Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module I - Introduction To Corporate Governance
Module I - Introduction To Corporate Governance
Uploaded by
Mae Richelle D. DacaraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module I - Introduction To Corporate Governance
Module I - Introduction To Corporate Governance
Uploaded by
Mae Richelle D. DacaraCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction to Corporate Governance
Expected Learning Outcomes
After studying the chapter, you should be able to:
1. Describe what governance involves
2. Enumerate the different contexts in which governance can be applied
3. Name and explain the characteristics of good governance
4. Explain the meaning, purpose and objectives of corporate governance
5. Know and describe the principles of effective corporate governance
6. Understand how the principles of good corporate governance can be applied
What is Governance?
Generally, governance refers to a process whereby elements in society wield power, authority
and influence and enact policies and decisions concerning public life and social upliftment. It
comprises all the processes of governing – whether undertaken by the government of a
country, by a market or by a network – over a social system and whether through the laws,
norms, power, or language of an organized society. Therefore, governance means the process
of decision-making and the process by which decisions are implemented (or not implemented)
through the exercise of power or authority by leaders of the country and/or organizations.
Further, it can be used in several context such as corporate governance, international
governance, national governance, and local governance.
Characteristics of Good Governance
• Participation
Participation by both men and women is a key cornerstone of good governance.
Participation could be either direct or through legitimate institutions or representatives.
It is important to point out that representative democracy does not necessarily mean that
the concern of the most vulnerable in society would not be taken into consideration in
decision making. Participation needs to be informed and organized. This means freedom
Reference: Cabrera, Ma. Elenita Balatbat. Corporate Governance, Business Ethics,
Risk Management, and Internal Control. Manila: GIC Enterprise & Co., Inc. © 2019
of association and expression on one hand and an organized civil society on the other
hand.
• Rule of Law
Good governance requires fair legal frameworks that are enforced impartially. It also
requires full protection of human rights, particularly those of minorities. Impartial
enforcement of laws requires an independent judiciary and an impartial and incorruptible
police force.
• Transparency
Transparency means that decisions taken and their enforcement are done in a manner
that follows rules and regulations. It means that information is freely available and
directly accessible to those who will be affected by such decisions and their
enforcement. It also means that enough information is provided and that it is provided in
easily understandable forms and media.
• Responsiveness
Good governance requires that institutions and processes try to serve the needs of all
stakeholders within a reasonable timeframe.
• Consensus Oriented
Good governance requires mediation of the different interests in society to reach a broad
consensus on what is in the best interest of the whole community and how this can be
achieved. It also requires a broad and long-term perspective on what is needed for
sustainable human development and how to achieve the goals of such development.
This can only result from an understanding of the historical, cultural and societal contexts
of a given society or community.
• Equity & Inclusiveness
Ensures that all its members feel that they have a stake in it and do not feel excluded
from the mainstream of society. This requires all groups, but particularly the most
vulnerable, have opportunities to improve or maintain their wellbeing.
• Effectiveness & Efficiency
Good governance means that processes and institutions produce results that meet the
needs of society while making the best use of resources at their disposal. The concept
of efficiency in the context of good governance also covers the sustainable use of natural
resources and the protection of the environment.
• Accountability
Accountability is a key requirement of good governance. Not only governmental
institutions but also the private sector and civil society organizations must be
accountable to the public and to their institutional stakeholders. Who is accountable to
whom varies depending on whether decisions or actions taken are internal or external
to an organization or institution. In general, an organization or an institution is
Reference: Cabrera, Ma. Elenita Balatbat. Corporate Governance, Business Ethics,
Risk Management, and Internal Control. Manila: GIC Enterprise & Co., Inc. © 2019
accountable to those who will be affected by its decisions or actions. Accountability
cannot be enforced without transparency and the rule of law.
Corporate Governance: An Overview
Corporate governance is defined as the system of rules, practices and processes by which
business corporations are directed and controlled. It basically involves balancing the interests
of a company's many stakeholders, such as shareholders, management, customers,
suppliers, financiers, government, and the community.
