Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Evidence-Based Practices - Michelle Lau 1. Visual Supports
Evidence-Based Practices - Michelle Lau 1. Visual Supports
Uploaded by
api-544801662Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Evidence-Based Practices - Michelle Lau 1. Visual Supports
Evidence-Based Practices - Michelle Lau 1. Visual Supports
Uploaded by
api-544801662Copyright:
Available Formats
Evidence-Based Practices – Michelle Lau
1. Visual Supports
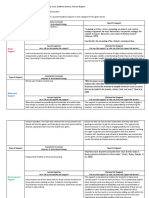
What are visual supports (VS)?
VS are concrete objects used to increase the learner’s ability to complete a specific skill or behaviour
Types of VS: Each type of VS can take on any of these cue forms
1. Visual direction Object – physically bringing student to playground
2. Instructional cue Photograph – showing real picture of their specific playground
3. Communication cue Picture/symbol – using playground symbol or drawing
4. Behaviour cue Text – “playground” written or typed on a cue card
5. Choice board
6. Labels/environmental visuals
Type of VS How does this help my student Example
with ASD?
What does this look like in my
classroom?
Visual Strategy to physically organize
Direction instructions for an activity or task.
Visual directions help increase
probability student will successfully
complete task
Physically separate the tasks into
its components (Math in one pile,
Science in another, OR worksheet 1
on the left, and then worksheet 2
on the right)
Helps with visually discriminating
one task with another, as well as
physically laying out what task
comes after another
Instructional Provides framework support for
Cues student to complete task
Includes graphic organizers,
adapted books, word walls, etc.
Choice Boards Used to visually represent choices
that learners can select
Increases autonomy and
independence of students.
Students learn more about their
own learning styles as well as likes
and dislikes
Includes objects, pictures, and/or
text
Labels/ Help students learn names of
Environment important objects in the classroom
Visuals as well as their location
Environment visuals also help
students anticipate what is
expected of them (ex: STOP = don’t
open this door)
Communication Allows students to express their
Cues needs and wants more freely
Teaches students to communicate
in more advance ways such as
asking a question or holding a
conversation (turn taking)
Cues become transferable skills
students can use when
communication and working with
their peers
Behaviour Help students understand and
Cues anticipate what is expected of
them in various situations
Cues can teach learners difference
between indoor vs outdoor voices,
as well as what “whole body
listening” looks like
2. Reinforcement
What is reinforcement (R+)?
R+ is a process that
o Teaches new skills (e.g. toilet training)
o Teaches a replacement behavior for an interfering behavior
o Increases appropriate behaviors
o Increases on-task behavior
Natural consequences of the skill/behaviour is paired with reinforcers, helping students with ASD create
stronger connections between actions and consequences
o Reinforces are removed slowly overtime to maintain the skill/behaviour
Three reinforcement procedures can be used for learners with ASD:
Procedure What is it? What Does It Look Like Examples for Students with ASD
in the Classroom
1. Positive Presenting a reinforce When student finishes
reinforcement (ex: food, praise, food) his work, he can play
after the learner does with this rubrik’s cube
the target for 5 minutes
skill/behaviour
2. Negative Removes a unwanted Student allowed to take Rise hand to ask for break.
reinforcement stimulus after a learner a body break after
does the target showing the teacher
skill/behaviour the “break” card
It is NOT a punishment.
Negative reinforcement
increases target
behaviour while
punishment decreases
target behaviour
3. Token Learners earn tokens Student’s goal is to
Economy after doing target raise her hand to ask a
skill/behaviour and can question. Teacher gives
use those tokens student token every
towards a desired time they ask a
reinforcer question in class. At the
end of each week,
student can use the
tokens to “buy”
something they like
from the class store.
