Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Overview of Structural Engineering - SJT
Overview of Structural Engineering - SJT
Uploaded by
Stephen Rajkumar JayakumarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Overview of Structural Engineering - SJT
Overview of Structural Engineering - SJT
Uploaded by
Stephen Rajkumar JayakumarCopyright:
Available Formats
Structural engineering – An Overview
By
Dr. S. Justin
Chief Engineering Manager
Health & Leisure – Structural
L&T – Construction – B&F (CB&A) - EDRC
GET & PGET Orientation
GOD HATH DONE EVERYTHING BEAUTIFUL IN HIS TIME
Outline of Presentation
What is Structural Engineering?
Structural Material
Structural General Behavior
Structural Elements and Its Behavior
Loads on Structures
Structural Analysis and Design – Overview
Preliminary dimensioning of Structural Element
Inter-Discipline Coordination – Structural Aspect
Structural engineering – An Overview 2
What is Structural Engineering?
Analysis and Design of Structures to
ensure Safety, Stability, Durability,
Functionality, Maintainable and
Economical.
If a structure was a human body then
the architect would be concerned with
the body shape and appearance, and
the structural engineer would be
concerned with the skeleton and
Muscular strength
Structural engineering – An Overview 3
What is Structural Engineering?
Structural engineering – An Overview 4
Structural Material - Concrete
Structural engineering – An Overview 5
Structural Material - Steel
Rebar Steel, Bar Coupler
Structural Steel
Structural engineering – An Overview 6
Structural Material – Post Tensioning
PT Strand
Casting
Anchor Block
Wedges
Duct
Structural engineering – An Overview 7
Structural Material – Shuttering
MIVAN Alu Formwork
Table Formwork
Slip Jump Formwork
Structural engineering – An Overview 8
Overall Structural Design Process
Conception
Modeling
Analysis
Design
Detailing
Drafting
Costing
Structural engineering – An Overview 9
Overall Structural Behavior – Safety & Serviceability
Safety: A structure must carry the expected loads without collapsing
as a whole and without any part of it collapsing
It depends upon Assessing Correct Load and Strength of material
Serviceability: A structure must be designed in such a way that it
deflection, crack width and vibration within permissible limit.
Structural Frequent Term: Force, Reaction, Stress, Moment
Structural engineering – An Overview 10
Overall Structural Behavior – Gravity Load
Frame
Structural engineering – An Overview 11
Overall Structural Behavior – Lateral Load
Braced Frame Infilled Frame Rigid Joints
Structural engineering – An Overview 12
Overall Structural Behavior - Strength
- Ability to withstand a given stress without failure
- Depends upon the Type of material
Tensile Failure Compressive Failure Shear Failure
Structural engineering – An Overview 13
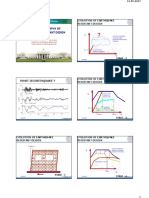
Overall Structural Behavior– Stiffness (Rigidity)
T Displacement
Force
DL
- Property Related to Deformation
- Stiffer structural elements deform
less under the same applied load
Lo - Depends E, Length, Shape
Axial Stiffness Bending Stiffness
Structural engineering – An Overview 14
Structural Element and Behavior - Foundation
Transfer of load from structure to Ground Soil – Footing, Raft, Pile
Structural engineering – An Overview 15
Structural Element and Behavior - Column
Vertical Element - Subjected to Compression and Bending
Structural engineering – An Overview 16
Structural Element and Behavior - Beam
Loads
Compression
Tension
Strength – Bending & Shear; Serviceability- Deflection & Crack width
Structural engineering – An Overview 17
Structural Element and Behavior - Beam
Simply Supported, Cantilever, Continuous Beam
Structural engineering – An Overview 18
Structural Element – Roof Slab
Conv. Slab, Flat slab, Flat Plate, Grid Slab, Folded Plate, Shell
Structural engineering – An Overview 19
Structural Element – Roof Slab
Various pattern of Load Transfer Path in Roof Slab
Structural engineering – An Overview 20
Structural Element – Wall
Boundary wall (RR/
BM/ RC/ RE)
RC Basement Wall
and Retaining Wall
Shear Wall
Structural engineering – An Overview 21
Structural Element and Behavior – Structural Steel
Truss: Triangular Units with straight members subjected to
nodal/joint forces, All members subjected to axial force only.