Moreover, corporate governance is a topic that has received growing attention in the public in
recent years as policy makers and others become more aware of the contribution good
corporate governance makes to financial market stability and economic growth. Good
corporate governance is all about controlling one's business and so is relevant, and indeed
vital, for all organizations, whatever size or structure.
The corporate governance structure specifies the distribution of rights and responsibilities
among different participants in the corporation, such as the board, managers, shareholders,
and other stakeholders, and spells out the rules and procedures for making decisions on
corporate affairs. By doing this, it also provides the structure through which the objectives are
set and the means of attaining those objectives and monitoring performance.
Purpose of Corporate Governance
The purpose of corporate governance is to facilitate effective, entrepreneurial and prudent
management that can deliver long-term success of the company. In simple terms, the
fundamental aim of corporate governance is to enhance shareholders' value and protect the
interests of other stakeholders by improving the corporate performance and accountability. It
is also about what the board of directors of a company does, how it sets the values of the
business firm.
Objectives of Corporate Governance
1. Fair and Equitable Treatment of Shareholders
A corporate governance structure ensures equitable and fair treatment of all
shareholders of the company. In some organizations, a group of high-net-worth
individual and institutions who have a substantial proportion of their portfolios invested
in the company, remain active through occupation of top-level positions that enable
them to guard their interest. However, all shareholders deserve equitable treatment,
and this equity is safeguarded by a good governance structure in any organization.
2. Self-Assessment
Corporate governance enables firms to assess their behavior and actions before they
are scrutinized by regulatory agencies. Business establishments with a strong
corporate governance system are better able to limit exposure to regulatory risks and
fines. An active and independent board can successfully point out deficiencies or
loopholes in the company operations and help solve issues internally on a timely basis.
Reference: Cabrera, Ma. Elenita Balatbat. Corporate Governance, Business Ethics,
Risk Management, and Internal Control. Manila: GIC Enterprise & Co., Inc. © 2019
3. Increase Shareholders' Wealth
Another corporate governance's main objective is to protect the long-term interests of
the shareholders. Firms with strong corporate governance structure are seen to have
higher valuation attached to their shares by businessmen. This only reflects the
positive perception that good corporate governance induces potential investors to
decide to invest in a company.
4. Transparency and Full Disclosure
Good corporate governance aims at ensuring a higher degree of transparency in an
organization by encouraging full disclosure of transactions in the company accounts.
Basic Principles of Effective Corporate Governance
Effective corporate governance is transparent, protects the rights of shareholders and includes
both strategic and operational risk management. It is concerned in both the long-term earning
potential as well as actual short-term earnings and holds directors accountable for their
stewardship of the business.
The basic principles of effective corporate governance are threefold as presented below:
Positive answers to the following questions indicate a firm’s conformance and compliance with
the basic principles of good corporate governance:
A. Transparency and Full Disclosure
• Does the board meet the information needs of investment communities?
• Does it safeguard integrity in financial reporting?
• Does the board have sound disclosure policies and practices?
➢ Does it make timely and balanced disclosure?
➢ Can an outsider meaningfully analyze the organization's actions and
performance?
B. Accountability
• Does the board clarify its role and that of management?
➢ Does it promote objective, ethical and responsible decision making?
➢ Does it lay solid foundations for management oversight?
➢ Does the composition mix of board membership ensure an appropriate range
and mix of expertise, diversity, knowledge and added value?
Reference: Cabrera, Ma. Elenita Balatbat. Corporate Governance, Business Ethics,
Risk Management, and Internal Control. Manila: GIC Enterprise & Co., Inc. © 2019
➢ Is the organization's senior official committed to widely accepted standards of
correct and proper behavior?
C. Corporate Control
• Has the board built long-term sustainable growth in shareholders' value for the
corporation?
• Does it create an environment to take risk?
➢ Does it encourage enhanced performance?
➢ Does it recognize and manage risk?
➢ Does it remunerate fairly and responsibly?
➢ Does it recognize the legitimate interests of stakeholders?
➢ Are conflicts of interest avoided such that the organization's best interests
prevail at all times?
