Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 10 - Managing Organization Structure and Culture (JG)
Chapter 10 - Managing Organization Structure and Culture (JG)
Uploaded by
Diva Tertia AlmiraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 10 - Managing Organization Structure and Culture (JG)
Chapter 10 - Managing Organization Structure and Culture (JG)
Uploaded by
Diva Tertia AlmiraCopyright:
Available Formats
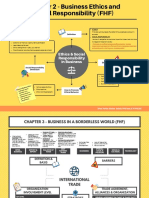
Organizational Design Job Design Grouping Jobs into Functions & Divisions
The process by which managers Job Enlargement: Increasing the Functional Structure: An organizational structure
make specific organizing choices number of different tasks in a composed of all the departments that an
that result in a particular kind of given job by changing the division organization requires to produce its goods or
organizational structure. of labor services.
Job Enrichment: Increasing the Divisional Structure: An organizational structure
Factors Affecting degree of responsibility a worker composed of separate business units, within Product Team Structure: An organizational
Organizational Structure has over his or her job which are the functions that work together to structure in which employees are
The Job Characteristics Model: five produce a specific kind of product for a specific permanently assigned to a crossfunctional
job characteristics affect an kind of customer team & report only to the product manager
employee’s motivation: Product Structure or to one of his or her direct subordinates
Skill variety Market Structure
Task identity Geographic Structure
Task significance Matrix Structure: An organizational structure that
Autonomy simultaneously groups people and resources by
Autonomy function and by product
ORGANIZATION STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONS & DIVISIONS
JOB DESIGN
Managing
Organization
ORGANIZATION CULTURE COORDINATION & INTEGRATION
Organizational Culture: The shared set Sources of an Hierarchy of Authority: An Integrating Mechanisms: Organizing tools
of beliefs, expectations, values, and Organization’s Culture. organization’s chain of command, to increase communication & coordination.
norms that influence how members of specifying the relative authority of each Types of Integrating Mechanisms:
an organization relate to one another manager.
and cooperate to achieve the Tall & Flat Organization: A tall organization
organization’s goals. has many levels of authority relative to
Adaptive cultures: values & norms company size; a flat organization has
fewer levels relative to company size
help an organization to build
Minimum chain of command
momentum & to grow and change to Centralization & decentralizing authority:
achieve its goals and be effective. Giving lower-level managers and
Inert cultures: values & norms fail to nonmanagerial employees the right to
motivate or inspire employees; they make important decisions about how to
lead to stagnation and failure. use organizational resources.
CHAPTER 10 - MANAGING ORGANIZATION STRUCTURE AND CULTURE (JG)
Diva Tertia Almira - Batch 78 Class A (470320)
CHAPTER 11 - Organization Control and Change (JG)
Diva Tertia Almira - Batch 78 Class A (470320)
Financial Measures of Performance
Profit ratios measure how Organizational Goals
Three Types of Control The Importance of efficiently managers are using the Organizationwide Goal Setting:
Organizational Control organization’s resources to
It helps managers obtain generate profits.
superior efficiency, quality, Liquidity ratios measure how well
responsiveness to customers, managers have protected
and innovation—the four organizational resources to be able
building blocks of competitive to meet short-term obligations.
advantage Leverage ratios measure the
Four Steps in degree to which managers use
Organizational Control debt (borrow money) or equity
(issue new shares) to finance
ongoing operations. Operating Budgets
Importance, Output A budget that states how managers
Types & Activity ratios show how well
managers are creating value from Control intend to use organizational resources to
Process
organizational assets. achieve organizational goals.
Clan Control
Organizational Change
Organization Clan
The control exerted on
individuals & groups in
The movement of an organization away Control an organization by
from its present state and toward some
preferred future state to increase its
Control & Change shared values, norms
standards of behavior,
efficiency and effectiveness & expectations.
