Professional Documents
Culture Documents
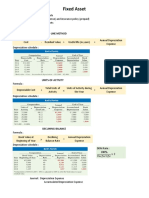
Cost Residual Value Useful Economic Life Depreciation %× (Cost Residual Value)
Cost Residual Value Useful Economic Life Depreciation %× (Cost Residual Value)
Uploaded by
theskepticaloneOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cost Residual Value Useful Economic Life Depreciation %× (Cost Residual Value)
Cost Residual Value Useful Economic Life Depreciation %× (Cost Residual Value)
Uploaded by
theskepticaloneCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 6: Non-Current Asset Depreciation
Depreciation:
o The decrease in value of a non-current asset over time which represents the cost of
using the asset
o The amount is recorded as an expense in the SoPL
o Accrual Concept: The cost of using the non-current asset is matched with the
revenues the asset helped generate in a given accounting period
o It is a non-cash transaction
Causes of Depreciation
o Wear and Tear
o Obsolescence
o Reduction of natural resources (mines)
o Passage of time (leases)
Methods of Depreciation
o Straight-Line Method
The same amount of depreciation is charged every year
Cost −Residual Value
Depreciation per year = Useful Economic Life
¿
¿
Depreciation per year = Depreciation % ×(Cost−Residual Value )
o Reducing Balance Method
A fixed percentage of the carrying value is depreciated each year
Carrying Value = Cost – Accumulated Depreciation
Depreciation expense in a given year
= Depreciation % ×Carrying Value of Asset
o Revaluation Method
Mainly used for a collection of important items that are individually not
worth a lot. Items such as printers, stationery, telephone etc.
The assets are simply revalued each year
The change (usually decrease) in value represents depreciation
o Effect on Profit
SL method: profit is reduced by the same amount every period
RB method: depreciation is higher in the early years and hence profit will be
lower.
Taking higher maintenance costs of later years into account, RB may
be an accurate representation of the actual costs of using the asset.
o Changing methods of depreciation
Must be done with good reason
The new method should be a more accurate representation of asset usage
than the previous method
Otherwise a change will violate the accounting concept of consistency and
may be an attempt to overstate or understate profits and asset value.
What if asset was purchased or sold during the year?
o Depreciate on a monthly basis (Pro rata)
o Full year of depreciation is charged in year of purchase and none in year of disposal
o Full year of depreciation is charged in year of disposal and none in year of purchase
Double Entry for Depreciation
o Depreciation is adjusted for at the end of the financial year
o Asset account is recorded at cost and is not adjusted at all
o Double Entry:
Debit Depreciation Expense: asset name (Expense account whose balance is
then transferred to statement of profit and loss)
Credit Provision for Depreciation: asset name (negative asset account that
records the accumulated depreciation of an asset and is shown on the
statement of financial position)
Disposal of Non-Current Assets
o Sell a non-current asset at the end of its useful life or prior to
o If the amount received is greater/less than its carrying value then there will be a
profit/loss on disposal
o Profit on disposal is recorded as other operating income
o Loss on disposal is reported as an expense
o Double Entry:
Remove the non-current asset (cost):
Debit Disposal account; Credit Non-current asset account
Remove accumulated depreciation on the disposed asset:
Debit Provision for depreciation: asset account; Credit Disposal
account
Record proceeds from disposal:
Debit Cash/Bank; Credit Disposal account
If the balance on disposal account is a credit/debit then there is an
expense/gain transferred to the SoPL at the end of the period
Part Exchange of an Asset
o Sometimes non-current assets are sold to acquire a new one (part exchange)
o Normally the company will need to pay an extra amount in addition to disposing the
old asset to acquire the new asset.