C
T C
C
T
Forces in Members
Structural engineering – An Overview 22
Structural Element – Composite section
Composite Deck Slab
Column, shear wall
Structural engineering – An Overview 23
Structural Element – Post Tensioning
PT Slab PT Beam
Structural engineering – An Overview 24
Structural Element – Precast
Cost effective, More quality and Time saving but Deficient in Expert,
Non Standard element size, improper Joint Detailing, Inadequate IS
code, Minimum Production Plant, Transportation & Erection difficulty,
Structural engineering – An Overview 25
Structural Element – Precast
Structural engineering – An Overview 26
Structural Behavior – Arch action
Pure Compression & Lateral Thrust, Span
large area by resolving forces into
compressive stresses and eliminating
Tensile stress
Arch
Structural engineering – An Overview 27
Structural Load
Dead/ Dead Imposed Load – Self Weight of Structure, Wall Load,
Heavy Equipment Load – Immovable Load
Live Load – People, Furniture, Equipment – Movable Load
Seismic Load (Earth quake) – Based on Location, Seismograph,
Structural system, Importance of building, Type of detailing
Wind Load – based on Terrain, Height, Topology
Thermal Load – Temperature Rise & Fall
Dynamic load – Moving Load, Vibration, Impact
Soil Earth Pressure and Water Pressure
Other Specific load – Snow, Settlement, Shrinkage, Creep,
Structural engineering – An Overview 28
Structural Analysis and Design – To Start with
Study of Master Plan
Survey Report Review
Geotechnical Report Review
Design Basis Report
Discussion with All Services
Preparation of Scheme Drawing
Peer Review
Detail Engineering with Quantification
Structural engineering – An Overview 29
Structural Analysis and Design – Scheme Preparation
Study of Architectural Drawing
Analyze Structural Criticality
Locate the Columns, Core Wall and Beams Layout
Structural Feasibility and Behavior
Arch & Service Requirement
Cost (Quantity) Effectiveness
Construction Easiness
Preliminary Dimension of all Structural Element
Structural engineering – An Overview 30
Structural Analysis and Design – Basic of Analysis
Structural analysis is to evaluate the external reactions, the
deformed shape and internal stresses (BM, SF) in the structure.
Structural engineering – An Overview 31
Structural Analysis and Design – Process
Use of Software such as STAAD Pro, ETABS, SAFE, SAP, etc.,
Structural Modal should Resemble the actual Modal
- Geometry Creation (Floor Plan and Elevation)
- Material & Member Property (Dimension of Element)
- Loading and Support Conditions
- Verification of Modal (Input)
- Analysis
- Verification of Result (Output)
- Design
- Detailing (It should reflect the assumption made in Analysis)
Structural engineering – An Overview 32
Structural Analysis and Design – Basic IS Codes
Loading -> IS 875s, IS 1893, IRC
Design -> IS 456, IS 800, IS 1343, IS 1905
Foundation -> IS 1904, IS 2911 , IS 2950,
Detailing -> SP 34, IS 13920
Other Important International Codes
BS 8110, BS 5950, BS 6399, Eurocodes
ACI 318, IBC (UBC)
Structural engineering – An Overview 33
Basic Structural Quantity - Optimize
Structural Quantity is depends upon the following Parameters
Type of Building (Hospital, Malls, IT Park, Residential etc.,)
Type of Structural System (Conventional RC Slab beam, Flat
slab, PT slab, Grid floor, Structural Steel, Composite Str)
Type of Loading (Seismic Zone, Wind Load, Machine Load)
No of Story, Grid Size
Basement Structure, Atrium, Canopy
Service Req (Pipe rack, External works, Plant room etc)
Type of Foundation (Footing, Raft, Pile)
Elevation features
Structural engineering – An Overview 34
Preliminary Dimension of Structural Element
Average Loading IT Blg – 16 kN/m2 ; Hospital - 20 kN/m2
Foundation - Plan Area = Approx unfac. Axial Load x 1.2/ SBC
Thickness = Cantilever Span / 7 + 50 mm &
Factored Axial Load/(column Perimeter x 1.37)
Column –No of Storey, Grid dimesion, Column Ht, Loading
Column c/s = No of storey x Grid area x 20 kN/sqm / 25
Shear Wall - 150 to 300 mm based on Axial, Flexure & Shear
Beam - Width b = Generally 300mm (L<6m), 350mm (6<L<9)