Evolutionary Change
Change that is gradual, incremental, Organizational Behavior
and narrowly focused Change Control Management by Objectives (MBO)
Revolutionary Change A goal-setting process in which a manager
Change that is rapid, dramatic, and and each of his or her subordinates
broadly focused. negotiate specific goals and objectives for
Direct Supervision
Steps in the Organizational Change Process The most immediate and potent form the subordinate to achieve and then
Lewin’s Force-Field Theory of Change periodically evaluate the extent to which
of behavior control is direct
A wide variety of forces arise from the the subordinate is achieving those goals.
supervision by managers who actively
way an organization operates—from Steps:
monitor and observe the behavior of
its structure, culture, and control systems 1. Specific goals are established at each
their subordinates, teach subordinates
—that make organizations resistant to level of the organization
the behaviors that are appropriate and
change 2. Managers & their subordinates
inappropriate, & intervene to take
corrective action as needed. together determine the goals
3. Managers and their subordinates
Bureaucratic control periodically review the subordinates’
Control of behavior by means of a progress toward meeting goals
comprehensive system of rules &standard
operating procedures.
You might also like
- OpenText Vendor Invoice Management For SAP Solutions 20.4 SPS4 - Release Notes For Invoice SolutionDocument61 pagesOpenText Vendor Invoice Management For SAP Solutions 20.4 SPS4 - Release Notes For Invoice SolutionSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Inventory 2 (Theories & Problems) With AnswersDocument11 pagesInventory 2 (Theories & Problems) With AnswersUzziehllah Ratuita100% (3)
- Mang Task 4 - OkDocument5 pagesMang Task 4 - OkTharindu DhananjayaNo ratings yet
- Chap5 - OrganizingDocument51 pagesChap5 - OrganizingPhạm PhátNo ratings yet
- 5 Restructuring OrganizationsDocument36 pages5 Restructuring OrganizationsWael ALyNo ratings yet
- 2 Structuring and Job AnalysisDocument23 pages2 Structuring and Job AnalysisSherif KhalifaNo ratings yet
- OrganizingDocument46 pagesOrganizingsneha sasidharanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document25 pagesChapter 1Maurren SalidoNo ratings yet
- Five Main Steps of The Organizing ProcessDocument3 pagesFive Main Steps of The Organizing ProcessAlly GuiaoNo ratings yet
- OrganizingDocument26 pagesOrganizingTolentino LilyNo ratings yet
- Eem IvmcqDocument15 pagesEem IvmcqMritunjay YadavNo ratings yet
- Strategy PlanningDocument32 pagesStrategy PlanningSirengo MauriceNo ratings yet
- Business Organization REVDocument6 pagesBusiness Organization REVTremolo backNo ratings yet
- Organization and ManagementDocument23 pagesOrganization and ManagementDvay PamintaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 11Document2 pagesChapter 9 11Espinosa Miscent SamanthaNo ratings yet
- Ehs302 Ob4Document64 pagesEhs302 Ob4SUGGALA RAM PRASAD 22810165503No ratings yet
- Organizational Effectiveness & EfficiencyDocument24 pagesOrganizational Effectiveness & EfficiencyDr. Sujoy SenNo ratings yet
- 1e413organisational StructureDocument23 pages1e413organisational StructurePooja GroverNo ratings yet
- Organizational StructureDocument17 pagesOrganizational StructureRomalie GalletoNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 Bs-Xii RK SinglaDocument29 pagesUnit-5 Bs-Xii RK Singlaaditya artsNo ratings yet
- Performance Management in Agile OrganizationsDocument8 pagesPerformance Management in Agile OrganizationsMohamed Elhaj HusseinNo ratings yet
- Pointers To ReviewDocument7 pagesPointers To ReviewAbegail LastimosoNo ratings yet
- Varma CommitteeDocument31 pagesVarma CommitteeDr-Shefali GargNo ratings yet
- CEPB323 Slide - Topic 2 Organization Structure (Sem 2 20172018)Document16 pagesCEPB323 Slide - Topic 2 Organization Structure (Sem 2 20172018)razNo ratings yet
- PGP21-OBII - Session 3 PDFDocument19 pagesPGP21-OBII - Session 3 PDFMegha SinhaNo ratings yet
