Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Enzymes: Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
Enzymes: Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
Uploaded by
Labeena0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesThe document provides information about the digestive system and blood. It includes diagrams to label of the digestive system and heart. Key points are summarized below:
1. The digestive system diagram labels parts like the stomach, small intestine, liver, and pancreas. The small intestine is adapted for efficient absorption of nutrients and bile helps emulsify fats.
2. The heart diagram labels structures like the atria, ventricles, and blood vessels. Blood is circulated through double circulation. The left side of the heart is thicker to pump blood to the body.
3. Coronary heart disease occurs when coronary arteries are narrowed, restricting blood flow. Risk factors include diet, smoking, and genetics. It can
Original Description:
Original Title
organ_systems_revision_poster
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides information about the digestive system and blood. It includes diagrams to label of the digestive system and heart. Key points are summarized below:
1. The digestive system diagram labels parts like the stomach, small intestine, liver, and pancreas. The small intestine is adapted for efficient absorption of nutrients and bile helps emulsify fats.
2. The heart diagram labels structures like the atria, ventricles, and blood vessels. Blood is circulated through double circulation. The left side of the heart is thicker to pump blood to the body.
3. Coronary heart disease occurs when coronary arteries are narrowed, restricting blood flow. Risk factors include diet, smoking, and genetics. It can
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesEnzymes: Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
Enzymes: Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
Uploaded by
LabeenaThe document provides information about the digestive system and blood. It includes diagrams to label of the digestive system and heart. Key points are summarized below:
1. The digestive system diagram labels parts like the stomach, small intestine, liver, and pancreas. The small intestine is adapted for efficient absorption of nutrients and bile helps emulsify fats.
2. The heart diagram labels structures like the atria, ventricles, and blood vessels. Blood is circulated through double circulation. The left side of the heart is thicker to pump blood to the body.
3. Coronary heart disease occurs when coronary arteries are narrowed, restricting blood flow. Risk factors include diet, smoking, and genetics. It can
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
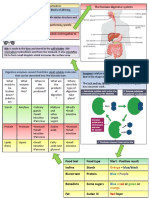
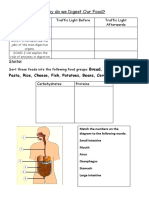
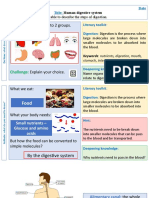
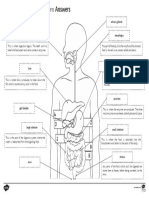
Digestive system Label the An alkaline solution that emulsifies fats and
neutralises the hydrochloric acid passing from Adaptations of the small
diagram the stomach to the small intestine.
intestine
When fats are broken down into smaller
droplets to increase their surface area for
digestion.
Where bile is stored.
Where excess water is absorbed.
Tube connecting the mouth to the stomach.
Food moves along by peristalsis.
The wave of muscle contractions that moves What is the role of the small
food along the oesophagus. intestine? How is it adapted to do its
Produces saliva to moisten food.
job?
Where absorption of soluble food takes places.
A muscular bag that mixes food with enzymes
and acid.
Enzymes in the digestive system
Enzyme Where Works on Products Enzymes Factors affecting enzyme activity
produced What are enzymes?
Carbohydrase
e.g. amylase
Lipase
What do we call the model that is
used to explain how enzymes work?
Protease
How does pH affect enzyme activity. Why
Food tests
is this important in the digestive system?
What happens to enzymes at high
temperatures?
Blood vessels Blood
The heart
Plasma
label
Red blood
cells
White
Describe and explain the structure and blood cells
function of each blood vessel. Platelets
How are red blood
Why is the left side of the heart thicker?
cells adapted?
What is the role of the coronary arteries?
What is meant by double circulation? Organs and
organ
Describe what
What is coronary heart disease systems Gas exchange happens when you
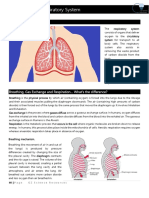
breathe in and out.
(CHD) and what are the risk factors? Label
How is CHD treated? What are the
advantages and disadvantages?
How are the alveoli
adapted for efficient
gas exchange?