o The part exchange value of the old asset is the difference between the amount paid
and the cost of the new asset
o A profit or loss on disposal is the difference between the part exchange value and
the carrying value
o Double entry:
Remove old asset: same as disposal
Remove accumulated depreciation: same as disposal
Acquire new asset:
debit non-current asset account twice;
credit cash/bank and credit disposal account (part exchange value)
Schedule of Non-Current Assets:
o Summary of the movement of non-current assets over the year
o Shows additions, disposals, revaluation, and depreciation charges to each type of
non-current asset
You might also like
- Full Download Human Resource Management 11th Edition Noe Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Human Resource Management 11th Edition Noe Solutions Manualdomitegloaming.0zd4100% (37)
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)From EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (17)
- Depreciation, Provisions and ReservesDocument27 pagesDepreciation, Provisions and Reservesabhinandbabu314No ratings yet
- Note Buổi 6Document5 pagesNote Buổi 6Long Chế Vũ BảoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 - DepreciationDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 8 - DepreciationMuhammad AdibNo ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument6 pagesDepreciationPakeeza JavedNo ratings yet
- Adjustments IDocument45 pagesAdjustments InarmadaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Concept: Fair Value Matching PrincipleDocument13 pagesAccounting Concept: Fair Value Matching PrincipleJohn ArthurNo ratings yet
- CHP 11 NotesDocument21 pagesCHP 11 NotesDhruvit DadNo ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument7 pagesDepreciationSoumendra RoyNo ratings yet
- Depreciation and AmortisationDocument25 pagesDepreciation and AmortisationNikhil RamalingamNo ratings yet
- 07 Long-Lived Non-Monetary Assets and Amortization - StudentDocument30 pages07 Long-Lived Non-Monetary Assets and Amortization - StudentNileshAgarwalNo ratings yet
- Depreciation and Provision For DepreciationDocument2 pagesDepreciation and Provision For DepreciationAnsha Twilight14No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document5 pagesChapter 3Hal kNo ratings yet
- DEPRECIATIONDocument6 pagesDEPRECIATIONShivaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Depreciation, Impairments and DepletionDocument24 pagesChapter 11: Depreciation, Impairments and DepletionRahat KhanNo ratings yet
- Accounts Rev NotesDocument13 pagesAccounts Rev NotesAsha SuryavanshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16Document16 pagesChapter 16soniadhingra1805No ratings yet
- Accounting Concept: C I D C CDocument9 pagesAccounting Concept: C I D C CRana FahadNo ratings yet
- Methods of DepreciationDocument12 pagesMethods of Depreciationamun din100% (1)
- M 2Document22 pagesM 2r79sivaNo ratings yet
- 4D - Depreciation, Replacement Analysis & Sensitivity AnalysisDocument3 pages4D - Depreciation, Replacement Analysis & Sensitivity AnalysisgidanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Accounting Adjustments IIDocument9 pagesChapter 6: Accounting Adjustments IIetextbooks lkNo ratings yet
- Depreciation 2023-2024 Iisjed Class For 12th Standard CBSEDocument29 pagesDepreciation 2023-2024 Iisjed Class For 12th Standard CBSETaLHa iNaM sameerNo ratings yet
- Fixed Assets Cheat SheetsDocument2 pagesFixed Assets Cheat SheetsSarah SafiraNo ratings yet
- Ch#4 Accounting For Non Current AssetsDocument7 pagesCh#4 Accounting For Non Current Assetseaglerealestate31No ratings yet
- Depreciation and Depletion: Mine Investment AnalysisDocument36 pagesDepreciation and Depletion: Mine Investment AnalysisFaidel AfrianNo ratings yet
- Depreciation Provisions and Reserves Class 11 NotesDocument48 pagesDepreciation Provisions and Reserves Class 11 Notesjainayan8190No ratings yet
- CH 4 Expenses Analysis - enDocument5 pagesCH 4 Expenses Analysis - enAnonymous Wq5xxrafNo ratings yet
- DEPRECIATIONDocument2 pagesDEPRECIATIONmaryellll457No ratings yet
- Depreciation Accounting (AS-6)Document21 pagesDepreciation Accounting (AS-6)Gopika SatheesanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering EconomicsDocument31 pagesChemical Engineering EconomicsDanish BaigNo ratings yet