References
Autism Focused Intervention Resources and Modules . (2020). Reinforcement. Retrieved from Reinforcement:
https://afirm.fpg.unc.edu/reinforcement
Autism Focused Intervention Resources and Modules . (2020). Visual Supports. Retrieved from Visual Supports:
https://afirm.fpg.unc.edu/visual-supports
Autism Speaks. (2011). Visual Supports and Autism. Retrieved from Visual Supports and Autism:
https://www.autismspeaks.org/sites/default/files/2018-08/Visual%20Supports%20Tool%20Kit.pdf
NEBRASKA AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDERS NETWORK. (2021). Reinforcement. Retrieved from Reinforcement:
https://www.unl.edu/asdnetwork/virtual-strategies/reinforcement
The National Professional Development Center of Autism Spectrum Disorder . (2020). What are Evidence-based
Practices? Retrieved from Evidence Based Practices : https://autismpdc.fpg.unc.edu/evidence-based-practices
You might also like
- CELT S Module 1 Task (Urooj Waqar)Document4 pagesCELT S Module 1 Task (Urooj Waqar)Urooj Waqar100% (4)
- Motivation Assessment Scale1 PDFDocument3 pagesMotivation Assessment Scale1 PDFDarlene Nelson100% (4)
- Iris Module - Week 5 1Document10 pagesIris Module - Week 5 1api-483468184100% (1)
- System Learning Plan Preparation: Krislizz International AcademyDocument11 pagesSystem Learning Plan Preparation: Krislizz International AcademyQhutie Little CatNo ratings yet
- Second Grade Science LessonDocument15 pagesSecond Grade Science Lessonlionheart10131333% (3)
- SCIENCE-3-COT 4th Quarter Science 2021Document3 pagesSCIENCE-3-COT 4th Quarter Science 2021Myralen Petinglay100% (21)
- Para Training Levels of Support and PromptingDocument53 pagesPara Training Levels of Support and Promptingapi-353333850No ratings yet
- Parent IEP Input FormDocument3 pagesParent IEP Input Formapi-544801662No ratings yet
- Projective Techniques IntroductionDocument16 pagesProjective Techniques IntroductionIsabel SamonteNo ratings yet
- Evidence-Based Practices - Michelle Lau 1. Visual SupportsDocument4 pagesEvidence-Based Practices - Michelle Lau 1. Visual Supportsapi-544801662No ratings yet
- Vlat 1 Planning Template 5b1 5d 1Document8 pagesVlat 1 Planning Template 5b1 5d 1api-433443544No ratings yet
- The Lorax Lesson Plan WeeblyDocument4 pagesThe Lorax Lesson Plan Weeblyapi-311937358No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Format For Science Teacher Education Candidates Ithaca College School of Humanities and SciencesDocument43 pagesLesson Plan Format For Science Teacher Education Candidates Ithaca College School of Humanities and Sciencesapi-404772398No ratings yet
- Name: - Sarah Grade Level Being Taught: K Subject/Content: Push and Pull Group Size: Whole Date of Lesson: 2/1/22Document8 pagesName: - Sarah Grade Level Being Taught: K Subject/Content: Push and Pull Group Size: Whole Date of Lesson: 2/1/22api-530094823No ratings yet
- 108 Learning Experience Plan5Document2 pages108 Learning Experience Plan5SaruNo ratings yet
- Bridging: MSMU Lesson Plan FormatDocument7 pagesBridging: MSMU Lesson Plan Formatapi-547294586No ratings yet
- IIED: ICT in Education Lesson Plan Format: TreesDocument5 pagesIIED: ICT in Education Lesson Plan Format: TreesstacyNo ratings yet
- Nicholas Mansour Web 2Document2 pagesNicholas Mansour Web 2api-691736066No ratings yet
- Self Assessment-3Document2 pagesSelf Assessment-3api-69011955No ratings yet
- Smart Goal ReflectionDocument3 pagesSmart Goal Reflectionapi-405728283No ratings yet
- Reflection 2 Classroom Management PlanDocument2 pagesReflection 2 Classroom Management Planapi-453648457No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan and Assessment 2 - Ariana SzepDocument7 pagesLesson Plan and Assessment 2 - Ariana Szepapi-666802127No ratings yet
- Ecc 707 - Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesEcc 707 - Lesson Planapi-584867199No ratings yet
