Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Neurogenic - Spinal Cord Injury at The - Have An Issue With - Hypotension, - Foley Catheter Placement
Neurogenic - Spinal Cord Injury at The - Have An Issue With - Hypotension, - Foley Catheter Placement
Uploaded by
abychloeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Rehab Cheat SheetDocument18 pagesRehab Cheat SheetZ A100% (3)
- RA Export 20230303-171712 (TEMPLATE-04 Haz) - ID230303164833 - Rev2023-03-03 - Cargo & Ballast Works - Ballast Water Treatment System FailureDocument3 pagesRA Export 20230303-171712 (TEMPLATE-04 Haz) - ID230303164833 - Rev2023-03-03 - Cargo & Ballast Works - Ballast Water Treatment System FailureHarman Sandhu100% (3)
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 1 - Script Ceu Azul 2023Document21 pages1 - Script Ceu Azul 2023Indigo Graficos50% (2)
- NCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion (Eclampsia)Document1 pageNCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion (Eclampsia)Jenny AjocNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Characteristics of Copper Mine TailingsDocument12 pagesGeotechnical Characteristics of Copper Mine TailingsJamie CuttingNo ratings yet
- All Cardio DiseasesDocument8 pagesAll Cardio Diseaseshiba sharjeelNo ratings yet
- Shock EditedDocument56 pagesShock EditedJeevan VelanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Fvd2Document2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Fvd2ghellersNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Fluid Volume Imbalances: SoluteDocument8 pagesWeek 7 Fluid Volume Imbalances: SoluteMaica LectanaNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorDocument2 pagesPredisposing Factor Precipitating FactorkamotenikimiNo ratings yet
- Hypovolemic Shock PathoDocument10 pagesHypovolemic Shock PathoLorebell100% (1)
- Blood VesselsDocument4 pagesBlood VesselsCrazy StrangerNo ratings yet
- Chapter+04 9th+edition ITLS 04-2020Document25 pagesChapter+04 9th+edition ITLS 04-2020Brhanemeskel MekonnenNo ratings yet
- Sodium Imbalances (Hyponatremia Vs Hypernatremia)Document17 pagesSodium Imbalances (Hyponatremia Vs Hypernatremia)Angel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Pathopyshiology-w-Risk-Factors - DTDocument3 pagesPathopyshiology-w-Risk-Factors - DTDivynne MadeloNo ratings yet
- Before: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott's Nursing Drug Guide, P. 407Document2 pagesBefore: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott's Nursing Drug Guide, P. 407SoniaMarieBalanayNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic Management of HypertensionDocument8 pagesPharmacologic Management of HypertensionL2 - MAKILALA, Zion joy B.No ratings yet
- Textbook Discussion On ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction - GicaroDocument12 pagesTextbook Discussion On ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction - GicaroJica Marie Bandiola GicaroNo ratings yet
- Doria. 30emergency DrugsDocument7 pagesDoria. 30emergency DrugsAbegail Bautista DoriaNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument8 pagesShockPIH SHTNo ratings yet
- Increased Intracranial PressureDocument10 pagesIncreased Intracranial Pressureapi-3822433100% (10)
- PathophysiologyDocument34 pagesPathophysiologyeunams_1195% (20)
- Hemodynamic Disorders Thromboembolic Disease and ShockDocument13 pagesHemodynamic Disorders Thromboembolic Disease and ShockAbu HuraraNo ratings yet
- SHOCKDocument1 pageSHOCKJessa Mae Alforque AsentistaNo ratings yet
- SHOCK - HandoutsDocument6 pagesSHOCK - HandoutsKim GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Arrythmias 2-3Document4 pagesArrythmias 2-3cayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Hypo: Low - Vol: Volume - Emic: Blood: Burns Fracture PancreasDocument5 pagesHypo: Low - Vol: Volume - Emic: Blood: Burns Fracture PancreasNicholas TagleNo ratings yet
- Shock and Its Management: Presented byDocument72 pagesShock and Its Management: Presented bysheme171150% (2)