Illustrative Application of the Basic Principles of Corporate Governance and Best
Practice Recommendations
Principles of Good Corporate Best Practice Recommendations
Governance
1. A company should lay solid foundation 1-a. Formalize and disclose the functions
for management and oversight. It should reserved to the board and those delegated
recognize and publish the respective roles to management.
and responsibilities of board and
management.
2. Structure the board to add value. Have a 2-a. A board should have independent
board of an effective composition, size and directors.
commitment to adequately discharge its 2-b. The roles of chairperson and chief
responsibilities and duties. executive officer should not be exercised by
the same individual.
2-c. The board should establish a
nomination committee.
3. Promote ethical and responsible 3-a. Establish a code of conduct to guide
decision-making. Actively promote ethical the directors, the chief executive officer (or
and responsible decision-making. equivalent), the chief financial officer (or
equivalent) and any other key executives
as to:
• The practices necessary to maintain
confidence in the company's
integrity; and
• The responsibility and accountability
of individuals for reporting and
investigating reports of unethical
practices.
3-b. Disclose the policy concerning trading
in company securities by directors, officers
and employees.
4. Safeguard integrity in financial reporting. 4-a. Require the chief executive (or
Have a structure to independently verify equivalent) and the chief financial officer (or
and safeguard the integrity of the equivalent) to state in writing to the board
company's financial reporting. that the company's financial reports present
a true and fair view, in all material respects,
of the company's financial condition and
operational results and are in accordance
with relevant accounting standards.
Reference: Cabrera, Ma. Elenita Balatbat. Corporate Governance, Business Ethics,
Risk Management, and Internal Control. Manila: GIC Enterprise & Co., Inc. © 2019
4-b. The board should establish an audit
committee.
4-c. Structure the audit committee so that it
consists of:
• Only non-executive or independent
directors;
• An independent chairperson, who is
not chairperson of the board; and
• At least three (3) members.
5. Make timely and balanced disclosure. 5-a. Establish written policies and
Promote timely and balanced disclosure of procedures designed to ensure compliance
all material matters concerning the with IFRS.
company. 5-b. Listing Rule disclosure requirements
and to ensure accountability at a senior
management level for compliance.
6. Respect the rights of shareholders and 6-a. Design and disclose a communications
facilitate the effective exercise of those strategy to promote effective
rights. communication with shareholders and
encourage effective participation at general
meetings.
6-b. Request the external auditor to attend
the annual general meeting and be
available to answer shareholder questions
about the audit.
7. Recognize and manage risk. Establish a 7-a. The board or appropriate board
sound system of risk oversight and committee should establish policies on
management and internal control. risk oversight and management.
2-a. The chief executive officer (or
equivalent) and the chief financial officer (or
equivalent) should state to the board in
writing that:
• The statement given in accordance
with best practice recommendation
4-a (the integrity of financial
statements) is founded on a sound
system of risk management and
internal compliance and control
which implements the policies
adopted by the board; and
• The company's risk management
and internal compliance and control
system is operating efficiently in all
material respects.
8. Encourage enhanced performance. 8-a. Disclose the process for performance
Fairly review and actively encourage evaluation of the board, its committees
enhanced board and management and individual directors, and key
effectiveness. executives.
9. Remunerate fairly and responsibly. 9-a. Provide disclosure in relation to the
Ensure that the level and composition of company's remuneration policies to enable
remuneration is sufficient and reasonable investors to understand:
and that its relationship to corporate and • The costs and benefits of those
individual performance is defined. policies; and
Reference: Cabrera, Ma. Elenita Balatbat. Corporate Governance, Business Ethics,
Risk Management, and Internal Control. Manila: GIC Enterprise & Co., Inc. © 2019
• The link between remuneration paid
to directors and key executives and
corporate performance.
9-b. The board should establish a
remuneration committee.
9-c. Clearly distinguish the structure of non-
executive director's remuneration from that
of executives.
9-d. Ensure that payment of equity-based
executive remuneration is made in
accordance with thresholds set in plans
approved by shareholders.