- ES6 Lec07a Depreciation Straight Line MethodDocument15 pagesES6 Lec07a Depreciation Straight Line MethodIroha IsshikiNo ratings yet
- Depreciation of Non Current AssetsDocument27 pagesDepreciation of Non Current Assetskimuli FreddieNo ratings yet
- Working Capital ManagementDocument8 pagesWorking Capital ManagementVirgil Kit Augustin AbanillaNo ratings yet
- Finance Crash Course Session 1Document36 pagesFinance Crash Course Session 1jackeggers1No ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument3 pagesDepreciationvaibhavksingh099No ratings yet
- 3900 Topper 21 101 503 550 8491 Depreciation Provisions and Reserves Up201608051529 1470391159 3522 PDFDocument17 pages3900 Topper 21 101 503 550 8491 Depreciation Provisions and Reserves Up201608051529 1470391159 3522 PDFManju BalajiNo ratings yet
- Ch16 Lecture NotesDocument40 pagesCh16 Lecture NotesAhmed TahmidNo ratings yet
- Accumulated Depreciation: Everything You Need To KnowDocument7 pagesAccumulated Depreciation: Everything You Need To KnowhieutlbkreportNo ratings yet
- Chap 5Document10 pagesChap 5khedira sami100% (1)
- Expressed As A Percentage of The Value of Revenue or Sales.: Balance Sheet: Reports What The Organization Owns and OwesDocument3 pagesExpressed As A Percentage of The Value of Revenue or Sales.: Balance Sheet: Reports What The Organization Owns and OwesDGNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 Fixed AssetsDocument6 pagesUnit 11 Fixed AssetsAnonymous Fn7Ko5riKTNo ratings yet
- Depreciation: Part - A: Theory SectionDocument19 pagesDepreciation: Part - A: Theory SectionDivya Punjabi0% (1)
- Depreciation: Historical MethodsDocument19 pagesDepreciation: Historical MethodsKiran PatilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document4 pagesChapter 9canadian_ehNo ratings yet
- Lec6 - Plant Assets DepreciationDocument58 pagesLec6 - Plant Assets DepreciationDylan Rabin Pereira100% (1)
- SOURCES (Inflows of Cash) USES (Outflows of Cash) : TranslateDocument2 pagesSOURCES (Inflows of Cash) USES (Outflows of Cash) : TranslateRahul KapurNo ratings yet
- Depreciation in AccountingDocument13 pagesDepreciation in AccountingNirmal PrasadNo ratings yet
- Depreciation and AmortizationDocument12 pagesDepreciation and Amortizationabdullahkhattak0076No ratings yet
- Depreciation: Depreciation Is A Term Used inDocument10 pagesDepreciation: Depreciation Is A Term Used inalbertNo ratings yet
- PDF NotesDocument7 pagesPDF NotesBinoy TrevadiaNo ratings yet
- Problems On DepreciationDocument13 pagesProblems On DepreciationEkansh DwivediNo ratings yet
- Epeng 308-2Document46 pagesEpeng 308-2gwemeowenNo ratings yet
- Abm 1Document7 pagesAbm 1Sachin ManjhiNo ratings yet
- INDE/EGRM 6617-02 Engineering Economy and Cost Estimating: Chapter 7: Depreciation and Income TaxesDocument40 pagesINDE/EGRM 6617-02 Engineering Economy and Cost Estimating: Chapter 7: Depreciation and Income Taxesfahad noumanNo ratings yet
- Depreciation AccountingDocument9 pagesDepreciation Accountingu1909030No ratings yet
- Financial Aspects of Project Analysis: ReferencesDocument40 pagesFinancial Aspects of Project Analysis: ReferencesRusty PlacinoNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة التاسعة والعاشرةDocument6 pagesالمحاضرة التاسعة والعاشرةAly SaadNo ratings yet
- Theory of DepreciationDocument7 pagesTheory of DepreciationNaman TyagiNo ratings yet
- Rudin's Ex. 6: M N P Q MQ+NP NQDocument3 pagesRudin's Ex. 6: M N P Q MQ+NP NQtheskepticaloneNo ratings yet
- Quadratics TestDocument4 pagesQuadratics TesttheskepticaloneNo ratings yet
- Rationals TestDocument2 pagesRationals TesttheskepticaloneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2theskepticaloneNo ratings yet
- Polynomials TestDocument2 pagesPolynomials TesttheskepticaloneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19Document3 pagesChapter 19theskepticaloneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21Document3 pagesChapter 21theskepticaloneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20Document1 pageChapter 20theskepticaloneNo ratings yet
- A) Translate The Shape A by The Vector and Label The New Shape C B) Describe Fully The Single Transformation That Maps Shape B Onto Shape ADocument6 pagesA) Translate The Shape A by The Vector and Label The New Shape C B) Describe Fully The Single Transformation That Maps Shape B Onto Shape AtheskepticaloneNo ratings yet