- Drug Study AbulenciaaaDocument3 pagesDrug Study AbulenciaaaKsksksksNo ratings yet
- Septic Shock and HypovolaemiaDocument2 pagesSeptic Shock and HypovolaemiasicatdianneNo ratings yet
- Doria. 30emergency DrugsDocument7 pagesDoria. 30emergency DrugsAbegail Bautista DoriaNo ratings yet
- 15 ShockDocument33 pages15 ShocknitsuhNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument29 pagesShockKoRnflakes100% (4)
- ER BatMC 2 Drug StudyDocument4 pagesER BatMC 2 Drug StudyFalqueza JanelleNo ratings yet
- Banan Harbi Lana Sbitan: Done By: Zaid Abu-Ameerah Mohammad AlotaibiDocument32 pagesBanan Harbi Lana Sbitan: Done By: Zaid Abu-Ameerah Mohammad AlotaibiSarahNo ratings yet
- HaemorrhageDocument19 pagesHaemorrhageSrishti SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Holy Angel University Angeles City: School of Nursing and Allied Medical SciencesDocument8 pagesHoly Angel University Angeles City: School of Nursing and Allied Medical SciencesMonica BorjaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 NCM 112Document4 pagesTopic 3 NCM 112Marielle ChuaNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument16 pagesEmergency DrugsDavid Hines LopezNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINOLOGYDocument28 pagesENDOCRINOLOGYjsreyes.402No ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument18 pagesFluids and ElectrolytesAbby Trisha MadularaNo ratings yet
- New ITLS 2020 AHADocument25 pagesNew ITLS 2020 AHAAhyar MohNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Agents ReviewerDocument18 pagesCardiovascular Agents ReviewerJoycel CeñidozaNo ratings yet
- NorvascDocument1 pageNorvascsoftwareitoNo ratings yet
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure OverviewDocument7 pagesPathoPhysiology of Renal Failure Overviewnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Shock: Anil PatidarDocument32 pagesShock: Anil Patidarjinal sutharNo ratings yet
- Neurogenic Shock SeminarDocument27 pagesNeurogenic Shock Seminaryishakemekonene850No ratings yet
- CVS AdaptationDocument20 pagesCVS AdaptationAlya KamarrudenNo ratings yet
- Shock and Multi OrganDocument90 pagesShock and Multi OrganElishaNo ratings yet
- DPT Case 6-7Document8 pagesDPT Case 6-7charlieNo ratings yet
- Alterations in Oxygen TransportDocument33 pagesAlterations in Oxygen TransportalanNo ratings yet
- Hypovolemic Shock: Dr. Sherwin BuluranDocument8 pagesHypovolemic Shock: Dr. Sherwin BuluranChristian UretaNo ratings yet
- Zalameda - Thiazides Loop Diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Potassium SparingDocument16 pagesZalameda - Thiazides Loop Diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Potassium SparingNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Penilaian Awal Pasien SyokDocument33 pagesPenilaian Awal Pasien SyokatikaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Type Type: Small Arteries Damaged Bleeding Into Brain Tissue Rupture of Saccular/ Berry AneurysmDocument1 pageType Type: Small Arteries Damaged Bleeding Into Brain Tissue Rupture of Saccular/ Berry AneurysmKristiene Kyle AquinoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System-Ms3-Maam RioDocument5 pagesEndocrine System-Ms3-Maam RioLovely Hope LugatimanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CHFDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CHFPerry Oliver AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology 2Document9 pagesCardiovascular Physiology 2lenoNo ratings yet
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideFrom EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- American Scientific Research Journal For Engineering, Technology, and Sciences (Asrjets), Vol 6, No 1 (2013), Issn (Print) 2313-44106Document2 pagesAmerican Scientific Research Journal For Engineering, Technology, and Sciences (Asrjets), Vol 6, No 1 (2013), Issn (Print) 2313-44106atilaelciNo ratings yet
- Study Questions 1Document2 pagesStudy Questions 1JamesNo ratings yet
- Jan W. Gooch, Biosketch - Jan. 2015Document15 pagesJan W. Gooch, Biosketch - Jan. 2015jan w goochNo ratings yet
