Crops Production) Quarter4-Learning Activity Sheet (LAS) For Grade 10 Week 1mervin tomas100% (4)
- Infectious Disease Naplex QuestionsDocument3 pagesInfectious Disease Naplex QuestionsSARANYA0% (1)
- MPI Painting CodeDocument28 pagesMPI Painting CodeGhayas JawedNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing PDFDocument18 pagesFundamentals of Nursing PDFJamaica Manuel Iglesias100% (6)
- Enverzo, Jelyn / SV 1: Agricultural Crop Production NC IDocument3 pagesEnverzo, Jelyn / SV 1: Agricultural Crop Production NC IRomeo Jr Vicente Ramirez100% (1)
- Tle Afa Agriculture9 Pov q3 Las 3Document10 pagesTle Afa Agriculture9 Pov q3 Las 3Yves Kim Casido Cabanting100% (1)
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in TLE - 8Document2 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in TLE - 8Leah Pinili Blanco0% (1)
- DLL Tle - 10Document6 pagesDLL Tle - 10janineNo ratings yet
- TVL - Afa (Agricultural Crop Production NC I) : Activity Sheet Quarter 3 - C3.1-3 Handling Materials and EquipmentDocument11 pagesTVL - Afa (Agricultural Crop Production NC I) : Activity Sheet Quarter 3 - C3.1-3 Handling Materials and EquipmentBai MonNo ratings yet
- Grade Level: Grade 9/10 Subject: TLE (Agri Crop Production NC II)Document8 pagesGrade Level: Grade 9/10 Subject: TLE (Agri Crop Production NC II)Jane AlbaniaNo ratings yet
- Agri Crop Nine ThreeDocument4 pagesAgri Crop Nine ThreeRhylyahnaraRhon Palla PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Pest and Pathogens Final 2Document3 pagesLesson Plan For Pest and Pathogens Final 2api-317146092100% (2)
- Q3-Tle-Agri-9-Week-1-2 Final EditedDocument11 pagesQ3-Tle-Agri-9-Week-1-2 Final EditedJay Aldin RoseteNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work For Work Agricultural Crop Production Components Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) No. Ofdays TaughtDocument3 pagesBudget of Work For Work Agricultural Crop Production Components Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) No. Ofdays TaughtRonald CortezanoNo ratings yet
- Fertilizer LONGDocument6 pagesFertilizer LONGJaideHizoleSapul100% (2)
- Iii - Learning Activities Vocabulary List: MANUAL HANDLING - Worker's Hands Move On Individual Containers ManuallyDocument8 pagesIii - Learning Activities Vocabulary List: MANUAL HANDLING - Worker's Hands Move On Individual Containers ManuallyRomeo Jr Vicente Ramirez100% (2)
- DLP Agriculture-9 Tools, Area.Document12 pagesDLP Agriculture-9 Tools, Area.Jeraldine RepolloNo ratings yet
- Lo 1 - Acp G11Document13 pagesLo 1 - Acp G11Omar Perez Dela Merced100% (2)
- Activity Sheet Quarter 3 - Week 1: Tvl-Afa - (Agricultural Crops Production Ncii)Document8 pagesActivity Sheet Quarter 3 - Week 1: Tvl-Afa - (Agricultural Crops Production Ncii)Ma Luisa Ancog AngsincoNo ratings yet
- LO 4: Clean Up On Completion of Cropping Work According To Company Standard ProceduresDocument37 pagesLO 4: Clean Up On Completion of Cropping Work According To Company Standard ProceduresRizaLeighFiguesNo ratings yet
- Care of SeedlingsDocument20 pagesCare of SeedlingsMJ Hudierez Geal100% (4)
- Agricrop Production-Quarter 2.grade 10Document79 pagesAgricrop Production-Quarter 2.grade 10Henry James Paglinawan Poon100% (1)
- Module 6 Lesson 1Document14 pagesModule 6 Lesson 1Norico Yvonne50% (2)
- TLE 10 May V. OnaDocument4 pagesTLE 10 May V. OnaJoy Alea-Abrenica WalesNo ratings yet
- Summative Test W 3-4.edited - EditedDocument3 pagesSummative Test W 3-4.edited - EditedRomar Santos100% (1)
- DLL COT Fro ObservationDocument12 pagesDLL COT Fro ObservationShirline Salva FabeNo ratings yet
- Technology and Livelihood Education: Quarter 1, Wk.8 - Module 9Document19 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education: Quarter 1, Wk.8 - Module 9Kristel AcordonNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet - 1 - : Learning Area - Grade Level: Date: I. Introductory ConceptDocument10 pagesLearning Activity Sheet - 1 - : Learning Area - Grade Level: Date: I. Introductory ConceptjaslorNo ratings yet
- (Agri-Crop Production NC1) : Technology and Livelihood Education Quarter 4 - Module 1Document3 pages(Agri-Crop Production NC1) : Technology and Livelihood Education Quarter 4 - Module 1Jess Anthony Efondo100% (2)
