Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Language Acquisition
Language Acquisition
Uploaded by
GIANELLA ARACELLY MENDOZA AQUINOOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Language Acquisition
Language Acquisition
Uploaded by
GIANELLA ARACELLY MENDOZA AQUINOCopyright:
Available Formats
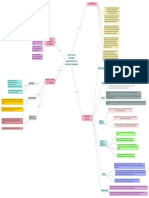
They could re-learn the language they had lost
While after puberty
Children generally do not regain their language
Lenneberg claimed that children under
the age of 3 or 4
Correct "bad grammar" That the attribution of language to brain areas ended at puberty
After adolescence lateralization
was impossible
How or what children learn
from adult feedback This includes
Reward for 'good Greater range than adult-directed speech
grammar'
Longer pauses between statements
Or how they discover and construct the correct
grammar rules
In a particular way called maternal speech
I would not answer the question of
Greater rhythmicity
Examples of A critical period
models are
obvious "teeth" Adults correct children's syntax
That they are exceptional for children's language Slower tempo
The role of correction Some people talk to babies and young children
Expressions
"Why is the sun like: Adults tend to favor higher pitch
They differ substantially from structures found in adult speech shining?"
Touch
.The role of child-directed speech Facial expression
.The role of imitation Also in communication devices such as
Eye contact
Is in greater doubt Children show a preference for this type the nature
of conversation. Point out
The first theory concerning
They cannot imitate structures The importance of imitation development of human intelligence
that they have not yet learned
inner feelings of the child crying Primitive
Jean
Due to the fact that children the first
is about the processes children apply as they create
generally
preparation for vocal communication their knowledge of the world
sensorimotor
child interaction is the 4 stages of cognitive development:
consists of two parts preoperational
caregiver the second
concrete operation
child's first vocalizations
cooing 02 months Pre-language
sees language acquisition as part of broader intellectual development. formal operation stage
DETERMINANTS
caregiver responses 1° communication attempts
articulation skills
babbling
control of their vocal apparatus
06 months Cognitive Theory on native language learning,
vowel
Behaviourism appeared to be a new
consonant syllabic sets approach to psychology Is generally a psychological theory
1° psycholinguistic stage canonical babbling
advanced in part as a response to
1° understandable words. conventional grammar.
08 - 12 months J.B. Watson bases on the analyses of
exposure to mother tongue the rule of the behaviourist human behaviour
words that refer to objects stimulus-response
successfully made the transition from an iconic creature to an
iconic creature
It concentrates on spoken language
intonal clues
holophrases use simple terms Behaviourist
contextual Theory All learning is a demonstration of habits as the consequence
gestural of reinforcement and reward
12 - 18 months holophrastic stage The one-word Stages is governed by operating principles.
1° one-word statements. LANGUAGE ACQUISITION Theories
Learning is the same for each individual
words they invent and use Linguist Noam
use idiomorphs Chomsky
eighteen to skills as uniquely human
twenty-four months The age considers infants’ language
express more complex information
interpretation of the child’s speech is
by context. strictly related to the structure of the brain
‘mini sentences’
The two-word
open-
class words
Braine’s theory
classifying
pivot-class words Nativist or His work on syntax and changed
Innateness Theory transformational grammar linguistics explanations of grammatical rules and transformations
became
Start producing more complex and longer the focus of psychological investigations on language use
grammatical structures
The telegraphic
control the order diversity and the natural-language
composition of syntactic rules. sophistication syntax is too difficult for children to
learn from what they hear
head-complement
and subject-VP patterns
discovered by the child from the data available to him/her.
Issues The assumptions of Chomsky’s hypothesis were that:
language explosion
understanding five times as many Furthermore, children would not learn their
Later development first language so fast if they did not rely on
inflectional morphemes
and non-lexical some innate capacity
variation in word-forms
determiners Competence Perception
and auxiliary verbs Competence and Performance a fact, of a system and event
its pronunciation is close to adult language Learn
unobservable ability to do something
Initiate a conversation
Comprehencion and Production Concrete manifestation or realization of competence
Give responses
Discourse Performance
for help, for an action
Identify if the information is
Listening and reading (proficiency)
Nature or nurture Comprehension
Children speak what they hear at home Language and thought
Speaking and writing (performance)
-Cajacuri Lajo Lady
Production
Imitation
Members Esteban Aliaga Nicoll Input One is born with an innate knowledge of language
-Mendoza Aquino Gianella Not demonstrated in our genes
Early language learning (echo)
-Pablo Machaca Jackeline
Children imitate the surface structure of language.