10. Recognize the legitimate interests of 10-a. Establish and disclose a code of
stakeholders. Recognize legal and other conduct to guide compliance with legal
obligations to all legitimate stakeholders. and other obligations to legitimate
stakeholders.
Review Questions
1. What does governance mean?
2. Explain whether the following statement is true or false.
“Governance is exercised only by the government of a country.”
3. Explain how governance can be used in the following contexts and give appropriate
examples:
a. national governance
b. local governance
c. corporate governance
d. international governance
4. Explain briefly the eight (8) bask characteristics of good governance.
5. Transparency and accountability arc synonymous. Explain whether the statement is
correct or not.
6. Explain whether the following statement is true or false.
“Responsiveness usually results to effectiveness and efficiency.”
7. Define corporate governance.
8. What does corporate governance structure involve?
9. State the purpose of corporate governance.
10. Explain the basic objectives of corporate governance.
11. Explain the three basic principles of effective corporate governance.
Prepared by:
Donald P. Sam-it
Faculty, College of Accountancy
University of the Cordilleras
Reference: Cabrera, Ma. Elenita Balatbat. Corporate Governance, Business Ethics,
Risk Management, and Internal Control. Manila: GIC Enterprise & Co., Inc. © 2019
You might also like
- Management ReportDocument24 pagesManagement ReportOana Lazar100% (1)
- A Quilt of A Country Discussion QuestionsDocument2 pagesA Quilt of A Country Discussion QuestionsmanuelaNo ratings yet
- FAR Module 1Document26 pagesFAR Module 1Fuentes, Ferdelyn F.No ratings yet
- Chapter 3, Basic Elements of Financial SystemDocument27 pagesChapter 3, Basic Elements of Financial Systemmiracle123No ratings yet
- A Comparison Between Batas Pambansa Bilang 68Document66 pagesA Comparison Between Batas Pambansa Bilang 68Elson Talotalo0% (1)
- Valley Bread IncDocument29 pagesValley Bread IncMae Richelle D. DacaraNo ratings yet
- Valley Bread IncDocument29 pagesValley Bread IncMae Richelle D. DacaraNo ratings yet
- Explorers 5 Units 0 and 1Document3 pagesExplorers 5 Units 0 and 1Raquel FL50% (2)
- CSRDocument3 pagesCSRDalrymple CasballedoNo ratings yet
- Module For Managerial Economics: Students Name: Year & Section: SY & SemesterDocument43 pagesModule For Managerial Economics: Students Name: Year & Section: SY & SemesterHow Not To Be YouNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Accounting (FAR By: Millan)Document91 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Accounting (FAR By: Millan)Lovely LimNo ratings yet
- Maputim ProblemDocument2 pagesMaputim ProblemRowel Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- BSP - Basic Guidelines in Establishing BanksDocument5 pagesBSP - Basic Guidelines in Establishing BanksKAKKAMPI100% (2)
- GGSR Reviewer Chap 1-2Document5 pagesGGSR Reviewer Chap 1-2Ray MundNo ratings yet
- Banking and Financial Institutions Chapter 3Document32 pagesBanking and Financial Institutions Chapter 3Lorena100% (1)
- Taxation 7Document6 pagesTaxation 7Bossx BellaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 Overview of Cost Management and StrategyDocument8 pagesChapter 01 Overview of Cost Management and StrategyAccounting MaterialsNo ratings yet
- 07 Quiz 1Document3 pages07 Quiz 1Janrey RomanNo ratings yet
