Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET)
Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET)
Uploaded by
iskelisaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Imat Preparation Guide PDFDocument36 pagesImat Preparation Guide PDFPhương Nghi50% (6)
- German-English Pocket Bilingual Dictionary Von UrDocument1 pageGerman-English Pocket Bilingual Dictionary Von Urskippygoat11No ratings yet
- Stat211 122 03 Q1Document4 pagesStat211 122 03 Q1mdasifkhan2013No ratings yet
- IELTS Academic Writing Task 2 SimonDocument62 pagesIELTS Academic Writing Task 2 SimonTrungtamanhngu KosmozNo ratings yet
- Essay AntonymDocument5 pagesEssay AntonymUbaydillah FalakhiNo ratings yet
- The Developmentof TVETProfilingfor Workforce Managementin Malaysia Ensuring The Validityand Reliabilityof TVETDataDocument12 pagesThe Developmentof TVETProfilingfor Workforce Managementin Malaysia Ensuring The Validityand Reliabilityof TVETDataRBT1062021 Divyasree VelooNo ratings yet
- Name Student: Sidra: Course: Higher EducationDocument39 pagesName Student: Sidra: Course: Higher EducationAsqa KhanNo ratings yet
- TVETDocument4 pagesTVETsultanalmokhalasNo ratings yet
- Employability of TVET GraduatesDocument11 pagesEmployability of TVET Graduatesvergel100% (1)
- Strategic Planning To Transform Malaysian TVET Students Into Future Ready ProfessionalsDocument11 pagesStrategic Planning To Transform Malaysian TVET Students Into Future Ready ProfessionalsMyra EmyraNo ratings yet
- TVET MGT 111 EeeeDocument130 pagesTVET MGT 111 EeeeFikadu GadisaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - FINAL DEFENSEDocument13 pagesChapter 1 - FINAL DEFENSEIrene MarticioNo ratings yet
- TVET MalaysiaDocument13 pagesTVET MalaysiaGhazally FaridahNo ratings yet
- English Language Competency in EnhancingDocument9 pagesEnglish Language Competency in EnhancingBALQIS BINTI HUSSIN A18PP0022No ratings yet
- Vocational EducationDocument4 pagesVocational EducationSeania DyNo ratings yet
- Malawi - National Education PolicyDocument24 pagesMalawi - National Education PolicyAndrew NkhomaNo ratings yet
- Penerbit,+4!29!39+Rene Luis Tadle Students Experience of Service QualityDocument11 pagesPenerbit,+4!29!39+Rene Luis Tadle Students Experience of Service QualityKryshia Mae CaldereroNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Written Assignment Ads514 - Education Policy ReportDocument28 pagesGroup 2 - Written Assignment Ads514 - Education Policy ReportNUR HIDAYAH AZIHNo ratings yet
- TVET ManagementDocument99 pagesTVET ManagementBizuneh getuNo ratings yet
- Mem 5205 Higher Education PlanningDocument113 pagesMem 5205 Higher Education PlanningEvans MutuaNo ratings yet
- Tvet 2Document9 pagesTvet 2Tu PangsapuriNo ratings yet
- Unit 8Document22 pagesUnit 8NeeteshNo ratings yet
- TVET in MalaysiaDocument4 pagesTVET in MalaysiaMuhamad Nu'man ZolkofleNo ratings yet
- Technical Vocational Education & Training (TVET) in Malaysia Selected WorksDocument178 pagesTechnical Vocational Education & Training (TVET) in Malaysia Selected WorksIntan Tamira Fa'izah Khusna intantamira.2017No ratings yet
- Malaysia Education Blueprint 2015-2025 (Higher Education)Document240 pagesMalaysia Education Blueprint 2015-2025 (Higher Education)Kolej Komuniti Hulu Selangor (Scribd Rasmi)100% (6)
- Indonesia: Basic StructureDocument4 pagesIndonesia: Basic StructureDaikong ShitamiNo ratings yet
- Executive Summary - BruneiDocument2 pagesExecutive Summary - Bruneiapi-330120353No ratings yet
- Jennifer E. Cotillon, Research IntroductionDocument2 pagesJennifer E. Cotillon, Research IntroductionJennifer CotillonNo ratings yet
- Philosophical and Sociological Overview of Technology and Vocational EducationDocument22 pagesPhilosophical and Sociological Overview of Technology and Vocational EducationAzmi Rizky AnisaNo ratings yet
- Vocationalization of Education PDFDocument12 pagesVocationalization of Education PDFPanjwani Divya RajkumarNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument56 pagesDownloadmathibettuNo ratings yet
- Sistem Pendukung Keputusan Untuk Pemilihan Perguruan Tinggi Penyelenggara Pendidikan Vokasi Di Bangka BelitungDocument12 pagesSistem Pendukung Keputusan Untuk Pemilihan Perguruan Tinggi Penyelenggara Pendidikan Vokasi Di Bangka BelitungRhyiina YeopakataNo ratings yet