Determines Language depends on cognitive development
-Tejada Cristobal Angie Piaget
how linguists describe and explain the interaction of the two
You might also like
- Kids Box New Generation 4 Activity BookDocument89 pagesKids Box New Generation 4 Activity BookMaría Cecilia Paris100% (4)
- Adult Esl - Level 1 - Curriculum Scope and SequenceDocument5 pagesAdult Esl - Level 1 - Curriculum Scope and Sequenceapi-534439517No ratings yet
- l2 Writing CapstoneDocument16 pagesl2 Writing Capstoneapi-369325039No ratings yet
- APA Guidelines ChapterDocument29 pagesAPA Guidelines ChapterElmahdi OuassouNo ratings yet
- Childline Se Dosti 2019Document30 pagesChildline Se Dosti 2019Sandip BaraiyaNo ratings yet
- Nature Vs NurtureDocument4 pagesNature Vs NurturemkpongkeabasiudohNo ratings yet
- Eyes That Kiss in The Corners-Extension FormDocument2 pagesEyes That Kiss in The Corners-Extension Formapi-550368270No ratings yet
- Teaching With Explore Our World-Pacing Guide (Nat Geo)Document15 pagesTeaching With Explore Our World-Pacing Guide (Nat Geo)looks4tranz100% (1)
- WileyBlevins PhonicsDocument6 pagesWileyBlevins PhonicsamurrayNo ratings yet
- How To Teach English Learners ColorsDocument1 pageHow To Teach English Learners ColorsGatika JessiNo ratings yet
- Exam Advice Yes No Not GivenDocument1 pageExam Advice Yes No Not GivenЕкатерина ГеращенкоNo ratings yet
- Vianna Hong Teaching Resume 2023Document1 pageVianna Hong Teaching Resume 2023api-659624788No ratings yet
- Creating A Supportive Teaching and Learning Environment For English Language LearnersDocument4 pagesCreating A Supportive Teaching and Learning Environment For English Language LearnersbeodethuongNo ratings yet
- Reading Report No. 5Document3 pagesReading Report No. 5Fernanda BonillaNo ratings yet
- Observation Task 5Document1 pageObservation Task 5api-294972438No ratings yet
- Stages of Literacy ChartsDocument3 pagesStages of Literacy Chartsbyunbacooon456No ratings yet
- When Children Are Not Read To at Home The Million.9Document4 pagesWhen Children Are Not Read To at Home The Million.9Lilian VillablancaNo ratings yet
- 4° Ingles WorkbookDocument19 pages4° Ingles WorkbookLISET NOELIA MENDIETA LEIVA100% (1)
- Adult GuidanceDocument1 pageAdult GuidanceМария ХохловаNo ratings yet
- Can-Do StatementsDocument1 pageCan-Do StatementsMesut YaylaNo ratings yet
- All About DialogicDocument5 pagesAll About Dialogicp.ioannidiNo ratings yet
- JilliandoughertyresumeeidDocument2 pagesJilliandoughertyresumeeidapi-659399074No ratings yet
- Teaching Resume December 2022Document3 pagesTeaching Resume December 2022Maria BNo ratings yet
- Assignament 1Document5 pagesAssignament 1silvanaNo ratings yet
- How Much of A Problem Is Bullying at School, 2017Document6 pagesHow Much of A Problem Is Bullying at School, 2017Antonio PortelaNo ratings yet
- Early Read and Erda 2Document8 pagesEarly Read and Erda 2One FaithNo ratings yet
- Parents Roles PDFDocument3 pagesParents Roles PDFhammads88No ratings yet
- PERDEV Handout - M3 (Developmental Stages Handout)Document2 pagesPERDEV Handout - M3 (Developmental Stages Handout)Ella MirandaNo ratings yet
- Eia3e Sampler PDFDocument19 pagesEia3e Sampler PDFAdman AlifAdmanNo ratings yet
- Advantages: How Young Children Learn English As Another LanguageDocument1 pageAdvantages: How Young Children Learn English As Another LanguageSaraa VictoriaNo ratings yet
