Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 viewsDeveloping A Science Lesson
Developing A Science Lesson
Uploaded by
RhoseThis document outlines how to develop effective science lessons and units. It discusses the importance of planning lessons in advance and considering factors like objectives, materials, and teaching methodology. The basic steps of a lesson plan are outlined as writing objectives, determining strategies, and incorporating aids. Key parts of a lesson plan include the objectives, subject matter, materials, background knowledge, lesson activities, and assessment. Sample lesson and unit plans are provided to demonstrate how to structure effective instructional content.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- TMN3705 - Assignment 02 - Tmn3705 - Unique No. 876529Document32 pagesTMN3705 - Assignment 02 - Tmn3705 - Unique No. 876529Roane Nel87% (15)
- Module in ProfEd-CDE (Curriculum Development and Evaluation With Emphasis On Trainers Methodology)Document49 pagesModule in ProfEd-CDE (Curriculum Development and Evaluation With Emphasis On Trainers Methodology)Kim So-Hyun89% (19)
- Lesson Planning PrinciplesDocument8 pagesLesson Planning PrinciplesRaymond Reynoso100% (1)
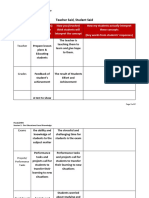
- Teacher Said, Student SaidDocument3 pagesTeacher Said, Student SaidRhose100% (2)
- Personal Management CurriculumDocument3 pagesPersonal Management Curriculumapi-302649043100% (1)
- Writing My First Learning Plan Learning TaskDocument22 pagesWriting My First Learning Plan Learning TaskKristine Joyce NodaloNo ratings yet
- Lesson Planning (EXTENSION)Document15 pagesLesson Planning (EXTENSION)select movieNo ratings yet
- Lesson Planningd2-3Document8 pagesLesson Planningd2-3demissedafursaNo ratings yet
- Developing Science LessonDocument20 pagesDeveloping Science LessonRowena CayogNo ratings yet
- Module 13 Lesson PlanningDocument15 pagesModule 13 Lesson PlanningNcle NaborNo ratings yet
- Worksheeet 4Document7 pagesWorksheeet 4Krisha rose donNo ratings yet
- Module 6-Instructional PlanningDocument12 pagesModule 6-Instructional PlanningTimothyLimNo ratings yet
- Lesson Planning: Prepared By: Ma. Elena K. ParaynoDocument14 pagesLesson Planning: Prepared By: Ma. Elena K. ParaynoJinky BanaagNo ratings yet
- Group 5 - AccountabilityDocument3 pagesGroup 5 - AccountabilityJay Rald SinampagaNo ratings yet
- 5 Common Types of Lesson PlansDocument12 pages5 Common Types of Lesson PlansJerome ManoguidNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Lesson 1 FLCTDocument14 pagesModule 4 Lesson 1 FLCTSheryll Jean UsoriaNo ratings yet
- Basic Parts of LPDocument35 pagesBasic Parts of LPTerrence MateoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Planning For Mother Tongue Instruction BEED 2A MTB OBIASCADocument6 pagesLesson Planning For Mother Tongue Instruction BEED 2A MTB OBIASCAJemiah Andrea DinoNo ratings yet
- Planning and Organizing For Instruction: Prepared By: Group 2 Flordela Sanchez Maria Leonora Patriarca Jherilyn ObcianaDocument21 pagesPlanning and Organizing For Instruction: Prepared By: Group 2 Flordela Sanchez Maria Leonora Patriarca Jherilyn ObcianaAmeil OrindayNo ratings yet
- UNIT IV-lesson 1-Lesson PlanDocument15 pagesUNIT IV-lesson 1-Lesson Planlalaabhi717No ratings yet
- Countdown Level Six Maths Teaching Guide PDFDocument52 pagesCountdown Level Six Maths Teaching Guide PDFkhalidnNo ratings yet
- LO 6 Revised - Planning Training Session 2Document12 pagesLO 6 Revised - Planning Training Session 2Kibrna Moges BantihunNo ratings yet
- 03 2017 How Will I Do This DTSDocument54 pages03 2017 How Will I Do This DTSChryz SantosNo ratings yet
- BEd-02Sem-DrRameshM-Teaching of Biological ScienceDocument84 pagesBEd-02Sem-DrRameshM-Teaching of Biological ScienceSabir JeeNo ratings yet
- Block - 3 Unit 4 Lesson Plans:-Meaning and Importance: StructureDocument26 pagesBlock - 3 Unit 4 Lesson Plans:-Meaning and Importance: StructureAlee MumtazNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plans:-Meaning and ImportanceDocument19 pagesLesson Plans:-Meaning and ImportanceJay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Method - Lesson Planning (As Per Revised Bloom Taxonomy)Document90 pagesMethod - Lesson Planning (As Per Revised Bloom Taxonomy)Dr. Tapan Kr. Dutta100% (1)
- LessonPlan ModuleDocument10 pagesLessonPlan ModuleEdel Guyuran VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Types of Lesson PlanDocument49 pagesTypes of Lesson PlanDondon100% (1)