Depth d = SS – L/20+50, Con- L/26+50, Cant- L/7+50
Structural engineering – An Overview 35
Preliminary Dimension of Structural Element
RC Conv. Slab – One way slab same as beam (with increase
ratio by 4 and reduce cover), Two way Slab – Shorter Span/ 35 + 25
RC Flat Slab - Longer Span / 35 + 25
RC Flat Plate - Longer Span / 30 + 25
PT Flat Slab - Longer Span / 50 + 25
Structural engineering – An Overview 36
Interdisciplinary Structural Coordination - Architect
Understanding Architect Concept and its Design Intend, not to
deviate
Review Floor Plan & RCP to finalize Location and Dimension of
structural element
FGL, NGL, FFL and FRL verification
Staircase system - architect requirement
Façade fixing system and BMU requirement
Brick wall Mullion system if longer wall
Structural engineering – An Overview 37
Interdisciplinary Structural Coordination - HVAC
Cooling tower & Chiller Plant supporting System
Basement Ventilation System
AHU and FAN Pedestals
Size and Location of HVAC Shaft
HVAC (Supply and Return Air) Duct size and layout coordinate
with Beam layout
Structural engineering – An Overview 38
Interdisciplinary Structural Coordination - Electrical
Transformer, DG and Stack supporting System
Concealed or Open Conduit system
Electrical Tray supporting systems
HSD Tank, Electrical Cable Trench,
Lift Machine Room and Shaft requirements
RMU, Substation Building
Structural engineering – An Overview 39
Interdisciplinary Structural Coordination - PHE
Terrace and Podium Slab Water Drainage (Screed)
Storm water Drainage System
Sub Surface Drainage System
STP & WTP Structural System
Sump and Water Tank Requirements
Terrace, Toilet, Landscape, Tank and Basement Water proofing
Waste disposal System
Pressure Pipe supporting System
Structural engineering – An Overview 40
Interdisciplinary Structural Coordination - FPS
Staircase Pressurization
Fire water Tank and Sump & Pump room
Fire Compartmentalization
Refuge Area in Multi storey Building
Structural engineering – An Overview 41
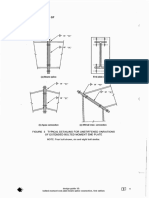
Interdisciplinary Structural Coordination - Geotech
Type of Soil strata from BH and Trial Pit
SBC and Subgrade Modulus of Soil
Type of foundation (Footing, Raft and Pile)
Soil Excavation and Various Shoring System
Dewatering Scheme
Pavement Design
Structural engineering – An Overview 42
Interdisciplinary Structural Coordination - Others
NBC and Local body Statutory Requirements
Elevated pipe rack system for all services if any
Project Specific Requirement such as Hospital project LINAC,
Medical Equipment and its Piping
Construction Friendliness
Quantity Reconciliation (Tener Vs Actual)
Coordination with External Consultant and Vendor
Structural engineering – An Overview 43
Discussion & Interaction
Structural engineering – An Overview 44
Quality, Quantity & Timely Delivery -> Design Preference
WINNING DOESN'T ALWAYS MEAN BEING FIRST, WINNING MEANS YOU'RE DOING BETTER
THAN YOU'VE DONE BEFORE - BONNIE BLAIR
You might also like
- Heights (Working At) : S W M S (SWMS) P 1Document14 pagesHeights (Working At) : S W M S (SWMS) P 1Benouna Fert100% (1)
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- First Principles An OverviewDocument2 pagesFirst Principles An Overviewapi-123486123No ratings yet
- ThanatiaDocument670 pagesThanatiaJoão ClaudioNo ratings yet
- SAP FICO MaterialDocument24 pagesSAP FICO MaterialNeelam Singh100% (1)
- Modeling in Etabs An IntroductionDocument38 pagesModeling in Etabs An IntroductionGeorge GeorgianNo ratings yet
- Notes From RCC Pillai MenonDocument71 pagesNotes From RCC Pillai MenonVaibhav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Structural Training Note (Print)Document87 pagesStructural Training Note (Print)timNo ratings yet
- Seismic Analysis of High-Rise BuildingDocument66 pagesSeismic Analysis of High-Rise BuildinglefratodriNo ratings yet
- RC DetailingDocument82 pagesRC DetailingkishoreNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Reinforcing Detailing of R.C.C MembersDocument15 pagesPresentation On Reinforcing Detailing of R.C.C Membersswapnil belsareNo ratings yet
