Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Isra University Hyderabad: Department of Civil Engineering Fluid Mechanics Lab
Isra University Hyderabad: Department of Civil Engineering Fluid Mechanics Lab
Uploaded by
Gulzar HussainOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Isra University Hyderabad: Department of Civil Engineering Fluid Mechanics Lab
Isra University Hyderabad: Department of Civil Engineering Fluid Mechanics Lab
Uploaded by
Gulzar HussainCopyright:
Available Formats
ISRA UNIVERSITY HYDERABAD
DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING
FLUID MECHANICS LAB
DETERMINATION OF HYDROSTATIC PRESSURE ON PARTIALLY SUBMERGED BODIES
Introduction:
Hydrostatic forces are the resultant force caused by the pressure loading of a liquid acting on submerged surfaces.
Calculation of the hydrostatic force and the location of the center of pressure are fundamental subjects in fluid
mechanics. The center of pressure is a point on the immersed surface at which the resultant hydrostatic pressure
force acts.
Practical Applications:
The location and magnitude of water pressure force acting on water-control structures, such as dams, levees, and
gates, are very important to their structural design. Hydrostatic force and its line of action are also required for the
design of many parts of hydraulic equipment.
Equipment’s:
Hydrostatic Pressure Apparatus
Centre of Pressure Apparatus
Loose weights
Procedure:
In this experiment, the hydrostatic force and center of
pressure acting on a vertical surface will be determined by
increasing the water depth in the apparatus water tank and by
reaching an equilibrium condition between the moments acting on the balance arm of the test apparatus. The forces
which create these moments are the weight applied to the balance arm and the hydrostatic force on the vertical
surface.
Hydrostatic Force: The hydrostatic force acting on partially
The magnitude of the resultant hydrostatic force (F) immersed surface the vertical face of the
applied to an immersed surface is given by: quadrant can be calculated as:
F=PA, P=W, W=mg, or m=p F=1/2 pgBd2
F=pgAh (N) Where:
P = density of fluid, B = width of the quadrant face,
A = Area of immersed surface d = depth of water from the base of the quadrant
h = Centroid of the immersed surface.
Observation Table:
a = 12cm, b = 7.5cm, d = 10cm, I = 30cm
S. No Y (g) Wth = 2.75y2 - 0.042y3 (g) Wac (g) Error = {(Wac - Wth)/Wth }* 100
01
02
03
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- S# Topic No of Hrs. Required Class Activity 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31Document1 pageS# Topic No of Hrs. Required Class Activity 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31Gulzar HussainNo ratings yet
- High-Shear Mixer: Principles of WorkDocument2 pagesHigh-Shear Mixer: Principles of WorkGulzar HussainNo ratings yet
- What Is Creep in RailDocument2 pagesWhat Is Creep in RailGulzar HussainNo ratings yet
- Design and Evaluation of Open Graded Hot Mix Asphalt Using Cement As A Grouting MaterialDocument1 pageDesign and Evaluation of Open Graded Hot Mix Asphalt Using Cement As A Grouting MaterialGulzar HussainNo ratings yet
- Rail JointsDocument15 pagesRail JointsGulzar HussainNo ratings yet
- Sleepers, Their TypesDocument42 pagesSleepers, Their TypesGulzar HussainNo ratings yet
- PRC LAB Lecture 03 Practical 02Document7 pagesPRC LAB Lecture 03 Practical 02Gulzar HussainNo ratings yet
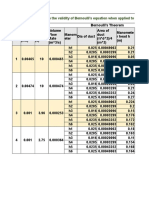
- PR # 7 Bernoulli TheoremDocument6 pagesPR # 7 Bernoulli TheoremGulzar HussainNo ratings yet
- Application For Final VivaDocument2 pagesApplication For Final VivaGulzar Hussain100% (1)
- Experiment No.14 Object: To Calculate Intersection Delay at Any Selected SignalisedDocument4 pagesExperiment No.14 Object: To Calculate Intersection Delay at Any Selected SignalisedGulzar HussainNo ratings yet