- Policy Guidelines On Lesson Plan Writing For K-12Document21 pagesPolicy Guidelines On Lesson Plan Writing For K-12Jamena abbasNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesParts of A Lesson PlanJanine Panti TaboNo ratings yet
- Profesionalisme Guru - Curriculum PlanningDocument46 pagesProfesionalisme Guru - Curriculum Planningsszma100% (1)
- Lesson and Demo PlanDocument74 pagesLesson and Demo PlanVikasNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plansbsgenosas00520No ratings yet
- MC ELT 3 Week 7 ActivityDocument5 pagesMC ELT 3 Week 7 ActivitySherylyn BonaobraNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanningDocument18 pagesLesson PlanningAlliah BulanonNo ratings yet
- Al TSSC 2Document4 pagesAl TSSC 2Khen Lloyd Montes MansuetoNo ratings yet
- Standard-Based Lesson PlanningDocument22 pagesStandard-Based Lesson PlanningJessamen TinoNo ratings yet
- Instructional DesignsDocument4 pagesInstructional DesignsDipti PunjalNo ratings yet
- Less0n Plan by AhmedDocument29 pagesLess0n Plan by AhmedashrafalisqNo ratings yet
- Basic of Instructional Planning Escorido BEEDDocument6 pagesBasic of Instructional Planning Escorido BEEDJessica Egalam EscoridoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Planning (2 HRS) : Specific ObjectivesDocument14 pagesLesson Planning (2 HRS) : Specific ObjectivesShijiThomasNo ratings yet
- BEEd23 Week7Document15 pagesBEEd23 Week7JENNY ESCOBIDONo ratings yet
- N TSSC 2Document4 pagesN TSSC 2Khen Lloyd Montes MansuetoNo ratings yet
- For Example, Suppose I Chose A Subject "Earth Science". Then, I Will Download Its Curriculum Guide (Shown Below)Document4 pagesFor Example, Suppose I Chose A Subject "Earth Science". Then, I Will Download Its Curriculum Guide (Shown Below)Mark Jerome De la PenaNo ratings yet
- Unit II Lesson 5 SC-PEHDocument8 pagesUnit II Lesson 5 SC-PEHJewin OmarNo ratings yet
- TeachCur MidtermDocument9 pagesTeachCur Midtermellagenie.lagusNo ratings yet
- Tugas Presentasi Cdma AriDocument28 pagesTugas Presentasi Cdma AriAffifah Ambar RafsanjaniNo ratings yet
- Countdown Math 6Document51 pagesCountdown Math 6zahoormunir673771% (14)
- DLP TemplateDocument2 pagesDLP TemplateJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Planning Guide REDESIGNDocument24 pagesLesson Planning Guide REDESIGNdiNo ratings yet
- Text Book Development Ii CC 6553: Unit 6 Allied MaterialDocument35 pagesText Book Development Ii CC 6553: Unit 6 Allied MaterialGES ISLAMIA PATTOKINo ratings yet
- Parts of A Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesParts of A Lesson PlanSophiaNo ratings yet
- Designing The CurriculumDocument6 pagesDesigning The CurriculumNicole DyguasoNo ratings yet
- Planning For TeachingDocument24 pagesPlanning For TeachingshahshahzaibkazmiNo ratings yet
- Ambily Mam EducationDocument25 pagesAmbily Mam EducationVismayamaliekalNo ratings yet
- TTLM Development 2Document43 pagesTTLM Development 2Amanuel Tekalign100% (5)
- Don Honorio Ventura State University: College of EducationDocument15 pagesDon Honorio Ventura State University: College of EducationRizaline ManalangNo ratings yet
- Teaching of History: Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesTeaching of History: Lesson PlanAria ImadNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Lesson 3Document52 pagesModule 4 Lesson 3Jasper Mina GerminoNo ratings yet
- Leadership Skills: High School Manual: Violence Prevention ProgramFrom EverandLeadership Skills: High School Manual: Violence Prevention ProgramNo ratings yet
- Teachers Monitoring Form 2BDocument2 pagesTeachers Monitoring Form 2BRhoseNo ratings yet
- Finding Missing Term in A ProportionDocument23 pagesFinding Missing Term in A ProportionRhoseNo ratings yet
- T-Square-Compass - Drawing Table - Triangles - Drawing: Third Quarter Summative Test T.L.EDocument2 pagesT-Square-Compass - Drawing Table - Triangles - Drawing: Third Quarter Summative Test T.L.ERhoseNo ratings yet
- WS1 Teacher Said Student Said TemplateDocument2 pagesWS1 Teacher Said Student Said TemplateRhose100% (1)
- Module 3B Study Notebook ABRIOL JOEYDocument5 pagesModule 3B Study Notebook ABRIOL JOEYRhoseNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Study Notebook ABRIOL JOEY O.Document5 pagesModule 1 Study Notebook ABRIOL JOEY O.RhoseNo ratings yet
- Module 3A Study Notebook ABRIOL JOEYDocument14 pagesModule 3A Study Notebook ABRIOL JOEYRhoseNo ratings yet