- Education System in MalaysiaDocument7 pagesEducation System in MalaysiaKevinNo ratings yet
- The Policies of Curriculum in Tvet (Technical Vocational Education and Training)Document18 pagesThe Policies of Curriculum in Tvet (Technical Vocational Education and Training)Vici Syahril ChairaniNo ratings yet
- Technical and Vocational Education and Training Issues in Malaysia and Asian Region: Where Do We Go From Here?Document11 pagesTechnical and Vocational Education and Training Issues in Malaysia and Asian Region: Where Do We Go From Here?Kamal JasmanNo ratings yet
- Penerbit, JTET 1 1-21Document21 pagesPenerbit, JTET 1 1-21Yousup AliNo ratings yet
- A Situational Analysis of The Faculties' Industrial Attachment Programme at Public Technical Training Institutes (TTIs) in BhutanDocument14 pagesA Situational Analysis of The Faculties' Industrial Attachment Programme at Public Technical Training Institutes (TTIs) in BhutanMamta AgarwalNo ratings yet
- EJ1210003Document8 pagesEJ1210003princecharlespuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Ethnic EmploymentDocument25 pagesChapter 3 Ethnic EmploymentAung Myo PaingNo ratings yet
- 142 Distance Education MalaysiaDocument20 pages142 Distance Education MalaysiaJuliana NorNo ratings yet
- Technical & Vocational Education & Training (TVET) From Malaysia PerspectiveDocument14 pagesTechnical & Vocational Education & Training (TVET) From Malaysia PerspectivewahaboyNo ratings yet
- TVET Challenges and Priorities in Developing CountriesDocument11 pagesTVET Challenges and Priorities in Developing CountriesNadia KhalidNo ratings yet
- Business Studies: By: Devan Kochar XI NalandaDocument13 pagesBusiness Studies: By: Devan Kochar XI NalandaDevan KocharNo ratings yet
- Phil TVET System - SyjucoDocument18 pagesPhil TVET System - SyjucosirjudsNo ratings yet
- Teacher Education and LicencingDocument5 pagesTeacher Education and LicencingCikguAmeliaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines Graduate Certificate in TVET Teaching Competency - Oct 2021Document41 pagesGuidelines Graduate Certificate in TVET Teaching Competency - Oct 2021Jamal Yusufi Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- The Linkage Between Vocational Schools and Industries CooperationDocument10 pagesThe Linkage Between Vocational Schools and Industries CooperationG PrasetiaNo ratings yet
- Report Study On TVE at Secondary Level PakistanDocument91 pagesReport Study On TVE at Secondary Level PakistanMarcus BarberNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument10 pagesLiterature Reviewmakawiss1100% (1)
- Training On HDP and TTLMDocument10 pagesTraining On HDP and TTLMMisaw KasyeNo ratings yet
- TVET Education in Kenya - What The Future Holds For UsDocument35 pagesTVET Education in Kenya - What The Future Holds For Us25142680No ratings yet
- Reflection On DPDDocument4 pagesReflection On DPDJohndie SarmientoNo ratings yet
- A Study On Higher Education in Bangladesh PDFDocument15 pagesA Study On Higher Education in Bangladesh PDFJerin100% (3)
- Utm Thesis Template - PTPTN Quality ManagementDocument22 pagesUtm Thesis Template - PTPTN Quality ManagementmatminNo ratings yet
- Vocational Education TERM PAPERDocument9 pagesVocational Education TERM PAPERSadia Tamanna RupaNo ratings yet
- ICT in Malaysian Schools Policy and StrategiesDocument6 pagesICT in Malaysian Schools Policy and StrategiesMisfit XavierNo ratings yet
- Policy On Technical EducationDocument8 pagesPolicy On Technical EducationHuyteang MengNo ratings yet
- E-Learning and Instructional Process in Tertiary Education Institutions (Tei) in NigeriaDocument7 pagesE-Learning and Instructional Process in Tertiary Education Institutions (Tei) in NigeriaresearchparksNo ratings yet
- Promoting Research Culture Among Politechnic'S Hospitality StudentsDocument14 pagesPromoting Research Culture Among Politechnic'S Hospitality StudentsRoy D. AlfonsooNo ratings yet
- STEM Education in Malaysia: Policy, Trajectories and InitiativesDocument12 pagesSTEM Education in Malaysia: Policy, Trajectories and InitiativesFariza ZahariNo ratings yet
- Brochure - Education Tomorrow.Document4 pagesBrochure - Education Tomorrow.satish vermaNo ratings yet