- Organizational Design & Strategic ControlDocument33 pagesOrganizational Design & Strategic ControlNazir AnsariNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - CE 3203 - CMPMDocument37 pagesGroup 2 - CE 3203 - CMPM21-04974No ratings yet
- POM - Lesson 5Document19 pagesPOM - Lesson 5Estefh Tatad LagmayNo ratings yet
- Organization & Principles: "It's All AboutDocument41 pagesOrganization & Principles: "It's All AboutPrasadNo ratings yet
- Organizing and StaffingDocument48 pagesOrganizing and StaffingKeshav NayakNo ratings yet
- Internal Assessment: Week 5Document30 pagesInternal Assessment: Week 5Ashilla OktaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Internal AssessementDocument30 pagesWeek 5 Internal AssessementIkhsan MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Internal AnalysisDocument20 pagesInternal AnalysisSujan SanjayNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document19 pagesCH 11Management StudiesNo ratings yet
- Iam Aln Asset Management Leadership White Paper v4Document10 pagesIam Aln Asset Management Leadership White Paper v4Fernando GasparNo ratings yet
- Ch-3 MGTDocument16 pagesCh-3 MGThai manNo ratings yet
- TQM Unit-IiiDocument13 pagesTQM Unit-IiiKalyan NaniNo ratings yet
- PerformDocument6 pagesPerformSandeep TiwariNo ratings yet
- Week008 Organizing1Document12 pagesWeek008 Organizing1Marie FeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Topic OutlineDocument2 pagesChapter 4 Topic OutlineLovely JillNo ratings yet
- Presentation On OCP and SAP by Ritul TripathiDocument30 pagesPresentation On OCP and SAP by Ritul TripathiritulNo ratings yet
- 9 Variance in Organistaional StructuresDocument17 pages9 Variance in Organistaional StructuresPraveen RavishankaranNo ratings yet
- Module 1, Part 1 OpAud-Synchronous, Definition, CharacteristicsDocument19 pagesModule 1, Part 1 OpAud-Synchronous, Definition, CharacteristicsMA. CARMELLA VALDEZNo ratings yet
- Organization & Principles: "It's All About WorkingDocument41 pagesOrganization & Principles: "It's All About WorkingEVISHA SONI 1927233No ratings yet
- Unit 5 OB 28pgs - RotatedDocument28 pagesUnit 5 OB 28pgs - Rotatedsasithar jaisankaranNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Strat ManDocument3 pagesReviewer Strat ManAngela VecinoNo ratings yet
- Wipro 2Document5 pagesWipro 2KESHAV AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Orgbev MidtermsDocument17 pagesOrgbev MidtermsJade MasiragNo ratings yet
- Organization & Principles: "It's All About WorkingDocument41 pagesOrganization & Principles: "It's All About WorkingnikhilNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument43 pagesUnit IIHarini SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 PresentationDocument29 pagesChapter 6 PresentationJuan LamasNo ratings yet
- On OrganisingDocument107 pagesOn Organisingdhanvi1259No ratings yet
- Tuhin OSD PresentationDocument17 pagesTuhin OSD PresentationtuhinvloggerNo ratings yet
- 9 Organizing ChuchuDocument46 pages9 Organizing ChuchuBheverly SorianoNo ratings yet
- Task 1: Prepare An Organisational Development Plan Organizational Development Plan BackgroundDocument15 pagesTask 1: Prepare An Organisational Development Plan Organizational Development Plan Backgroundpramod thakuri75% (4)
- PMSDocument4 pagesPMSAbiguel JoyceNo ratings yet
- Team Culminating Project Milestone 2Document5 pagesTeam Culminating Project Milestone 2api-650427702No ratings yet
- Performance ManagementDocument57 pagesPerformance ManagementAvinaw KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document19 pagesChapter 11Madhav AroraNo ratings yet
- Bab 15 Foundations of Organization StructureDocument14 pagesBab 15 Foundations of Organization StructureNiken NikenNo ratings yet
- Building Winning Organisations: A complete guide to sustaining best-in-class performance for all organisationsFrom EverandBuilding Winning Organisations: A complete guide to sustaining best-in-class performance for all organisationsNo ratings yet