- Foundational Elements of A Steam Learning Model For Elementary SCDocument146 pagesFoundational Elements of A Steam Learning Model For Elementary SCRhose100% (1)
- Traditional Method VS ModernDocument2 pagesTraditional Method VS ModernRhoseNo ratings yet
- 270298481Document84 pages270298481RhoseNo ratings yet
- Math 6 Week 3 Module PDFDocument9 pagesMath 6 Week 3 Module PDFRhoseNo ratings yet
- ST 1 - Tle 6 - Q1Document2 pagesST 1 - Tle 6 - Q1RhoseNo ratings yet
- Reporter: Maria Katrina S. MacapazDocument21 pagesReporter: Maria Katrina S. MacapazRhoseNo ratings yet
- Technical of Formulated FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTIONDocument5 pagesTechnical of Formulated FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTIONRhoseNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency (Mean, Median, Mode)Document6 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency (Mean, Median, Mode)RhoseNo ratings yet
- DLL - Tle 6 - Q4 - W2Document6 pagesDLL - Tle 6 - Q4 - W2RhoseNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument6 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogRhoseNo ratings yet
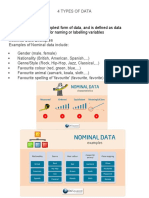
- Nominal Data Is The Simplest Form of Data, and Is Defined As Data That Is Used For Naming or Labelling VariablesDocument9 pagesNominal Data Is The Simplest Form of Data, and Is Defined As Data That Is Used For Naming or Labelling VariablesRhoseNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log: I. ObjectivesDocument5 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log: I. ObjectivesRhoseNo ratings yet
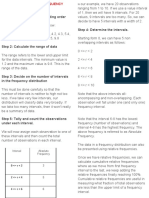
- How To Construct A Frequency Distribution DataDocument3 pagesHow To Construct A Frequency Distribution DataRhoseNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument6 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogRhoseNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument3 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogRhoseNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument5 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogRhoseNo ratings yet
- Answers To Lab 1 Access PDFDocument4 pagesAnswers To Lab 1 Access PDFKIKE RILEY HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Designing Modules For LearningDocument12 pagesDesigning Modules For LearningAmirullah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics in The Scope of Informatics Engineering EducationDocument7 pagesComputer Graphics in The Scope of Informatics Engineering EducationABDUL ASISNo ratings yet
- Parental Care and Academic PerformanceDocument75 pagesParental Care and Academic PerformanceGaniyu MosesNo ratings yet
- 255 Church ST, Fredericton, NB - Hjksz@stu - Ca - 902-476-0698Document3 pages255 Church ST, Fredericton, NB - Hjksz@stu - Ca - 902-476-0698api-331295760No ratings yet
- Guronasyon Foundation Inc. National High School: I. Project Title Wushu Club II. ProponentDocument2 pagesGuronasyon Foundation Inc. National High School: I. Project Title Wushu Club II. ProponentJeff Nieva CardelNo ratings yet
- Randy Sprick 7-26-2013 H2Document25 pagesRandy Sprick 7-26-2013 H2Region8ksNo ratings yet
- Sed Letters To Parents Principle and IntroDocument3 pagesSed Letters To Parents Principle and Introapi-268824137No ratings yet
- (The Cultural and Social Foundations of Education) Ted Newell (Auth.) - Five Paradigms ForDocument174 pages(The Cultural and Social Foundations of Education) Ted Newell (Auth.) - Five Paradigms ForNavisa DinniNo ratings yet
- Attendance Automation For Classroom Management - A Mobile Application Using Barcode Scanning and Facial Recognition SystemDocument7 pagesAttendance Automation For Classroom Management - A Mobile Application Using Barcode Scanning and Facial Recognition SystemKathy BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Individual Performance Commitment and Review Form: Sandra J. AgudoDocument4 pagesIndividual Performance Commitment and Review Form: Sandra J. Agudosharonlayson0% (1)
- The Family Book in CaliforniaDocument2 pagesThe Family Book in CaliforniancacensorshipNo ratings yet
- Republic Act. 7836 and 9293Document13 pagesRepublic Act. 7836 and 9293JC SabasNo ratings yet
- Action Research (Final)Document23 pagesAction Research (Final)CynthiaNo ratings yet