You might also like
- Freebie Bundle-50 Pages.Document76 pagesFreebie Bundle-50 Pages.Kia MercadoNo ratings yet
- Visceral Anatomy For OsteopathyDocument152 pagesVisceral Anatomy For OsteopathyHossein Khorrami100% (1)
- Organisation and Digestive SystemDocument10 pagesOrganisation and Digestive Systemmyjr54bx4mNo ratings yet
- Science HelpDocument5 pagesScience HelpDena AL-SHOWALINo ratings yet
- Laboratory & Lecture QUIZZESDocument7 pagesLaboratory & Lecture QUIZZESJULIANNAH ATHENA MERCADONo ratings yet
- Science Matters Volume B - Term 1-2Document61 pagesScience Matters Volume B - Term 1-2Andrea Nguyen100% (2)
- Why Do We Digest LowerDocument2 pagesWhy Do We Digest LowerSaima UsmanNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Digest HigherDocument3 pagesWhy Do We Digest HigherSaima UsmanNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument17 pagesEnzymesanika tNo ratings yet
- Biology - Course - Haidar RahhalDocument36 pagesBiology - Course - Haidar RahhalFatima SlimNo ratings yet
- Digestive WorksheetDocument8 pagesDigestive WorksheetBrandon KnightNo ratings yet
- Life Processes Notes (Nutrition & Respiration) - 1Document6 pagesLife Processes Notes (Nutrition & Respiration) - 1ARSHAD JAMILNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Learning JourneyDocument3 pagesEnzymes Learning JourneyArooj AbidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Answer KeyDocument2 pagesChapter 8 Answer KeyzakiyaNo ratings yet
- ESWS 7C BiologysamplechapterDocument16 pagesESWS 7C BiologysamplechapterAFuentesCaballeroNo ratings yet
- Human SystemsDocument3 pagesHuman SystemsEl TatoNo ratings yet
- Enzymes and DigestionDocument24 pagesEnzymes and DigestionAndy DlobelaNo ratings yet
- Y10 Week 34 CirculationDocument1 pageY10 Week 34 CirculationAntriana MiliotiNo ratings yet
- 9.6 Introduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument75 pages9.6 Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiologydmnnfn8hkgNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: By: Shreen, Kausthubhi, Sreemayi, Riyaan, Srikar, Prathyush and HarshDocument7 pagesEnzymes: By: Shreen, Kausthubhi, Sreemayi, Riyaan, Srikar, Prathyush and HarshKausthubhi KillamsettiNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 OrganisationDocument31 pagesTopic 2 OrganisationMeriNo ratings yet
- Activity 3. Human Body CareDocument8 pagesActivity 3. Human Body CareARACELI DIAZ TERRIQUEZNo ratings yet
- WK3 - Digestive SystemDocument23 pagesWK3 - Digestive SystemSAMA ELHASSAN OSMAN ELAMINNo ratings yet
- 21.12.22 Lec-1 Science With NumberDocument6 pages21.12.22 Lec-1 Science With NumberMuhammad JawadNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Digestive SystemDocument1 pageStudy Guide Digestive SystemkyleporgyNo ratings yet
- 3.1 - The Digestive SystemDocument21 pages3.1 - The Digestive SystemJavierNo ratings yet
- Digestive Form 4Document43 pagesDigestive Form 4miraazizNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Are Biological Catalyst That Alters The Rate of A Chemical ReactionDocument9 pagesEnzymes Are Biological Catalyst That Alters The Rate of A Chemical Reactionsmbdy tbhhhNo ratings yet
- DigestionDocument1 pageDigestionPratham KamaniNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument4 pagesEnzymesMhariane MabborangNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument25 pagesBiologycarlotarubioperez123No ratings yet
- System Organ Function Illness Digestive System Mouth: Crohn's DiseaseDocument6 pagesSystem Organ Function Illness Digestive System Mouth: Crohn's DiseaseFharida AmuraoNo ratings yet
- TRIPLE Topic 2 OrganisationDocument22 pagesTRIPLE Topic 2 OrganisationjayakantharushanNo ratings yet
- What Is The Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesWhat Is The Digestive Systemsu966No ratings yet
- MN The Human Digestive SystemDocument14 pagesMN The Human Digestive SystemelizabethNo ratings yet