- FINMAR Chapter 1 (Reviewer)Document4 pagesFINMAR Chapter 1 (Reviewer)Charisse VisteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Financial ManagementDocument28 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Financial ManagementArminda Villamin100% (1)
- A. SWOT Analysis: StrengthsDocument2 pagesA. SWOT Analysis: StrengthsJAY MARK TANONo ratings yet
- Notes in Business Law by Fidelito Soriano PDF 16Document2 pagesNotes in Business Law by Fidelito Soriano PDF 16Getty Reagan Dy0% (2)
- Lesson 10 Expanding The Boundaries of BankingDocument29 pagesLesson 10 Expanding The Boundaries of Bankingshai291321No ratings yet
- Effects of Obligation: Accessory ObligationsDocument2 pagesEffects of Obligation: Accessory ObligationsAndrea EllisNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7good Gov - Mary Ann DomincelDocument39 pagesCHAPTER 7good Gov - Mary Ann DomincelMA Valdez100% (1)
- Assessment On The Practice of Corporate Social ResponsibilityDocument12 pagesAssessment On The Practice of Corporate Social ResponsibilityJayson Tom Briva CapazNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS LAW MODULE 2 RevisedDocument12 pagesBUSINESS LAW MODULE 2 RevisedArchill YapparconNo ratings yet
- Oblicon 1 PDFDocument25 pagesOblicon 1 PDFKristine Perez100% (1)
- Types of Business: Sole ProprietorshipDocument4 pagesTypes of Business: Sole ProprietorshipedrianclydeNo ratings yet
- Las 4Document8 pagesLas 4Venus Abarico Banque-AbenionNo ratings yet
- Accounting ReviewerDocument11 pagesAccounting ReviewerKyrzen NovillaNo ratings yet
- Mark Jeremy Bombita Case Study 1 To 3.Document9 pagesMark Jeremy Bombita Case Study 1 To 3.Mark jeremy bombitaNo ratings yet
- Respecting Rights of Stakeholders and Effective Redress For Violation of StakeholderDocument2 pagesRespecting Rights of Stakeholders and Effective Redress For Violation of StakeholderEDELYN PoblacionNo ratings yet
- Millennium Company - Projected Financial StatementDocument2 pagesMillennium Company - Projected Financial StatementKathleenCusipagNo ratings yet
- Notes For Civil Code Article 1177 and Article 1178Document5 pagesNotes For Civil Code Article 1177 and Article 1178Chasz CarandangNo ratings yet
- Case 7Document1 pageCase 7jona empalNo ratings yet
- CORPORATE PROTECTION WITHIN LEGAL BOUNDARIES (Chapt. 3)Document14 pagesCORPORATE PROTECTION WITHIN LEGAL BOUNDARIES (Chapt. 3)Qyle Jobes Elmido0% (1)
- Ratio Used To Gauge Asset Management Efficiency and Liquidity Name Formula SignificanceDocument9 pagesRatio Used To Gauge Asset Management Efficiency and Liquidity Name Formula SignificanceAko Si JheszaNo ratings yet
- Income Taxation by Tabag 2021Document620 pagesIncome Taxation by Tabag 2021Grezil PitogoNo ratings yet
- Compensation IncomeDocument3 pagesCompensation IncomePaula Jane Raby RicamaraNo ratings yet
- What Are The Other Classifications of Corporations? (PT 2)Document17 pagesWhat Are The Other Classifications of Corporations? (PT 2)jobelle barcellanoNo ratings yet
- HRM AnuDocument13 pagesHRM AnuBharath BMNo ratings yet
- Explanation of Article 1226Document3 pagesExplanation of Article 1226hyunsuk fhebieNo ratings yet
- BACC 222 Business LawDocument3 pagesBACC 222 Business Lawmarinel juneNo ratings yet
- GGSR Chapter 1 Corporation and Corporate Governance 1Document16 pagesGGSR Chapter 1 Corporation and Corporate Governance 1Aspire DellNo ratings yet
- Human Behavior in OrganizationDocument22 pagesHuman Behavior in Organizationmirmo tokiNo ratings yet
- IPS-09 2 Impact of 4Ps On Labor Market Outcomes AO-VP-newDocument12 pagesIPS-09 2 Impact of 4Ps On Labor Market Outcomes AO-VP-newApril Elenor JucoNo ratings yet