- Rommel C. Bautista, Ceso V School Division Superintendent Division of Cavite Trece Martires City, CaviteDocument2 pagesRommel C. Bautista, Ceso V School Division Superintendent Division of Cavite Trece Martires City, CaviteChristina Aguila NavarroNo ratings yet
- Speaking May 2023Document47 pagesSpeaking May 2023Trần Nhật Vân Ly Trần Khải LâmNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Education ContextsDocument15 pages21st Century Education ContextsJazz AcostaNo ratings yet
- Critical Material PDFDocument12 pagesCritical Material PDFTanya GoncearNo ratings yet
- Buku UmumDocument531 pagesBuku UmumZaen Yuki-Tech0% (2)
- The Teacher Trainer, Summer 2021Document29 pagesThe Teacher Trainer, Summer 2021Amir Esmaeili100% (1)
- Holdman - Classroom Management Implementation PlanDocument4 pagesHoldman - Classroom Management Implementation Planapi-210118947No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1GROUP1-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 1GROUP1-WPS OfficeAsia's MNo ratings yet
- Aaron Loeb: Preschool TeacherDocument1 pageAaron Loeb: Preschool TeacherRounok BiswasNo ratings yet
- Mead L Ela201 s237572 Assignment 2 Semester 1Document11 pagesMead L Ela201 s237572 Assignment 2 Semester 1api-249799367No ratings yet
- Positive Reinforcements PDFDocument49 pagesPositive Reinforcements PDFbabybear8910No ratings yet
- Contoh Pidato Bahasa Inggris Tentang Pendidikan KarakterDocument3 pagesContoh Pidato Bahasa Inggris Tentang Pendidikan KarakterYenti YenNo ratings yet
- Educ 622 Final Exam Answer SheetDocument8 pagesEduc 622 Final Exam Answer SheetNeneng Kuna100% (1)
- Syllabus 2023 Beed Peh Dennis HabalaDocument9 pagesSyllabus 2023 Beed Peh Dennis HabalaDennis HabalaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 ReflectionDocument1 pageAssignment 2 ReflectionCamlon KhajarNo ratings yet
Developing A Science Lesson
Developing A Science Lesson
Uploaded by
Rhose0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views16 pagesThis document outlines how to develop effective science lessons and units. It discusses the importance of planning lessons in advance and considering factors like objectives, materials, and teaching methodology. The basic steps of a lesson plan are outlined as writing objectives, determining strategies, and incorporating aids. Key parts of a lesson plan include the objectives, subject matter, materials, background knowledge, lesson activities, and assessment. Sample lesson and unit plans are provided to demonstrate how to structure effective instructional content.
Original Description:
Original Title
lesson6-130929212033-phpapp02
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines how to develop effective science lessons and units. It discusses the importance of planning lessons in advance and considering factors like objectives, materials, and teaching methodology. The basic steps of a lesson plan are outlined as writing objectives, determining strategies, and incorporating aids. Key parts of a lesson plan include the objectives, subject matter, materials, background knowledge, lesson activities, and assessment. Sample lesson and unit plans are provided to demonstrate how to structure effective instructional content.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views16 pagesDeveloping A Science Lesson
Developing A Science Lesson
Uploaded by
RhoseThis document outlines how to develop effective science lessons and units. It discusses the importance of planning lessons in advance and considering factors like objectives, materials, and teaching methodology. The basic steps of a lesson plan are outlined as writing objectives, determining strategies, and incorporating aids. Key parts of a lesson plan include the objectives, subject matter, materials, background knowledge, lesson activities, and assessment. Sample lesson and unit plans are provided to demonstrate how to structure effective instructional content.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 16
Developing a Science Lesson
A. The Need for Planning
Why should you plan early enough?
Assurance of an A good and reliable
effective procedure plan can definitely
and a complete enhance your self-
coverage of the subject confidence. Together
that you aim to teach. with a relaxed and
The activities that you “authoritative poise”
need to perform which will make it easy
together with the for you to control the
corresponding time class.
allotment will enable
you to progress
smoothly.