- PE General Lesson Plan Template: What Is The Big Idea or Focus Question of The Lesson?Document3 pagesPE General Lesson Plan Template: What Is The Big Idea or Focus Question of The Lesson?api-417358924No ratings yet
- Harley Brooks Assignment7-1Document9 pagesHarley Brooks Assignment7-1api-239089066No ratings yet
- Evidence Based PractiseDocument40 pagesEvidence Based PractiseNelly EliNo ratings yet
- PLC 5Document25 pagesPLC 5api-265560161No ratings yet
- Pe Sailors Sharks Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesPe Sailors Sharks Lesson Planapi-393055116No ratings yet
- PLC 3Document23 pagesPLC 3api-265560161No ratings yet
- Comments Professionalism: EACH Student's Understanding or AchievementDocument4 pagesComments Professionalism: EACH Student's Understanding or AchievementHob151219!No ratings yet
- Evidence 7 (Rubric 12) : Provide Student Feedback To Guide LearningDocument4 pagesEvidence 7 (Rubric 12) : Provide Student Feedback To Guide Learningapi-483842715No ratings yet
- Direct Instruction Lesson Siana BergDocument2 pagesDirect Instruction Lesson Siana Bergapi-488045418No ratings yet
- Kartick - wk1 - SEL - (F1) - T2 JOURNALDocument7 pagesKartick - wk1 - SEL - (F1) - T2 JOURNALkartick.nationsNo ratings yet
- Week 2 and 3 Pec 6 and Pec 7Document10 pagesWeek 2 and 3 Pec 6 and Pec 7Jason Binondo75% (4)
- Professional Growth Plan Parker BijlDocument4 pagesProfessional Growth Plan Parker Bijlapi-384125792No ratings yet
- Drama Lesson Plan - Audrey BurnsDocument3 pagesDrama Lesson Plan - Audrey Burnsapi-743257332No ratings yet
- Science Microteach 1Document4 pagesScience Microteach 1api-656950304No ratings yet
- Research-Based Teaching and Learning in The 21st CenturyDocument70 pagesResearch-Based Teaching and Learning in The 21st CenturyAnonymous E8yT3R4iNo ratings yet
- IIED ICT FINAL Product Lesson Plan TemplateDocument5 pagesIIED ICT FINAL Product Lesson Plan TemplatestacyNo ratings yet
- Direct Instruction Lesson Plan TemplateDocument4 pagesDirect Instruction Lesson Plan Templateapi-404292238No ratings yet
- Activity 4Document6 pagesActivity 4api-347435906No ratings yet
- PLC 2Document16 pagesPLC 2api-265560161No ratings yet
- 1 Presentation 208Document25 pages1 Presentation 208Yuki SeishiroNo ratings yet
- Inquiry Uh Lesson Plan TemplateDocument7 pagesInquiry Uh Lesson Plan Templateapi-602779832No ratings yet
- Elementary School Lesson Plan 8Document6 pagesElementary School Lesson Plan 8api-347936911No ratings yet
- Stem Activity Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesStem Activity Lesson Planapi-668801294No ratings yet
- LRMDS Bat. ADM Module Template Gr.7 10 05242020 English 1Document22 pagesLRMDS Bat. ADM Module Template Gr.7 10 05242020 English 1Rhenz Ang MacaranasNo ratings yet
- Earth Science: Quarter 2 - Module 5 Rock Behaviors Under StressDocument21 pagesEarth Science: Quarter 2 - Module 5 Rock Behaviors Under StresssammieNo ratings yet
- So3 Pre-Observation ReflectionDocument2 pagesSo3 Pre-Observation Reflectionapi-309758533No ratings yet
- Communication: Quarter 1 - Learning Packet 1 Look and Respond When Spoken ToDocument20 pagesCommunication: Quarter 1 - Learning Packet 1 Look and Respond When Spoken ToChie FilomemaNo ratings yet
- Movement and Dance Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesMovement and Dance Lesson Planapi-742617301No ratings yet
- Direct Instruction Lesson Plan-1 2Document4 pagesDirect Instruction Lesson Plan-1 2api-532851463No ratings yet
- 2of3 Cep Lesson Plan TemplateDocument9 pages2of3 Cep Lesson Plan Templateapi-643149038No ratings yet
- Direct Instruction Lesson Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesDirect Instruction Lesson Plan Templateapi-487720035No ratings yet