- Is-1893-Part-1-2016 - ReviewsDocument27 pagesIs-1893-Part-1-2016 - ReviewskapilshwetaNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design of RC Buildingsrahul Leslie080815 151125071557 Lva1 App6891Document194 pagesSeismic Design of RC Buildingsrahul Leslie080815 151125071557 Lva1 App6891hipreyashNo ratings yet
- Steel StructureDocument295 pagesSteel StructureSahir Khan100% (2)
- Staad Pro PPT 2018Document36 pagesStaad Pro PPT 2018Malay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction and BOLTED CONNECTIONS PDFDocument38 pagesUnit 1 Introduction and BOLTED CONNECTIONS PDFmoondonoo7No ratings yet
- Bentley - Cominto - STAAD PRO - Seminar Presentation - 2019Document66 pagesBentley - Cominto - STAAD PRO - Seminar Presentation - 2019buildings departmentNo ratings yet
- Structural Design: Cocnrete Technology Interview QuestionsDocument9 pagesStructural Design: Cocnrete Technology Interview Questionsmtech structuresNo ratings yet
- Staad ProjectDocument60 pagesStaad Projectsaisssms9116100% (3)
- Rubber As Material of ConstructionDocument15 pagesRubber As Material of ConstructionpandianvijaybharathiNo ratings yet
- RCC Unit-1 PDFDocument40 pagesRCC Unit-1 PDFSandeep GowdaNo ratings yet
- Waffle and Rib SlabDocument9 pagesWaffle and Rib SlabAshish PandeyNo ratings yet
- Civil Works in Power PlantsDocument19 pagesCivil Works in Power PlantsAadi JainNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel: Steel Shape Profile Cross Section Chemical Composition Standards I-Beams Second Moments of AreaDocument10 pagesStructural Steel: Steel Shape Profile Cross Section Chemical Composition Standards I-Beams Second Moments of AreaAnonymous nABFA4lNo ratings yet
- Base Plate MCCDocument7 pagesBase Plate MCCabbasamuNo ratings yet
- Design & Construction of RCC Elevated Water TanksDocument98 pagesDesign & Construction of RCC Elevated Water Tanksyieldstress123No ratings yet
- Centering and FormworkDocument50 pagesCentering and FormworkSakshi RawatNo ratings yet
- Professional Training Report in STRUCTURAL ANALYSISDocument18 pagesProfessional Training Report in STRUCTURAL ANALYSISNipunGoelNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 2 Introduction To Steel StructuresDocument89 pagesLecture - 2 Introduction To Steel Structureshammads88No ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Lateral Load Resisting Systems in Tall Structures-Ijaerdv05i0482912Document10 pagesA Comparative Study of Lateral Load Resisting Systems in Tall Structures-Ijaerdv05i0482912Pradeep ChandraNo ratings yet
- Staad Pro Analysis PDFDocument36 pagesStaad Pro Analysis PDFJapnam SodhiNo ratings yet
- Concrete Crack Width MeasurementDocument6 pagesConcrete Crack Width MeasurementcedaserdnaNo ratings yet
- Time Saving Design AidsDocument86 pagesTime Saving Design AidsPurvish Joshi50% (2)
- 3 Structural Analysis HandoutDocument2 pages3 Structural Analysis HandoutAlex DimulescuNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument3 pagesStrength of Materialsvp0209198825% (4)
- PEB CodesDocument8 pagesPEB CodesMahmood MuftiNo ratings yet
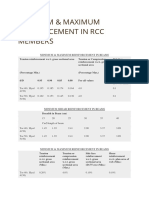
- Minimum & Maximum SteelDocument3 pagesMinimum & Maximum SteelSathishNo ratings yet
- Career Opportunities in Civil EngineeringDocument39 pagesCareer Opportunities in Civil EngineeringRabnawaz ImamNo ratings yet
- 2introduction To Civil Engineering Drawing 2Document6 pages2introduction To Civil Engineering Drawing 2Eddey KendiNo ratings yet
- Guidelines Report Writing PDFDocument13 pagesGuidelines Report Writing PDFShubham PawarNo ratings yet
- INSDAGDocument8 pagesINSDAGSowmya Majumder100% (1)
- 07 Ductile Detailing RC BuildingsDocument52 pages07 Ductile Detailing RC BuildingsManju BirjeNo ratings yet
- Design RCCDocument27 pagesDesign RCCAnonymous HJ7hmihhNo ratings yet
- Openstaad - Reference ManualDocument206 pagesOpenstaad - Reference ManualAnay KarambelkarNo ratings yet
- Staad Pro NotesDocument134 pagesStaad Pro Notespwd2007No ratings yet
- Structural DesignDocument25 pagesStructural DesignkozmologNo ratings yet