- A. Expand and Simplify 2 (X 3 Y) +3 (Y 2 X)Document6 pagesA. Expand and Simplify 2 (X 3 Y) +3 (Y 2 X)theskepticaloneNo ratings yet
- A. Rotate The Shape A 90 Degrees Counter-Clockwise About The Origin and Label The New Shape BDocument5 pagesA. Rotate The Shape A 90 Degrees Counter-Clockwise About The Origin and Label The New Shape BtheskepticaloneNo ratings yet
- EnlargementDocument6 pagesEnlargementtheskepticaloneNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Differentiation ReviewDocument10 pagesIGCSE Differentiation ReviewtheskepticaloneNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Kinematics ReviewDocument5 pagesIGCSE Kinematics ReviewtheskepticaloneNo ratings yet
- Diffrentiation Mini TestDocument6 pagesDiffrentiation Mini TesttheskepticaloneNo ratings yet
- GRP 1 Articles of IncorporationDocument4 pagesGRP 1 Articles of IncorporationQueenVictoriaAshleyPrietoNo ratings yet
- Ppog50 1Document12 pagesPpog50 1DrogNo ratings yet
- Options 101 Get Trading With Options NPDocument47 pagesOptions 101 Get Trading With Options NPjoseluisvazquez100% (1)
- Stock in Transit (GR - IR Regrouping - Reclassification) - SAP BlogsDocument7 pagesStock in Transit (GR - IR Regrouping - Reclassification) - SAP BlogsusamaNo ratings yet
- Example PresentationDocument7 pagesExample PresentationMaryam AKHARAZENo ratings yet
- TransmittalllDocument1 pageTransmittalllElaine LabaoNo ratings yet
- Home - Michael MegaritDocument6 pagesHome - Michael MegaritMax FNo ratings yet
- Livelihood Sustainabilityof Street Vendors AStudyin Dhaka CityDocument8 pagesLivelihood Sustainabilityof Street Vendors AStudyin Dhaka CityNathaniel PohNo ratings yet
- 2018 Shelby Township Bill RunsDocument893 pages2018 Shelby Township Bill RunsBlahNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Pendukung 5Document17 pagesJurnal Pendukung 5ARIF MUDJIONONo ratings yet
- 10 Steps Your Software Implementation Should Have - LISO BLOGDocument19 pages10 Steps Your Software Implementation Should Have - LISO BLOGSo RineatzaNo ratings yet
- McKinsey Accelerating Digital TransformationDocument29 pagesMcKinsey Accelerating Digital Transformationgppp86% (7)
- E-Commerce Presentation Plan - CreativeDocument15 pagesE-Commerce Presentation Plan - CreativeMUKUL DOBHALNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument2 pagesCase StudyXie marquezNo ratings yet
- Ferrari NV Annual Report FY 2022 - Form 20FDocument301 pagesFerrari NV Annual Report FY 2022 - Form 20Fjumicoro0210No ratings yet
- BDA 2021 End of Year Report FinalDocument20 pagesBDA 2021 End of Year Report FinalBernewsAdminNo ratings yet
- 2021년 가공식품 세분시장 현황조사 - 비건식품Document320 pages2021년 가공식품 세분시장 현황조사 - 비건식품도토리만두100% (1)
- Annual Report of IOCL 196Document1 pageAnnual Report of IOCL 196Nikunj ParmarNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument144 pagesStrategic Managementalex abrha100% (1)
- Distribution Management - CHAPTER 4Document43 pagesDistribution Management - CHAPTER 4Abhishek TiwariNo ratings yet
- 1 Assignment TO BIG TOO FAILDocument2 pages1 Assignment TO BIG TOO FAILHaroon Z. ChoudhryNo ratings yet
- JRC Assessment Framework Final v2Document26 pagesJRC Assessment Framework Final v2Jerome PercepiedNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive IllustrationDocument12 pagesComprehensive IllustrationNucke Febriana Putri RZNo ratings yet
- Econ Quantitative Case StudyDocument5 pagesEcon Quantitative Case StudyLena PhanNo ratings yet
- This Is An Individual Activity For You To Carry Out. The Activities Should Be Completed and Submitted On Putrablast by The Due DateDocument2 pagesThis Is An Individual Activity For You To Carry Out. The Activities Should Be Completed and Submitted On Putrablast by The Due DatesarasNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research 7th Edition Burns Test BankDocument25 pagesMarketing Research 7th Edition Burns Test BankJenniferNicholsonqknj100% (61)
- Chapter - 11 MarketingDocument25 pagesChapter - 11 Marketingsakshamkohli97No ratings yet
- A Study On "Port Industry" - An Empirical ResearchDocument55 pagesA Study On "Port Industry" - An Empirical ResearchDimpu Sarath KumarNo ratings yet
- Intention To Acquire Goods in The FutureDocument21 pagesIntention To Acquire Goods in The Futurecynthia reyesNo ratings yet