- Module 2) : Quarter 1 (Characteristics of Southeast Asian ArtDocument24 pagesModule 2) : Quarter 1 (Characteristics of Southeast Asian ArtRisnaDPejoNo ratings yet
- Hope Quarter 4 - Lesson 1 2ND SemesterDocument16 pagesHope Quarter 4 - Lesson 1 2ND SemesterAwrey CutieNo ratings yet
- Direct Instruction Lesson Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesDirect Instruction Lesson Plan Templateapi-378219640No ratings yet
- Pe Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesPe Lesson Planapi-371637054No ratings yet
- Hula-Hut Attack Lesson WeeblyDocument4 pagesHula-Hut Attack Lesson Weeblyapi-311937358No ratings yet
- Medaille College Department of Education Lesson PlanDocument27 pagesMedaille College Department of Education Lesson Planapi-418542426No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Tiered Lesson Template 2017Document10 pagesAssignment 1 Tiered Lesson Template 2017api-527207076No ratings yet
- Task2 PLC Spring21Document3 pagesTask2 PLC Spring21api-549604532No ratings yet
- 4.4c Analysis of A Case Study #17 - Michelle Lau: Strategy 1: Complete Strength-Based Student ProfileDocument5 pages4.4c Analysis of A Case Study #17 - Michelle Lau: Strategy 1: Complete Strength-Based Student Profileapi-544801662No ratings yet
- Apply UDL Strategies: 6.4 Action and Expression - Michelle LauDocument5 pagesApply UDL Strategies: 6.4 Action and Expression - Michelle Lauapi-544801662No ratings yet
- Environmental Adaptations Example How/Why Does This Help?Document4 pagesEnvironmental Adaptations Example How/Why Does This Help?api-544801662No ratings yet
- Communication Method Frequency of Use PurposeDocument1 pageCommunication Method Frequency of Use Purposeapi-544801662No ratings yet
- MY Problems Won'T Quit: Case #9Document20 pagesMY Problems Won'T Quit: Case #9api-544801662No ratings yet
- Clues ArticleDocument13 pagesClues Articleapi-544801662No ratings yet
- 5.1b Resources On The Web - Michelle Lau: NameDocument2 pages5.1b Resources On The Web - Michelle Lau: Nameapi-544801662No ratings yet
- 5.4b DI in Lesson Plans - Michelle Lau: BackgroundDocument3 pages5.4b DI in Lesson Plans - Michelle Lau: Backgroundapi-544801662No ratings yet
- 4.3c Math Research - Michelle Lau: "Using Online Whiteboards To Boost Student Engagement and Confidence in Math"Document2 pages4.3c Math Research - Michelle Lau: "Using Online Whiteboards To Boost Student Engagement and Confidence in Math"api-544801662No ratings yet
- RTI Framework - Michelle Lau: Screening ProcessDocument3 pagesRTI Framework - Michelle Lau: Screening Processapi-544801662No ratings yet
- What Is Rti: RTI Stands For Response To InterventionDocument27 pagesWhat Is Rti: RTI Stands For Response To Interventionapi-544801662No ratings yet
- Emoji Understanding ScaleDocument3 pagesEmoji Understanding Scaleapi-544801662No ratings yet
- Positive Personal and Cultural Identity Social Responsibility Personal Awareness and ResponsibilityDocument3 pagesPositive Personal and Cultural Identity Social Responsibility Personal Awareness and Responsibilityapi-544801662No ratings yet
- IEP Stakeholders and Their Roles: Michelle LauDocument19 pagesIEP Stakeholders and Their Roles: Michelle Lauapi-544801662No ratings yet
- Section 1Document2 pagesSection 1api-544801662No ratings yet
- My Iep StoryDocument16 pagesMy Iep Storyapi-544801662No ratings yet
- Discussing Social Stretches - Michelle LauDocument2 pagesDiscussing Social Stretches - Michelle Lauapi-544801662No ratings yet
- Communication Method Frequency of Use PurposeDocument2 pagesCommunication Method Frequency of Use Purposeapi-544801662No ratings yet
- Asd Brochure - Michelle LauDocument5 pagesAsd Brochure - Michelle Lauapi-544801662No ratings yet
- This Is A Picture of Me: Some Words That Describe Me AreDocument1 pageThis Is A Picture of Me: Some Words That Describe Me Areapi-544801662No ratings yet