- Enraf-Nonius Manumed Basic ENDocument16 pagesEnraf-Nonius Manumed Basic ENFlexxxy SssNo ratings yet
- Murdter Sample Lesson Plan Pmea Template 6th Grade General MusicDocument3 pagesMurdter Sample Lesson Plan Pmea Template 6th Grade General Musicapi-661316294No ratings yet
- ISO ImageDocument3 pagesISO ImageNicolaescu NicuNo ratings yet
- What Is A Bijamantra?: Aghori - It 1Document20 pagesWhat Is A Bijamantra?: Aghori - It 1er arNo ratings yet
- LGCSE Mathematics SyllabusDocument20 pagesLGCSE Mathematics SyllabusKhotsofalang Nqhoaki100% (5)
- Adeshwar Nursing Institute Khamhargaon, Jagdalpur: Community Health Nursing Lesson Plan ON Wound DressingDocument8 pagesAdeshwar Nursing Institute Khamhargaon, Jagdalpur: Community Health Nursing Lesson Plan ON Wound DressingNitesh BhuraNo ratings yet
- Positive Personality Adjectives Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesPositive Personality Adjectives Cheat SheetSzilvi KonczolNo ratings yet
- The Nano World and Gene TherapyDocument6 pagesThe Nano World and Gene TherapyEriel P. GamengNo ratings yet
- Feed Formulation Manual 2017Document40 pagesFeed Formulation Manual 2017Jennifer Legaspi86% (7)
- API EG - USE.ELEC - KH.PC DS2 en Excel v2 4251410Document67 pagesAPI EG - USE.ELEC - KH.PC DS2 en Excel v2 4251410upper paunglaungNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - The Dialog Between Business and ITDocument46 pagesLecture 5 - The Dialog Between Business and ITNegar ZamiriNo ratings yet
- What Is Seed and Angel FundingDocument2 pagesWhat Is Seed and Angel FundingQueen ValleNo ratings yet
- 65-1404 Victor HP I CatalogoDocument76 pages65-1404 Victor HP I CatalogocarlosNo ratings yet
- Ethics: Ethics or Moral Philosophy Is The Branch ofDocument15 pagesEthics: Ethics or Moral Philosophy Is The Branch ofChirag ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Faculty of Civil Engineering and Built EnvironmentDocument35 pagesUniversity Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Faculty of Civil Engineering and Built Environmentmohamed abdirisaaqNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Spirit TermsDocument6 pagesGlossary of Spirit TermssunwayjbNo ratings yet
- 1 Enterprise Lan Switching Cisco Ccna 200 125 200 105 m1 SlidesDocument65 pages1 Enterprise Lan Switching Cisco Ccna 200 125 200 105 m1 SlidesMiticuta SurubNo ratings yet
- 3-Parallel Lines and TransversalsDocument6 pages3-Parallel Lines and Transversalsshela26No ratings yet
- Electromechanical Active Body ControlDocument10 pagesElectromechanical Active Body ControlAmir RNo ratings yet
- Explained: Choosing Representation, Mutation, and Crossover in Genetic AlgorithmsDocument2 pagesExplained: Choosing Representation, Mutation, and Crossover in Genetic AlgorithmsJosephNo ratings yet
- 1st August (Porifera)Document7 pages1st August (Porifera)tayyabuetlhrNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology: Laboratory Safety and PrecautionDocument7 pagesMolecular Biology: Laboratory Safety and PrecautionSamantha100% (1)
- Mountain Pastures ChieamDocument188 pagesMountain Pastures ChieamioannesturrisoricisNo ratings yet
- The Importance of TeamworkDocument8 pagesThe Importance of TeamworkBraga MihaelaNo ratings yet
Neurogenic - Spinal Cord Injury at The - Have An Issue With - Hypotension, - Foley Catheter Placement
Neurogenic - Spinal Cord Injury at The - Have An Issue With - Hypotension, - Foley Catheter Placement
Uploaded by
abychloeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Neurogenic - Spinal Cord Injury at The - Have An Issue With - Hypotension, - Foley Catheter Placement
Neurogenic - Spinal Cord Injury at The - Have An Issue With - Hypotension, - Foley Catheter Placement
Uploaded by
abychloeCopyright:
Available Formats
Abena A Yeboah
Professor Ward
Nurs 400
The quiz assignment will be to create a chart listing the different types of shock, what type are
they, distributive, obstructive etc., what is the etiology (cause) pathophysiology (what happens),
how does the patient present and what is the treatment.