- Change Management in TVET Colleges: Lessons Learnt from the Field of PracticeFrom EverandChange Management in TVET Colleges: Lessons Learnt from the Field of PracticeNo ratings yet
- Tamansiswa Accounting Journal International: Volume 1, No 1, April 2021From EverandTamansiswa Accounting Journal International: Volume 1, No 1, April 2021No ratings yet
- 1ST Sem - Fidp (WK1) - Empowerment11 - EditedDocument2 pages1ST Sem - Fidp (WK1) - Empowerment11 - EditedMarielle AlystraNo ratings yet
- Inventory of Bank Accounts As of June 2019Document96 pagesInventory of Bank Accounts As of June 2019Tim PuertosNo ratings yet
- Entertainment SpeechDocument5 pagesEntertainment SpeechAhcel Ortiz SomodioNo ratings yet
- History of Zionism (1915)Document20 pagesHistory of Zionism (1915)Maldiniroso100% (9)
- The Inconvenient Truth Behind Waiting For SupermanDocument2 pagesThe Inconvenient Truth Behind Waiting For SupermanGrassroots Education Movement (NYC)100% (1)
- Fleet Safety DetailsDocument9 pagesFleet Safety DetailsanupamkayalNo ratings yet
- LET Review Prof Education Assessment of LearningDocument32 pagesLET Review Prof Education Assessment of LearningAngelo Aniag Unay93% (14)
- Gianna ResumeDocument2 pagesGianna Resumeapi-450835853No ratings yet
- Conditions Tuition Fees Scholarships PDFDocument2 pagesConditions Tuition Fees Scholarships PDFArjun D KarthaNo ratings yet
- Innovation and Economic Growth SDocument7 pagesInnovation and Economic Growth Smeshael FahadNo ratings yet
- Form 138 ShsDocument6 pagesForm 138 ShsRhia Pineda DizonNo ratings yet
- Evaluating A Mobile Instant Messaging Tool For Efficient Large-Class Speaking InstructionDocument30 pagesEvaluating A Mobile Instant Messaging Tool For Efficient Large-Class Speaking InstructionNatashya ChambaNo ratings yet
- Third Grade - Chicago History Unit PlanDocument51 pagesThird Grade - Chicago History Unit Planapi-253795006100% (1)
- Chapter 7 - Case Study ResearchDocument24 pagesChapter 7 - Case Study ResearchNoor SalmanNo ratings yet
- IITB Placement Common Aptitude TestDocument3 pagesIITB Placement Common Aptitude TestSourav Mondal100% (3)
- Lets Delay - Sel - Selfcontrol - gr8 - Lessonplan - GeDocument4 pagesLets Delay - Sel - Selfcontrol - gr8 - Lessonplan - GeIt's Supa DaveNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson LOG School: Grade Level:: Teacher: English Teaching Dates/Time: QuarterDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson LOG School: Grade Level:: Teacher: English Teaching Dates/Time: QuarterGISELLE DIMAUNNo ratings yet
- In Philosophy, It Is "The Science or Doctrine That Attempts To Explain The Universe in Terms of Ends or Final Causes"Document2 pagesIn Philosophy, It Is "The Science or Doctrine That Attempts To Explain The Universe in Terms of Ends or Final Causes"Delsie FalculanNo ratings yet
- Assignment Unit 2Document2 pagesAssignment Unit 2talk2tomaNo ratings yet
- Daniel I.A. Cohen - Introduction To Computer Theory (1996, John Wiley & Sons) PDFDocument336 pagesDaniel I.A. Cohen - Introduction To Computer Theory (1996, John Wiley & Sons) PDFName GamNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing Booklet-2i0h2moDocument8 pagesAcademic Writing Booklet-2i0h2moernie92832No ratings yet
- Unit 2, Lesson 2.3 - Pronunciation & SpeakingDocument3 pagesUnit 2, Lesson 2.3 - Pronunciation & SpeakingHuyền TrầnNo ratings yet
- Field Study 1Document6 pagesField Study 1Genevive Mee AbanillaNo ratings yet
- Nineteenth Century Radical TraditionsDocument254 pagesNineteenth Century Radical TraditionsMénades Editorial75% (4)
- Kavayitri Bahinabai Chaudhari North Maharashtra University: Count of Student: 59Document3 pagesKavayitri Bahinabai Chaudhari North Maharashtra University: Count of Student: 59jaisnsjsjaNo ratings yet
Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET)
Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET)
Uploaded by
iskelisaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET)
Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET)
Uploaded by
iskelisaCopyright:
Available Formats
Technical and vocational education and
training (TVET) in Malaysia
by StudyMalaysia on October 12, 2016 | Top Stories
What is TVET?
Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET) includes formal, non-
formal and informal learning that prepare young people with the knowledge and
skills required in the world of work. According to the United Nations Organisation for
Education, Science and Culture (UNESCO), TVET has been called many names
over the years – apprenticeship training, vocational education, technical education,
technical-vocational education, occupational education, vocational education and
training, professional and vocational education, career and technical education,
workforce education, workplace education, and others.
ADVERTISEMENT
No matter its name, the common feature of TVET as defined by UNESCO is that it involves “in
addition to general education, the study of technologies and related sciences as well as the
acquisition of practical skills, attitudes, understanding, and knowledge relating to occupations in
various sectors of economics and social life”. In TVET, young people have the opportunity to
learn from basic to advanced levels across a wide range of institutional and work settings.
Did you know?
TVET programmes in Malaysia are offered at certificate, diploma, and degree levels
by seven ministries that include MOHE.
According to MOHE’s Malaysia Education Blueprint (Higher Education), there will
be an increase in demand for an additional 1.3 million TVET workers by 2020 in the 12
National Key Economic Areas (NKEA) identified under the government’s Economic
Transformation Programme (ETP).
To meet this demand, the government has increased the development expenditure
given to public TVET institutions from RM 1.8 billion in 2010 to RM 2.1 billion in 2014.
There are over 1,000 TVET institutions in Malaysia of which 506 are public
institutions.
Public institutions like polytechnics, community colleges, vocational colleges and
other higher learning institutions can accommodate about 230,000 students.
In 2013, out of the 429,000 students who sat for the SPM examination, 321,000
students enrolled in higher education and training programmes, with more than 50%
enrolling at TVET institutions.
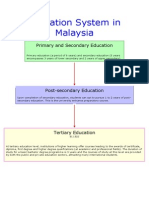
Studying TVET programmes in Malaysia
TVET programmes in Malaysia are offered at certificate, diploma, and degree levels
by seven ministries that include the Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE), which
offers the most TVET programmes to the highest number of students.
Presently, qualifications for academic (higher education) and vocational education
sectors offered by MOHE’s universities, polytechnics, and community colleges are
accredited by the Malaysian Qualifications Agency (MQA), whereas skills training
programmes offered by skills training institutions are accredited by the Department
for Skill Development (DSD) of the Ministry of Human Resources.