- Human Nutrition: Mechanical Digestion: Large Insoluble MoleculesDocument16 pagesHuman Nutrition: Mechanical Digestion: Large Insoluble MoleculesyourmoNo ratings yet
- Intro To DigestionDocument18 pagesIntro To DigestionelizabethNo ratings yet
- Body PhysiologyDocument19 pagesBody PhysiologydrmfhNo ratings yet
- Science Revision For Topic 8ADocument3 pagesScience Revision For Topic 8AsaniaNo ratings yet
- L2 How Organ Systems RespondDocument16 pagesL2 How Organ Systems RespondelizaclassroomNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Educational Video in Red Pink Illustrative StyleDocument15 pagesDigestive System Educational Video in Red Pink Illustrative Stylefarrahfahad72No ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument3 pagesEnzymescpagente01No ratings yet
- The Role of Enzymes in The Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesThe Role of Enzymes in The Digestive SystemJeanAnzurezNo ratings yet
- Adani Public School: Nanakapaya, Mundra 2020 - 2021 Science (Class 10)Document44 pagesAdani Public School: Nanakapaya, Mundra 2020 - 2021 Science (Class 10)Siddharth SouravNo ratings yet
- Digestive System & Animal NutritionDocument29 pagesDigestive System & Animal NutritiontalaaaNo ratings yet
- ScP025 Organs ResearchDocument1 pageScP025 Organs ResearchORBeducationNo ratings yet
- Group1 AnimalorganDocument62 pagesGroup1 AnimalorgandddsssoffNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument36 pagesDigestive SystemNyasha RumhezaNo ratings yet
- Human PhysiologyDocument85 pagesHuman PhysiologyDr-Qussai ZuriegatNo ratings yet
- The Human Digestive System AnswersDocument1 pageThe Human Digestive System AnswersKatherina FrancisNo ratings yet
- Nurition in Mammals - 2Document3 pagesNurition in Mammals - 2Farzan ButtNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Is It Outdated? Or...... Adapted?Document9 pagesDigestive System: Is It Outdated? Or...... Adapted?Monojit DharNo ratings yet
- ScP018 BiologyDocument1 pageScP018 BiologyORBeducationNo ratings yet
- IB HL Biology Notes: DigestionDocument9 pagesIB HL Biology Notes: DigestionayushfmNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in AnimalsDocument46 pagesNutrition in AnimalsFreshNo ratings yet
- Study Guide CHPT 1-5Document21 pagesStudy Guide CHPT 1-5peytonNo ratings yet
- Bal Bharati Public School, Pitampura, Delhi - 110034 Subject: Biology Class X: Chapter: Life Processes Topic-Life Processes (Heterotrophic Nutrition)Document5 pagesBal Bharati Public School, Pitampura, Delhi - 110034 Subject: Biology Class X: Chapter: Life Processes Topic-Life Processes (Heterotrophic Nutrition)SUHANEERIYANo ratings yet
- Biology GCSE Unit 2 Part 4 Enzymes and DigestionDocument3 pagesBiology GCSE Unit 2 Part 4 Enzymes and DigestiontahamidNo ratings yet
- Crammer Powerpoint b2Document35 pagesCrammer Powerpoint b2Mrs S BakerNo ratings yet
- DigestionDocument14 pagesDigestioncmizalpccfuNo ratings yet
- Liver, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandLiver, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- p13 Waves Electromagnetism and Space Electromagnetic WavesDocument1 pagep13 Waves Electromagnetism and Space Electromagnetic WavesLabeenaNo ratings yet
- HCF and LCM No Calculator: Exam-Type Questions A1 A2 A3 A4Document1 pageHCF and LCM No Calculator: Exam-Type Questions A1 A2 A3 A4LabeenaNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Organiser: Section 1: Key Terms Section 2: RustingDocument3 pagesKnowledge Organiser: Section 1: Key Terms Section 2: RustingLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Controlling Water and Nitrogen Balance in The BodyDocument1 pageControlling Water and Nitrogen Balance in The BodyLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Organiser: Section 1: Key Terms Section 3: Pressure in A Liquid at Rest Continued (HT)Document1 pageKnowledge Organiser: Section 1: Key Terms Section 3: Pressure in A Liquid at Rest Continued (HT)LabeenaNo ratings yet