Your plan can be Experience gained
submitted to your from your daily lesson
department head or planning task can
head teacher for serve as well-earned
comments and qualification for future
suggestions, thus classroom activities.
adding to your learning
experience.
A systematically The choice of
conceived lesson plan appropriate
speaks of an orderly instructional materials
work and study habits can be decided and
of teachers worthy of included in the plan.
commendation.
B. Factors to Consider
In order to be able to prepare a complete lesson
plan, teachers should be ready with the
following:
Adequate knowledge Appropriate teaching
about the subject methodology to be
matter to be taught- followed- This shall
The number of be considered
concepts and depending on the
subtopics to be background
covered and the time knowledge, level of
allowed shall have understanding of the
been determined students and the
ahead of time. nature of the
concepts to be
taught.
Instructional materials and supplies – They
must be sufficient.
Equipment and laboratory tools to be used-
They must be ready to be operated during
the class hours.
Books references and other instructional
devices must be handy at the time of need.
C. Basic Steps and Parts of a Lesson
Plan
Steps in Preparing A Lesson Plan
1. Writing the objectives
2. Determining the teaching strategies
to be followed.
3. Identifying and incorporating
appropriate instructional aids to be
used
4. Designing the assignments
Parts of a Lesson Plan:
1. Objectives
2. Subject matter
3. Materials Needed
4. Background knowledge
5. Lesson proper
a. Preliminary activities
b. Motivation
c. Planned activities including questions for
discussions and direction
d. Concluding statement
6. Assessment
7. Assignment
D. Planning the Lesson
• The Lesson Objectives
• The Subject
• The Methodology
• The Materials and Equipment
• The Lesson Proper
• Assessment
• Additional Activities
• Assignment
E. Evaluating Effectiveness of the
Plan
1. General Classroom Atmosphere
2. Student Interactions
3. Student Performance
4. Self-evaluation
F. A Sample of Lesson Plan
G. A Sample of a Detailed Plan
H. Developing a Unit
The FORMAT
Title of the Unit
Relevance of the Unit
Concepts Included
Useful Background Knowledge
Instructional Objectives
Suggested Activities for the Unit
Summary
Evaluation of the Unit
References
Equipment/ Materials Needed
Culminating Activity
I. Developing a Course
Syllabus
Parts of a Syllabus
1. Course Number and Title
2. Course Description
3. Course Prerequisite
4. Course Credit
5. Course Objectives
6. Course Outline
7. Course Methodology
8. Time Allotment
9. Course Requirements
10. Suggested References
You might also like
- TMN3705 - Assignment 02 - Tmn3705 - Unique No. 876529Document32 pagesTMN3705 - Assignment 02 - Tmn3705 - Unique No. 876529Roane Nel87% (15)
- Module in ProfEd-CDE (Curriculum Development and Evaluation With Emphasis On Trainers Methodology)Document49 pagesModule in ProfEd-CDE (Curriculum Development and Evaluation With Emphasis On Trainers Methodology)Kim So-Hyun89% (19)
- Lesson Planning PrinciplesDocument8 pagesLesson Planning PrinciplesRaymond Reynoso100% (1)
- Teacher Said, Student SaidDocument3 pagesTeacher Said, Student SaidRhose100% (2)
- Personal Management CurriculumDocument3 pagesPersonal Management Curriculumapi-302649043100% (1)
- Writing My First Learning Plan Learning TaskDocument22 pagesWriting My First Learning Plan Learning TaskKristine Joyce NodaloNo ratings yet
- Lesson Planning (EXTENSION)Document15 pagesLesson Planning (EXTENSION)select movieNo ratings yet
- Lesson Planningd2-3Document8 pagesLesson Planningd2-3demissedafursaNo ratings yet
- Developing Science LessonDocument20 pagesDeveloping Science LessonRowena CayogNo ratings yet
- Module 13 Lesson PlanningDocument15 pagesModule 13 Lesson PlanningNcle NaborNo ratings yet
- Worksheeet 4Document7 pagesWorksheeet 4Krisha rose donNo ratings yet
- Module 6-Instructional PlanningDocument12 pagesModule 6-Instructional PlanningTimothyLimNo ratings yet
- Lesson Planning: Prepared By: Ma. Elena K. ParaynoDocument14 pagesLesson Planning: Prepared By: Ma. Elena K. ParaynoJinky BanaagNo ratings yet