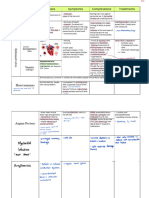
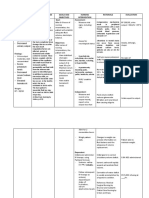
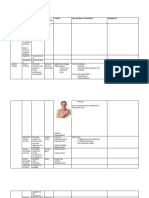
Types of Shock Etiology Physiology Presentation Treatment
-Pump Failure -When the -Low blood - Reperfusion
because of heart does not pressure (heart cath)
heart failure pump enough -Tachycardia - Increase cardiac
- Acute MI- blood - decreased output
blocked by - Filling/ cardiac output - Ventilation-
Cardiogenic Shock
plaque of contraction -Increase HR mech & diuretics
fat( decrease issues or -kidney: - Maintain
blood flow to dysrhythmias, decrease hemodynamic
the muscle) structure defect perfusion
- There is low - Fluid
- Patient with - Tachycardia
fluid volume replacement via
heat stroke -Hypotension
in the crystalloids,
- Any - Cold/clammy
circulatory colloid, blood, or
condition that skin
system blood products
cause fluid to - Low urinary
- Cells will and correcting
leave the output
start to die the cause of
system - Altered mental
- Decrease shock
- Massive status
amount of -
bleeding from
fluid volume
surgery or
Hypovolemic Shock that will return
injury,
to the heart
urination,
vomiting, or
- Going to
diarrhea)
affect cardiac
- Or inside
preload
fluid shift
- Decrease in
(internal
stroke volume
bleeding, long
which will
bone fracture,
decrease
severe burns)
cardiac output
Distributive Shock: - - Spinal Cord - - Have an -Foley catheter
Neurogenic, injury at the issue with -Hypotension, placement,
Anaphylactic, and cervical or sympathetic bradycardia, rewarming
Septic upper system, major hypothermia, devices for
thoracic hemodynamic warm/dry hypothermia,
region, taken changes extremities but a administering
drugs that - -Vasodilation cold body atropine for
affect the decrease the - Difficulty bradycardia
autonomic resistance breathing, - Removing the
sympathetic which affect inability to allergen,
- - Food can cardiac output speak, swelling, administering
cause shock - -Anaphylactic wheezing, runny epinephrine,
(Shellfish, reaction the nose, watery placing the
peanuts, eggs, patient has to eyes, patient in the
milk) or undergo hypotension, supine position
medications sensitization increased heart with the leg
- - Sepsis and - - Allergen rate, itchy skin, elevated,
leads to causes the diarrhea, nausea, education
major mast cells or vomiting - Fluid
decreased basophils to - Early: warm replacement,
tissue release flushed skin, vasopressor,
perfusion massive increased heart oxygenation
amount of and respiratory (mechanical
histamine rate, ventilation),
- - Massive restlessness, glucose control,
system-wide fever, increased monitor serum
vasodilation, or normal lactate, Foley
increased cardiac output catheter to
capillary and decrease measure urine
permeability systemic output,
(leads to vascular hemodynamic
relative resistance, monitoring,
hypovolemia) decreased blood enteral nutrition
, clot pressure
formation in - Late:
the small cold/clammy
vessels. All of skin, severe
these factors hypotension,
contribute to respiratory
decreased failure, oliguria
tissue (renal failure),
perfusion and low cardiac
output
leads to
shock.