You might also like
- Imat Preparation Guide PDFDocument36 pagesImat Preparation Guide PDFPhương Nghi50% (6)
- German-English Pocket Bilingual Dictionary Von UrDocument1 pageGerman-English Pocket Bilingual Dictionary Von Urskippygoat11No ratings yet
- Stat211 122 03 Q1Document4 pagesStat211 122 03 Q1mdasifkhan2013No ratings yet
- IELTS Academic Writing Task 2 SimonDocument62 pagesIELTS Academic Writing Task 2 SimonTrungtamanhngu KosmozNo ratings yet
- Essay AntonymDocument5 pagesEssay AntonymUbaydillah FalakhiNo ratings yet
- The Developmentof TVETProfilingfor Workforce Managementin Malaysia Ensuring The Validityand Reliabilityof TVETDataDocument12 pagesThe Developmentof TVETProfilingfor Workforce Managementin Malaysia Ensuring The Validityand Reliabilityof TVETDataRBT1062021 Divyasree VelooNo ratings yet
- Name Student: Sidra: Course: Higher EducationDocument39 pagesName Student: Sidra: Course: Higher EducationAsqa KhanNo ratings yet
- TVETDocument4 pagesTVETsultanalmokhalasNo ratings yet
- Employability of TVET GraduatesDocument11 pagesEmployability of TVET Graduatesvergel100% (1)
- Strategic Planning To Transform Malaysian TVET Students Into Future Ready ProfessionalsDocument11 pagesStrategic Planning To Transform Malaysian TVET Students Into Future Ready ProfessionalsMyra EmyraNo ratings yet
- TVET MGT 111 EeeeDocument130 pagesTVET MGT 111 EeeeFikadu GadisaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - FINAL DEFENSEDocument13 pagesChapter 1 - FINAL DEFENSEIrene MarticioNo ratings yet
- TVET MalaysiaDocument13 pagesTVET MalaysiaGhazally FaridahNo ratings yet
- English Language Competency in EnhancingDocument9 pagesEnglish Language Competency in EnhancingBALQIS BINTI HUSSIN A18PP0022No ratings yet
- Vocational EducationDocument4 pagesVocational EducationSeania DyNo ratings yet
- Malawi - National Education PolicyDocument24 pagesMalawi - National Education PolicyAndrew NkhomaNo ratings yet
- Penerbit,+4!29!39+Rene Luis Tadle Students Experience of Service QualityDocument11 pagesPenerbit,+4!29!39+Rene Luis Tadle Students Experience of Service QualityKryshia Mae CaldereroNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Written Assignment Ads514 - Education Policy ReportDocument28 pagesGroup 2 - Written Assignment Ads514 - Education Policy ReportNUR HIDAYAH AZIHNo ratings yet
- TVET ManagementDocument99 pagesTVET ManagementBizuneh getuNo ratings yet
- Mem 5205 Higher Education PlanningDocument113 pagesMem 5205 Higher Education PlanningEvans MutuaNo ratings yet
- Tvet 2Document9 pagesTvet 2Tu PangsapuriNo ratings yet
- Unit 8Document22 pagesUnit 8NeeteshNo ratings yet
- TVET in MalaysiaDocument4 pagesTVET in MalaysiaMuhamad Nu'man ZolkofleNo ratings yet
- Technical Vocational Education & Training (TVET) in Malaysia Selected WorksDocument178 pagesTechnical Vocational Education & Training (TVET) in Malaysia Selected WorksIntan Tamira Fa'izah Khusna intantamira.2017No ratings yet
- Malaysia Education Blueprint 2015-2025 (Higher Education)Document240 pagesMalaysia Education Blueprint 2015-2025 (Higher Education)Kolej Komuniti Hulu Selangor (Scribd Rasmi)100% (6)
- Indonesia: Basic StructureDocument4 pagesIndonesia: Basic StructureDaikong ShitamiNo ratings yet
- Executive Summary - BruneiDocument2 pagesExecutive Summary - Bruneiapi-330120353No ratings yet
- Jennifer E. Cotillon, Research IntroductionDocument2 pagesJennifer E. Cotillon, Research IntroductionJennifer CotillonNo ratings yet
- Philosophical and Sociological Overview of Technology and Vocational EducationDocument22 pagesPhilosophical and Sociological Overview of Technology and Vocational EducationAzmi Rizky AnisaNo ratings yet
- Vocationalization of Education PDFDocument12 pagesVocationalization of Education PDFPanjwani Divya RajkumarNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument56 pagesDownloadmathibettuNo ratings yet
- Sistem Pendukung Keputusan Untuk Pemilihan Perguruan Tinggi Penyelenggara Pendidikan Vokasi Di Bangka BelitungDocument12 pagesSistem Pendukung Keputusan Untuk Pemilihan Perguruan Tinggi Penyelenggara Pendidikan Vokasi Di Bangka BelitungRhyiina YeopakataNo ratings yet