- Group 5 - AccountabilityDocument3 pagesGroup 5 - AccountabilityJay Rald SinampagaNo ratings yet
- 5 Common Types of Lesson PlansDocument12 pages5 Common Types of Lesson PlansJerome ManoguidNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Lesson 1 FLCTDocument14 pagesModule 4 Lesson 1 FLCTSheryll Jean UsoriaNo ratings yet
- Basic Parts of LPDocument35 pagesBasic Parts of LPTerrence MateoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Planning For Mother Tongue Instruction BEED 2A MTB OBIASCADocument6 pagesLesson Planning For Mother Tongue Instruction BEED 2A MTB OBIASCAJemiah Andrea DinoNo ratings yet
- Planning and Organizing For Instruction: Prepared By: Group 2 Flordela Sanchez Maria Leonora Patriarca Jherilyn ObcianaDocument21 pagesPlanning and Organizing For Instruction: Prepared By: Group 2 Flordela Sanchez Maria Leonora Patriarca Jherilyn ObcianaAmeil OrindayNo ratings yet
- UNIT IV-lesson 1-Lesson PlanDocument15 pagesUNIT IV-lesson 1-Lesson Planlalaabhi717No ratings yet
- Countdown Level Six Maths Teaching Guide PDFDocument52 pagesCountdown Level Six Maths Teaching Guide PDFkhalidnNo ratings yet
- LO 6 Revised - Planning Training Session 2Document12 pagesLO 6 Revised - Planning Training Session 2Kibrna Moges BantihunNo ratings yet
- 03 2017 How Will I Do This DTSDocument54 pages03 2017 How Will I Do This DTSChryz SantosNo ratings yet
- BEd-02Sem-DrRameshM-Teaching of Biological ScienceDocument84 pagesBEd-02Sem-DrRameshM-Teaching of Biological ScienceSabir JeeNo ratings yet
- Block - 3 Unit 4 Lesson Plans:-Meaning and Importance: StructureDocument26 pagesBlock - 3 Unit 4 Lesson Plans:-Meaning and Importance: StructureAlee MumtazNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plans:-Meaning and ImportanceDocument19 pagesLesson Plans:-Meaning and ImportanceJay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Method - Lesson Planning (As Per Revised Bloom Taxonomy)Document90 pagesMethod - Lesson Planning (As Per Revised Bloom Taxonomy)Dr. Tapan Kr. Dutta100% (1)
- LessonPlan ModuleDocument10 pagesLessonPlan ModuleEdel Guyuran VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Types of Lesson PlanDocument49 pagesTypes of Lesson PlanDondon100% (1)
- Policy Guidelines On Lesson Plan Writing For K-12Document21 pagesPolicy Guidelines On Lesson Plan Writing For K-12Jamena abbasNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesParts of A Lesson PlanJanine Panti TaboNo ratings yet
- Profesionalisme Guru - Curriculum PlanningDocument46 pagesProfesionalisme Guru - Curriculum Planningsszma100% (1)
- Lesson and Demo PlanDocument74 pagesLesson and Demo PlanVikasNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plansbsgenosas00520No ratings yet
- MC ELT 3 Week 7 ActivityDocument5 pagesMC ELT 3 Week 7 ActivitySherylyn BonaobraNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanningDocument18 pagesLesson PlanningAlliah BulanonNo ratings yet
- Al TSSC 2Document4 pagesAl TSSC 2Khen Lloyd Montes MansuetoNo ratings yet
- Standard-Based Lesson PlanningDocument22 pagesStandard-Based Lesson PlanningJessamen TinoNo ratings yet
- Instructional DesignsDocument4 pagesInstructional DesignsDipti PunjalNo ratings yet
- Less0n Plan by AhmedDocument29 pagesLess0n Plan by AhmedashrafalisqNo ratings yet
- Basic of Instructional Planning Escorido BEEDDocument6 pagesBasic of Instructional Planning Escorido BEEDJessica Egalam EscoridoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Planning (2 HRS) : Specific ObjectivesDocument14 pagesLesson Planning (2 HRS) : Specific ObjectivesShijiThomasNo ratings yet
- BEEd23 Week7Document15 pagesBEEd23 Week7JENNY ESCOBIDONo ratings yet
- N TSSC 2Document4 pagesN TSSC 2Khen Lloyd Montes MansuetoNo ratings yet
- For Example, Suppose I Chose A Subject "Earth Science". Then, I Will Download Its Curriculum Guide (Shown Below)Document4 pagesFor Example, Suppose I Chose A Subject "Earth Science". Then, I Will Download Its Curriculum Guide (Shown Below)Mark Jerome De la PenaNo ratings yet
- Unit II Lesson 5 SC-PEHDocument8 pagesUnit II Lesson 5 SC-PEHJewin OmarNo ratings yet
- TeachCur MidtermDocument9 pagesTeachCur Midtermellagenie.lagusNo ratings yet
- Tugas Presentasi Cdma AriDocument28 pagesTugas Presentasi Cdma AriAffifah Ambar RafsanjaniNo ratings yet