- Animal Farm - Knowledge OrganiserDocument2 pagesAnimal Farm - Knowledge OrganiserLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Science - Chemistry Elements KODocument1 pageScience - Chemistry Elements KOLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Colour HuntDocument1 pageColour HuntLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Solutions HCF LCM ReviewDocument1 pageSolutions HCF LCM ReviewLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 6 Area and Perimeter Gr9 9 26 JuneDocument21 pagesWorksheet 1 6 Area and Perimeter Gr9 9 26 JuneLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Energy and Energy Transformations: Energy Makes Things HappenDocument8 pagesEnergy and Energy Transformations: Energy Makes Things HappenLabeenaNo ratings yet
- What Is This Number in Words 256780? What Is This Line:: The First 5 Prime NumbersDocument8 pagesWhat Is This Number in Words 256780? What Is This Line:: The First 5 Prime NumbersLabeenaNo ratings yet
- B1 - Test 1 Cell Biology Beginner: AQA - Combined Science BiologyDocument20 pagesB1 - Test 1 Cell Biology Beginner: AQA - Combined Science BiologyLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Aqa Chem Ms 1 June 2018 HigherDocument19 pagesAqa Chem Ms 1 June 2018 HigherLabeenaNo ratings yet
- 5 Questions, 5 Sentences, 5 Words GCSE Science: InstructionsDocument6 pages5 Questions, 5 Sentences, 5 Words GCSE Science: InstructionsLabeenaNo ratings yet
- P1 Test 1 Beginner QPDocument21 pagesP1 Test 1 Beginner QPLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Combined Science: Trilogy: 8464/P/1H - Physics Paper 1 - Higher Tier Mark SchemeDocument14 pagesCombined Science: Trilogy: 8464/P/1H - Physics Paper 1 - Higher Tier Mark SchemeLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) November 2018: Pearson Edexcel GCSE (9 - 1) in Mathematics (1MA1) Foundation (Calculator) Paper 2FDocument22 pagesMark Scheme (Results) November 2018: Pearson Edexcel GCSE (9 - 1) in Mathematics (1MA1) Foundation (Calculator) Paper 2FLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: P1 - Test 1 BeginnerDocument9 pagesMark Scheme: P1 - Test 1 BeginnerLabeena100% (1)
- Combined Science: Trilogy: 8464/B/1F - Biology Paper 1 Foundation Tier Mark SchemeDocument22 pagesCombined Science: Trilogy: 8464/B/1F - Biology Paper 1 Foundation Tier Mark SchemeLabeenaNo ratings yet
- What Do They Mean : DefineDocument3 pagesWhat Do They Mean : DefineLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Neutralisation Reactions Year 10 GZDocument4 pagesNeutralisation Reactions Year 10 GZLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Cells Science Year 9 GZDocument4 pagesCells Science Year 9 GZLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Science Revision BookletDocument25 pagesYear 9 Science Revision BookletLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Mirrors and Lenses: Ray Diagrams in A Plane MirrorDocument6 pagesMirrors and Lenses: Ray Diagrams in A Plane MirrorLabeenaNo ratings yet
- p3 Higher QsDocument26 pagesp3 Higher QsLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Forces: Force Can Cause An Object To Change Its Velocity or ShapeDocument8 pagesForces: Force Can Cause An Object To Change Its Velocity or ShapeLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory System Year 10 GZDocument6 pagesHuman Respiratory System Year 10 GZLabeenaNo ratings yet
- P2 Revision Question LoopDocument3 pagesP2 Revision Question LoopLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Afo Ssil Fuel Form Edf Rom The Rem Ains Ofd Ead Pla Nts A Nda Nim Als T Hat L Ived in TH Ese ADocument3 pagesAfo Ssil Fuel Form Edf Rom The Rem Ains Ofd Ead Pla Nts A Nda Nim Als T Hat L Ived in TH Ese ALabeenaNo ratings yet