- Is 1893 - Philosophy of Earthquake Resistant DesignDocument11 pagesIs 1893 - Philosophy of Earthquake Resistant DesignsudhajagannathanNo ratings yet
- Designing Connections - RC and STAAD - TRNC03499 - PPT PDFDocument10 pagesDesigning Connections - RC and STAAD - TRNC03499 - PPT PDFAKS100% (1)
- Durability of Concrete StructuresDocument38 pagesDurability of Concrete StructuresSharath WankdothNo ratings yet
- Valve Pit Wall DesignDocument3 pagesValve Pit Wall DesignersivarajNo ratings yet
- Quantity Surveying and ValuationDocument102 pagesQuantity Surveying and ValuationarnNo ratings yet
- Cold Formed Steel Members and SheetingDocument14 pagesCold Formed Steel Members and SheetingMihai MariusNo ratings yet
- RCC StructuresDocument106 pagesRCC Structuresjitesh100% (1)
- RISA Seismic Moment ConnectionsDocument11 pagesRISA Seismic Moment ConnectionsJackNo ratings yet
- Design of Concrete StructuresDocument3 pagesDesign of Concrete StructuresArmaan GuptaNo ratings yet
- ASI Design Guide 10 - Bolted Moment End Plate Beam Splice Connections 13Document1 pageASI Design Guide 10 - Bolted Moment End Plate Beam Splice Connections 13Anonymous 0x2pwMCWgjNo ratings yet
- ADMIN Building Calculation SheetDocument95 pagesADMIN Building Calculation Sheetorode franklynNo ratings yet
- Design Recommendations For Steel Deck Floor SlabsDocument32 pagesDesign Recommendations For Steel Deck Floor Slabscaptnjack1No ratings yet
- Structural Design of Steel StructuresDocument43 pagesStructural Design of Steel Structureskiran sreekumarNo ratings yet
- Final DocumentDocument82 pagesFinal Documentsudarshan royalNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Reinforced Concrete Design 2023Document20 pages1.introduction To Reinforced Concrete Design 2023priscamushi601No ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Reinforced Concrete DesignDocument21 pages1.introduction To Reinforced Concrete DesignGeneralis MremaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Steel DesignDocument22 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Steel Designjbjuanzon100% (1)
- Structural Engineering TalkDocument43 pagesStructural Engineering TalkVince Bagsit PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Pipe Excavation-CDocument18 pagesPipe Excavation-CStephen Rajkumar JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Larsen & Toubro Limited: ECC Division - EDRCDocument32 pagesLarsen & Toubro Limited: ECC Division - EDRCStephen Rajkumar JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Road Qty - S-R-SH-10-Total Project ECL - PCL OffsetDocument1 pageRoad Qty - S-R-SH-10-Total Project ECL - PCL OffsetStephen Rajkumar JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Volume I - TENDER RANCHI MUNICIPAL CORPDocument85 pagesVolume I - TENDER RANCHI MUNICIPAL CORPStephen Rajkumar JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Summary For Pavement CompositionsDocument56 pagesSummary For Pavement CompositionsStephen Rajkumar JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Entry & Exit Ramps - S-R-SH-10 R2Document16 pagesEntry & Exit Ramps - S-R-SH-10 R2Stephen Rajkumar JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Abstract of Quantities For Truck LaybyDocument3 pagesAbstract of Quantities For Truck LaybyStephen Rajkumar JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Volume II SpecificationDocument263 pagesVolume II SpecificationStephen Rajkumar JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Drain Qnty - S-R-SH-10 R6Document23 pagesDrain Qnty - S-R-SH-10 R6Stephen Rajkumar JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Volume V - Financial BidDocument14 pagesVolume V - Financial BidStephen Rajkumar JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Summary of Curve Quantities Total 3930 1058.4 35210 353 4700 67585Document20 pagesSummary of Curve Quantities Total 3930 1058.4 35210 353 4700 67585Stephen Rajkumar JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Bus Bays - S-R-SH-10 R2Document6 pagesBus Bays - S-R-SH-10 R2Stephen Rajkumar JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Volume III - O&MDocument25 pagesVolume III - O&MStephen Rajkumar JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Parenting SkillsDocument107 pagesParenting SkillsStephen Rajkumar JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Spirit Storm: Acts 2:1-4 NIVDocument6 pagesSpirit Storm: Acts 2:1-4 NIVStephen Rajkumar JayakumarNo ratings yet