- Countdown Math 6Document51 pagesCountdown Math 6zahoormunir673771% (14)
- DLP TemplateDocument2 pagesDLP TemplateJoon Bok NamleeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Planning Guide REDESIGNDocument24 pagesLesson Planning Guide REDESIGNdiNo ratings yet
- Text Book Development Ii CC 6553: Unit 6 Allied MaterialDocument35 pagesText Book Development Ii CC 6553: Unit 6 Allied MaterialGES ISLAMIA PATTOKINo ratings yet
- Parts of A Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesParts of A Lesson PlanSophiaNo ratings yet
- Designing The CurriculumDocument6 pagesDesigning The CurriculumNicole DyguasoNo ratings yet
- Planning For TeachingDocument24 pagesPlanning For TeachingshahshahzaibkazmiNo ratings yet
- Ambily Mam EducationDocument25 pagesAmbily Mam EducationVismayamaliekalNo ratings yet
- TTLM Development 2Document43 pagesTTLM Development 2Amanuel Tekalign100% (5)
- Don Honorio Ventura State University: College of EducationDocument15 pagesDon Honorio Ventura State University: College of EducationRizaline ManalangNo ratings yet
- Teaching of History: Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesTeaching of History: Lesson PlanAria ImadNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Lesson 3Document52 pagesModule 4 Lesson 3Jasper Mina GerminoNo ratings yet
- Leadership Skills: High School Manual: Violence Prevention ProgramFrom EverandLeadership Skills: High School Manual: Violence Prevention ProgramNo ratings yet
- Teachers Monitoring Form 2BDocument2 pagesTeachers Monitoring Form 2BRhoseNo ratings yet
- Finding Missing Term in A ProportionDocument23 pagesFinding Missing Term in A ProportionRhoseNo ratings yet
- T-Square-Compass - Drawing Table - Triangles - Drawing: Third Quarter Summative Test T.L.EDocument2 pagesT-Square-Compass - Drawing Table - Triangles - Drawing: Third Quarter Summative Test T.L.ERhoseNo ratings yet
- WS1 Teacher Said Student Said TemplateDocument2 pagesWS1 Teacher Said Student Said TemplateRhose100% (1)
- Module 3B Study Notebook ABRIOL JOEYDocument5 pagesModule 3B Study Notebook ABRIOL JOEYRhoseNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Study Notebook ABRIOL JOEY O.Document5 pagesModule 1 Study Notebook ABRIOL JOEY O.RhoseNo ratings yet
- Module 3A Study Notebook ABRIOL JOEYDocument14 pagesModule 3A Study Notebook ABRIOL JOEYRhoseNo ratings yet
- Foundational Elements of A Steam Learning Model For Elementary SCDocument146 pagesFoundational Elements of A Steam Learning Model For Elementary SCRhose100% (1)
- Traditional Method VS ModernDocument2 pagesTraditional Method VS ModernRhoseNo ratings yet
- 270298481Document84 pages270298481RhoseNo ratings yet
- Math 6 Week 3 Module PDFDocument9 pagesMath 6 Week 3 Module PDFRhoseNo ratings yet
- ST 1 - Tle 6 - Q1Document2 pagesST 1 - Tle 6 - Q1RhoseNo ratings yet
- Reporter: Maria Katrina S. MacapazDocument21 pagesReporter: Maria Katrina S. MacapazRhoseNo ratings yet
- Technical of Formulated FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTIONDocument5 pagesTechnical of Formulated FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTIONRhoseNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency (Mean, Median, Mode)Document6 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency (Mean, Median, Mode)RhoseNo ratings yet
- DLL - Tle 6 - Q4 - W2Document6 pagesDLL - Tle 6 - Q4 - W2RhoseNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument6 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogRhoseNo ratings yet
- Nominal Data Is The Simplest Form of Data, and Is Defined As Data That Is Used For Naming or Labelling VariablesDocument9 pagesNominal Data Is The Simplest Form of Data, and Is Defined As Data That Is Used For Naming or Labelling VariablesRhoseNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log: I. ObjectivesDocument5 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log: I. ObjectivesRhoseNo ratings yet
- How To Construct A Frequency Distribution DataDocument3 pagesHow To Construct A Frequency Distribution DataRhoseNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument6 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogRhoseNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument3 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogRhoseNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument5 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogRhoseNo ratings yet