- Diverticular Disease and Intestinal ObstructionDocument31 pagesDiverticular Disease and Intestinal ObstructionPauLa Cheneree Peña ÜNo ratings yet
- S4 2021 Half Yearly Exam (Paper 1 & 2) Marking Scheme V4Document4 pagesS4 2021 Half Yearly Exam (Paper 1 & 2) Marking Scheme V4dream oNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka: Option Com - Journal - Review&idDocument2 pagesDaftar Pustaka: Option Com - Journal - Review&idYogi OktiandiNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis - Gallstones: Overview, Causes, & Risk FactorsDocument3 pagesCholelithiasis - Gallstones: Overview, Causes, & Risk FactorsPipih Pertiwi Days'No ratings yet
- Case Study CholecystitisDocument13 pagesCase Study Cholecystitissanthyakunjumon100% (1)
- Rapid One Step Helicobacter Pylori Card TestDocument2 pagesRapid One Step Helicobacter Pylori Card TestTimNo ratings yet
- 014 Physiology MCQ ACEM Primary Digestion and AbsorptionDocument2 pages014 Physiology MCQ ACEM Primary Digestion and AbsorptionYasif AbbasNo ratings yet
- Internal Diagnosis II Good NotesDocument83 pagesInternal Diagnosis II Good Notesbjpalmer100% (2)
- Peri Ampullary TumorDocument69 pagesPeri Ampullary TumorMuhammed Muzzammil SanganiNo ratings yet
- Human Feces - WikipediaDocument62 pagesHuman Feces - Wikipediabdaniel79No ratings yet
- Volvulus MedscapeDocument7 pagesVolvulus MedscapeHanny Novia RiniNo ratings yet
- Trắc Nghiệm AVCN Dược 1Document12 pagesTrắc Nghiệm AVCN Dược 119150004No ratings yet
- PathoPhysiology of Diarrhea-PattyDocument5 pagesPathoPhysiology of Diarrhea-Pattyjap kurotsukiNo ratings yet
- Special Procudure (UGIS) : Body Habitus HyposthenicDocument12 pagesSpecial Procudure (UGIS) : Body Habitus HyposthenicJoeriz Bartolome100% (1)
- Intestinal ObstructionDocument9 pagesIntestinal ObstructionHamss AhmedNo ratings yet
- Melena, Diarrhea, NauseaDocument5 pagesMelena, Diarrhea, Nauseakelompok 6B IDIKNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis With Cholelithiasis: Free Nursing LecturesDocument9 pagesCholecystitis With Cholelithiasis: Free Nursing LecturesKath CacatianNo ratings yet
- Histology Digestive Tract Small Large IntestinesDocument28 pagesHistology Digestive Tract Small Large IntestinesAimie DagaleaNo ratings yet
- Early Postoperative Small Bowel Obstruction-The American Journal of Surgery 2015Document6 pagesEarly Postoperative Small Bowel Obstruction-The American Journal of Surgery 2015Trí Cương NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Practical Nursing Diploma Program Pre-Clinical Nursing Care Research Assignment "Prep and Plan"Document7 pagesPractical Nursing Diploma Program Pre-Clinical Nursing Care Research Assignment "Prep and Plan"Jeremy ThomasNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Alterations For Medical Surgical NursingDocument26 pagesGastrointestinal Alterations For Medical Surgical NursingyolondanicNo ratings yet
- This Is A New Doc Very NewDocument6 pagesThis Is A New Doc Very NewhusseinNo ratings yet
- Gastric Outlet ObstructionDocument10 pagesGastric Outlet ObstructionMpanso Ahmad AlhijjNo ratings yet
- Information Leaflet - Dyspepsia (Indigestion) : Understanding DigestionDocument3 pagesInformation Leaflet - Dyspepsia (Indigestion) : Understanding DigestionAdil moerdiono zainNo ratings yet
- The EsophagusDocument3 pagesThe EsophagusjosetelhadoNo ratings yet
- Adenomatous Polyps of The Colon 2006Document7 pagesAdenomatous Polyps of The Colon 2006Anelise SchaedlerNo ratings yet
- 69 Obstrucc - IntestinalDocument10 pages69 Obstrucc - IntestinalMaria Jose GiraldoNo ratings yet
- Anus and Rectum: Sam Grasso2019 Cara Reitz 2018 Joshua Dilday2017 Jake Swann 2016Document49 pagesAnus and Rectum: Sam Grasso2019 Cara Reitz 2018 Joshua Dilday2017 Jake Swann 2016Naresh DuthaluriNo ratings yet
- Https Cghs - Nic.in Reports View Hospital - JSPDocument36 pagesHttps Cghs - Nic.in Reports View Hospital - JSPRTI ActivistNo ratings yet