- CF04 Part 3 - Petty Cash FundDocument51 pagesCF04 Part 3 - Petty Cash FundABMAYALADANO ,ErvinNo ratings yet
- NOTE 1n YT-Law-on-Obligations-and-Contracts-1156-1170Document6 pagesNOTE 1n YT-Law-on-Obligations-and-Contracts-1156-1170Jonathan BatalunaNo ratings yet
- Questions Bsba Quiz BeeDocument5 pagesQuestions Bsba Quiz BeeMaria Charise TongolNo ratings yet
- Module II - Corporate Governance Responsibilities and AccountabilitiesDocument7 pagesModule II - Corporate Governance Responsibilities and AccountabilitiesMae Richelle D. Dacara100% (1)
- Pointers For Prelim Exam Managerial Economics 2021Document6 pagesPointers For Prelim Exam Managerial Economics 2021Strawberry ShakeNo ratings yet
- Oblicon-Reviewer - 1156 - 1190Document10 pagesOblicon-Reviewer - 1156 - 1190Ash JuamanNo ratings yet
- Financial Controllership Course SyllabusDocument2 pagesFinancial Controllership Course SyllabusReiner GGay100% (1)
- MGT 209 - CH 13 NotesDocument6 pagesMGT 209 - CH 13 NotesAmiel Christian MendozaNo ratings yet
- Philippine History 101 Assignment: AnswerDocument7 pagesPhilippine History 101 Assignment: AnswerRoschelle MiguelNo ratings yet
- AIS 01 - Handout - 1Document7 pagesAIS 01 - Handout - 1Melchie RepospoloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 and 3 Lopez BookDocument4 pagesChapter 2 and 3 Lopez BookSam CorsigaNo ratings yet
- FMPR2 Module BookletDocument66 pagesFMPR2 Module BookletMarjorie Onggay MacheteNo ratings yet
- Inventories - ExercisesDocument3 pagesInventories - ExercisesAleiza MalaluanNo ratings yet
- Actbas 2 Downloaded Lecture NotesDocument57 pagesActbas 2 Downloaded Lecture NotesCharles Reginald K. Hwang100% (2)
- Introduction To Corporate GovernanceDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Corporate GovernancegarciarhodjeannemarthaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance, Business Ethics, Risj Manage Ment and Internal ControlDocument19 pagesCorporate Governance, Business Ethics, Risj Manage Ment and Internal ControlKEYL ENNo ratings yet
- What Is Governance?Document21 pagesWhat Is Governance?Jhazreel BiasuraNo ratings yet
- Govbri - ReviewerDocument185 pagesGovbri - ReviewerFabia, Micah B.No ratings yet
- Contract of SaleDocument5 pagesContract of SaleMae Richelle D. DacaraNo ratings yet
- University of The Cordilleras College of Accountancy MODULE in TechnopreneurshipDocument8 pagesUniversity of The Cordilleras College of Accountancy MODULE in TechnopreneurshipMae Richelle D. DacaraNo ratings yet
- UC MODULE TECHNO 100 - Unit 2 Lesson 3Document4 pagesUC MODULE TECHNO 100 - Unit 2 Lesson 3Mae Richelle D. DacaraNo ratings yet
- University of The Cordilleras College of Accountancy MODULE in TechnopreneurshipDocument5 pagesUniversity of The Cordilleras College of Accountancy MODULE in TechnopreneurshipMae Richelle D. DacaraNo ratings yet
- Technopreneurship: Dr. Thelma Domingo PalaoagDocument14 pagesTechnopreneurship: Dr. Thelma Domingo PalaoagMae Richelle D. DacaraNo ratings yet
- UC MODULE TECHNO 100 - Unit 1 - Course Presentaion (Lecture Notes & Activities)Document10 pagesUC MODULE TECHNO 100 - Unit 1 - Course Presentaion (Lecture Notes & Activities)Mae Richelle D. DacaraNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsMae Richelle D. DacaraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Warranties, Sale by InstallmentsDocument9 pagesLesson 3 - Warranties, Sale by InstallmentsMae Richelle D. DacaraNo ratings yet