-
-
-
- Tension
- - The inability . - Low blood
pneumothorax
to produce pressure
- Pulmonary
adequate - Rapid pulse
Obstructive embolism - - Relieve the
cardiac output - unequal breath
Shock - And cardiac obstruction
- - Loss of sounds
tamponade
perfusion - trouble
- Not the most
- - breathing
common;
You might also like
- Rehab Cheat SheetDocument18 pagesRehab Cheat SheetZ A100% (3)
- RA Export 20230303-171712 (TEMPLATE-04 Haz) - ID230303164833 - Rev2023-03-03 - Cargo & Ballast Works - Ballast Water Treatment System FailureDocument3 pagesRA Export 20230303-171712 (TEMPLATE-04 Haz) - ID230303164833 - Rev2023-03-03 - Cargo & Ballast Works - Ballast Water Treatment System FailureHarman Sandhu100% (3)
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 1 - Script Ceu Azul 2023Document21 pages1 - Script Ceu Azul 2023Indigo Graficos50% (2)
- NCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion (Eclampsia)Document1 pageNCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion (Eclampsia)Jenny AjocNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Characteristics of Copper Mine TailingsDocument12 pagesGeotechnical Characteristics of Copper Mine TailingsJamie CuttingNo ratings yet
- All Cardio DiseasesDocument8 pagesAll Cardio Diseaseshiba sharjeelNo ratings yet
- Shock EditedDocument56 pagesShock EditedJeevan VelanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Fvd2Document2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Fvd2ghellersNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Fluid Volume Imbalances: SoluteDocument8 pagesWeek 7 Fluid Volume Imbalances: SoluteMaica LectanaNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorDocument2 pagesPredisposing Factor Precipitating FactorkamotenikimiNo ratings yet
- Hypovolemic Shock PathoDocument10 pagesHypovolemic Shock PathoLorebell100% (1)
- Blood VesselsDocument4 pagesBlood VesselsCrazy StrangerNo ratings yet
- Chapter+04 9th+edition ITLS 04-2020Document25 pagesChapter+04 9th+edition ITLS 04-2020Brhanemeskel MekonnenNo ratings yet
- Sodium Imbalances (Hyponatremia Vs Hypernatremia)Document17 pagesSodium Imbalances (Hyponatremia Vs Hypernatremia)Angel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Pathopyshiology-w-Risk-Factors - DTDocument3 pagesPathopyshiology-w-Risk-Factors - DTDivynne MadeloNo ratings yet
- Before: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott's Nursing Drug Guide, P. 407Document2 pagesBefore: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott's Nursing Drug Guide, P. 407SoniaMarieBalanayNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic Management of HypertensionDocument8 pagesPharmacologic Management of HypertensionL2 - MAKILALA, Zion joy B.No ratings yet
- Textbook Discussion On ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction - GicaroDocument12 pagesTextbook Discussion On ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction - GicaroJica Marie Bandiola GicaroNo ratings yet
- Doria. 30emergency DrugsDocument7 pagesDoria. 30emergency DrugsAbegail Bautista DoriaNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument8 pagesShockPIH SHTNo ratings yet
- Increased Intracranial PressureDocument10 pagesIncreased Intracranial Pressureapi-3822433100% (10)
- PathophysiologyDocument34 pagesPathophysiologyeunams_1195% (20)
- Hemodynamic Disorders Thromboembolic Disease and ShockDocument13 pagesHemodynamic Disorders Thromboembolic Disease and ShockAbu HuraraNo ratings yet
- SHOCKDocument1 pageSHOCKJessa Mae Alforque AsentistaNo ratings yet
- SHOCK - HandoutsDocument6 pagesSHOCK - HandoutsKim GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Arrythmias 2-3Document4 pagesArrythmias 2-3cayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Hypo: Low - Vol: Volume - Emic: Blood: Burns Fracture PancreasDocument5 pagesHypo: Low - Vol: Volume - Emic: Blood: Burns Fracture PancreasNicholas TagleNo ratings yet