- All About Seeds: Maiko Gil D. Hiwatig Trainer ACP NC I & IIDocument75 pagesAll About Seeds: Maiko Gil D. Hiwatig Trainer ACP NC I & IIMaiko Gil HiwatigNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Crop Production NC IDocument22 pagesAgricultural Crop Production NC IEJ Atsilab50% (2)
- DLL For Agricultural Crops Production February 5Document3 pagesDLL For Agricultural Crops Production February 5Jayson Balajadia100% (2)
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesA Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanRia LopezNo ratings yet
- Tle10 Afa Agricropprod q4 Mod2 Cleaninguponcompletion of Irrigationactivities v4Document33 pagesTle10 Afa Agricropprod q4 Mod2 Cleaninguponcompletion of Irrigationactivities v4Rene Rulete Mapalad100% (2)
- TLE-AGRI CROP 2Q-WEEK 6-Final (Procedures For Disposal of Wastee Materials)Document11 pagesTLE-AGRI CROP 2Q-WEEK 6-Final (Procedures For Disposal of Wastee Materials)Mary Grace Pesalbo100% (1)
- Technology and Livelihood Education Quarter 1, Wk.4 - Module 4 Afa-Agri Crop Production-Use of PPE in Agricultural CropDocument12 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education Quarter 1, Wk.4 - Module 4 Afa-Agri Crop Production-Use of PPE in Agricultural Cropjose ariel barroa jrNo ratings yet
- Q4 Tle 9 Week 2Document7 pagesQ4 Tle 9 Week 2Mj MartNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Tle-9: I-Objective/Learning CompetenciesDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Tle-9: I-Objective/Learning CompetenciesVal Basil100% (1)
- TLE10 - ACP-NC-II - G10 - Q1 - Mod4 - Prepare Production Plan According To Enterprise Requirements - v3Document24 pagesTLE10 - ACP-NC-II - G10 - Q1 - Mod4 - Prepare Production Plan According To Enterprise Requirements - v3carolina lizardo100% (1)
- Module 1Document12 pagesModule 1ashi ravenNo ratings yet
- Crop ProductionDocument3 pagesCrop ProductionArchie Añasco50% (2)
- Tle 9 19Document8 pagesTle 9 19Romeo Jr Vicente RamirezNo ratings yet
- Content and Learning Competencies Based On CGDocument7 pagesContent and Learning Competencies Based On CGAntonio CaballeroNo ratings yet
- SG LO2 Apply Fertilizer (GoldTown)Document2 pagesSG LO2 Apply Fertilizer (GoldTown)Mayiendlesslove WhiteNo ratings yet
- HENJEL - LE TVi - Q4 - Return To Storage Cabin or Dispose The Materials According To Company Standard Procedures and Supervisor's Instruction - 4.1Document9 pagesHENJEL - LE TVi - Q4 - Return To Storage Cabin or Dispose The Materials According To Company Standard Procedures and Supervisor's Instruction - 4.1HENJEL PERALES100% (1)
- Budget of Work: Grade Level: Subject: ComponentDocument10 pagesBudget of Work: Grade Level: Subject: ComponentMarycon Nacito100% (4)
- Methods of Soil SterilizationDocument38 pagesMethods of Soil SterilizationArianneNo ratings yet
- Tle Agriculture 9 3RD Quarter 3 and 4Document3 pagesTle Agriculture 9 3RD Quarter 3 and 4Mark Jim Torero100% (2)
- Demonstrate Care and Management of Seedlings: Lesson 3Document17 pagesDemonstrate Care and Management of Seedlings: Lesson 3Marycon Nacito100% (1)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in AgricultureDocument5 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in AgricultureReajean EscosaisNo ratings yet
- Sdo Aurora Tle10 Afa-Acp q4 m3Document13 pagesSdo Aurora Tle10 Afa-Acp q4 m3miel park100% (1)
- TLE (Agri Crop Production NC II) Grade Level 1 - 4Th QuarterDocument4 pagesTLE (Agri Crop Production NC II) Grade Level 1 - 4Th QuarterPhoebe JaeNo ratings yet
- Tle 9 Las Q3 M1Document21 pagesTle 9 Las Q3 M1Jhon Marvin Arienza100% (1)
- Y4 - Module 6 - Performing Post-Harvest OperationsDocument11 pagesY4 - Module 6 - Performing Post-Harvest OperationsKevin Bermudez AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Personal Protective Equipment: Use, Responsibility, and CostDocument7 pagesChapter 4 - Personal Protective Equipment: Use, Responsibility, and CostGiovanni Paolito YodicoNo ratings yet
- Complete Guide To PPEDocument5 pagesComplete Guide To PPEChiean CalebNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal Relationship and Communication - wk7Document14 pagesInterpersonal Relationship and Communication - wk7mervin tomas100% (1)