- STP DrawingsDocument100 pagesSTP DrawingsStephen Rajkumar JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Electrical For Non-Electrical EngineersDocument62 pagesElectrical For Non-Electrical EngineersStephen Rajkumar JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Submitted by Deepa PriyadarshiniDocument22 pagesSubmitted by Deepa PriyadarshiniStephen Rajkumar Jayakumar100% (1)
- Road Studs Other Than Curve Location As Per Manual TotalDocument7 pagesRoad Studs Other Than Curve Location As Per Manual TotalStephen Rajkumar JayakumarNo ratings yet
- VAASTUDocument62 pagesVAASTUStephen Rajkumar JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Concrete Design - Comparison is-BSDocument10 pagesConcrete Design - Comparison is-BSStephen Rajkumar JayakumarNo ratings yet
- ClaytonDocument1 pageClaytonapi-3831340No ratings yet
- D 12332Document108 pagesD 12332jesus_hfNo ratings yet
- Soal BAHASA INGGRIS XIIDocument5 pagesSoal BAHASA INGGRIS XIIZiyad Frnandaa SyamsNo ratings yet
- D197-Lab Exercise 2.2 - Bihay and SumaljagDocument5 pagesD197-Lab Exercise 2.2 - Bihay and Sumaljagjelly bihayNo ratings yet
- 1884 Journey From Heraut To Khiva Moscow and ST Petersburgh Vol 2 by Abbott S PDFDocument342 pages1884 Journey From Heraut To Khiva Moscow and ST Petersburgh Vol 2 by Abbott S PDFBilal AfridiNo ratings yet
- Oracle Business Intelligence Answers: Presentation ServicesDocument6 pagesOracle Business Intelligence Answers: Presentation Servicesvenkatesh.gollaNo ratings yet
- Skript Version30 PDFDocument90 pagesSkript Version30 PDFNguyễn TúNo ratings yet
- Challenges of Copyright in A Digital Age by Wandi KawecheDocument5 pagesChallenges of Copyright in A Digital Age by Wandi Kawechepoppy peterNo ratings yet
- Rotational Dynamics: Points To RememberDocument9 pagesRotational Dynamics: Points To RememberJayashri Bhavsar 31No ratings yet
- Swathi Final Project AnilDocument100 pagesSwathi Final Project AnilHussainNo ratings yet
- Testbank ch01Document14 pagesTestbank ch01HườngNo ratings yet
- The Migration Industry and Future Directions For Migration PolicyDocument4 pagesThe Migration Industry and Future Directions For Migration PolicyGabriella VillaçaNo ratings yet
- A&H Carrefour LayoutDocument1 pageA&H Carrefour LayoutAshraf EhabNo ratings yet
- Road Construction MethodsDocument163 pagesRoad Construction MethodsVetcher ColumnaNo ratings yet
- FPM Brochur 2016-17Document56 pagesFPM Brochur 2016-17Rithima SinghNo ratings yet
- BIOLS102-UOB-Chapter 10Document8 pagesBIOLS102-UOB-Chapter 10Noor JanahiNo ratings yet
- Matrices of Violence: A Post-Structural Feminist Rendering of Nawal El Saadawi's Woman at Point Zero and Lola Soneyin's The Secrets of Baba Segi's WivesDocument6 pagesMatrices of Violence: A Post-Structural Feminist Rendering of Nawal El Saadawi's Woman at Point Zero and Lola Soneyin's The Secrets of Baba Segi's WivesIJELS Research JournalNo ratings yet
- ATS Kingston Heath CustomerDocument63 pagesATS Kingston Heath CustomerDevNo ratings yet
- Compiler Construction LabDocument11 pagesCompiler Construction LabSunny0% (1)
- Santa Cruz Scanner FreqsDocument35 pagesSanta Cruz Scanner FreqsdonsterthemonsterNo ratings yet
- wst03 01 Que 20220611 1Document28 pageswst03 01 Que 20220611 1Rehan RagibNo ratings yet
- ITSM Gap Analysis TemplateDocument57 pagesITSM Gap Analysis TemplateSuresh RajamaniNo ratings yet
- WSS ProdCat 2013 Lowres Final v2 PDFDocument861 pagesWSS ProdCat 2013 Lowres Final v2 PDFJuriandi SaputraNo ratings yet
- 3 PBDocument11 pages3 PBSuci DwiNo ratings yet
- Accounting All ChaptersDocument155 pagesAccounting All ChaptersHasnain Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Welcome Back! B1 SVDocument4 pagesWelcome Back! B1 SVMagda StręciwilkNo ratings yet