- Shock and Its Management: Presented byDocument72 pagesShock and Its Management: Presented bysheme171150% (2)
- Drug Study AbulenciaaaDocument3 pagesDrug Study AbulenciaaaKsksksksNo ratings yet
- Septic Shock and HypovolaemiaDocument2 pagesSeptic Shock and HypovolaemiasicatdianneNo ratings yet
- Doria. 30emergency DrugsDocument7 pagesDoria. 30emergency DrugsAbegail Bautista DoriaNo ratings yet
- 15 ShockDocument33 pages15 ShocknitsuhNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument29 pagesShockKoRnflakes100% (4)
- ER BatMC 2 Drug StudyDocument4 pagesER BatMC 2 Drug StudyFalqueza JanelleNo ratings yet
- Banan Harbi Lana Sbitan: Done By: Zaid Abu-Ameerah Mohammad AlotaibiDocument32 pagesBanan Harbi Lana Sbitan: Done By: Zaid Abu-Ameerah Mohammad AlotaibiSarahNo ratings yet
- HaemorrhageDocument19 pagesHaemorrhageSrishti SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Holy Angel University Angeles City: School of Nursing and Allied Medical SciencesDocument8 pagesHoly Angel University Angeles City: School of Nursing and Allied Medical SciencesMonica BorjaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 NCM 112Document4 pagesTopic 3 NCM 112Marielle ChuaNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument16 pagesEmergency DrugsDavid Hines LopezNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINOLOGYDocument28 pagesENDOCRINOLOGYjsreyes.402No ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument18 pagesFluids and ElectrolytesAbby Trisha MadularaNo ratings yet
- New ITLS 2020 AHADocument25 pagesNew ITLS 2020 AHAAhyar MohNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Agents ReviewerDocument18 pagesCardiovascular Agents ReviewerJoycel CeñidozaNo ratings yet
- NorvascDocument1 pageNorvascsoftwareitoNo ratings yet
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure OverviewDocument7 pagesPathoPhysiology of Renal Failure Overviewnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Shock: Anil PatidarDocument32 pagesShock: Anil Patidarjinal sutharNo ratings yet
- Neurogenic Shock SeminarDocument27 pagesNeurogenic Shock Seminaryishakemekonene850No ratings yet
- CVS AdaptationDocument20 pagesCVS AdaptationAlya KamarrudenNo ratings yet
- Shock and Multi OrganDocument90 pagesShock and Multi OrganElishaNo ratings yet
- DPT Case 6-7Document8 pagesDPT Case 6-7charlieNo ratings yet
- Alterations in Oxygen TransportDocument33 pagesAlterations in Oxygen TransportalanNo ratings yet
- Hypovolemic Shock: Dr. Sherwin BuluranDocument8 pagesHypovolemic Shock: Dr. Sherwin BuluranChristian UretaNo ratings yet
- Zalameda - Thiazides Loop Diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Potassium SparingDocument16 pagesZalameda - Thiazides Loop Diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Potassium SparingNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Penilaian Awal Pasien SyokDocument33 pagesPenilaian Awal Pasien SyokatikaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Type Type: Small Arteries Damaged Bleeding Into Brain Tissue Rupture of Saccular/ Berry AneurysmDocument1 pageType Type: Small Arteries Damaged Bleeding Into Brain Tissue Rupture of Saccular/ Berry AneurysmKristiene Kyle AquinoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System-Ms3-Maam RioDocument5 pagesEndocrine System-Ms3-Maam RioLovely Hope LugatimanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CHFDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CHFPerry Oliver AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology 2Document9 pagesCardiovascular Physiology 2lenoNo ratings yet