- Module II - Corporate Governance Responsibilities and AccountabilitiesDocument7 pagesModule II - Corporate Governance Responsibilities and AccountabilitiesMae Richelle D. Dacara100% (1)
- Lesson 2 - Rights and Obligations of PartiesDocument9 pagesLesson 2 - Rights and Obligations of PartiesMae Richelle D. DacaraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Nature, Form & Requisites of SaleDocument7 pagesLesson 1 - Nature, Form & Requisites of SaleMae Richelle D. DacaraNo ratings yet
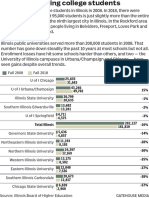
- Illinois College Enrollment Trends, 2008-2018Document2 pagesIllinois College Enrollment Trends, 2008-2018corina curry100% (1)
- Summative Test 1ST Q PR1Document4 pagesSummative Test 1ST Q PR1Claribel C. AyananNo ratings yet
- Moser Baer - Performance Appraisal SystemDocument100 pagesMoser Baer - Performance Appraisal SystemSami ZamaNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and Phonology - MidtermDocument5 pagesPhonetics and Phonology - MidtermTrung NguyenNo ratings yet
- No Smoking in The TriangleDocument60 pagesNo Smoking in The TriangleThomas L HaydenNo ratings yet
- N.S Prabhu InterviewDocument83 pagesN.S Prabhu InterviewSusarla SuryaNo ratings yet
- Advt 02 20 ORA Engl R - 0 PDFDocument47 pagesAdvt 02 20 ORA Engl R - 0 PDFVikin JainNo ratings yet
- Assessment Task 1Document5 pagesAssessment Task 1Dorothy PoonNo ratings yet
- VP Director HR in Greater New York City Resume Debbie RyanDocument2 pagesVP Director HR in Greater New York City Resume Debbie RyanDebbie RyanNo ratings yet
- Teachers Guide LTEDocument43 pagesTeachers Guide LTEttt ttNo ratings yet
- Rajnikant Sharma Resume-1 PDFDocument3 pagesRajnikant Sharma Resume-1 PDFKuldipsinh MevadaNo ratings yet
- OECD MTG 3 - 26may2023Document31 pagesOECD MTG 3 - 26may2023rusu.elenaNo ratings yet
- Cerro Casale Alteration Report WV3 1Document26 pagesCerro Casale Alteration Report WV3 1Juan LauraNo ratings yet
- Letter of MotivationDocument2 pagesLetter of Motivationsagar ashraf100% (1)
- Coordinating Conjunction Kel 12Document7 pagesCoordinating Conjunction Kel 12Yuli AnggrianiNo ratings yet
- Thermax Paper Candidate Experiences National Power Training Institute ER Durgapur 29 September 2010Document2 pagesThermax Paper Candidate Experiences National Power Training Institute ER Durgapur 29 September 2010SylvesterNo ratings yet
- Medicine BookDocument46 pagesMedicine BookSaif Ahmed100% (1)
- 1 Metal: Dear Hendro SantosoDocument4 pages1 Metal: Dear Hendro SantosoHendro SantosoNo ratings yet
- HRM Qualification Structure and UnitsDocument56 pagesHRM Qualification Structure and UnitsAnca BodianNo ratings yet
- Repo TableDocument2 pagesRepo TableVivek BansalNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument17 pagesCase StudysakshiNo ratings yet
- W1 8 - Epp6 - Home Economics - Activity Sheets 1Document49 pagesW1 8 - Epp6 - Home Economics - Activity Sheets 1JOECEL MAR AMBIDNo ratings yet
- Todd Rubin Admin ResumeDocument4 pagesTodd Rubin Admin Resumeapi-120066271No ratings yet
- Human Computer Interaction Dissertation TopicsDocument8 pagesHuman Computer Interaction Dissertation TopicsNeedSomeoneToWriteMyPaperForMeWestValleyCity100% (1)
- What Is A Concept PaperDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Concept PaperMarvelous Saint JumanoyNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1-Week5-6Document22 pagesPractical Research 1-Week5-6XYRA LOU SEDANo ratings yet
- Diploma in Business ManagementDocument3 pagesDiploma in Business ManagementMIT,PuneNo ratings yet