- Education System in MalaysiaDocument7 pagesEducation System in MalaysiaKevinNo ratings yet
- The Policies of Curriculum in Tvet (Technical Vocational Education and Training)Document18 pagesThe Policies of Curriculum in Tvet (Technical Vocational Education and Training)Vici Syahril ChairaniNo ratings yet
- Technical and Vocational Education and Training Issues in Malaysia and Asian Region: Where Do We Go From Here?Document11 pagesTechnical and Vocational Education and Training Issues in Malaysia and Asian Region: Where Do We Go From Here?Kamal JasmanNo ratings yet
- Penerbit, JTET 1 1-21Document21 pagesPenerbit, JTET 1 1-21Yousup AliNo ratings yet
- A Situational Analysis of The Faculties' Industrial Attachment Programme at Public Technical Training Institutes (TTIs) in BhutanDocument14 pagesA Situational Analysis of The Faculties' Industrial Attachment Programme at Public Technical Training Institutes (TTIs) in BhutanMamta AgarwalNo ratings yet
- EJ1210003Document8 pagesEJ1210003princecharlespuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Ethnic EmploymentDocument25 pagesChapter 3 Ethnic EmploymentAung Myo PaingNo ratings yet
- 142 Distance Education MalaysiaDocument20 pages142 Distance Education MalaysiaJuliana NorNo ratings yet
- Technical & Vocational Education & Training (TVET) From Malaysia PerspectiveDocument14 pagesTechnical & Vocational Education & Training (TVET) From Malaysia PerspectivewahaboyNo ratings yet
- TVET Challenges and Priorities in Developing CountriesDocument11 pagesTVET Challenges and Priorities in Developing CountriesNadia KhalidNo ratings yet
- Business Studies: By: Devan Kochar XI NalandaDocument13 pagesBusiness Studies: By: Devan Kochar XI NalandaDevan KocharNo ratings yet
- Phil TVET System - SyjucoDocument18 pagesPhil TVET System - SyjucosirjudsNo ratings yet
- Teacher Education and LicencingDocument5 pagesTeacher Education and LicencingCikguAmeliaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines Graduate Certificate in TVET Teaching Competency - Oct 2021Document41 pagesGuidelines Graduate Certificate in TVET Teaching Competency - Oct 2021Jamal Yusufi Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- The Linkage Between Vocational Schools and Industries CooperationDocument10 pagesThe Linkage Between Vocational Schools and Industries CooperationG PrasetiaNo ratings yet
- Report Study On TVE at Secondary Level PakistanDocument91 pagesReport Study On TVE at Secondary Level PakistanMarcus BarberNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument10 pagesLiterature Reviewmakawiss1100% (1)
- Training On HDP and TTLMDocument10 pagesTraining On HDP and TTLMMisaw KasyeNo ratings yet
- TVET Education in Kenya - What The Future Holds For UsDocument35 pagesTVET Education in Kenya - What The Future Holds For Us25142680No ratings yet
- Reflection On DPDDocument4 pagesReflection On DPDJohndie SarmientoNo ratings yet
- A Study On Higher Education in Bangladesh PDFDocument15 pagesA Study On Higher Education in Bangladesh PDFJerin100% (3)
- Utm Thesis Template - PTPTN Quality ManagementDocument22 pagesUtm Thesis Template - PTPTN Quality ManagementmatminNo ratings yet
- Vocational Education TERM PAPERDocument9 pagesVocational Education TERM PAPERSadia Tamanna RupaNo ratings yet
- ICT in Malaysian Schools Policy and StrategiesDocument6 pagesICT in Malaysian Schools Policy and StrategiesMisfit XavierNo ratings yet
- Policy On Technical EducationDocument8 pagesPolicy On Technical EducationHuyteang MengNo ratings yet
- E-Learning and Instructional Process in Tertiary Education Institutions (Tei) in NigeriaDocument7 pagesE-Learning and Instructional Process in Tertiary Education Institutions (Tei) in NigeriaresearchparksNo ratings yet
- Promoting Research Culture Among Politechnic'S Hospitality StudentsDocument14 pagesPromoting Research Culture Among Politechnic'S Hospitality StudentsRoy D. AlfonsooNo ratings yet