- NCM 116 NutritionDocument9 pagesNCM 116 Nutritionrommel magoNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument2 pagesAbstracthp chromebook0% (1)
- PD Session Oct 16 2017Document1 pagePD Session Oct 16 2017api-331006019No ratings yet
- Increasing Parenting Skills and Parenting E Cacy: Parent-Training Program Based Seamless Learning To Promoting Assessment Child DevelopmentDocument1 pageIncreasing Parenting Skills and Parenting E Cacy: Parent-Training Program Based Seamless Learning To Promoting Assessment Child Developmentkerja malamNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Mastery of Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) in Gr7 FilipinoDocument4 pagesConsolidated Mastery of Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) in Gr7 FilipinoMaria Camille CaylanNo ratings yet
- Speciationvocabpresentations lp3Document4 pagesSpeciationvocabpresentations lp3api-332032383No ratings yet
- Working Smarter Not HarderDocument9 pagesWorking Smarter Not Harderיובל נברוNo ratings yet
- Your Education: Securing A Good Start in Life Roadblocks To Post-Secondary EducationDocument1 pageYour Education: Securing A Good Start in Life Roadblocks To Post-Secondary EducationMayara Atherino MacedoNo ratings yet
- cm-102 ResumeDocument2 pagescm-102 Resumeapi-547933828No ratings yet
- Action ResearchDocument10 pagesAction ResearchRain Fryx RoscoNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Social Studies Curriculum: Us History Ii - The Industrial Revolution To The PresentDocument16 pagesGrade 11 Social Studies Curriculum: Us History Ii - The Industrial Revolution To The PresentjethNo ratings yet
- Workbook: Creating Young Thinkers With Great FuturesDocument1 pageWorkbook: Creating Young Thinkers With Great FuturesJoAnne K. ANo ratings yet
- 5 ReasonsposterDocument1 page5 Reasonsposterapi-459495093No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Template WritingDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Template Writingapi-665823233No ratings yet
- Mistaken Goal Chart 2023Document1 pageMistaken Goal Chart 2023Lynn LimNo ratings yet
- Owl English k2Document8 pagesOwl English k2Mariana TeleseNo ratings yet
- Owl English k2Document8 pagesOwl English k2winata linggaNo ratings yet
- CH 10 Intelligence: Differences in Brain Area Size Through Bumps On The SkullDocument5 pagesCH 10 Intelligence: Differences in Brain Area Size Through Bumps On The SkullEmma LofgrenNo ratings yet
- Lara Leinss Resume 2023Document3 pagesLara Leinss Resume 2023api-492585707No ratings yet
- Annual Planning A1 - 1 PDFDocument10 pagesAnnual Planning A1 - 1 PDFAnonymous ibSRqUNo ratings yet
- Oye CanciónDocument13 pagesOye CanciónClemente TorresNo ratings yet
- Keto Chai Latte - A Spicy Classic, Creamy Blend - Diet DoctorDocument1 pageKeto Chai Latte - A Spicy Classic, Creamy Blend - Diet DoctoranwarNo ratings yet
- Teaching Reading Skills To Children With Down SyndromeDocument4 pagesTeaching Reading Skills To Children With Down SyndromeyusrizainolabidinNo ratings yet
- Absentees or LateDocument2 pagesAbsentees or LateMa. Fatima RabulanNo ratings yet
- Skillful L&S 2 TB Unit 2Document10 pagesSkillful L&S 2 TB Unit 2Shayan MokhtariNo ratings yet
- Esther LR Matrix TemplateDocument2 pagesEsther LR Matrix TemplateEsther Donny KimsiongNo ratings yet