- Answers To Lab 1 Access PDFDocument4 pagesAnswers To Lab 1 Access PDFKIKE RILEY HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Designing Modules For LearningDocument12 pagesDesigning Modules For LearningAmirullah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics in The Scope of Informatics Engineering EducationDocument7 pagesComputer Graphics in The Scope of Informatics Engineering EducationABDUL ASISNo ratings yet
- Parental Care and Academic PerformanceDocument75 pagesParental Care and Academic PerformanceGaniyu MosesNo ratings yet
- 255 Church ST, Fredericton, NB - Hjksz@stu - Ca - 902-476-0698Document3 pages255 Church ST, Fredericton, NB - Hjksz@stu - Ca - 902-476-0698api-331295760No ratings yet
- Guronasyon Foundation Inc. National High School: I. Project Title Wushu Club II. ProponentDocument2 pagesGuronasyon Foundation Inc. National High School: I. Project Title Wushu Club II. ProponentJeff Nieva CardelNo ratings yet
- Randy Sprick 7-26-2013 H2Document25 pagesRandy Sprick 7-26-2013 H2Region8ksNo ratings yet
- Sed Letters To Parents Principle and IntroDocument3 pagesSed Letters To Parents Principle and Introapi-268824137No ratings yet
- (The Cultural and Social Foundations of Education) Ted Newell (Auth.) - Five Paradigms ForDocument174 pages(The Cultural and Social Foundations of Education) Ted Newell (Auth.) - Five Paradigms ForNavisa DinniNo ratings yet
- Attendance Automation For Classroom Management - A Mobile Application Using Barcode Scanning and Facial Recognition SystemDocument7 pagesAttendance Automation For Classroom Management - A Mobile Application Using Barcode Scanning and Facial Recognition SystemKathy BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Individual Performance Commitment and Review Form: Sandra J. AgudoDocument4 pagesIndividual Performance Commitment and Review Form: Sandra J. Agudosharonlayson0% (1)
- The Family Book in CaliforniaDocument2 pagesThe Family Book in CaliforniancacensorshipNo ratings yet
- Republic Act. 7836 and 9293Document13 pagesRepublic Act. 7836 and 9293JC SabasNo ratings yet
- Action Research (Final)Document23 pagesAction Research (Final)CynthiaNo ratings yet
- Rommel C. Bautista, Ceso V School Division Superintendent Division of Cavite Trece Martires City, CaviteDocument2 pagesRommel C. Bautista, Ceso V School Division Superintendent Division of Cavite Trece Martires City, CaviteChristina Aguila NavarroNo ratings yet
- Speaking May 2023Document47 pagesSpeaking May 2023Trần Nhật Vân Ly Trần Khải LâmNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Education ContextsDocument15 pages21st Century Education ContextsJazz AcostaNo ratings yet
- Critical Material PDFDocument12 pagesCritical Material PDFTanya GoncearNo ratings yet
- Buku UmumDocument531 pagesBuku UmumZaen Yuki-Tech0% (2)
- The Teacher Trainer, Summer 2021Document29 pagesThe Teacher Trainer, Summer 2021Amir Esmaeili100% (1)
- Holdman - Classroom Management Implementation PlanDocument4 pagesHoldman - Classroom Management Implementation Planapi-210118947No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1GROUP1-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 1GROUP1-WPS OfficeAsia's MNo ratings yet
- Aaron Loeb: Preschool TeacherDocument1 pageAaron Loeb: Preschool TeacherRounok BiswasNo ratings yet
- Mead L Ela201 s237572 Assignment 2 Semester 1Document11 pagesMead L Ela201 s237572 Assignment 2 Semester 1api-249799367No ratings yet
- Positive Reinforcements PDFDocument49 pagesPositive Reinforcements PDFbabybear8910No ratings yet
- Contoh Pidato Bahasa Inggris Tentang Pendidikan KarakterDocument3 pagesContoh Pidato Bahasa Inggris Tentang Pendidikan KarakterYenti YenNo ratings yet
- Educ 622 Final Exam Answer SheetDocument8 pagesEduc 622 Final Exam Answer SheetNeneng Kuna100% (1)
- Syllabus 2023 Beed Peh Dennis HabalaDocument9 pagesSyllabus 2023 Beed Peh Dennis HabalaDennis HabalaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 ReflectionDocument1 pageAssignment 2 ReflectionCamlon KhajarNo ratings yet