- STEM Education in Malaysia: Policy, Trajectories and InitiativesDocument12 pagesSTEM Education in Malaysia: Policy, Trajectories and InitiativesFariza ZahariNo ratings yet
- Brochure - Education Tomorrow.Document4 pagesBrochure - Education Tomorrow.satish vermaNo ratings yet
- Change Management in TVET Colleges: Lessons Learnt from the Field of PracticeFrom EverandChange Management in TVET Colleges: Lessons Learnt from the Field of PracticeNo ratings yet
- Tamansiswa Accounting Journal International: Volume 1, No 1, April 2021From EverandTamansiswa Accounting Journal International: Volume 1, No 1, April 2021No ratings yet
- 1ST Sem - Fidp (WK1) - Empowerment11 - EditedDocument2 pages1ST Sem - Fidp (WK1) - Empowerment11 - EditedMarielle AlystraNo ratings yet
- Inventory of Bank Accounts As of June 2019Document96 pagesInventory of Bank Accounts As of June 2019Tim PuertosNo ratings yet
- Entertainment SpeechDocument5 pagesEntertainment SpeechAhcel Ortiz SomodioNo ratings yet
- History of Zionism (1915)Document20 pagesHistory of Zionism (1915)Maldiniroso100% (9)
- The Inconvenient Truth Behind Waiting For SupermanDocument2 pagesThe Inconvenient Truth Behind Waiting For SupermanGrassroots Education Movement (NYC)100% (1)
- Fleet Safety DetailsDocument9 pagesFleet Safety DetailsanupamkayalNo ratings yet
- LET Review Prof Education Assessment of LearningDocument32 pagesLET Review Prof Education Assessment of LearningAngelo Aniag Unay93% (14)
- Gianna ResumeDocument2 pagesGianna Resumeapi-450835853No ratings yet
- Conditions Tuition Fees Scholarships PDFDocument2 pagesConditions Tuition Fees Scholarships PDFArjun D KarthaNo ratings yet
- Innovation and Economic Growth SDocument7 pagesInnovation and Economic Growth Smeshael FahadNo ratings yet
- Form 138 ShsDocument6 pagesForm 138 ShsRhia Pineda DizonNo ratings yet
- Evaluating A Mobile Instant Messaging Tool For Efficient Large-Class Speaking InstructionDocument30 pagesEvaluating A Mobile Instant Messaging Tool For Efficient Large-Class Speaking InstructionNatashya ChambaNo ratings yet
- Third Grade - Chicago History Unit PlanDocument51 pagesThird Grade - Chicago History Unit Planapi-253795006100% (1)
- Chapter 7 - Case Study ResearchDocument24 pagesChapter 7 - Case Study ResearchNoor SalmanNo ratings yet
- IITB Placement Common Aptitude TestDocument3 pagesIITB Placement Common Aptitude TestSourav Mondal100% (3)
- Lets Delay - Sel - Selfcontrol - gr8 - Lessonplan - GeDocument4 pagesLets Delay - Sel - Selfcontrol - gr8 - Lessonplan - GeIt's Supa DaveNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson LOG School: Grade Level:: Teacher: English Teaching Dates/Time: QuarterDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson LOG School: Grade Level:: Teacher: English Teaching Dates/Time: QuarterGISELLE DIMAUNNo ratings yet
- In Philosophy, It Is "The Science or Doctrine That Attempts To Explain The Universe in Terms of Ends or Final Causes"Document2 pagesIn Philosophy, It Is "The Science or Doctrine That Attempts To Explain The Universe in Terms of Ends or Final Causes"Delsie FalculanNo ratings yet
- Assignment Unit 2Document2 pagesAssignment Unit 2talk2tomaNo ratings yet
- Daniel I.A. Cohen - Introduction To Computer Theory (1996, John Wiley & Sons) PDFDocument336 pagesDaniel I.A. Cohen - Introduction To Computer Theory (1996, John Wiley & Sons) PDFName GamNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing Booklet-2i0h2moDocument8 pagesAcademic Writing Booklet-2i0h2moernie92832No ratings yet
- Unit 2, Lesson 2.3 - Pronunciation & SpeakingDocument3 pagesUnit 2, Lesson 2.3 - Pronunciation & SpeakingHuyền TrầnNo ratings yet
- Field Study 1Document6 pagesField Study 1Genevive Mee AbanillaNo ratings yet
- Nineteenth Century Radical TraditionsDocument254 pagesNineteenth Century Radical TraditionsMénades Editorial75% (4)
- Kavayitri Bahinabai Chaudhari North Maharashtra University: Count of Student: 59Document3 pagesKavayitri Bahinabai Chaudhari North Maharashtra University: Count of Student: 59jaisnsjsjaNo ratings yet