- Early Intervention and MilestonesDocument2 pagesEarly Intervention and Milestoneslin eeNo ratings yet
- Advanced Assessment On Language TeachingDocument24 pagesAdvanced Assessment On Language Teachingjon daanNo ratings yet
- Synopsis: of Speech Act (Chapter: 09) of Book Introducing English Semantics by Charles WDocument8 pagesSynopsis: of Speech Act (Chapter: 09) of Book Introducing English Semantics by Charles Wkhushal waseemNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 English Halfyearly Set 2checkedDocument7 pagesGrade 5 English Halfyearly Set 2checkedswetha swithinNo ratings yet
- IELTS Self Study GuideDocument16 pagesIELTS Self Study Guidewalid hassanNo ratings yet
- A3 ADVERBS - Ingles 2Document22 pagesA3 ADVERBS - Ingles 2Leandro LópezNo ratings yet
- "Psycholinguistics": "Language & Brain (Neurolinguistics) "Document12 pages"Psycholinguistics": "Language & Brain (Neurolinguistics) "Muhammad Hashir AzizNo ratings yet
- Sentence FragmentsDocument5 pagesSentence Fragmentsjeleen endaya100% (1)
- ProductivityDocument10 pagesProductivityAdeNov ChannelNo ratings yet
- X SeralDocument7 pagesX SeralOana-Violeta Si Cornel SelaruNo ratings yet
- Baranova GrammarDocument64 pagesBaranova GrammarNadiia ShamraiNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension in The TOEFL PBTDocument12 pagesReading Comprehension in The TOEFL PBTannisa AnnisaNo ratings yet
- Onomatopoeia Sound Word BoxDocument2 pagesOnomatopoeia Sound Word BoxEdgar SenevirathnaNo ratings yet
- Comparative and Superlative Chart. - RGJU - 5IV9Document2 pagesComparative and Superlative Chart. - RGJU - 5IV9JONH RGNo ratings yet
- TGS 2 Structure - Sheilla RivandaDocument3 pagesTGS 2 Structure - Sheilla RivandaLILISNo ratings yet
- French TheoryDocument13 pagesFrench TheoryKudzai TaruwonaNo ratings yet
- Movies: Vocabulary BankDocument7 pagesMovies: Vocabulary BankArturo PerezNo ratings yet
- كتاب جميل لتعلم التدقيق اللغويDocument205 pagesكتاب جميل لتعلم التدقيق اللغويMoshira MahmoudNo ratings yet
- S Giáo D C Và Đào T o Bình DươngDocument4 pagesS Giáo D C Và Đào T o Bình DươngAnh Tuấn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- How 2 Master Hebrew VerbsDocument25 pagesHow 2 Master Hebrew Verbsivrit4generalesNo ratings yet
- Place of ArticulationDocument13 pagesPlace of ArticulationAarohi JagtapNo ratings yet
- Tingkatan 5 English Week 1-4Document11 pagesTingkatan 5 English Week 1-4Ruban RubanNo ratings yet
- Language Standardization in General Point of View: e-ISSN: 2, p-ISSNDocument7 pagesLanguage Standardization in General Point of View: e-ISSN: 2, p-ISSNZara NurNo ratings yet
- Ngu Phap Nang CaoDocument25 pagesNgu Phap Nang CaoSamNo ratings yet
- Prototype Theory and Meaning PDFDocument405 pagesPrototype Theory and Meaning PDFNaddiNo ratings yet
- FILE - Second and Third ConditionalsDocument4 pagesFILE - Second and Third ConditionalsIsha Claire AliliranNo ratings yet
- Ms Dung Research Proposal 4Document15 pagesMs Dung Research Proposal 4Đào Nguyễn Duy TùngNo ratings yet
- Elementary Unit Test 1: GrammarDocument1 pageElementary Unit Test 1: GrammarDanny PintoNo ratings yet
- Presupposition, Negation, and Entailment 20231113 061025 0000Document29 pagesPresupposition, Negation, and Entailment 20231113 061025 0000Caryl Simbajon EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Reflection Language LossDocument4 pagesReflection Language LossDurga DeVadassNo ratings yet