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideFrom EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- American Scientific Research Journal For Engineering, Technology, and Sciences (Asrjets), Vol 6, No 1 (2013), Issn (Print) 2313-44106Document2 pagesAmerican Scientific Research Journal For Engineering, Technology, and Sciences (Asrjets), Vol 6, No 1 (2013), Issn (Print) 2313-44106atilaelciNo ratings yet
- Study Questions 1Document2 pagesStudy Questions 1JamesNo ratings yet
- Jan W. Gooch, Biosketch - Jan. 2015Document15 pagesJan W. Gooch, Biosketch - Jan. 2015jan w goochNo ratings yet
- Enraf-Nonius Manumed Basic ENDocument16 pagesEnraf-Nonius Manumed Basic ENFlexxxy SssNo ratings yet
- Murdter Sample Lesson Plan Pmea Template 6th Grade General MusicDocument3 pagesMurdter Sample Lesson Plan Pmea Template 6th Grade General Musicapi-661316294No ratings yet
- ISO ImageDocument3 pagesISO ImageNicolaescu NicuNo ratings yet
- What Is A Bijamantra?: Aghori - It 1Document20 pagesWhat Is A Bijamantra?: Aghori - It 1er arNo ratings yet
- LGCSE Mathematics SyllabusDocument20 pagesLGCSE Mathematics SyllabusKhotsofalang Nqhoaki100% (5)
- Adeshwar Nursing Institute Khamhargaon, Jagdalpur: Community Health Nursing Lesson Plan ON Wound DressingDocument8 pagesAdeshwar Nursing Institute Khamhargaon, Jagdalpur: Community Health Nursing Lesson Plan ON Wound DressingNitesh BhuraNo ratings yet
- Positive Personality Adjectives Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesPositive Personality Adjectives Cheat SheetSzilvi KonczolNo ratings yet
- The Nano World and Gene TherapyDocument6 pagesThe Nano World and Gene TherapyEriel P. GamengNo ratings yet
- Feed Formulation Manual 2017Document40 pagesFeed Formulation Manual 2017Jennifer Legaspi86% (7)
- API EG - USE.ELEC - KH.PC DS2 en Excel v2 4251410Document67 pagesAPI EG - USE.ELEC - KH.PC DS2 en Excel v2 4251410upper paunglaungNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - The Dialog Between Business and ITDocument46 pagesLecture 5 - The Dialog Between Business and ITNegar ZamiriNo ratings yet
- What Is Seed and Angel FundingDocument2 pagesWhat Is Seed and Angel FundingQueen ValleNo ratings yet
- 65-1404 Victor HP I CatalogoDocument76 pages65-1404 Victor HP I CatalogocarlosNo ratings yet
- Ethics: Ethics or Moral Philosophy Is The Branch ofDocument15 pagesEthics: Ethics or Moral Philosophy Is The Branch ofChirag ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Faculty of Civil Engineering and Built EnvironmentDocument35 pagesUniversity Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Faculty of Civil Engineering and Built Environmentmohamed abdirisaaqNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Spirit TermsDocument6 pagesGlossary of Spirit TermssunwayjbNo ratings yet
- 1 Enterprise Lan Switching Cisco Ccna 200 125 200 105 m1 SlidesDocument65 pages1 Enterprise Lan Switching Cisco Ccna 200 125 200 105 m1 SlidesMiticuta SurubNo ratings yet
- 3-Parallel Lines and TransversalsDocument6 pages3-Parallel Lines and Transversalsshela26No ratings yet
- Electromechanical Active Body ControlDocument10 pagesElectromechanical Active Body ControlAmir RNo ratings yet
- Explained: Choosing Representation, Mutation, and Crossover in Genetic AlgorithmsDocument2 pagesExplained: Choosing Representation, Mutation, and Crossover in Genetic AlgorithmsJosephNo ratings yet
- 1st August (Porifera)Document7 pages1st August (Porifera)tayyabuetlhrNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology: Laboratory Safety and PrecautionDocument7 pagesMolecular Biology: Laboratory Safety and PrecautionSamantha100% (1)
- Mountain Pastures ChieamDocument188 pagesMountain Pastures ChieamioannesturrisoricisNo ratings yet
- The Importance of TeamworkDocument8 pagesThe Importance of TeamworkBraga MihaelaNo ratings yet