- TipstalkingparentsDocument2 pagesTipstalkingparentsapi-544801662No ratings yet
- 1 Fba TemplateDocument2 pages1 Fba Templateapi-544801662No ratings yet
- My Iep StoryDocument16 pagesMy Iep Storyapi-544801662No ratings yet
- Individual Education Plan: Tom BangleDocument3 pagesIndividual Education Plan: Tom Bangleapi-544801662No ratings yet
- CC - Social Awareness and Self-Assessment SupportDocument25 pagesCC - Social Awareness and Self-Assessment Supportapi-544801662No ratings yet
- Teachers' Perceptions of Implementing Differentiated Instruction For English Language LearnersDocument156 pagesTeachers' Perceptions of Implementing Differentiated Instruction For English Language LearnersRubie Bag-oyenNo ratings yet
- Peter Case StudyDocument3 pagesPeter Case StudyEden Mae R. OrtalizaNo ratings yet
- COUNCELLINGDocument4 pagesCOUNCELLINGKay BarretoNo ratings yet
- HRM - 5 - TrainingDocument3 pagesHRM - 5 - TrainingSk. Wahed BariNo ratings yet
- Parkers Updated ResumeDocument2 pagesParkers Updated Resumeapi-356372900No ratings yet
- Smart Goals Rubric 2Document2 pagesSmart Goals Rubric 2api-338549230100% (2)
- Chapter 04 Leading Change and InnovationDocument21 pagesChapter 04 Leading Change and InnovationranaNo ratings yet
- Selection Test Matrix: Test Type Cognitive AbilityDocument41 pagesSelection Test Matrix: Test Type Cognitive AbilityNamjaa EnkhbatNo ratings yet
- Michael Parondo Lenie Allegre: Prepared byDocument32 pagesMichael Parondo Lenie Allegre: Prepared byArcee Ardiente Mondragon100% (1)
- Brief Version of The Fear of Negative Evaluation SDocument10 pagesBrief Version of The Fear of Negative Evaluation Sselamet apriyantoNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Motivation and Intelligence PDFDocument1 pageAssignment On Motivation and Intelligence PDFTasfiq WahedNo ratings yet
- OJT Matrix Performance Evaluation FormDocument1 pageOJT Matrix Performance Evaluation FormAnonymous SUnOiY73No ratings yet
- Independent Passion Project Rubric 1Document2 pagesIndependent Passion Project Rubric 1api-511164497No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan COT English Grade IDocument3 pagesLesson Plan COT English Grade IRhealyn RiveraNo ratings yet
- Cyberbullying 101Document16 pagesCyberbullying 101fahmilastquncy100% (1)
- QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesQuestionnairemohammed issaka100% (8)
- St. Anthony College Calapan City, Inc.: Remedial Instruction in EnglishDocument3 pagesSt. Anthony College Calapan City, Inc.: Remedial Instruction in EnglishlNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal Support Evaluation List (ISEL) : ReferenceDocument6 pagesInterpersonal Support Evaluation List (ISEL) : ReferenceAndreea AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Belonging and Love Needs in AntigoneDocument5 pagesBelonging and Love Needs in AntigoneIpoenk Zuhro0% (1)
- Disability Assessment in Mental Illnesses Using Indian Disability Evaluation Assessment Scale (IDEAS)Document5 pagesDisability Assessment in Mental Illnesses Using Indian Disability Evaluation Assessment Scale (IDEAS)vinodksahu100% (1)
- Bud Not Buddy Survive ThriveDocument3 pagesBud Not Buddy Survive Thriveapi-265263932No ratings yet
- Eed 10 M5 F1Document4 pagesEed 10 M5 F1CRING TVNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Student Answer Template 2020Document3 pagesChapter 3 Student Answer Template 2020api-545241189No ratings yet
- Trauma Can Affect Your BrainDocument5 pagesTrauma Can Affect Your BrainhaNo ratings yet
- Team Dynamics & ManagementDocument37 pagesTeam Dynamics & Managementguineapi9No ratings yet
- The Effect of Cultural Shock in Adult Language Learning: Victoria SarasúaDocument7 pagesThe Effect of Cultural Shock in Adult Language Learning: Victoria SarasúaAnonymous tc7XPINo ratings yet