- (Demonstrating Correct Manual Handling Procedures & Techniques When Loading and Unloading Materials) Wk4Document8 pages(Demonstrating Correct Manual Handling Procedures & Techniques When Loading and Unloading Materials) Wk4mervin tomas100% (3)
- SAFE, APPROPRIATE & ENVIRONMENTALLY SOUND NURSERY - wk6Document8 pagesSAFE, APPROPRIATE & ENVIRONMENTALLY SOUND NURSERY - wk6mervin tomasNo ratings yet
- COMMON OHS Hazards, Risks, and Its Controls - wk4Document8 pagesCOMMON OHS Hazards, Risks, and Its Controls - wk4mervin tomasNo ratings yet
- Agri-Fishery Arts (Agricultural Crops Production) Quarter 3-Learning Activity Sheet (LAS) For Grade 9Document18 pagesAgri-Fishery Arts (Agricultural Crops Production) Quarter 3-Learning Activity Sheet (LAS) For Grade 9mervin tomasNo ratings yet
- Brief History of The SINHSDocument5 pagesBrief History of The SINHSmervin tomasNo ratings yet
- Module 1o MilDocument10 pagesModule 1o Milmervin tomasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 15 Motion Information and MediaDocument48 pagesLesson 15 Motion Information and Mediamervin tomas90% (10)
- Gujarat Cancer and Research Institute RatesDocument33 pagesGujarat Cancer and Research Institute RatesNimhans HospitalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project 2021-2022Document19 pagesChemistry Project 2021-2022Rudra SathwaraNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Facebook Usage On Academic PerformanceDocument2 pagesThe Impact of Facebook Usage On Academic PerformanceChristine Tabada PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Interactive Effect of Caste and Disability: An AnalysisDocument8 pagesInteractive Effect of Caste and Disability: An AnalysisIJELS Research JournalNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Lymph SystemDocument7 pagesPhysiology of Lymph SystemMwangi NyawiraNo ratings yet
- PintoDocument18 pagesPintosinagadianNo ratings yet
- Pro 3 Mplusdevipplus 07Document6 pagesPro 3 Mplusdevipplus 07daylavianNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry HomeworkDocument3 pagesInorganic Chemistry HomeworkAlpNo ratings yet
- Criticism Herzberg TheoryDocument3 pagesCriticism Herzberg TheoryCaroline NerbasNo ratings yet
- Dec. 4 2021 Bldg. Tech ReviewDocument58 pagesDec. 4 2021 Bldg. Tech Reviewadyjoy antonioNo ratings yet
- Background of The StudyDocument13 pagesBackground of The Studyjeffrey rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Social Studies jss2 First Term EXAMSDocument5 pagesSocial Studies jss2 First Term EXAMSalmightyfavouriteNo ratings yet
- Walking AidsDocument2 pagesWalking AidsSofia P. PanlilioNo ratings yet
- Covalence S1301-M Epoxy Primer: DescriptionDocument4 pagesCovalence S1301-M Epoxy Primer: DescriptionJuan Carlos Contreras CherresNo ratings yet
- Food and Nutrition Multiple Choice Questions With AnswersDocument6 pagesFood and Nutrition Multiple Choice Questions With AnswersMark Busalpa40% (5)
- Cp1018 Boric Acid MsdsDocument6 pagesCp1018 Boric Acid MsdsPanneer SelvamNo ratings yet
- Job Hazard AnalysisDocument1 pageJob Hazard AnalysisZaul tatingNo ratings yet
- PhilRice - Fertilizer CalculationDocument21 pagesPhilRice - Fertilizer CalculationMichelle Ann SoledadNo ratings yet
- 956-0302 Onan DFE Operator's and Parts Manual (4-1977)Document54 pages956-0302 Onan DFE Operator's and Parts Manual (4-1977)appplesNo ratings yet
- Thesis Van Ende FinalDocument277 pagesThesis Van Ende FinalArtem KravchenkoNo ratings yet
- XT Mobile Shear: Reference GuideDocument12 pagesXT Mobile Shear: Reference GuidePrudzNo ratings yet
- Case Study On A Highway Project: Environmental Impact AssesmentDocument10 pagesCase Study On A Highway Project: Environmental Impact AssesmentSRUTHI FRANCIS M.Tech Environmental Engineering 2020-2022No ratings yet
- Barcode v1Document31 pagesBarcode v1Desinta OctavianiNo ratings yet
- Neon NagaramDocument235 pagesNeon NagaramShammeer0% (1)
- Acceptance Criteria of Weld Defects As Per Different CodesDocument17 pagesAcceptance Criteria of Weld Defects As Per Different CodesMidhun K Chandrabose96% (25)