- EVALUATING THE ROLE OF CORE COMPETENCIES IN IMPROVING PERFORMANCE OF MANUFACTURING INDUSTRIESFrom EverandEVALUATING THE ROLE OF CORE COMPETENCIES IN IMPROVING PERFORMANCE OF MANUFACTURING INDUSTRIESNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Risk and Return Self Test ST1 Year Ra RB rAB A B ABDocument17 pagesChapter 6 - Risk and Return Self Test ST1 Year Ra RB rAB A B ABDiva Tertia AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 4 - Business Case MCDONALDDocument10 pagesKelompok 4 - Business Case MCDONALDDiva Tertia AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Business & Management Mind Map - W2Document3 pagesBusiness & Management Mind Map - W2Diva Tertia AlmiraNo ratings yet
- π= x= μ= λ= σ σ = x= P (0 z) = a= b= N= n= μ s= df= P (0 t) =: SymbolsDocument11 pagesπ= x= μ= λ= σ σ = x= P (0 z) = a= b= N= n= μ s= df= P (0 t) =: SymbolsDiva Tertia AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Roadrunner CaseDocument7 pagesRoadrunner CasephuongvietngoNo ratings yet
- Schneider Ecofit - Low and Medium Voltage Distribution Switchboards FPXDocument150 pagesSchneider Ecofit - Low and Medium Voltage Distribution Switchboards FPXlisley perezNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics & Social ResponsibilityDocument7 pagesBusiness Ethics & Social ResponsibilityAnoosha Mazhar100% (1)
- Survey RequestDocument2 pagesSurvey RequestsunmarineNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle Cost Analysis of Commercial Building: Seminar - 2Document3 pagesLife Cycle Cost Analysis of Commercial Building: Seminar - 2Vashuka GhritlahreNo ratings yet
- InternshipsDocument5 pagesInternshipsBradley BlakeNo ratings yet
- Building Brand EquityDocument3 pagesBuilding Brand EquityGlorrya TambotoNo ratings yet
- Safety Pre-Construction Meeting GKS .Document66 pagesSafety Pre-Construction Meeting GKS .ce.rashed12No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document4 pagesChapter 5Risalyn BiongNo ratings yet
- Nikhil KanthDocument76 pagesNikhil Kanthharpreet singh100% (1)
- Hala Arrabi Managerial Finance Assignment Chapter 3-Part 1 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument3 pagesHala Arrabi Managerial Finance Assignment Chapter 3-Part 1 Multiple Choice QuestionsMohamad Haytham ElturkNo ratings yet
- Prepaway TestDocument40 pagesPrepaway TestmamoudNo ratings yet
- IAS Hub Web UI PDFDocument1 pageIAS Hub Web UI PDFKABIR BATRANo ratings yet
- Abm For SuccessDocument21 pagesAbm For SuccessJaime PalizardoNo ratings yet
- Leiblein What Makes A Decision Strategic 2018 Strategy ScienceDocument18 pagesLeiblein What Makes A Decision Strategic 2018 Strategy ScienceSeah Jia huiNo ratings yet
- 12th Commerce Study Material English MediumDocument97 pages12th Commerce Study Material English MediumDeepak ajar100% (1)
- The Impact of Brand PositioningDocument17 pagesThe Impact of Brand PositioningLisnawati LimbongNo ratings yet
- How To Write Your Performance Objective Statements: Our Top TipsDocument2 pagesHow To Write Your Performance Objective Statements: Our Top TipsShruti KochharNo ratings yet
- Driving The Global Cannabis Industry: February 2019Document22 pagesDriving The Global Cannabis Industry: February 2019Sameer MahomedNo ratings yet
- Renders Chapter Six HomeworkDocument8 pagesRenders Chapter Six HomeworkAsad Ehsan Warraich0% (1)
- Inventory JournalDocument6 pagesInventory JournalhendranatjNo ratings yet
- GD Slots Format-JSSDocument12 pagesGD Slots Format-JSSMITUL GARGNo ratings yet
- Final Thesis-NelsonDocument38 pagesFinal Thesis-NelsonsmrshaikhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Cost TermsDocument35 pagesChapter 2 - Cost TermsCarina Carollo MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Administration Without Borders PDFDocument11 pagesJurnal Administration Without Borders PDFgrahma96No ratings yet
- NSE FNO Lot Size As On 22.12.2022Document14 pagesNSE FNO Lot Size As On 22.12.2022Mahammad Rafi DNo ratings yet
- SRS DocumentDocument8 pagesSRS Documentshreyastha2058No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Marketing Organization For EggsDocument4 pagesChapter 4 - Marketing Organization For EggsTest OneNo ratings yet